当前位置:网站首页>[search] two way search + A*
[search] two way search + A*
2022-07-27 04:57:00 【Xuanche_】

Two way search
Generally used to solve “ The minimum number of steps ” Model problem
Two way wide search can avoid wasting time on deep subtrees .
In some questions , Not only the problem have “ Initial state ”, also Have a clear “ Terminal state ”, And the search tree generated by reverse search from the initial state to the final state can cover the entire state space .
Under such conditions , May adopt Two way search —— Starting from the initial state and the final state, search for half the states respectively , Generate two search trees with half the depth , Meet in the middle , Combine into the final answer .
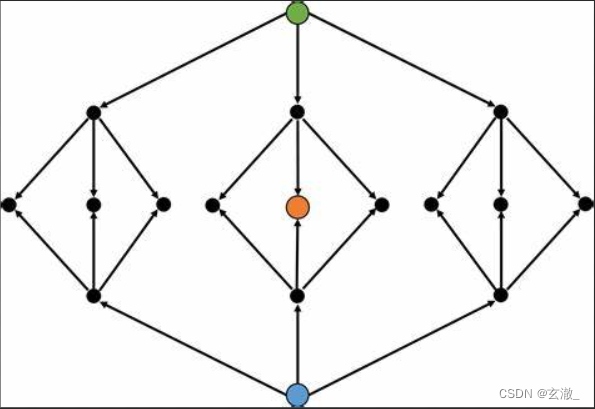
AcWing 190. String transformation ( Two way search )
sample input :
abcd xyz abc xu ud y y yzsample output :
3
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #include <unordered_map> using namespace std; const int N = 6; int n; string A, B; string a[N], b[N]; int extend(queue<string>& q, unordered_map<string, int>&da, unordered_map<string, int>& db, string a[N], string b[N]) { int d = da[q.front()]; while (q.size() && da[q.front()] == d) { auto t = q.front(); q.pop(); for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ) for (int j = 0; j < t.size(); j ++ ) if (t.substr(j, a[i].size()) == a[i]) { string r = t.substr(0, j) + b[i] + t.substr(j + a[i].size()); if (db.count(r)) return da[t] + db[r] + 1; if (da.count(r)) continue; da[r] = da[t] + 1; q.push(r); } } return 11; } int bfs() { if (A == B) return 0; queue<string> qa, qb; unordered_map<string, int> da, db; qa.push(A), qb.push(B); da[A] = db[B] = 0; int step = 0; while (qa.size() && qb.size()) { int t; if (qa.size() < qb.size()) t = extend(qa, da, db, a, b); else t = extend(qb, db, da, b, a); if (t <= 10) return t; if ( ++ step == 10) return -1; } return -1; } int main() { cin >> A >> B; while (cin >> a[n] >> b[n]) n ++ ; int t = bfs(); if (t == -1) puts("NO ANSWER!"); else cout << t << endl; return 0; }
A*
About priority queues BFS Algorithm , The algorithm maintains a priority queue ( Binary heap ), Keep getting out of the heap “ The current cost is the least ” The state of ( Top of pile ) Expand . When each state is first removed from the heap , We get the minimum cost from the initial state to this state .
If given a “ Target state ”, We need to find the minimum cost from the initial state to the target state , Your priority queue BFS This “ Priority strategy ” Is not perfect . The current cost of a state is minimal , It only shows that the cost from the starting point to this state is very small , And in the future search , It may cost a lot to go from this state to the target state . in addition , Some states, although the current cost is slightly higher , But the cost of reaching the target state in the future may be small , So the total cost from the initial state to the target state is better .
Priority queue BFS Choose the branch of the former first , As a result, the amount of search for the optimal solution increases . In order to improve efficiency , It can be done to Estimate the possible costs in the future .
We can design a “ Valuation function ”, With “ Any state ” For input , Calculate the estimated cost of moving from this state to the target state . In search , A heap still needs to be maintained , Keep getting out of the heap “ The current cost + Future valuation ” Expand the minimum state .
In order to ensure that the optimal solution is obtained when the target state is taken out of the heap for the first time , The valuation function we designed needs to meet a basic criterion
Set the current state state The estimate required to reach the target state is f(state)
Set in future search , Actually find out from the current state state The minimum cost of reaching the target state is g(state)
For arbitrary state , Should have
in other words , The valuation of the valuation function cannot be greater than the actual future cost , The valuation is better than the actual cost
AcWing 179. Eight digital
sample input :
2 3 4 1 5 x 7 6 8sample output
ullddrurdllurdruldr
Valuation function : The sum of Manhattan distances between each number in the current state and its target location
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int f(string state)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < state.size(); i ++ )
if (state[i] != 'x')
{
int t = state[i] - '1';
res += abs(i / 3 - t / 3) + abs(i % 3 - t % 3);
}
return res;
}
string bfs(string start)
{
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
char op[4] = {'u', 'r', 'd', 'l'};
string end = "12345678x";
unordered_map<string, int> dist;
unordered_map<string, pair<string, char>> prev;
priority_queue<pair<int, string>, vector<pair<int, string>>, greater<pair<int, string>>> heap;
heap.push({f(start), start});
dist[start] = 0;
while (heap.size())
{
auto t = heap.top();
heap.pop();
string state = t.second;
if (state == end) break;
int step = dist[state];
int x, y;
for (int i = 0; i < state.size(); i ++ )
if (state[i] == 'x')
{
x = i / 3, y = i % 3;
break;
}
string source = state;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ )
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if (a >= 0 && a < 3 && b >= 0 && b < 3)
{
swap(state[x * 3 + y], state[a * 3 + b]);
if (!dist.count(state) || dist[state] > step + 1)
{
dist[state] = step + 1;
prev[state] = {source, op[i]};
heap.push({dist[state] + f(state), state});
}
swap(state[x * 3 + y], state[a * 3 + b]);
}
}
}
string res;
while (end != start)
{
res += prev[end].second;
end = prev[end].first;
}
reverse(res.begin(), res.end());
return res;
}
int main()
{
string g, c, seq;
while (cin >> c)
{
g += c;
if (c != "x") seq += c;
}
int t = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < seq.size(); i ++ )
for (int j = i + 1; j < seq.size(); j ++ )
if (seq[i] > seq[j])
t ++ ;
if (t % 2) puts("unsolvable");
else cout << bfs(g) << endl;
return 0;
}AcWing 178. The first K A short circuit
sample input :
2 2 1 2 5 2 1 4 1 2 2sample output :
14
use Dijkstra The idea of the shortest path , Every expansion The shortest path , The first k The length of the path when reaching the destination for the second time is k Length of short circuit .
Because the algorithm is equivalent to simultaneous k The shortest circuit of secondary unit , Time and space may exceed the limit , therefore Preprocess the shortest distance from each point to the end point as the evaluation function , utilize A∗ Algorithm optimization .
The complexity is 
#include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #include <queue> #define x first #define y second using namespace std; typedef pair<int, int> PII; typedef pair<int, PII> PIII; const int N = 1010, M = 200010; int n, m, S, T, K; int h[N], rh[N], e[M], w[M], ne[M], idx; int dist[N], cnt[N]; bool st[N]; void add(int h[], int a, int b, int c) { e[idx] = b, w[idx] = c, ne[idx] = h[a], h[a] = idx ++ ; } void dijkstra() { priority_queue<PII, vector<PII>, greater<PII>> heap; heap.push({0, T}); memset(dist, 0x3f, sizeof dist); dist[T] = 0; while (heap.size()) { auto t = heap.top(); heap.pop(); int ver = t.y; if (st[ver]) continue; st[ver] = true; for (int i = rh[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (dist[j] > dist[ver] + w[i]) { dist[j] = dist[ver] + w[i]; heap.push({dist[j], j}); } } } } int astar() { priority_queue<PIII, vector<PIII>, greater<PIII>> heap; heap.push({dist[S], {0, S}}); while (heap.size()) { auto t = heap.top(); heap.pop(); int ver = t.y.y, distance = t.y.x; cnt[ver] ++ ; if (cnt[T] == K) return distance; for (int i = h[ver]; ~i; i = ne[i]) { int j = e[i]; if (cnt[j] < K) heap.push({distance + w[i] + dist[j], {distance + w[i], j}}); } } return -1; } int main() { scanf("%d%d", &n, &m); memset(h, -1, sizeof h); memset(rh, -1, sizeof rh); for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ ) { int a, b, c; scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c); add(h, a, b, c); add(rh, b, a, c); } scanf("%d%d%d", &S, &T, &K); if (S == T) K ++ ; dijkstra(); printf("%d\n", astar()); return 0; }
边栏推荐
- js小技巧
- Technology sharing | gtid that needs to be configured carefully_ mode
- 【搜索】双向广搜 + A*
- Cloudcompare & PCL match point distance suppression
- STM32 cubeMX HAL-----PWM—改变频率
- JS tips
- Final Cut Pro中文教程 (1) 基础认识Final Cut Pro
- STM32 Hal serial port (uart/usart) debugging experience (I) -- basic knowledge of serial port communication +hal library code understanding
- 如何做数据平滑迁移:双写方案
- Pinia uses plug-ins for persistent storage.
猜你喜欢

TCP's three handshakes and four waves

Final Cut Pro中文教程 (1) 基础认识Final Cut Pro

Affine transformation module and conditional batch Standardization (CBN) of detailed text generated images

HCIA static routing comprehensive experiment

双向重发布实验

利用Power Automate,轻松下载Power BI报告中的数据

如何将Photoshop图层复制到其他文档

CDH集群集成外部Flink(改进版-与时俱进)

Photoshop各历史版本回顾以及系统要求

详解左值、右值、左值引用以及右值引用
随机推荐
使用Unity做一个艺术字系统
Three cores of Redux
State Hook
C语言 通讯录管理系统(链表,手机号码分段存储,txt文件存取,完整源码)
Use unity to build a WordArt system
HCIA dynamic routing OSPF experiment
Grid layout
What is the difference between using varchar type and using date type for timestamp column?
Dry goods | how can independent station operation improve online chat customer service?
ceph操作
Structural mode - facade mode
els_ Rectangle drawing, code planning and backup
Yolov4网络详解
js小技巧
Yolov4 network details
RN development series < 9 > --mobx (1) Introduction
博云容器云、DevOps 平台斩获可信云“技术最佳实践奖”
The price reduction of iphone13 is just a show. Consumers are waiting for iphone14
消防安全培训资料汇总
【搜索】DFS之连通性模型 + 搜索顺序



