当前位置:网站首页>Introduction to JVM principle and process
Introduction to JVM principle and process
2022-07-05 04:46:00 【xmh-sxh-1314】
 The operating environment represents Java platform , Developers write Java Code (.java file ), Then compile it into bytecode (.class file ), Then bytecode is loaded into memory , Once the bytecode enters the virtual machine , It will be interpreted and executed by the interpreter , Or it can be selectively converted into machine code by the real-time code generator for execution .
The operating environment represents Java platform , Developers write Java Code (.java file ), Then compile it into bytecode (.class file ), Then bytecode is loaded into memory , Once the bytecode enters the virtual machine , It will be interpreted and executed by the interpreter , Or it can be selectively converted into machine code by the real-time code generator for execution .
Java Platform by Java Virtual machine and Java Application interface building ,Java Language is the access to this platform , use Java Programs written and compiled by language can run on this platform . The structure of this platform is shown in the figure below :
stay Java In the structure of the platform , It can be seen that ,Java virtual machine (JVM) At the core , It is the key that the program has nothing to do with the underlying operating system and hardware . Below it is the porting interface , The porting interface consists of two parts : Adapter and Java operating system , The part that depends on the platform is called the adapter ;JVM Through the porting interface in the specific platform and operating system ; stay JVM At the top is Java The basic and extended class libraries and their API, utilize Java API Written applications (application) And small program (Java applet) Can be in any Java Running on the platform without considering the underlying platform , It's because of Java virtual machine (JVM) Realize the separation of program and operating system , So that Java Platform independence .
JVM There is a clear task in its life cycle , That's running Java Program , So when Java When the program starts , Produce JVM An example of ; When the program is finished , The example also disappeared . So let's start with JVM The system structure and its operation process are two aspects to conduct a more in-depth study of it .
1、Java The architecture of virtual machine
· Every JVM There are two mechanisms :
① Class loading subsystem : Load a class or interface with a suitable name
② Execution engine : Responsible for executing instructions contained in a loaded class or interface
· Every JVM Both contain :
Method area 、Java Pile up 、Java Stack 、 Native Method Stack 、 Instruction counter and other implicit registers
about JVM Learning from , In my opinion, these parts are the most important :
Java The whole process of code compilation and execution
JVM Memory management and garbage collection mechanism
These parts are described below :
2、Java The whole process of code compilation and execution
And as I said before ,Java The whole process of compiling and executing code is probably : Developers write Java Code (.java file ), Then compile it into bytecode (.class file ), Then bytecode is loaded into memory , Once the bytecode enters the virtual machine , It will be interpreted and executed by the interpreter , Or it can be selectively converted into machine code by the real-time code generator for execution .
(1)Java The code is compiled by Java Source compiler to complete , That is to say Java Code to JVM Bytecode (.class file ) The process of . The flow chart is shown below :
(2)Java Bytecode is executed by JVM Execute the engine to complete , The flow chart is shown below :
Java The whole process of code compilation and execution includes the following three important mechanisms :
·Java Source compilation mechanism
· Class loading mechanism
· Class execution mechanism
(1)Java Source compilation mechanism
Java Source compilation consists of the following three procedures :
① Analyze and input to symbol table
② Annotation Processing
③ Semantic analysis and generation class file
The flow chart is shown below :
Last generated class The document consists of :
① structural information : Include class File format version number and information about the number and size of each part
② Metadata : Corresponding to Java Information about declarations and constants in the source code . Containing class / Inherited superclasses / Declaration information of the implemented interface 、 Domain and method declaration information and constant pools
③ Methods information : Corresponding Java Information corresponding to statements and expressions in source code . Contains bytecode 、 Exception handler table 、 Evaluation stack and local variable area size 、 Type record of evaluation stack 、 Debug symbol information
(2) Class loading mechanism
JVM The class of is loaded through ClassLoader And its subclasses , The hierarchical relationship and loading order of classes can be described in the following figure :
①Bootstrap ClassLoader
Responsible for loading $JAVA_HOME in jre/lib/rt.jar All in class, from C++ Realization , No ClassLoader Subclass
②Extension ClassLoader
Responsible for loading java Some of the extensions in the platform jar package , Include $JAVA_HOME in jre/lib/*.jar or -Djava.ext.dirs Specify... In the directory jar package
③App ClassLoader
Responsible for recording classpath Specified in the jar Package and directory class
④Custom ClassLoader
It belongs to the application customized according to its own needs ClassLoader, Such as tomcat、jboss Will be based on j2ee Norms are self actualized ClassLoader
During the loading process, it will check whether the class has been loaded , The inspection sequence is bottom-up , from Custom ClassLoader To BootStrap ClassLoader Check layer by layer , Just one classloader Loaded is treated as loaded , Guarantee that only ClassLoader To load a . And the order of loading is top-down , That is, the upper layer will try to load this class layer by layer .
(3) Class execution mechanism
JVM Is a stack based virtual machine .JVM Assign a stack to each newly created thread . in other words , For one Java Procedure , It's run by operating on the stack . Stack saves the state of the thread in frames .JVM There are only two operations on the stack : Stack pressing and stack out operation based on frame .
JVM perform class Bytecode , After thread creation , Will generate program counters (PC) And the stack (Stack), The program counter stores the offset within the method of the next instruction to be executed , Stack frames are stored in the stack , Every stack frame corresponds to every call of every method , And stack frame is composed of local variable area and operand stack , The local variable area is used to store the local variables and parameters in the method , The stack of operands is used to store intermediate results generated during method execution . The structure of the stack is shown in the figure below :
3、JVM Memory management and garbage collection mechanism
JVM The memory structure is divided into : Method area (method), Stack memory (stack), Heap memory (heap), Native Method Stack (java Medium jni call ), The structure diagram is shown below :
(1) Heap memory (heap)
All through new The memory of the created objects is allocated in the heap , Its size can pass through -Xmx and -Xms To control .
The operating system has a linked list of free memory addresses , When the system receives an application for a program , Will traverse the list , Find the first heap node whose space is larger than the applied space , Then delete the node from the free node list , And allocate the space of the node to the program , in addition , For most systems , The size of this allocation will be recorded at the first address in this memory space , So in the code delete Statement can correctly release the memory space . However, the size of the found heap node is not necessarily equal to the size of the application , The system will automatically put the extra part back into the free list . At this time new Allocated memory , Generally speaking, it's slow , And it's prone to memory fragmentation , But it's the most convenient . in addition , stay WINDOWS Next , The best way is to use VirtualAlloc Allocate memory , It's not stacking , It's not on the stack , Instead, a piece of memory is reserved directly in the address space of the process , Although this method is the most inconvenient to use , But fast , And the most flexible . Heap memory is a data structure that extends to high addresses , It's a discontinuous memory area . Because the system uses a linked list to store the free memory address , Nature is not continuous , The traversal direction of the list is from low address to high address . The size of the heap is limited by the virtual memory available in the computer system . thus it can be seen , The heap gets more flexible space , It's bigger .
(2) Stack memory (stack)
stay Windows Next , Stacks are data structures that extend to low addresses , It's a continuous memory area . The address at the top of the stack and the maximum capacity of the stack are predetermined by the system , stay WINDOWS Next , The size of the stack is fixed ( Is a constant determined at compile time ), If the requested space exceeds the remaining space of the stack , Will prompt overflow. therefore , The space available from the stack is small . As long as the remaining space of the stack is larger than the requested space , The system will provide memory for the program , Otherwise, an exception will be reported indicating that the stack overflows . Automatically assigned by the system , Faster . But programmers can't control it .
Heap memory and stack memory need explanation :
Basic data types are allocated directly in stack space , The formal parameters of the method , Allocate directly in stack space , When the method call is complete, it is recovered from the stack space . Reference data type , Need to use new To create , An address space is allocated in the stack space , The class variable of the object is allocated in the heap space . Method reference parameters , Allocate an address space in the stack space , And point to the object area of heap space , When the method call is complete, it is recovered from the stack space . local variable new When you come out , Allocate space in stack space and heap space , When the life cycle of a local variable ends , Stack space is immediately recycled , Heap space area waiting GC Recycling . Passed in when the method is called literal Parameters , First allocate the stack space , Withdraw from stack space after method call . String constant 、static stay DATA Regional distribution ,this Allocate heap space . Array allocates array names in stack space , Allocate the actual size of the array in heap space .
Such as :
(3) Native Method Stack (java Medium jni call )
Used to support native Method execution , It stores everything native The state of the method invocation . For local method interfaces , Realization JVM It is not necessary to have its support , There can even be no .Sun The company realizes Java Local interface (JNI) For portability , Of course, we can also design other local interfaces to replace Sun The company's JNI. But these design and implementation are more complex things , You need to ensure that the garbage collector does not release objects that are being called by local methods .
(4) Method area (method)
It holds the method code ( The compiled java Code ) And the symbol table . Stored the class information to be loaded 、 Static variables 、final Constant of type 、 Property and method information .JVM With persistent generation (Permanet Generation) To store the method area , It can be done by -XX:PermSize and -XX:MaxPermSize To specify the minimum and maximum values .
边栏推荐
- Live broadcast preview | container service ack elasticity prediction best practice
- 程序员应该怎么学数学
- [groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | this, owner, delegate member assignment and source code analysis)
- windows下Redis-cluster集群搭建
- jmeter -- 分布式压测
- [crampon programming] lintcode decoding Encyclopedia - 1100 strange printer
- Séparation et combinaison de la construction du système qualité
- The difference between bundle, chunk and module
- Wenet: E2E speech recognition tool for industrial implementation
- 解密函数计算异步任务能力之「任务的状态及生命周期管理」
猜你喜欢

TPG x AIDU | AI leading talent recruitment plan in progress!
Is there a sudden failure on the line? How to make emergency diagnosis, troubleshooting and recovery
Emlog博客主题模板源码简约好看响应式

【acwing】240. food chain
Thinking of 2022 American College Students' mathematical modeling competition
函數(易錯)
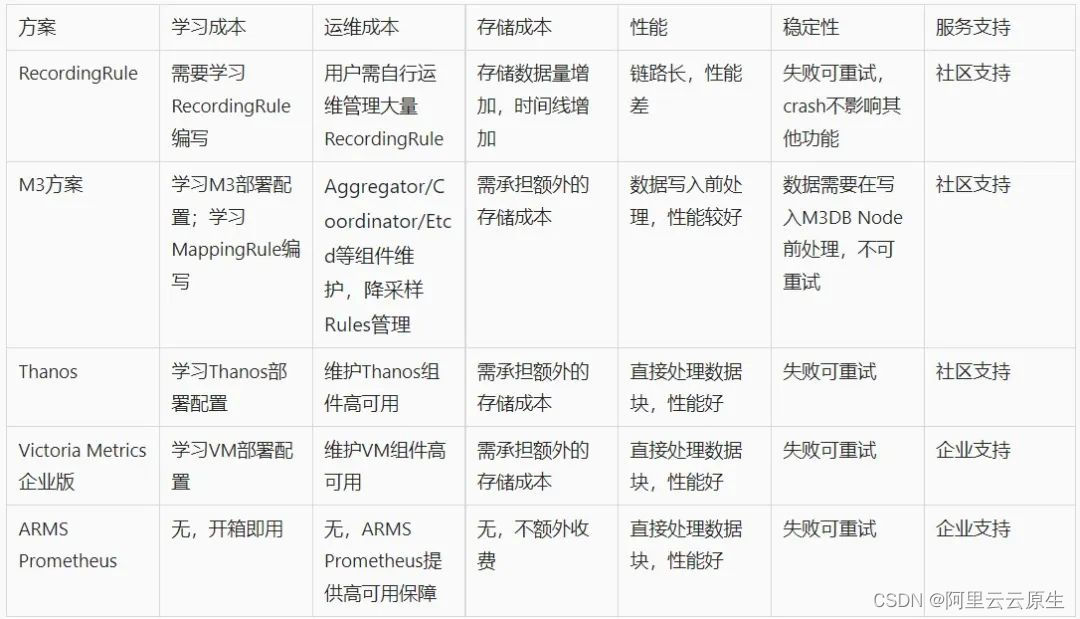
Observable time series data downsampling practice in Prometheus

Special information | finance, accounting, audit - 22.1.23

File upload bypass summary (upload labs 21 customs clearance tutorial attached)
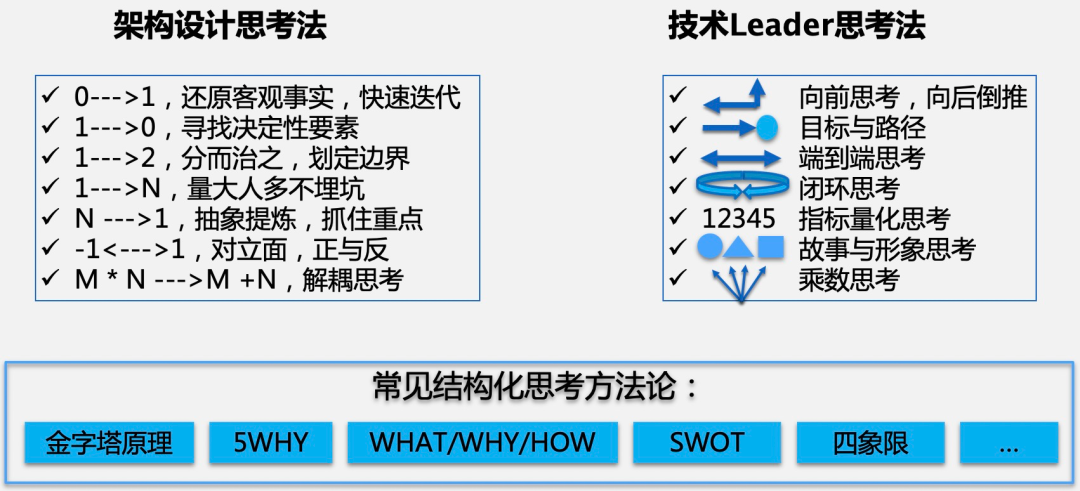
揭秘技术 Leader 必备的七大清奇脑回路
随机推荐
level17
2022-2028 global and Chinese FPGA prototype system Market Research Report
2022 American College Students' mathematical modeling ABCDEF problem thinking /2022 American match ABCDEF problem analysis
指针函数(基础)
Private collection project practice sharing [Yugong series] February 2022 U3D full stack class 006 unity toolbar
File upload bypass summary (upload labs 21 customs clearance tutorial attached)
[crampon game] MC tutorial - first day of survival
[groovy] closure (Introduction to closure class closure | closure parametertypes and maximumnumberofparameters member usage)
Label exchange experiment
Observable time series data downsampling practice in Prometheus
猿人学第一题
質量體系建設之路的分分合合
[popular science] basic knowledge of thermal design: heat dissipation analysis of 5g optical devices
Solution of circular dependency
JVM 原理和流程简介
Pointer function (basic)
Mode in BST (binary tree & Notes on question brushing)
Leetcode hot topic Hot 100 day 33: "subset"
The 22nd Spring Festival Gala, an immersive stage for the yuan universe to shine into reality
jmeter -- 分布式压测