当前位置:网站首页>【HIT-SC-LAB1】哈工大2022软件构造 实验1
【HIT-SC-LAB1】哈工大2022软件构造 实验1
2022-08-04 05:32:00 【XMeow】

2022年春季学期
计算学部《软件构造》课程
Lab 2实验报告
3.1.1 Get the code and prepare Git repository· 1
3.1.2 Problem 1: Test Graph <String>· 1
3.1.3 Problem 2: Implement Graph <String>· 1
3.1.3.1 Implement ConcreteEdgesGraph· 2
3.1.3.2 Implement ConcreteVerticesGraph· 2
3.1.4 Problem 3: Implement generic Graph<L>· 2
3.1.4.1 Make the implementations generic· 2
3.1.4.2 Implement Graph.empty()· 2
3.1.5 Problem 4: Poetic walks· 2
3.1.5.2 Implement GraphPoet· 2
本次实验训练抽象数据类型(ADT)的设计、规约、测试,并使用面向对象
编程(OOP)技术实现 ADT。具体来说:
针对给定的应用问题,从问题描述中识别所需的 ADT;
设计 ADT 规约(pre-condition、post-condition)并评估规约的质量;
根据 ADT 的规约设计测试用例;
ADT 的泛型化;
根据规约设计 ADT 的多种不同的实现;针对每种实现,设计其表示
(representation)、表示不变性(rep invariant)、抽象过程(abstraction
function)
使用 OOP 实现 ADT,并判定表示不变性是否违反、各实现是否存在表
示泄露(rep exposure);
测试 ADT 的实现并评估测试的覆盖度;
使用 ADT 及其实现,为应用问题开发程序;
在测试代码中,能够写出 testing strategy 并据此设计测试用例。
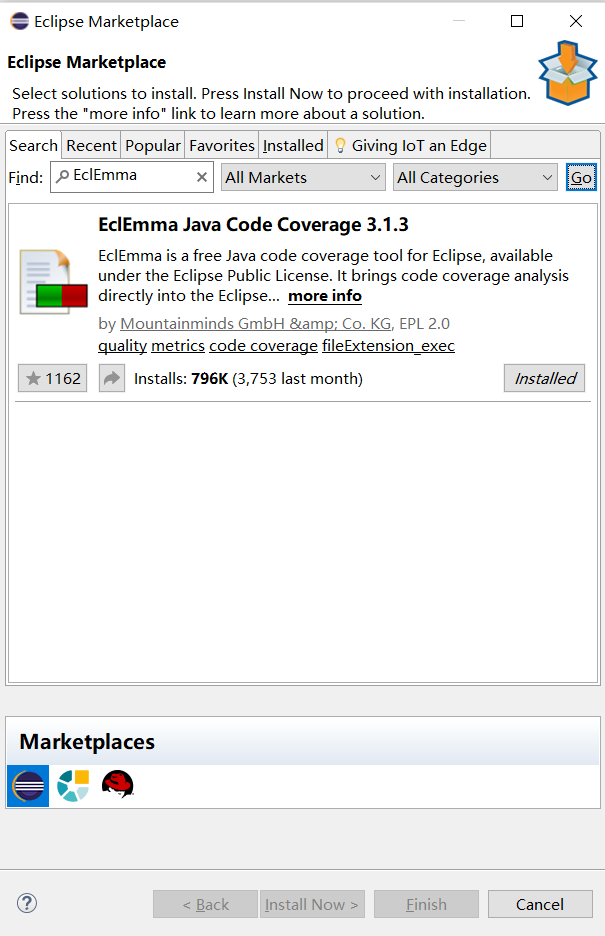
本次实验需要特殊配置的只有EclEmma,一般来说EclEmma会随着Eclipse附件下载,这一点可以在Eclipse Marketplace中验证。
https://github.com/ComputerScienceHIT/HIT-Lab2-120L020731
本任务基于有向图来达到“写诗”的目的。
图有两种实现,边图和点图,它们都继承了Graph接口。
在图的存储上,运用了泛型。
实现图的基本方法,如add/set/remove/targets/sources/vertices
要实现写诗,即实现GraphPoet类,需要判断两个相邻单词之间是否有桥接词。
git clone GitHub - rainywang/Spring2022_HITCS_SC_Lab2
使用git bash来clone项目
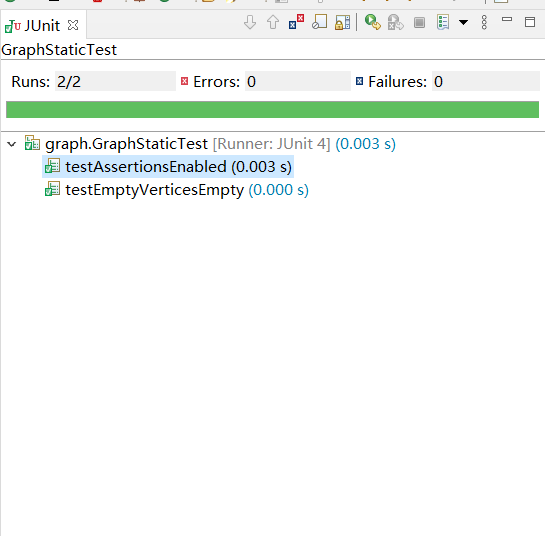
- Problem 1: Test Graph <String>
测试用静态方法生成String型的Graph
- Problem 2: Implement Graph <String>
- Implement ConcreteEdgesGraph
- Problem 2: Implement Graph <String>
首先,我们需要填写边图的元素“Edge”类,它包含三个变量 source target 以及weight
//fields
privatefinal String source, target;
privatefinalint weight;
根据edge类的约束条件,weight应该为非负整数,source和target不能够为同一个点。
//checkRep
privatevoidcheckRep(){
assert(weight >0&&!source.equals(target));
}
类内包含的几个方法,写出基本的取值方法和比较相同的sameEdge方法就行,没什么特别。
实现完Edge之后 只需要依次添加ConcreteEdgesGraph中的函数就可以了。
//constructor
ConcreteEdgesGraph(){
}
checkRep中需要检测图中的所有顶点不为空,边不为空
//checkRep
privatevoidcheckRep(){
for(String vertex : vertices)
assert(vertex !=null);
for(Edge edge : edges)
assert(edge !=null);
}
对于Graph的操作,这里着重讲解几个比较难写的函数。
set :设置一条新的边,它包含三个参数:source target weight,其中source不能等于target,因为一条边的两端点不能是同一点。同时,weight不能为负,为0时代表删除这条边。
@Override
publicintset(String source, String target,int weight){
if(weight <0)
thrownew RuntimeException("Negative weight");
if(!vertices.contains(source)||!vertices.contains(target)){
if(!vertices.contains(source))
this.add(source);
if(!vertices.contains(target))
this.add(target);
}
if(source.equals(target))//出入点相同,无法创建新的边
return0;
//遍历L邻接的所有边,找到相同的边
Iterator<Edge> it = edges.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Edge edge = it.next();
if(edge.sameEdge(source, target)){
int lastEdgeWeight = edge.weight();
it.remove();
if(weight >0){
Edge newEdge =new Edge (source, target, weight);
edges.add(newEdge);
}
elseif(weight ==0)
return0;//若weight == 0 则不添加新的边
checkRep();
return lastEdgeWeight;
}
}
//建立新的边
Edge newEdge =new Edge (source, target, weight);
edges.add(newEdge);
checkRep();
return0;
}
sources/targets 锁定一点,查询所有边的另外一个端点,写一个遍历就可以找到。
@Override
public Map<String, Integer>sources(String target){
Map<String, Integer> sources =new HashMap<>();
for(Edge edge : edges){
if(target.equals(edge.target())){
sources.put((L) edge.source(), edge.weight());
}
}
checkRep();
return sources;
}
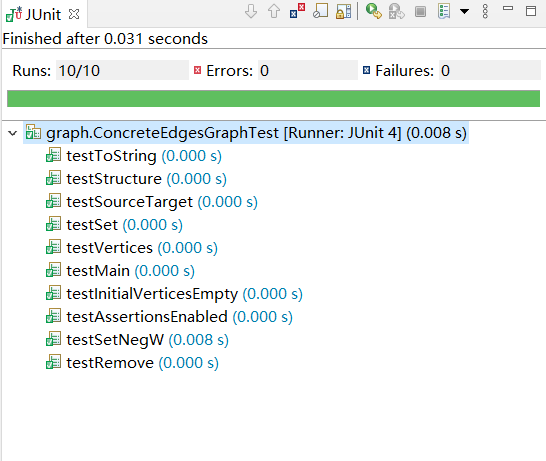
测试样例全部通过
- Implement ConcreteVerticesGraph
VerticesGraph和EdgesGraph的区别在于存储图的类不同。VerticesGraph的数据存储在节点内,节点包括这个点,以及与其邻接的所有边。
// fields
privatefinal String ThisVertex;
privatefinal Map<String, Integer> inEdges =new HashMap<>();
privatefinal Map<String, Integer> outEdges =new HashMap<>();
checkRep函数需要保证每条边的权值都为正整数
// checkRep
privatevoidcheckRep(){
for(String key : inEdges.keySet())
assert(inEdges.get(key)>0);
for(String key : outEdges.keySet())
assert(outEdges.get(key)>0);
}
方法部分需要特别提到的是这里的取值方法和EdgesGraph中的targets/sources类似
public Map<String, Integer>sources(){
Map<String, Integer> sources =new HashMap<>();
sources.putAll(inEdges);
return sources;
}
而在这里set和remove的方法被写入了单元类中,总体思路相同,先检测输入合理性,再建立新边,在建立后checkRep();
publicintsetInEdge(String source,int weight){
if(weight <=0)
return0;
Iterator it =inEdges.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
L key = it.next();
if(key.equals(source)){
int lastEdgeWeight = inEdges.get(key);
it.remove();
inEdges.put(source, weight);
return lastEdgeWeight;
}
}
inEdges.put(source, weight);
checkRep();
return0;
}
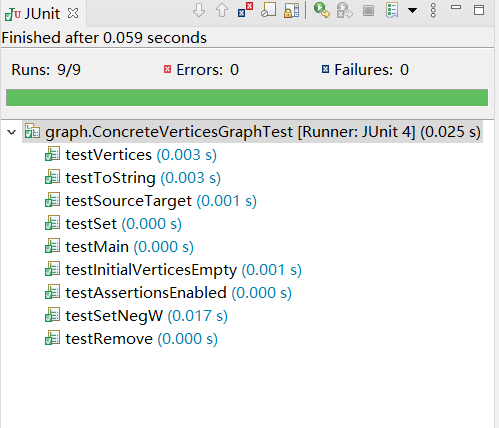
Ctrl + F调出查询窗口,将String参量换为L即可。
- Implement Graph.empty()
使Graph.empty()返回一个新的空示例
publicstatic Graph<String>empty(){
returnnew ConcreteEdgesGraph();
}
- Problem 4: Poetic walks
- Test GraphPoet
- Problem 4: Poetic walks
在基于预设的测试用例基础上,增加等价类划分的多种情况。
等价类划分:两个单词之间不存在连接词,两个单词之间只有一个连接词,两个单词之间有多个连接词。
此外还要注意句末的句号,测试当一个句子最后一个词是“桥”的一端。
- Implement GraphPoet
CheckRep
所有的点(单词)都不能为空。
// checkRep
privatevoidcheckRep(){
Set<String> vertices = graph.vertices();
for(String vertex : vertices)
assert(vertex !=null);
}
GraphPoet
将词库输入图的函数,主要思路为使用bufferedreader和split方法来将单词作为点存在图中,将单词之间的相邻关系作为边存入图中。
while((line = reader.readLine())!=null){
line = line.replace("."," ");
words = line.split(" ");
for(int i =0; i < words.length; i++){
graph.add(words[i].toLowerCase());
if(i >0){
int lastEdgeWeight = graph.set(words[i -1].toLowerCase(), words[i].toLowerCase(),1);
if(lastEdgeWeight !=0)
graph.set(words[i -1].toLowerCase(), words[i].toLowerCase(), lastEdgeWeight +1);
}
}
}
poem
检测相邻的两个单词之间是否有中间词,若单词不在图中则加入图中,若在图中则用targets和sources求两点的中间点中找路权重最大的加入answer。
找桥
targets = graph.targets(words[i -1].toLowerCase());
sources = graph.sources(words[i].toLowerCase());
intersection = sources.keySet();
intersection.retainAll(targets.keySet());
找最大桥
for(String key : intersection){
if(sources.get(key)+ targets.get(key)> maxBridge){
maxBridge = sources.get(key)+ targets.get(key);
bridge = key;
}
}
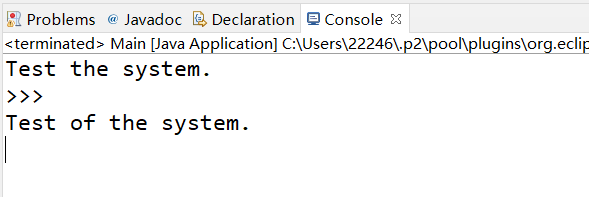
* <p>For example, given this corpus:
* <pre> This is a test of the Mugar Omni Theater sound system. </pre>
* <p>on this input:
* <pre> Test the system. </pre>
* <p>the output poem would be:
* <pre> Test of the system. </pre>
测试poem的样例 完全一致
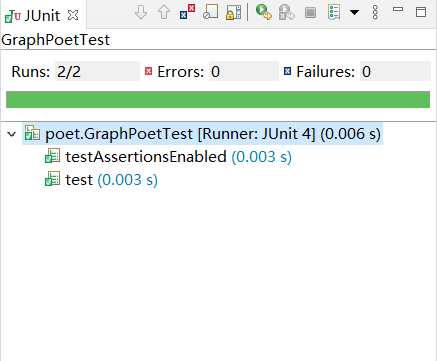
Junit测试 通过
请按照Problem Set 2: Poetic Walks的说明,检查你的程序。
如何通过Git提交当前版本到GitHub上你的Lab2仓库。
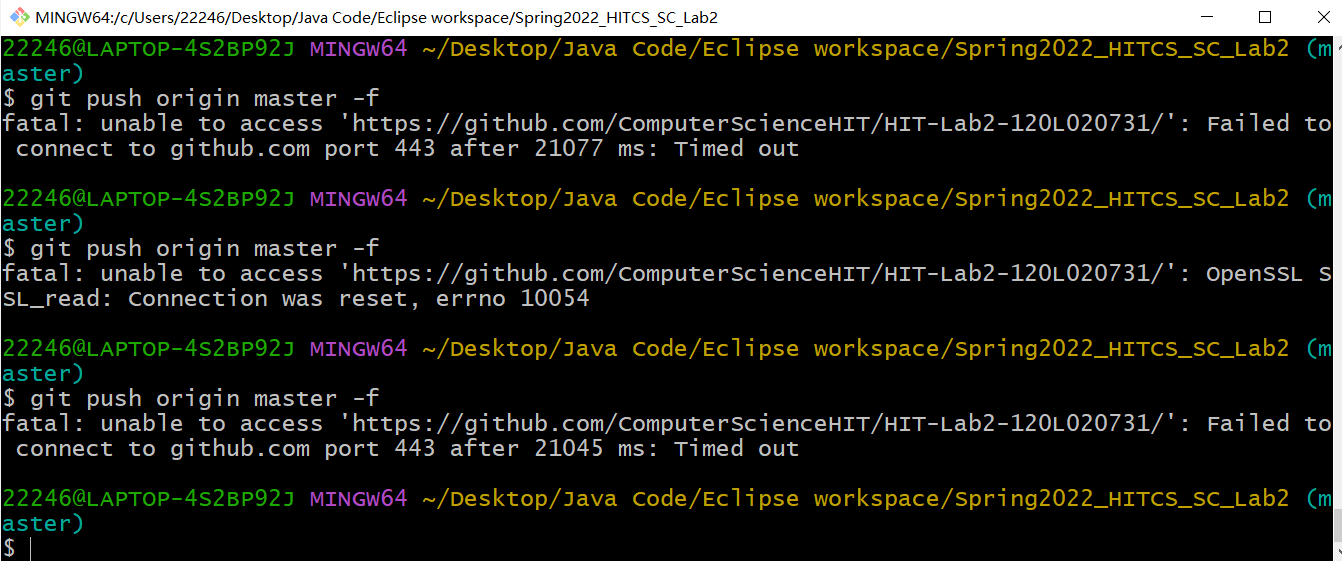
git不好用 这里为了节约时间 直接远程上传了。
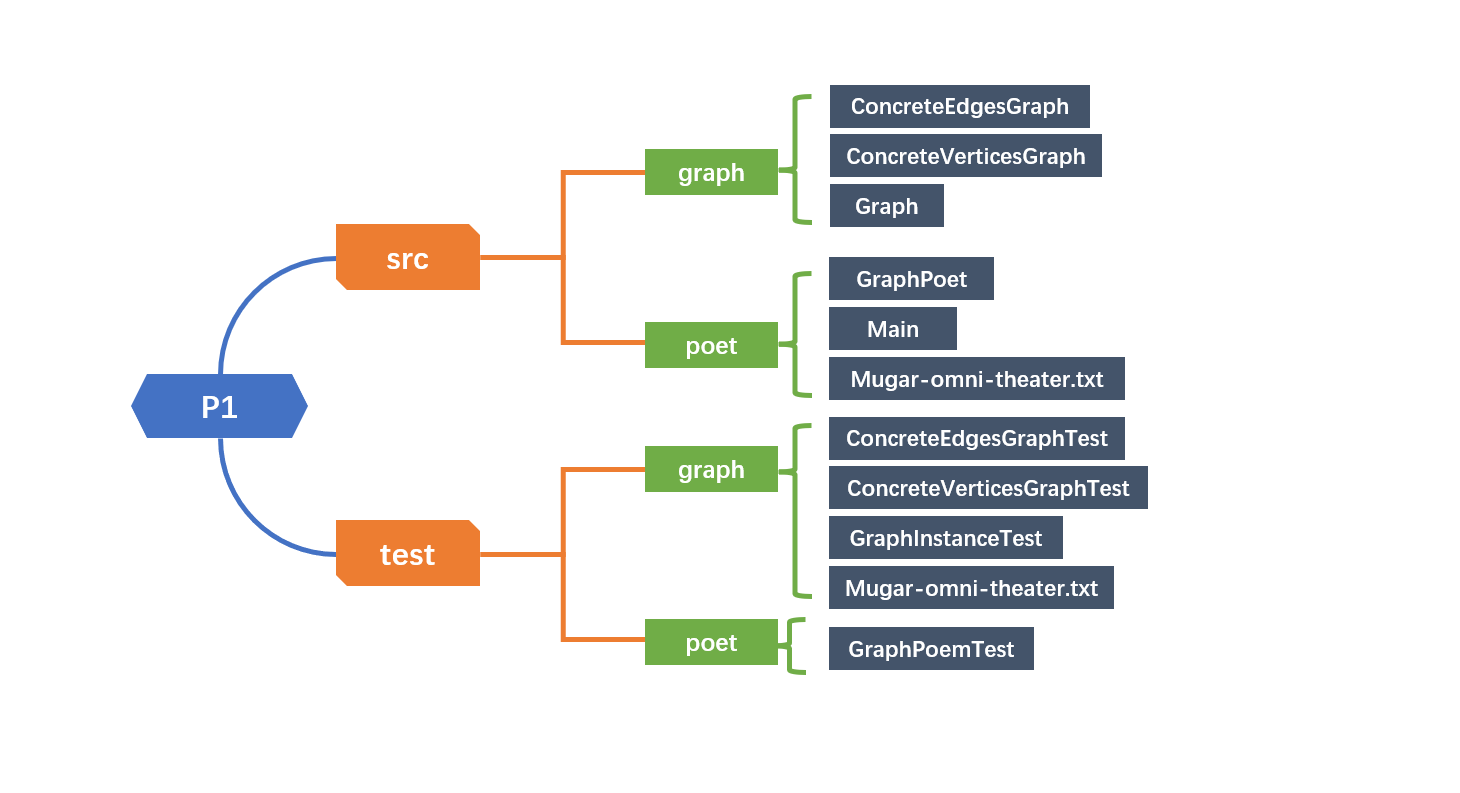
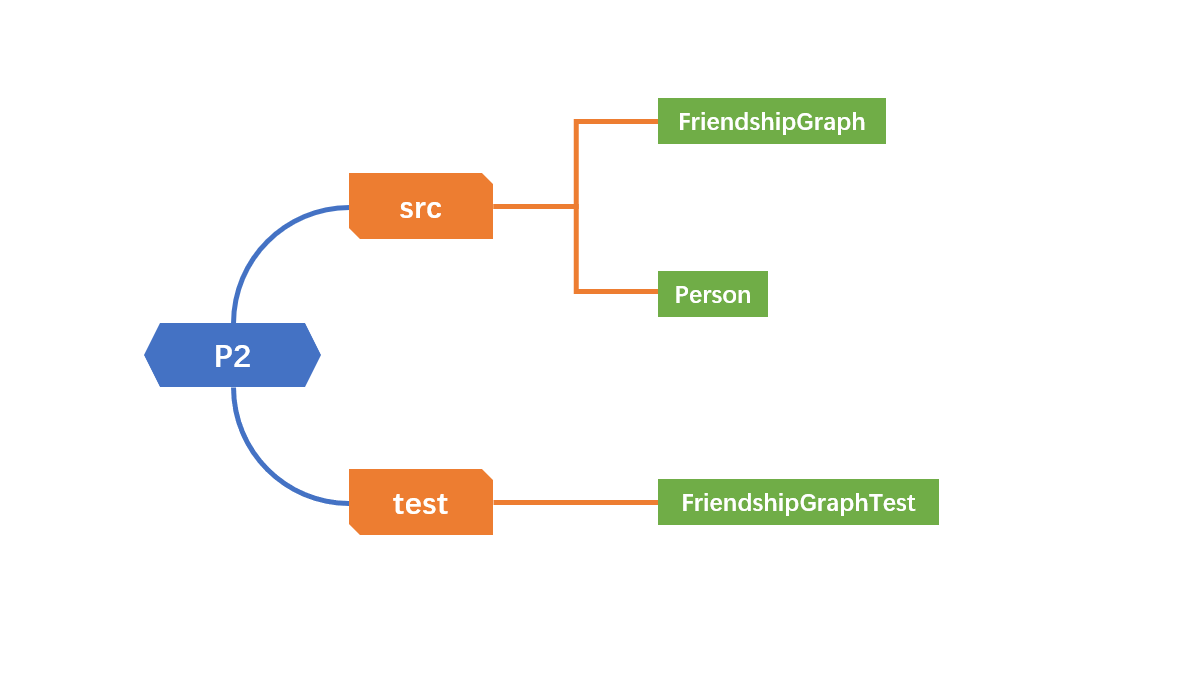
在这里给出你的项目的目录结构树状示意图。
将Lab1中实现Friendship的方法用Lab2中的Graph类重写一遍,其实影响不大,因为Lab1我也是用HashMap写的,所以几乎不需要修改。
具体算法和LAB1中没有变化 这里重新说明一次。
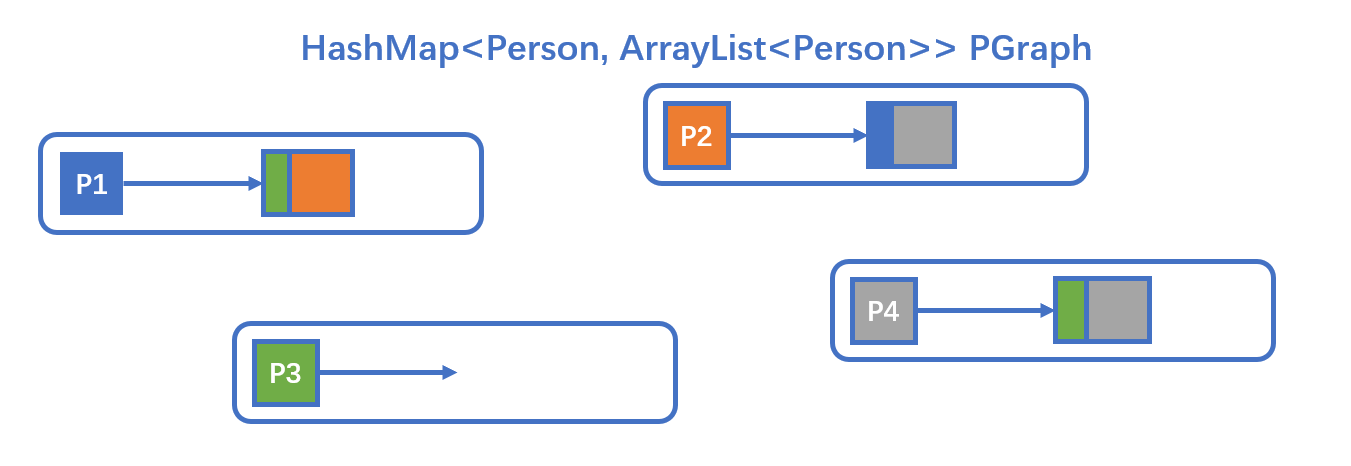
使用存储了人以及与人相邻的边的数据结构来储存数据,Lab1中为HashMap,Lab2中换成了Graph类。
addVertex
publicbooleanaddVertex(Person P){
return graph.add(P);
}
addEdge
publicintaddEdge(Person P1, Person P2){
int lastWeight;
lastWeight = graph.set(P1, P2,1);
lastWeight = graph.set(P2, P1,1);
return lastWeight;
}
getDistance
与Lab1一样 使用广度优先搜索,用HashMap来存储距离,输出时读取HashMap的值
publicintgetDistance(Person P1, Person P2){
if(graph.vertices().contains(P1)==false){
System.out.println("WHO IS"+P1.getName()+"? NEVER EXISTED BEFORE");
}
if(graph.vertices().contains(P2)==false){
System.out.println("WHO IS"+P2.getName()+"? NEVER EXISTED BEFORE");
}
if(graph.targets(P1).isEmpty()|| graph.targets(P2).isEmpty())
return-1;
if(P1 .equals(P2))
return0;
List<Person> list =new ArrayList<Person>();
LevelMap.put(P1,0);
list.add(P1);
while(!list.isEmpty()){
for(Person p : graph.targets(list.get(0)).keySet()){
if(p == P2){
int dist = LevelMap.get(list.get(0))+1;
list.clear();
LevelMap.clear();
return dist;
}
if(!LevelMap.containsKey(p)){
LevelMap.put(p, LevelMap.get(list.get(0))+1);
list.add(p);
list.remove(0);
}
}
}
return-1;
}
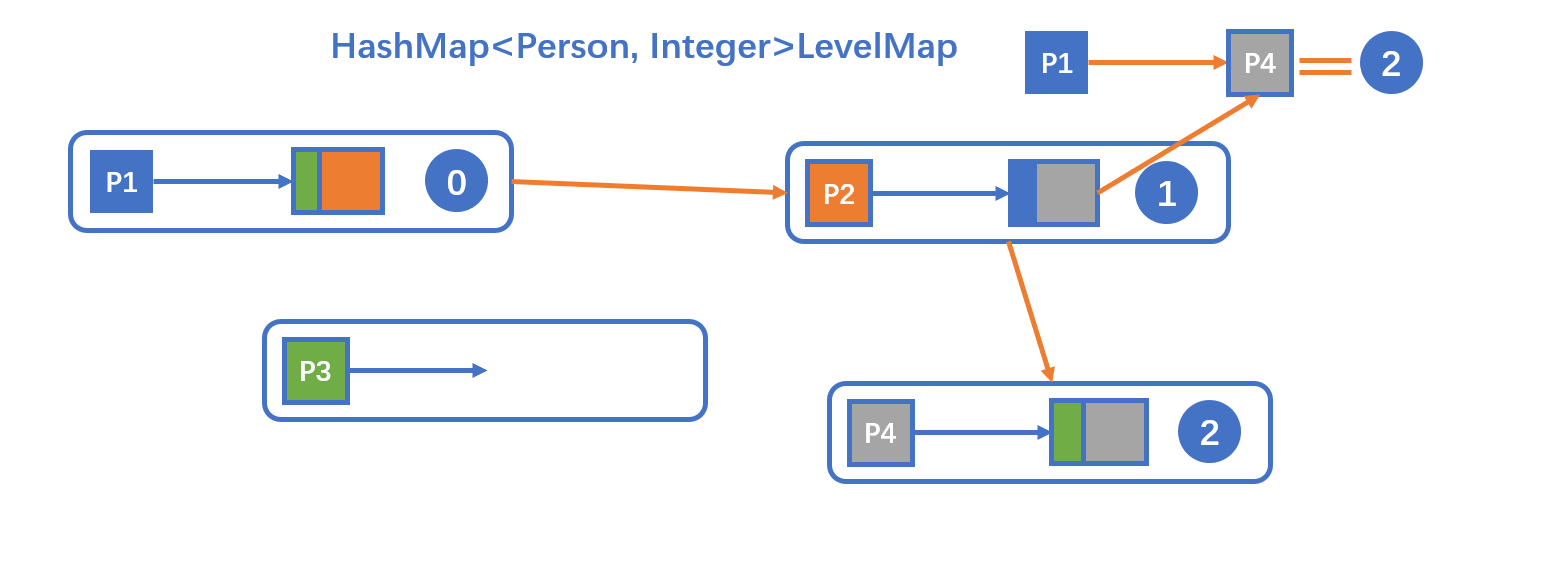
跟Lab1完全一致,不需要修改。
- 客户端main()
跟Lab1完全一致,不需要修改,因为本身是测试样例,不为实现方法所影响。
publicstaticvoidmain(String args[]){
FriendshipGraph graph =new FriendshipGraph();
Person rachel =new Person("Rachel");
Person ross =new Person("Ross");
Person ben =new Person("Ben");
Person kramer =new Person("Kramer");
graph.addVertex(rachel);
graph.addVertex(ross);
graph.addVertex(ben);
graph.addVertex(kramer);
graph.addEdge(rachel, ross);
graph.addEdge(ross, rachel);
graph.addEdge(ross, ben);
graph.addEdge(ben, ross);
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel, ross));//should print 1.
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel, ben));//should print 2.
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel, rachel));//should print 0.
System.out.println(graph.getDistance(rachel, kramer));//should print ‐1
}
沿用了Lab1的测试样例,设计复杂一些的无向图,然后测试点之间的距离。

FriendshipGraph中没覆盖到的主要是会导致程序停止的输入检测语句。主要函数覆盖率均达标。
- 提交至Git仓库
如何通过Git提交当前版本到GitHub上你的Lab2仓库。
同上。。git不好用 连接不上
在这里给出你的项目的目录结构树状示意图。
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
【五一专属】阿里云ECS大测评#五一专属|向所有热爱分享的“技术劳动者”致敬#
MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition - From Perceptrons to Convolutional Neural Networks
文件权限管理 ugo
bind()系统调用的用处
vs2017 redist 下载地址
Vmmem 进程(WSL2)消耗内存巨大
2020-03-27
tmux概念和使用
指针运算相关面试题详解【C语言】
LeetCode_22_Apr_2nd_Week
MNIST Handwritten Digit Recognition - Image Analysis Method for Binary Classification
IDEA中创建web项目实现步骤
file permission management ugo
多线程顺序输出
Detailed steps to install MySQL
实现高并发服务器(二)
Amazon Cloud Technology Build On-Amazon Neptune's Knowledge Graph-Based Recommendation Model Building Experience
Copy Siege Lion's Annual "Battle" | Review 2020
C语言对文件的操作(完整版)
webrtc代码解读二:音视频播放同步过程