当前位置:网站首页>自定义线程池
自定义线程池
2022-08-05 00:44:00 【周雨彤的小迷弟】
1、自定义线程池的实现
自定义线程池应包括 线程池 + 阻塞队列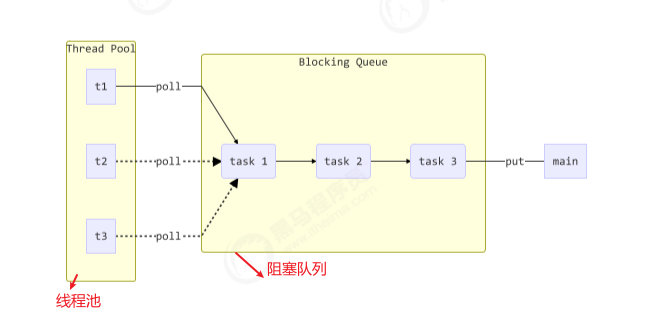
实现
/** * @author houChen * @date 2022/6/14 21:36 * @Description: 自定义线程池 */
@Slf4j(topic = "c.main")
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
//线程池
@Slf4j(topic = "c.testPool")
class ThreadPool {
//阻塞队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//超时时间
private long timeOut;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
//执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
synchronized (workers) {
//【注意】 当任务个数大于核心线程数时,先向任务队列push, 当任务队列满了,再创建max - core的线程数,最后再是任务队列的丢弃策略
//如果任务数小于核心线程数,直接交给worker对象执行
//当任务数超过核心线程数,加入任务队列暂存
if (workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker{},task{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", task);
taskQueue.push(task);
}
}
}
//构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeOut, TimeUnit timeUnit, int capcity) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeOut = timeOut;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(capcity);
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
//构造器
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//执行任务
//1)task不为空时,执行任务
//2)task为空时,从任务队列取出任务并执行
if (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}", task);
this.task.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker{} 被移除",this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
}
//阻塞队列
class BlockingQueue<T> {
//1.任务队列
private Deque<T> queue;
//2.锁 当多个线程来取队列中的任务时,保证其互斥性
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
//4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
//5.容量
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capcity) {
this.queue = new ArrayDeque<>(capcity);
}
//阻塞获取 (从队列中获取一个任务)
public T take() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
//当队列为空时,阻塞
try {
emptyWaitSet.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//超时阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
//将timeout统一转换成纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
//当队列为空时,阻塞
try {
if (nanos < 0) {
return null;
}
//返回值是剩余等待时间
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞添加
public void push(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capcity) {
//当队列为空时,阻塞
try {
fullWaitSet.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.addLast(element);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void push(T element) {
}
//获取队列的大小
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
2、当任务数大于 core + 任务队列的长度时
当线程池需要执行的任务数 > 核心线程数 + 任务队列的容量时, 剩余的 任务应该怎么处理,由线程池的拒绝策略决定
3、任务队列push方法增强 - 带超时时间的阻塞添加
//带超时时间的阻塞添加
public boolean pushP(T element,long timeOut,TimeUnit timeUnit) {
lock.lock();
try {
//将timeout统一转换成纳秒
long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeOut);
while (queue.size() == capcity) {
//当队列处于满
try {
if (nanos < 0) {
return false;
}
//返回值是剩余等待时间
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", element);
queue.addLast(element);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
4、自定义线程池拒绝策略
1、定义一个函数式接口(也就是一个拒绝策略)
//线程池的拒绝策略
@FunctionalInterface
interface RejectPolicy<T> {
// 需要传入阻塞队列是因为拒绝这个行为是发生在队列上的
// 需要传入一个t,是因为阻塞队列对t进行处理
void reject(BlockingQueue<T> queue,T t);
}
2、线程池注入该策略
class ThreadPool {
//阻塞队列
private BlockingQueue<Runnable> taskQueue;
//线程集合
private HashSet<Worker> workers = new HashSet();
//核心线程数
private int coreSize;
//超时时间
private long timeOut;
private TimeUnit timeUnit;
//线程池的拒绝策略
private RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPilicy;
//执行任务
public void execute(Runnable task) {
synchronized (workers) {
//【注意】 当任务个数大于核心线程数时,先向任务队列push, 当任务队列满了,再创建max - core的线程数,最后再是任务队列的丢弃策略
//如果任务数小于核心线程数,直接交给worker对象执行
//当任务数超过核心线程数,加入任务队列暂存
if (workers.size() < coreSize) {
Worker worker = new Worker(task);
log.debug("新增worker{},task{}", worker, task);
workers.add(worker);
worker.start();
} else {
//taskQueue.push(task);
//当任务队列满了,有以下几种方式
//1)死等
//2)超时等待 (加入任务队列超时,就放弃该任务)
//3)让调用者放弃任务执行
//4)让调用者抛出异常
//让任务队列来决定怎么处理该任务
taskQueue.tryPut(rejectPilicy,task);
}
}
}
//构造方法
public ThreadPool(int coreSize, long timeOut, TimeUnit timeUnit, int capcity, RejectPolicy<Runnable> rejectPilicy) {
this.coreSize = coreSize;
this.timeOut = timeOut;
this.timeUnit = timeUnit;
this.taskQueue = new BlockingQueue<>(capcity);
this.rejectPilicy = rejectPilicy;
}
class Worker extends Thread {
private Runnable task;
//构造器
public Worker(Runnable task) {
this.task = task;
}
@Override
public void run() {
//执行任务
//1)task不为空时,执行任务
//2)task为空时,从任务队列取出任务并执行
if (task != null || (task = taskQueue.take()) != null) {
try {
log.debug("正在执行...{}", task);
this.task.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
task = null;
}
}
synchronized (workers) {
log.debug("worker{} 被移除",this);
workers.remove(this);
}
}
}
}
3、在阻塞队列的方法 tryPut中,根据传入的策略对 task进行处理
class BlockingQueue<T> {
//1.任务队列
private Deque<T> queue;
//2.锁 当多个线程来取队列中的任务时,保证其互斥性
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
//3.生产者条件变量
private Condition fullWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
//4.消费者条件变量
private Condition emptyWaitSet = lock.newCondition();
//5.容量
private int capcity;
public BlockingQueue(int capcity) {
this.queue = new ArrayDeque<>(capcity);
}
//阻塞获取 (从队列中获取一个任务)
public T take() {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
//当队列为空时,阻塞
try {
emptyWaitSet.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//超时阻塞获取
public T poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
lock.lock();
try {
//将timeout统一转换成纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
while (queue.isEmpty()) {
//当队列为空时,阻塞
try {
if (nanos < 0) {
return null;
}
//返回值是剩余等待时间
nanos = emptyWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
T t = queue.removeFirst();
fullWaitSet.signal();
return t;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//阻塞添加
public void push(T element) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == capcity) {
//当队列为空时,阻塞
try {
fullWaitSet.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", element);
queue.addLast(element);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//带超时时间的阻塞添加
public boolean pushP(T element,long timeOut,TimeUnit timeUnit) {
lock.lock();
try {
//将timeout统一转换成纳秒
long nanos = timeUnit.toNanos(timeOut);
while (queue.size() == capcity) {
//当队列处于满
try {
if (nanos < 0) {
return false;
}
//返回值是剩余等待时间
nanos = fullWaitSet.awaitNanos(nanos);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", element);
queue.addLast(element);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//获取队列的大小
public int size() {
lock.lock();
try {
return queue.size();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//线程池任务队列的拒绝策略
public void tryPut(RejectPolicy<T> rejectPilicy, T task) {
lock.lock();
try {
if(queue.size() == capcity) {
//阻塞队列满了,就使用策略来处理任务
rejectPilicy.reject(this, task);
} else {
// 阻塞队列没满,则加入队列
log.debug("加入任务队列{}", task);
queue.addLast(task);
emptyWaitSet.signal();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
4、测试时,构造线程池时,需要传入策略的具体实现
public class TestPool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPool threadPool = new ThreadPool(2, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, 10, (queue,task) -> {
queue.push(task);
});
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int j = i;
threadPool.execute(() -> {
log.debug("{}", j);
});
}
}
}
边栏推荐
- tiup update
- 2022牛客多校训练第二场 J题 Link with Arithmetic Progression
- Pytorch使用和技巧
- Software testing interview questions: What are the seven-layer network protocols?
- torch.autograd.grad求二阶导数
- Software testing interview questions: What are the three modules of LoadRunner?
- Bit rate vs. resolution, which one is more important?
- [idea] idea configures sql formatting
- 2021年11月网络规划设计师上午题知识点(下)
- 2022 Nioke Multi-School Training Session H Question H Take the Elevator
猜你喜欢
node uses redis
Matlab uses plotting method for data simulation and simulation
SV 类的虚方法 多态
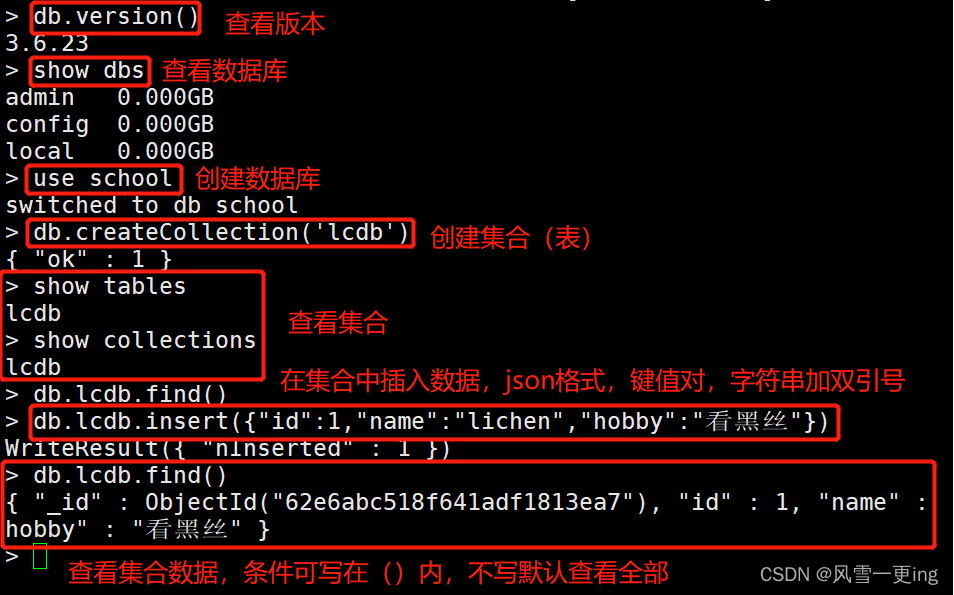
MongoDB搭建及基础操作
QSunSync Qiniu cloud file synchronization tool, batch upload
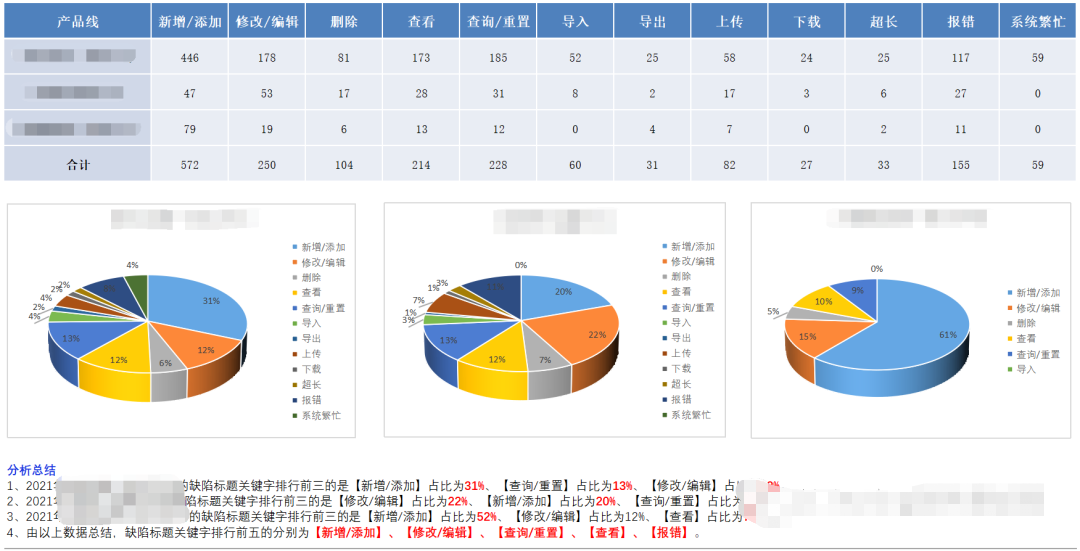
After the staged testing is complete, have you performed defect analysis?

创意代码表白

node使用redis
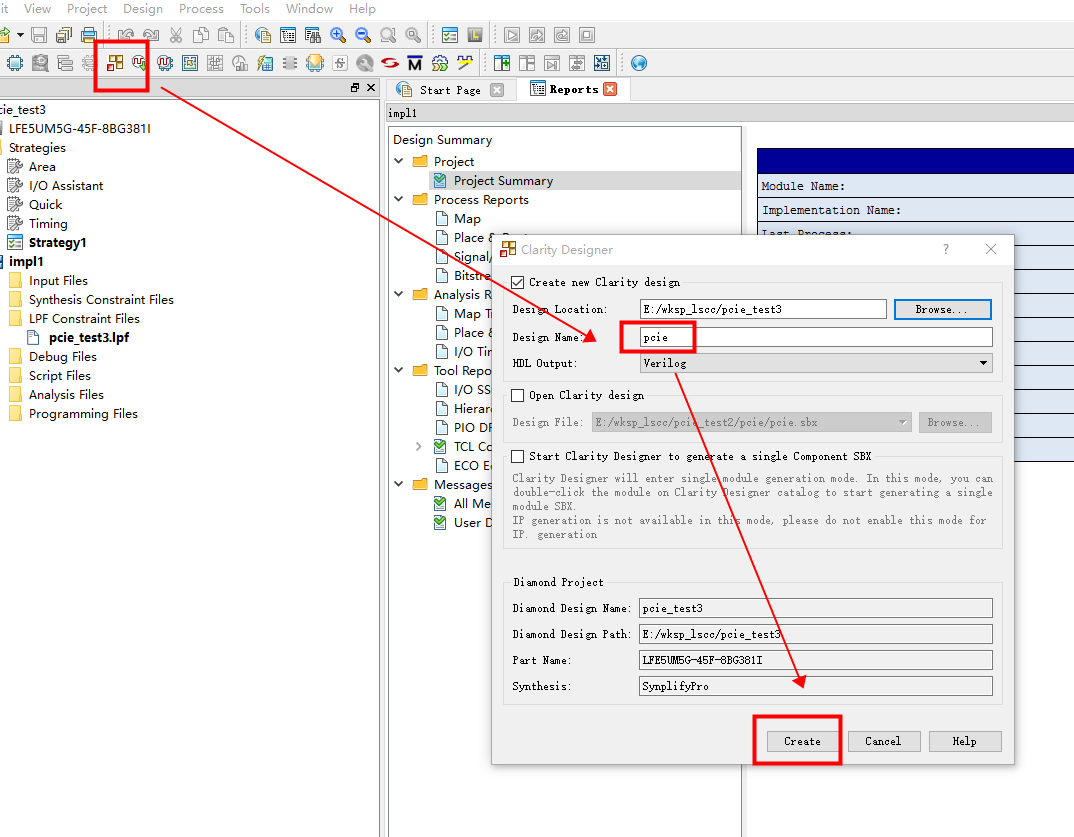
PCIe Core Configuration
![[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy](/img/33/3177b4c3de34d4920d741fed7526ee.png)
[FreeRTOS] FreeRTOS and stm32 built-in stack occupancy
随机推荐
More than 2022 cattle school training topic Link with the second L Level Editor I
3. pcie.v file
Binary tree [full solution] (C language)
LiveVideoStackCon 2022 Shanghai Station opens tomorrow!
2022 Hangzhou Electric Power Multi-School Session 3 Question B Boss Rush
软件测试面试题:LoadRunner 分为哪三个模块?
2022杭电多校第三场 K题 Taxi
执掌图表
Software Testing Interview Questions: What is Software Testing?The purpose and principle of software testing?
GCC:头文件和库文件的路径
ORA-00257
主库预警日志报错ORA-00270
Software Testing Interview Questions: What's the Key to a Good Test Plan?
2022 The Third J Question Journey
2022 Nioke Multi-School Training Session 2 J Question Link with Arithmetic Progression
matlab 采用描点法进行数据模拟和仿真
tensor.nozero(), mask, [mask]
Difference between MBps and Mbps
could not build server_names_hash, you should increase server_names_hash_bucket_size: 32
Software Testing Interview Questions: What aspects should be considered when designing test cases, i.e. what aspects should different test cases test against?