当前位置:网站首页>Asynchronous programming solution Generator generator function, iterator iterator, async/await, Promise
Asynchronous programming solution Generator generator function, iterator iterator, async/await, Promise
2022-08-04 02:36:00 【rananie】
文章目录
异步编程解决方案 Generator生成器函数、iterator迭代器、async/await、Promise
Generator生成器函数
面试题
- generator用来做什么, generator函数的使用场景
- 介绍下es6 generator函数
- generator 实现 async await
Generator生成器函数
语法:function * 函数名(){}
是什么
Generator 函数是 ES6 提供的一种异步编程解决方案.Internally it can be seen as a state machine,返回迭代器对象,调用next方法进入下一个状态.yieldA flag to pause while expression
使用的场景
- Generator 函数会返回一个迭代器对象,因此可以把 Generator 赋值给对象的
Symbol.iterator属性,从而使得该对象具有 Iterator 接口. - async/awaitIt has its own actuatorGenerator对象
GeneratorComplementary to the use of generator functions 了解
generator函数可以用next方法来传参,该参数就会被当作上一个yield表达式的返回值.yield表达式本身没有返回值,返回undefined
所以第一次next传参是没用的,只有从第二次开始next传参才有用GeneratorGenerator function if there is a return value is the last timenext的返回值
{value:xxx:done:true}
function* gen() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 3, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: undefined, done: true }
// 有return值
function* gen() {
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
return 4
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 1, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 2, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 3, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 4, done: true }
yield后面跟promise,函数立即执行
function f1(val){
return Promise.resolve(val);
}
function f2(val){
return new Promise(resolve=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(val)},1000);
})
}
function* gen() {
yield f1(1);
yield f2(2);
return 'ending';
}
const g = gen()
console.log(g.next()) // { value: Promise { 1 }, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: Promise { <pending> }, done: false }
console.log(g.next()) // { value: 3, done: true }
基于Promise对象的简单自动执行器
function f1(val){
return Promise.resolve(val);
}
function f2(val){
return new Promise(resolve=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(val)},1000);
})
}
function* gen() {
console.log(yield f1(1)); //1
console.log(yield f2(2)); //2
console.log(yield 'xxx');//'xxx'
return 'ending';
}
function run(gen){
var g = gen();
function next(data){
var result = g.next(data); //{ value: Promise { 1 }, done: false }
if (result.done) return result.value; //You can return after the execution is complete
Promise.resolve(result.value).then(function(data){
//获取promise的执行结果
console.log(data); //1,2,xxx
next(data); //将1作为yieId f1()执行的结果
});
}
next();
}
run(gen);
iterator迭代器
iterator迭代器
The collection concept has arrays、对象、Map、Set,There needs to be a unified interface mechanism to handle all the different data structures
是什么
迭代器iterator是一种接口,为不同的数据结构提供统一的访问机制
好处
- 为各种数据结构,提供一个统一的、简便的访问接口
- 任何数据结构只要部署 Iterator 接口,就可以完成
for..of遍历操作 - 使得数据结构的成员能够按某种次序排列
原理是什么?
迭代器对象,有一个next方法,每次调用nextmethods will return a result.结果值是一个object {value:xxx,done},value表示具体的返回值, done 是布尔类型的,表示集合是否遍历完成.
A pointer is maintained internally,用来指向当前集合的位置,每调用一次 next 方法,指针都会向后移动一个位置.
// Reverse the order if necessary:i初始化为items.length-1,依次i--
//[Symbol.iterator] = createIterator
function createIterator(items) {
var i = 0;
return {
//迭代器对象,它具有一个 next 方法,该方法会返回一个对象,包含 value 和 done 两个属性
next: function () {
var done = i >= items.length;
var val = !done ? items[i++] : undefined;
return {
done: done,
value: val
}
}
}
}
//测试
var it = createIterator(['a', 'b', 'c']);
console.log(it.next());// {value: "a", done: false}
console.log(it.next());// {value: "b", done: false}
console.log(it.next());// {value: "c", done: false}
console.log(it.next());// "{ value: undefined, done: true }"
console.log(it.next());// "{ value: undefined, done: true }"
console.log(it.next());// "{ value: undefined, done: true }"
可迭代对象
- Iterable data has it all inside
[Symbol.iterator]的属性,Also called realizedIterator接口 [Symbol.iterator]的属性会返回一个函数createIterator函数,Methods for creating iterator objects[Symbol.iterator]The returned function will return an iterator object after execution[Symbol.iterator]The iterator object returned by the function has a name called next的方法- next方法每次执行都会返回一个对象
{value: 10, done: false} - 这个对象中存储了当前取出的数据和是否取完了的标记
使用场景
- for-of 遍历
- 扩展运算符(…)也会调用默认的 Iterator 接口.
- 对数组和 Set 结构进行解构赋值时,会默认调用Symbol.iterator方法.
async/await
面试题
- async / await 的特点以及使用场景
- 为什么async/await要成对出现,只有await可以吗?
- async/await内部通过什么来实现的
- 说一下promise和async/await,分别是怎么捕获错误的?如果把promise写在try/catch里面会捕获到错误吗?
- await/async与generator函数的区别
async/await是什么? 使用场景是什么?
是什么
async函数是自带执行器的generator函数,是generator函数的语法糖,当函数执行遇到await时候, The function surrenders execution rights.
有什么作用
async/await是回调地狱的最佳解决方案,以同步的方式去写异步代码.
asyncThe state of the function's return value
async函数返回的Promise对象,必须等到内部所有await命令后面的 Promise 对象执行完,才会发生状态改变,除非遇到return语句或者抛出错误.
await/async与generator函数的区别
- With its own actuatorgenerator函数,不需要通过
next()到下一个状态 - async函数的返回值是promise,generator返回值是Iterator迭代器对象
- await命令后面,可以是 Promise 对象和原始类型的值,
await可以看成是then的语法糖.yield命令后面只能是 Thunk 函数或 Promise 对象,Cannot be a value of primitive type.
await/async内部实现原理 Generator函数和自动执行器
- 用async实现Generator函数
function f1(val){
return Promise.resolve(val);
}
function f2(val){
return new Promise(resolve=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
resolve(val)},1000);
})
}
//async函数写法
async function gen () => {
console.log(await f1(1)); //1
console.log(await f2(2)); //2
console.log(await 'xxx');//'xxx'
return 'ending';
}
//Genrator函数写法
function* gen() {
console.log(yield f1(1)); //1
console.log(yield f2(2)); //2
console.log(yield 'xxx');//'xxx'
return 'ending';
}
- async是自带执行器的Generator 函数
async 函数的实现原理,就是将 Generator 函数和自动执行器,包装在一个函数里.
async function fn(args){
//.....代码
}
//等价于
//将Generator函数 Add automatic executors 变成async函数
function fn(args){
return run(function*(){
//runFunctions are executed automaticallygenerator函数
//.....代码
})
})
}
//Same as the previous suggested version,Added detection,next的参数从data变成了函数
function run(genF) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const result = genF(); //获取迭代器对象
function getState(nextF) {
let obj;
try {
obj = nextF();//Execute the iterator function 获取value {value:xxx.done:xxx}
} catch(e) {
return reject(e);
}
if(obj.done) {
//Whether the iterator has finished executing
return resolve(obj.value);
}
Promise.resolve(obj.value).then(function(val){
getState(function(){
return result.next(val) });
}, function(e){
getState(function(){
return result.throw(e)});
});
}
getState(() => result.next()); //Start executing the iterator
});
}
async错误捕获方式
async错误捕获方式
- await只能得到成功的结果,失败的结果需用try-catch
function f1(val){
return Promise.reject(val*2);
}
async function fn(){
try {
await f1(3);
} catch (error) {
console.log(error); //6
}
}
fn()
- try catch只能捕获同步代码,不能捕获异步代码,在async函数内使用await之后相当于异步代码变成了同步代码.
try catch为什么不可以捕获到异步代码?
try catch是同步代码在执行栈中,异步任务会被推进队列中,根据事件循环机制,会先将执行栈中的代码执行完毕再去执行队列中的任务.
Promise
Promise.all/Promise.race/Promise.allSettled
状态只能改变一次,当状态已经改变时,resolve和rejectReturn as soon as you enter,不会获取data,Modify the state to execute the corresponding callback
Promise.all(数组):返回一个Promise A- 参数中所有的promise都成功,A的状态为成功,成功的值 为参数promise返回的值 组成的数组,The order is the same as the array in the parameter.
- 数组中有promise失败,则A的状态为失败,The value is the first to fail.
Promise.race(数组):返回一个promise,结果由第一个完成的promise结果决定.- 使用场景:promise超时请求,控制xxxms后请求超时
Promise.allSettIed(数组):返回一个成功的promise,promise的值为数组,The array contains eachpromiseThe status and return value of the execution,当所有的promise状态都改变后,将数组返回.- 使用场景: 希望等一组异步操作都结束了,不管每一个操作是成功还是失败,再进行下一步操作.
手写Promise.all/Promise.race/Promise.allSettled
Promise.all()
- 返回一个promise,promise的结果由数组中的元素执行结果决定
- 依次取出数组中元素的执行结果,注意如果元素是值是没有.then的,所以可以Promise.resolve(元素) 来让非promise值也有.then
- 如果成功就按promise在数组中的顺序放进结果数组中,全部成功调用resolve(结果数组).如果失败就执行reject,表示返回的promise对象失败了
Promise.all = function(iterator){
let count = 0;
let res = new Array(iterator.length);
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
iterator.forEach((element,index) => {
Promise.resolve(element).then(value=>{
count++;
res[index] = value;
if(count == iterator.length) resolve(res);
},reason=>{
reject(resolve)
})
});
})
}
const p1 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
resolve('成功了')
})
const p2 = Promise.resolve('success')
const p3 = Promise.reject('失败')
Promise.all([p1, p2]).then((result) => {
console.log(result) //["成功了", "success"]
}).catch((error) => {
//未被调用
})
Promise.all([p1, p3, p2]).then((result) => {
//未被调用
}).catch((error) => {
console.log(error) //"失败"
});
Promise.allSettled ()
Promise.allSettled = function(iterator){
let res = new Array(iterator.length);
let count = 0 ;
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
const pushResult = (index,status,value)=>{
res[index]= {
status:status,value:value};
count++;
if(count == iterator.length)resolve(res);
}
iterator.forEach((element,index) => {
Promise.resolve(element).then(value=>{
fn(index,'fulfilled',value);
},reason=>{
fn(index,'rejected',reason);
})
});
})
}
手写题:Terminate if the request is not completed within five seconds
//Two simulations are providedAPI
api = () =>{
};
warning = ()=>{
};
function timing(){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
setTimeout(()=>{
reject();
},5000)
})
}
function apiTiming(){
const arr = [api(),timing()];
Promise.race(arr).then(res=>{
console.log(res);
}),catch(e=>{
warnning(e);
})
}
promise实现并发的异步任务调度器
实现一个具有并发数量限制的异步任务调度器,可以规定最大同时运行的任务.
JS实现一个带并发限制的异步调度器Scheduler,保证同时运行的任务最多有两个.完善下面代码的Scheduler类,使以下程序能够正常输出:
class Scheduler {
add(promiseCreator) {
... }
// ...
}
const timeout = time => new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time);
})
const scheduler = new Scheduler(2);
const addTask = (time,order) => {
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time).then(()=>console.log(order))) //实现1: addThe method parameter is not onepromise 不用管返回值
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time)).then(()=>console.log(order)) //实现2: add方法参数是一个promise,返回一个promise
}
addTask(1000, '1');
addTask(500, '2');
addTask(300, '3');
addTask(400, '4');
// output: 2 3 1 4
分析
任务调度器-控制任务的执行,当资源不足时将任务加入等待队列,当资源足够时,将等待队列中的任务取出执行
在调度器中一般会有一个等待队列queue,存放当资源不够时等待执行的任务.
具有并发数据限制,假设通过max设置允许同时运行的任务,还需要count表示当前正在执行的任务数量.
当需要执行一个任务A时,先判断count==max 如果相等说明任务A不能执行,应该被阻塞,阻塞的任务放进queue中,等待任务调度器管理.
如果count<max说明正在执行的任务数没有达到最大容量,那么count++执行任务A,执行完毕后count--.
此时如果queue中有值,说明之前有任务因为并发数量限制而被阻塞,现在count<max,任务调度器会将对头的任务弹出执行.
// output: 2 3 1 4
class Scheduler {
constructor(max) {
this.tasks = [], // task to run
this.count = 0 // 正在运行的任务
this.max = max;
}
// promiseCreator 是一个异步函数,return Promise
add(promiseCreator) {
//add需要返回promise
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
promiseCreator.resolve = resolve //将resolve保存起来,等待promiseCreator执行后,在startcall controladd返回
if (this.count < this.max) {
this.start(promiseCreator)
} else {
this.tasks.push(promiseCreator)
}
})
}
start(promiseCreator) {
this.count++;
promiseCreator().then(() => {
promiseCreator.resolve(); //add返回
this.count--;
if (this.tasks.length) {
this.start(this.tasks.shift())
}
})
}
}
const timeout = (time) => new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time);
})
const scheduler = new Scheduler(2)
const addTask = (time, order) => {
//() => new Promise(setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time)).then(() => console.log(order))
}
addTask(1000, '1');
addTask(500, '2');
addTask(300, '3');
addTask(400, '4');
async和await
class Scheduler {
constructor(max) {
this.tasks= []
this.count = 0;
this.max =max;
}
async add(promiseCreator) {
if(this.count >= this.max) await new Promise(resolve => this.tasks.push(resolve)); //将resolvePut in a queue to wait for execution
this.count++
const res = await promiseCreator()
this.count--
if(this.tasks.length) this.tasks.shift()()
return res
}
}
const timeout = (time) => new Promise(resolve => {
setTimeout(resolve, time);
})
const scheduler = new Scheduler(2)
const addTask = (time, order) => {
//() => new Promise(setTimeout(resolve, 1000))
scheduler.add(() => timeout(time)).then(() => console.log(order))
}
addTask(1000, '1');
addTask(500, '2');
addTask(300, '3');
addTask(400, '4');
同步任务
1.addTask(1000, ‘1’)执行到const res = await promiseCreator()的时候,交出执行权,执行下一步
2.addTask(500, ‘2’)同1
3.addTask(300, ‘3’)此时count = 2 所以执行到await new Promise(resolve => this.tasks.push(resolve))when the enforcement power is surrendered,执行下一步
4.addTask(400, ‘4’)同3
异步任务
1.time=500的定时器resolve, addTask(500, ‘2’)The function regains execution rights,Start executing the subsequent code in it:
this.count-- //count = 1
if(this.tasks.length) this.tasks.shift()() //使waitQueueThe first async task in resolve,addTask(300, '3')regain execution
return res //遇到return,则async函数返回的Promise的状态resolved, 所以.then(() => console.log(time, order))输出 500 '2'
2.addTask(300, ‘3’)The function regains execution rights,执行到const res = await promiseCreator()交出执行权
3.time=300的定时器resolve, The subsequent process is the same5
4.addTask(400, ‘4’)The function regains execution rights, 后续同6
5.time=1000的定时器resolve, The subsequent process is the same5
6.time=400的定时器resolve, The subsequent process is the same5
边栏推荐
- sudo 权限控制,简易
- 小程序:扫码打开参数解析
- Zabbix设置邮件告警+企业微信告警
- 一文看懂推荐系统:召回05:矩阵补充、最近邻查找,工业界基本不用了,但是有助于理解双塔模型
- C# 构造函数业务场景测试项目
- What is the source of flinkcdc consuming mysql binlog data without sqltype=delete
- How to read the resources files in the directory path?
- 2022.8.3-----leetcode.899
- Good bosses, please ask the flink CDC oracle to Doris, found that the CPU is unusual, a run down
- 融云「音视频架构实践」技术专场【内含完整PPT】
猜你喜欢
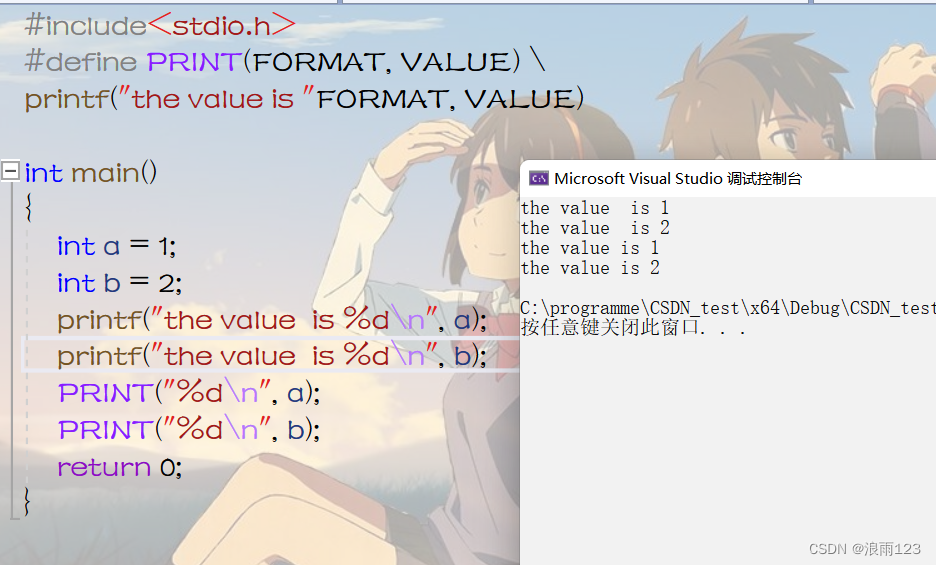
C program compilation and predefined detailed explanation

There are n steps in total, and you can go up to 1 or 2 steps each time. How many ways are there?
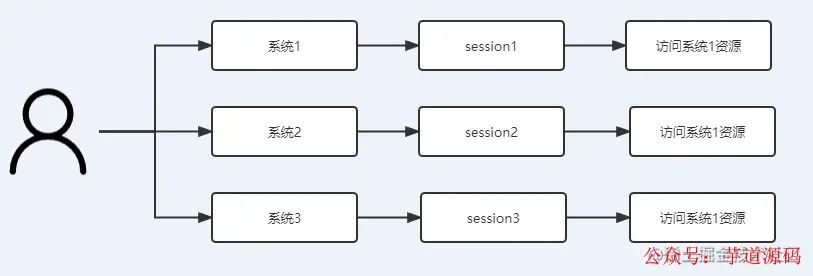
There are too many systems, how to realize multi-account interworking?
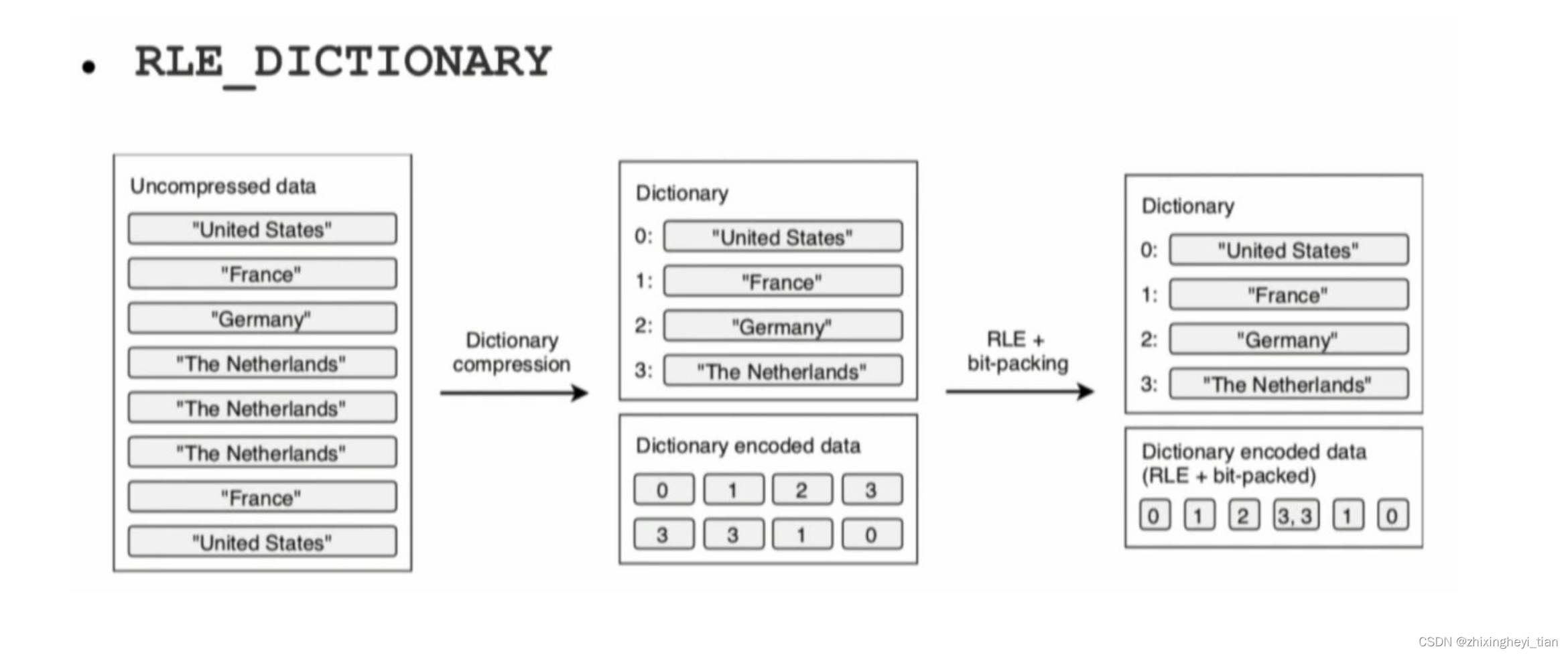
Parquet encoding
在更一般意义上验算移位距离和假设
pytorch应用于MNIST手写字体识别

LeetCode:899. 有序队列【思维题】

小程序+新零售,玩转行业新玩法!
Security First: Tools You Need to Know to Implement DevSecOps Best Practices
Small Turtle Compilation Notes
随机推荐
Snake game bug analysis and function expansion
Big guys, it takes a long time to read mysql3 million single tables, what parameters can be discounted, or is there any way to hurry up
实例035:设置输出颜色
FileNotFoundException: This file can not be opened as a file descriptor; it is probably compressed
Utilities of Ruineng Micrometer Chip RN2026
yum 仅下载包
activiti流程执行过程中,数据库表的使用关系
The browser
Security First: Tools You Need to Know to Implement DevSecOps Best Practices
在更一般意义上验算移位距离和假设
Continuing to invest in product research and development, Dingdong Maicai wins in supply chain investment
Flutter3.0线程——四步教你如何全方位了解(事件队列)
html select tag assignment database query result
DDTL: Domain Transfer Learning at a Distance
Day13 Postman的使用
Detailed analysis of scaffolding content
[Original] Start the XPS/OXPS reader that comes with Windows 10
安全至上:落地DevSecOps最佳实践你不得不知道的工具
查看mysql死锁语法
sqoop ETL tool