当前位置:网站首页>Long summary (code with comments) number structure (C language) -- Chapter 4, string (Part 1)
Long summary (code with comments) number structure (C language) -- Chapter 4, string (Part 1)
2022-07-02 09:12:00 【Qigui】
Individuality signature : The most important part of the whole building is the foundation , The foundation is unstable , The earth trembled and the mountains swayed . And to learn technology, we should lay a solid foundation , Pay attention to me , Take you to firm the foundation of the neighborhood of each plate .
Blog home page : Qigui's blog
special column : data structure (C Language version )
It's not easy to create , Don't forget to hit three in a row when you pass by !!!
Focus on the author , Not only lucky , The future is more promising !!!
Code , There are notes !!!
Triple attack( Three strikes in a row ):Comment,Like and Collect—>Attention
List of articles
One 、 strand
( One )、 Definition
- strand , String character (string) Is a finite sequence of zero or more characters . The character sequence enclosed in quotation marks is the value of the string ; It could be letters 、 Numbers 、 Chinese or other characters ; The number of characters in the string n Called the length of the string .n=0 When the string is empty, it is called an empty string .
- Substring : Any one of the strings Successive A subsequence of characters
- Main string : A string containing substrings
- The position of the character in the main string : The serial number of the character in the string
- The position of a substring in the main string : The position of the first character of the substring in the main string
- Be careful : Bit order from 1 Start not from 0 Start
- Empty string :M=‘’, Is a string that does not contain any characters , Its length n by 0
An empty string is a substring of any string ; Any string s All are s Substring of itself , except s Itself ,s The other substrings of are called s The real string . - Space string :N=’ ', A string of one or more spaces , Its length n Is the number of space characters ;
- String is a special linear table , There is a linear relationship between data elements ; Usually, the “ Substring ” It is the operation object of adding, deleting, modifying and querying .
- Two strings are equal If and only if the length of the two strings is equal and the characters in each corresponding position are the same .
( Two )、 Basic operation
1、StrAssign(&s,cstr):
String assignment , The string constant cstr Assign to string s, That is, generate a value equal to cstr String of s
2、DestroyStr(&s):
Destroy the string , Release as string s Allocated storage space ( Reclaim storage space )
3、StrCopy(&s,t):
String copy , String t Assign to string s
4、StrEqual(s,t):
Determine whether the strings are equal , If two strings are equal, it returns true ; Otherwise return false
5、StrLen(s):
Find the length of the string , Return string s The number of characters in
6、Strcat(s,t):
String connection , Return consists of two strings s and t A new string connected together
7、SubStr(s,i,j):
substring , Return string s From the first i Consecutive starting characters j A substring of characters
8、InsertStr(s1,i,s2):
Substring insertion , String s2 Insert into string s1 Of the i A place , A new string parallel is generated
9、DelStr(s,i,j):
Substring deletion , From the string s Delete from paragraph i The starting length of characters is j The string of , A new string parallel is generated
10、RepStr(s,i,j,t):
Substring substitution , In the string s Lt i It starts with a character j Substrings of characters are strings t Replace , A new string parallel is generated
11、DispStr(s):
String output , Output string s All character values of
12、StrCmp(s,t):
Comparison operation , Ruoshan s> strand t, Return value >0; Ruoshan s= strand t, Return value =0; Ruoshan s< strand t, Return value <0;
13、IndexStr(s,t):
Positioning operation ( Pattern matching ), If the main string s Domain string exists in t Same value substring , Returns the position where it first appears in the main string , Otherwise, the function value is 0
Two 、 String storage structure
( One )、 Sequential storage of strings
1、 Fixed length sequential storage representation : Use a set of storage units with continuous addresses to store the string value character sequence , Belong to Static storage The way
#define MaxSize 255 // The predefined maximum string length is 255
// Static array implementation ( Fixed length sequential storage )
typedef struct
{
char data[MaxSize]; // Each component stores one character
int length; // The actual length of the string
}SqString;
2、 Heap allocation storage represents : Use a set of storage units with continuous addresses to store the string value character sequence , But the storage space is in the process of program execution Dynamic allocation And get .
// Dynamic array implementation ( Heap allocation storage )
typedef struct
{
char *data; // Allocate storage by string length ,ch Point to the base address of the string
int length // The length of the string
}SdqString;
SdqString s;
s.data=(char *)malloc(MaxSize*sizeof(char));
s.length=0;
1、StrAssign(&s,cstr):
What are referential parameters ? Please refer to the column : Number structure (C Language )—— Chapter two 、 The linear table
Reference type parameters It's a point !!! Be sure to
// Put a string constant c( With ‘\0’ The character marks the end ) Assign to sequence string , That is, generate a value equal to cstr String of s
void StrAssign(SqString &s,char cstr[]) //s Is a reference parameter
{
int i;
for(i=0;cstr[i]!='\0';i++)
s.data[i]=cstr[i];
s.length=i; // Set string s The length of
}
2、DestroyStr(&s):
Because the sequence string is represented by the sequence string itself , Instead of sequential string pointers , Its storage space is managed by the operating system , That is, the operating system allocates its storage space , And release its storage space when it exceeds the scope . There is no operation to destroy the string .
3、StrCopy(&s,t):
// String copy , String t Assign to string s
void StrCopy(SqString &s,SqString t) //s Is a reference parameter
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<t.length;i++) // Copy t All characters of
s.data[i]=t.data[i];
s.length=t.length; // Set string s The length of
}
4、StrEqual(s,t):
// Determine whether the strings are equal , If two strings are equal, it returns true ; Otherwise return false
bool StrEqual(SqString s,SqString t)
{
bool same=true;
int i;
if(s.length!=t.length) // When the length is different, it returns
same=false;
else
for(i=0;i<s.length;i++)
if(s.data[i]!=t.data[i]) // If there is a corresponding character that is not the same, return
{
same=false;
break;
}
return same;
}
5、StrLen(s):
// Find the length of the string , Return string s The number of characters in
int StrLen(SqString s)
{
return s.length;
}
6、Strcat(s,t):
// String connection , Return consists of two strings s and t A new string connected together
SqString Strcat(SqString s,SqString t)
{
SqString str; // Define result string str
int i;
str.length=s.length+t.length;
for(i=0;i<s.length;i++) // take s.data[0..s.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[i]=s.data[i];
for(i=0;i<t.length;i++) // take t.data[0..t.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[s.length+i]=t.data[i];
return str;
}
7、SubStr(s,i,j):
// substring , Return string s From the first i Consecutive starting characters j A substring of characters . When the parameter is incorrect, an empty string is returned
SqString SubStr(SqString s,int i,int j)
{
int k;
SqString str; // Define result string
str.length=0; Set up str For the empty string
if(i<=0||i>s.length||j<0||i+j-1>s.length)
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=i-1;k<i+j-1;k++) // take s.data[0..s.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[k-i+1]=s.data[k];
str.length=j;
return str;
}
8、InsertStr(s1,i,s2):
// Substring insertion , String s2 Insert into string s1 Of the i A place , A new string parallel is generated . When the parameter is incorrect, an empty string is returned
SqString InsertStr(SqString s1,int i,SqString s2)
{
int j;
SqString str; // Define result string
str.length=0; // Set up str For the empty string
if(i<=0||i>s1.length+1) // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
return str;
for(j=0;j<i-1;j++) // take s1.data[0..i-2] Copied to the str
str.data[j]=s1.data[j];
for(j=0;j<s2.length;j++) // take s2.data[0..s2.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[j]=s2.data[j];
for(j=i-1;j<s1.length;j++) // take s1.data[i-1..s1.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[s2.length+j]=s1.data[j];
str.length=s1.length+s2.length;
return str;
}
9、DelStr(s,i,j):
// Substring deletion , From the string s Delete from paragraph i The starting length of characters is j The string of , A new string parallel is generated . When the parameter is incorrect, an empty string is returned
SqString DelStr(SqString s,int i,int j)
{
int k;
SqString s; // Define result string
str.length=0; // Set up str For the empty string
if(i<=0||i>s.length||i+j>s.length+1)
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=0;k<i-1;k++) // take s.data[0..i-2] Copied to the str
str.data[k]=s.data[k];
for(k=i+j-1;k<s.length;k++) // take s.data[i+j-1..s.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[k-j]=s.data[k];
str.length=s.length-j;
return str;
}
10、RepStr(s,i,j,t):
// Substring substitution , In the string s Lt i It starts with a character j Substrings of characters are strings t Replace , A new string parallel is generated . When the parameter is incorrect, an empty string is returned
SqString RepStr(SqString s,int i,int j,SqString t)
{
int k;
SqString str; // Define result string
str.length=0; // Set up str For the empty string
if(i<=0||i>s.length||i+j-1>s.length)
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=0;k<i-1;k++) // take s.data[0..i-2] Copied to the str
str.data[k]=s.data[k];
for(k=0;k<t.length;k++) // take t.data[0..t.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[i+k-1]=t.data[k];
for(k=i+j-1;k<s.length;k++) // take s,data[i+j-1..s.length-1] Copied to the str
str.data[t.length+k-j]=s.data[k];
str.length=s.length-j+t.length;
return str;
}
11、DispStr(s):
// String output , Output string s All character values of
void DispStr(SqString s)
{
int i;
if(s.length>0)
{
if(i=0;i<s.length;i++)
printf("%c",s.data[i]);
printf("\n");
}
}
12、StrCmp(s,t):
// Comparison operation , Ruoshan s> strand t, Return value >0; Ruoshan s= strand t, Return value =0; Ruoshan s< strand t, Return value <0;
int StrCmp(SqString s,SqString t)
{
int i;
fro(i=0;i<s.length&&i<t.length;i++)
if(s.data[i]!=t.data[i])
return s.data[i]-t.data[i];
// All the characters scanned are the same , Then the long string is larger
return s.length-t.length;
}
13、IndexStr(s,t):
// Positioning operation ( Pattern matching ), If the main string s Domain string exists in t Same value substring , Returns the position where it first appears in the main string , Otherwise, the function value is 0
int IndexStr(SqString s,SqString t)
{
int i=1,n=StrLen(s),m=StrLen(t);
SqString str; // Define result string
while(i<=n-m+1)
{
SubStr(str,s,i,m);
if(StrCmp(str,t)!=0)
i++;
else // Returns the position of the substring in the main string
return i;
}
return 0; //s There is no such thing as t Equal substrings
}
( Two )、 Chain storage of strings
The block chain storage representation of a string : Chain storage
typedef struct StrNode
{
char data; // Each node stores one character , Low storage density
struct StrNode *next;
}LinkStrNode;
typedef struct StrNode
{
char data[4]; // Store multiple characters per node , Increase storage density
struct StrNode *next;
}LinkStrNode;
1、StrAssign(&s,cstr):
// Put a string constant c( With ‘\0’ The character marks the end ) Assign to sequence string , That is, generate a value equal to cstr String of s
void StrAssign(LinkStrNode *&s,char cstr[])
{
int i;
LinkStrNode *r,*p;
s=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
r=s; //r Always point to the end node
for(i=0;cstr[i]!='\0';i++)
{
p=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
p->data=cstr[i];
r->next=p;
r=p;
}
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
}
2、DestroyStr(&s):
// Destroy the string , Release as string s Allocated storage space ( Reclaim storage space ). It is the same as destroying the head node single linked list
void DestoryStr(LinkStrNode *&s)
{
LinkStrNode *pre=s,*p=s->next; //pre Point to the node p The precursor node of
while(p!=NULL) // Scan chain s
{
free(pre); // Release pre node
pre=p; //pre、p Move one node back in sync
p=pre->next;
}
free(pre); // At the end of the loop p by NULL,pre Point to the tail node , Release it
}
3、StrCopy(&s,t):
// String copy , String t Assign to string s
void StrCopy(LinkStrNode *&s,LinkStrNode *t)
{
LinkStrNode *p=t->next,*q,*r;
s=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
r=s; //r Always point to the end node
while(p!=NULL) // Scan chain t All of the nodes
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data; // take p Nodes are copied to q node
r->next=q; // take q Nodes are linked to chains s At the end of
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
}
4、StrEqual(s,t):
// If the length of two strings is equal and the characters of corresponding positions are the same , Then return to true ; Otherwise return false
bool StrEqual(LinkStrNode *s,LinkStrNode *t)
{
LinkStrNode *p=s->next,*q=t->next; //p、q Scan the chain respectively s and t Data nodes of
while(p!=NULL&&q!=NULL&&p->data==q->data)
{
p=p->next;
q=q->next;
}
if(p==NULL&&q==NULL) //s and t The length of is equal and the characters in the corresponding positions are the same
return true;
else
return false;
}
5、StrLen(s):
// Find the length of the string , Return string s The number of characters in
int StrLen(LinkStrNode *s)
{
int i=0; //i Used to accumulate the number of data nodes
LinkStrNode *p=s->next; //p Point to the chain s The first node of
while(p!=NULL) // Scan all data nodes
{
i++;
p=p->next;
}
return i;
}
6、Strcat(s,t):
// String connection , Return consists of two strings s and t A new string connected together
LinkStrNode *Strcat(LinkStrNode *s,LinkStrNode *t)
{
LinkStrNode *str,*p=s->next;*q,*r;
str=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
r=str; //r Point to the end of the result string
while(p!=NULL) // use p scanning s All data nodes
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data; // take p Copy nodes to q node
r->next=q; // take q Nodes are linked to str At the end of
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
p=t->next;
while(p!=NULL) // use p scanning t All data nodes
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data; // take p Copy nodes to q node
r->next=q; // take q Nodes are linked to str At the end of
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
return str;
}
7、SubStr(s,i,j):
// substring , Return string s From the first i Consecutive starting characters j A substring of characters
LinkStrNode *DelStr(LinkStrNode *s,int i,int j)
{
int k;
LinkStrNode *str,*p=s->next,*q,*r;
str=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
str->next=NULL; // Set the result string str For the empty string
r=str; //r Point to the end of the result string
if(i<=0||i>StrLength(s)||j<0||i+j-1>StrLength(s))
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=0;k<i-1;k++) // take s Of co The first i Starting with a node j Copy nodes to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
for(k=0;k<j;k++) // Give Way p Point to the chain s Of the i Data nodes
p=p->next;
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
return str;
}
8、InsertStr(s1,i,s2):
// Substring insertion , String s2 Insert into string s1 Of the i A place , A new string parallel is generated
LinkStrNode *RepStr(LinkStrNode *s,int i,int j,LinkStrNode *t)
{
int k;
LinkStrNode *str,*p=s->next,p1=t->next,*q,*r;
str=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
str->next=NULL; // Set the result string str For the empty string
r=str; //r Point to the end of the result string
if(i<=0||i>StrLength(s)||j<0||i+j-1>StrLength(s))
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=0;k<i-1;k++) // take s Before i-1 Data nodes are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
while(p1!=NULL) // take t All data nodes of are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p1->data;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p1=p1->next;
}
while(p!=NULL) take p Nodes and subsequent nodes are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
return str;
}
9、DelStr(s,i,j):
// Substring deletion , From the string s Delete from paragraph i The starting length of characters is j The string of , A new string parallel is generated
LinkStrNode *DelStr(LinkStrNode *s,int i,int j)
{
int k;
LinkStrNode *str,*p=s->next,*q,*r;
str=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
str->next=NULL; // Set the result string str For the empty string
r=str; //r Point to the end of the result string
if(i<=0||i>StrLength(s)||j<0||i+j-1>StrLength(s))
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=0;k<i-1;k++) // take s Before i-1 Data nodes are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
for(k=0;k<j;k++) // Give Way p Along the next jump j Nodes
p=p->next;
while(p!=NULL) take p Nodes and subsequent nodes are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
return str;
}
10、RepStr(s,i,j,t):
// Substring substitution , In the string s Lt i It starts with a character j Substrings of characters are strings t Replace , A new string parallel is generated
LinkStrNode *RepStr(LinkStrNode *s,int i,int j,LinkStrNode *t)
{
int k;
LinkStrNode *str,*p=s->next,p1=t->next,*q,*r;
str=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
str->next=NULL; // Set the result string str For the empty string
r=str; //r Point to the end of the result string
if(i<=0||i>StrLength(s)||j<0||i+j-1>StrLength(s))
return str; // An empty string is returned when the parameter is incorrect
for(k=0;k<i-1;k++) // take s Before i-1 Data nodes are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
q->next=NULL;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
for(k=0;k<j;k++) // Give Way p Along the next jump j Nodes
p=p->next;
while(p1!=NULL) // take t All data nodes of are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p1->data;
q->next=NULL;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p1=p1->next;
}
while(p!=NULL) take p The node and subsequent nodes are copied to str
{
q=(LinkStrNode *)malloc(sizeof(LinkStrNode));
q->data=p->data;
q->next=NULL;
r->next=q;
r=q;
p=p->next;
}
r->next=NULL; // At the end next Field is set to empty
return str;
}
11、DispStr(s):
// String output , Output string s All character values of
void DispStr(LinkStrNode *s)
{
LinkStrNode *p=s->next; //p Point to the chain s The first node of
while(p!=NULL) // scanning s All data nodes
{
printf("%c",p->data); // Output p Node values
p=p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
3、 ... and 、 Pattern matching of strings
Pattern matching is the substring positioning operation : Find the same substring as the pattern string in the main string , And return to where it is
IndexStr(s,t):
Positioning operation ( Pattern matching ), If the main string s Domain string exists in t Same value substring , Returns the position where it first appears in the main string , Otherwise, the function value is 0.
( One )、 Simple matching algorithm (BF Algorithm )
Use k To record the starting position of the substring currently checked , As long as one character is different , You can stop checking the current substring ; The characters in all corresponding positions are the same , Then the match is successful , return k
int BF(SqString s,SqString t)
{
int k=1;
int i=k,j=1;
while(i<s.length&&j<t.length) // Loop when both strings are not scanned
{
if(s.data[i]==t.data[j]) // The two characters in the current comparison are the same
{
i++;
j++; // Continue comparing subsequent characters
}
else // The two characters currently compared are different
{
k++; // Check the next substring
i=k; // Scan the destination string i Back off
j=1; // Substrings match from the beginning
}
}
if(j>=t.length) //j Superboundary , Represents a string t It's a string s The string of
return k; // return t stay s Position in
else // Pattern matching failed
return 0;
}
// Textbook version code
int BF(SqString s,SqString t)
{
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<s.length&&j<t.length) // Loop when both strings are not scanned
{
if(s.data[i]==t.data[j]) // The two characters in the current comparison are the same
{
i++;
j++; // Continue comparing subsequent characters
}
else // The two characters currently compared are different
{
i=i-j+1
j=0; // Substrings match from the beginning
}
}
if(j>=t.length) //j Superboundary , Represents a string t It's a string s The string of
return (i-t.length); // return t stay s Position in
else // Pattern matching failed
return (-1);
}
If the length of the main string is n, The string length is m, be
- 1、 A better situation : The... Of each substring 1 All characters do not match the pattern string ,
The best time complexity for successful matching :O(m),
The best time complexity for matching failure :O(n-m+1)=O(n-m)=O(n) - 2、 The worst : The first of each substring n-1 All characters match the pattern string , Only the first one m Characters don't match , Until the match is successful / Matching failure requires at most (n-m+1)*m Compare it to , Worst time complexity :O(nm)
( Two )、KMP Algorithm
1、 Find pattern string t Of next Array
- next Array : When the first... Of the pattern string j When a character match fails , Make the mode string jump to next[j] And continue to match
- The prefix of the string : Contains first character , And does not contain the substring of the last character
- Suffix of string : Contains the last character , And does not contain the substring of the first character
- computing method : When the first j Character matching failed , From before 1~j-1 A string of characters is marked as s,
be :next[j]=s The length of the longest prefix equals the length of the prefix +1, Special ,next[1]=0
// Find pattern string t Of next Array
int GetNext(SqString t,int next[])
{
int i=0,j=-1; //i Record t,j Record t[i] Before and t The number of characters with the same beginning
next[0]=-1; // Set up next[1] Value
while(i<t.length) // The cycle condition may be j<t.length-1, seek t In all places next value
{
if(j=-1||t.data[i]==t.data[j]) //j=-1 When the characters are equal
{
i++; //i,j Move to the next character in turn
j++;
// if pi=pj, be next[j+1]=next[j]+1
next[i]=j;
}
else // Otherwise the j=next[j], The cycle continues
j=next[j]; //k Back off
}
}
2、KMP Algorithm
int KMP(SqString s,SqString t)
{
int i=0,j=0;
while(i<s.length&&j<t.length) // Loop when both strings are not scanned
{
if(j=-1||s.data[i]==t.data[j]) // The two characters in the current comparison are the same
{
i++;
j++; // Continue comparing subsequent characters
}
else
j=next[j]; //i unchanged ,j back off
}
if(j>=t.length) // The match is successful
return (i-t.length); // return t stay s Position in
else // Pattern matching failed
return (-1);
}
KMP Algorithm : When the substring does not match the pattern string , Main string pointer i Don't go back , Mode string pointer j=next[j] The average time complexity of the algorithm :O(n+m)
3、 The improved KMP Algorithm
int GetNext(SqString t,int nextval[])
{
int i=0,j=-1;
nextval[0]=-1;
while(j<t.length)
{
if(j=-1||t.data[i]==t.data[j])
{
i++;
j++;
if(t.data[i]!=t.data[j])
nextval[i]=j;
else
nextval[i]=nextval[j];
}
else
j=nextval[j];
}
}
int KMP(SqString s,SqString t)
{
int nextval[MaxSize],i=0,j=0;
GetNext(t,nextval);
while(i<s.length&&j<t.length)
{
if(j=-1||s.data[i]==t.data[j])
{
i++;
j++;
}
else
j=nextval[j];
}
if(j>=t.length)
return (i-t.length);
else
return (-1);
}
The most detailed summary of 20000 words ( With code ) Number structure (C Language )—— Chapter two 、 The linear table
A comprehensive summary of 15000 words ( With code ) Number structure (C Language )—— The third chapter 、 Stacks and queues
边栏推荐
- cmd窗口中中文呈现乱码解决方法
- ORA-12514问题解决方法
- C language implementation of mine sweeping game
- 【Go实战基础】gin 如何验证请求参数
- 汉诺塔问题的求解与分析
- gocv opencv exit status 3221225785
- Dix ans d'expérience dans le développement de programmeurs vous disent quelles compétences de base vous manquez encore?
- 【Go实战基础】gin 如何获取 GET 和 POST 的请求参数
- C nail development: obtain all employee address books and send work notices
- [staff] time mark and note duration (staff time mark | full note rest | half note rest | quarter note rest | eighth note rest | sixteenth note rest | thirty second note rest)
猜你喜欢

Installing Oracle database 19C RAC on Linux

Hengyuan cloud_ Can aiphacode replace programmers?
Troubleshooting and handling of an online problem caused by redis zadd
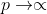
From concept to method, the statistical learning method -- Chapter 3, k-nearest neighbor method

Talk about the secret of high performance of message queue -- zero copy technology
MYSQL安装出现问题(The service already exists)
C language - Blue Bridge Cup - 7 segment code
Servlet全解:继承关系、生命周期、容器和请求转发与重定向等
Introduction to the basic concept of queue and typical application examples

微服务实战|原生态实现服务的发现与调用
随机推荐
Oracle 相关统计
队列管理器running状态下无法查看通道
「Redis源码系列」关于源码阅读的学习与思考
AMQ6126问题解决思路
[go practical basis] how to set the route in gin
Jingdong senior engineer has developed for ten years and compiled "core technology of 100 million traffic website architecture"
洞见云原生|微服务及微服务架构浅析
Kubernetes deploys Loki logging system
Redis sorted set data type API and application scenario analysis
【Go实战基础】如何安装和使用 gin
Matplotlib swordsman Tour - an artist tutorial to accommodate all rivers
Oracle modify database character set
Introduction to the basic concept of queue and typical application examples
【Go实战基础】gin 如何验证请求参数
WSL安装、美化、网络代理和远程开发
AMQ 4043 solution for errors when using IBM MQ remote connection
Cartoon rendering - average normal stroke
Find the node with the smallest value range in the linked list and move it to the front of the linked list
京东高级工程师开发十年,编写出:“亿级流量网站架构核心技术”
2022/2/13 summary