当前位置:网站首页>Heap can also be regarded as a tree structure. It is specified that the root node must be greater than or less than the left and right child nodes, but the size order of the left and right child nodes
Heap can also be regarded as a tree structure. It is specified that the root node must be greater than or less than the left and right child nodes, but the size order of the left and right child nodes
2022-06-11 08:27:00 【Van Gogh's pig V】
List of articles
Pile up
Heap is not a data structure , It is just a general term for a class of data structures , A complete binary tree is usually used to implement heap .
A complete binary tree is a tree with the exception of leaf nodes , There must be a tree of left and right child nodes . Incomplete binary trees are not only leaf nodes , There are one or more nodes that do not completely exist .
I mentioned in the previous Xiaobian , The tree does not have to be implemented with a structure like a linked list , We can use arrays , The advantage of using arrays is , Can quickly traverse , According to a node , We can quickly get its parent node or child node , See the structure of the array storage tree in the following figure :
If the position of a node is k, Then the location of its parent node is k/2, Its left child node is k/2, The right child node is k/2+1. secondly , The root node of the tree must be larger than the left and right child nodes , However, the storage of the left and right child nodes is not specified .
Go up
The concept of floating up occurs when you put an element in the heap , Because we use arrays to store heap elements , So when we put an element in the heap , Can only be placed to the last bit of the array , But the elements put in do not ensure that the heap rules are met , That is, the parent node of the upper layer must be larger than any value of the left and right child nodes , At this time, the heap should be adjusted , Call it floating :
Please look at the picture , If you want to insert a letter S, Only the last bit of the last element of the array can be placed , According to the correspondence between binary tree and array position , This node can only be H Right child of . however S It's better than H Big ( In alphabetical order ), So you have to go up , And H Swap places , After exchanging , And found out P Than S smaller , Continue to work with P Swap places , Until you find that the parent node of the upper layer is larger than yourself , Just stop switching .
float downward
Going down is just the opposite of going up , That is, when you want to delete the root node T When , We need to select a node as the root node , There is actually a very clever algorithm , The root node is swapped with the last node , Then let the root node point to null, At this time, the original node in the last position becomes the root node , But this root node does not conform to heap rules , It may be smaller than the left and right child nodes , So we have to sink :
Look at the picture above , Original T On the root node , Because we want to delete T, So it's different from the last node G Delete , Then switch positions first , And then delete T, This is the time G Become the root node , And does not conform to heap rules , So adjust the heap , Go down :
The only thing you can't get around when floating down is whether to float down to the left node or the right node , In fact, it is possible , Just float down to the largest node among the child nodes ? Why not the smallest ? Because if we exchange with the smallest , The smallest one becomes the root node , It is smaller than the right node , Because it is smaller than the right node . And float down to the largest child node , The purpose is to exchange with the child node , This child node acts as the root node , Still larger than its own child nodes , To comply with the rules of the heap .
Code
package com.hyb.ds. Pile up ;
public class Heap <T extends Comparable<T>>{
private T[] items;
private int n;
public Heap(int cap){
// because T Inherited Comparable, So we need to new This , instead of Object
// from 1 Start
// this.items= (T[]) new Object[cap+1];
this.items=(T[])new Comparable[cap+1];
this.n=0;
}
// Compare the size of the two positions
public boolean less(int i,int j){
return items[i].compareTo(items[j])<0;
}
public void swap(int i,int j){
T t=items[i];
items[i]=items[j];
items[j]=t;
}
// Insert an element into the heap , from 1 Start
public void insert(T t){
items[++n]=t;
swim(n);
}
// Float the adjustment reactor
public void swim(int k){
while (k>1){
// If the parent node is smaller than the current node
if (less(k/2,k)){
// Switching nodes
swap(k/2,k);
k=k/2;
}else break;
// Adjust the position
}
}
// Delete the largest element of the heap
public T delMax(){
T max=items[1];
// The root node is the largest node
// Swap the largest node and the last node
swap(1,n);
// Delete maximum node
items[n]=null;
//n--
n--;
// Let the root node sink
sink(1);
return max;
}
// Let the root node sink
public void sink(int index){
while ((2*index+1)<=n){
int maxChild;
if (less(2*index,2*index+1))
maxChild=2*index+1;
else
maxChild=2*index;
if (less(maxChild,index))
break;
swap(maxChild,index);
index=maxChild;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Heap<String> stringHeap = new Heap<>(10);
stringHeap.insert("A");
stringHeap.insert("B");
stringHeap.insert("C");
stringHeap.insert("D");
stringHeap.insert("E");
stringHeap.insert("F");
stringHeap.insert("G");
String result=null;
while ((result=stringHeap.delMax())!=null){
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
Heap sort
This is the last of the eight sorting algorithms , The heap is stored in an array , So you can use the characteristics of the heap to sort the array .
The previous Xiaobian said , The root node must be larger than the left and right child nodes , So we output when deleting , It can be output from large to small .
Next, let's sort the above figure , From small to large , The order should be A->G
We just need to put A And G Make a change , It looks like G It reaches the highest position in the array , because G It's the biggest , So in the end . At the moment A At the root node , Breaking heap rules , So you need to adjust the heap , Need to put A sinking ,. Then continue to swap the root node with the last node in the array position , Be careful , This last node is B, because A The location has been changed , No more exchanges .
With this idea , Next, Xiaobian will do a test , Convert array to heap , Then sort the heap from small to large :
// Sink according to the range
public void sink(int index,int range){
while (2*index+1<=range){
// Determine the larger child nodes in the current node
int max;
if (less(2*index,2*index+1)){
max=2*index+1;
}else max=2*index;
// Compare the current node with the largest child node
if (less(max,index)){
break;
}
swap(index,max);
index=max;
}
}
// According to the passed array , Make heaps
public void ArrayHeap(T[] heap){
// First copy all the elements into the heap
System.arraycopy(heap,0,items,1,heap.length);
// And then we're going to sink the elements , Here is from the length of 1/2 Start , Because the rest are leaf nodes
for (int i=heap.length/2;i>0;i--){
// sinking
sink(i,heap.length-1);
}
}
// Heap sort
public void heapSort(T[] heap){
ArrayHeap(heap);
// Mark the last node location exchanged with the root node
int last=heap.length;
while (last!=1){
// Exchange the head node and tail node
swap(1,last);
// Give Way last change
last--;
// Let the head node sink
sink(1,last);
}
// take heap And then copy the data in
System.arraycopy(items,1,heap,0,heap.length);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Heap<String> stringHeap = new Heap<>(7);
// stringHeap.insert("A");
// stringHeap.insert("B");
// stringHeap.insert("C");
// stringHeap.insert("D");
// stringHeap.insert("E");
// stringHeap.insert("F");
// stringHeap.insert("G");
// String result=null;
// while ((result=stringHeap.delMax())!=null){
// System.out.println(result);
// }
String[] a=new String[]{
"G","F","E","D","C","B","A"};
stringHeap.heapSort(a);
for (String s :
a) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
Reactor application
- From the nature of the heap , The heap can be implemented as a priority queue , Because we know that the root node of the heap must be larger than the left and right child nodes , This makes it easy to store priority queues , When we need to take out the element with the highest priority , Just take out the root node .
- One of the heap applications is the index queue , In a normal heap , The elements are disordered , We can only get its maximum or minimum , And the middle value cannot be obtained , So we store the elements in the array to implement the heap . In this way, you can quickly get the corresponding value from the subscript :

But there is another problem , If we swap the values of some two index positions , Then adjust the heap , At this time, the original value is not at the initial position , It leads to disorder in the end , Unable to get value from start position .
To solve this problem , We use an auxiliary tree to solve the problem , This auxiliary tree is used to store the index of each value in our heap :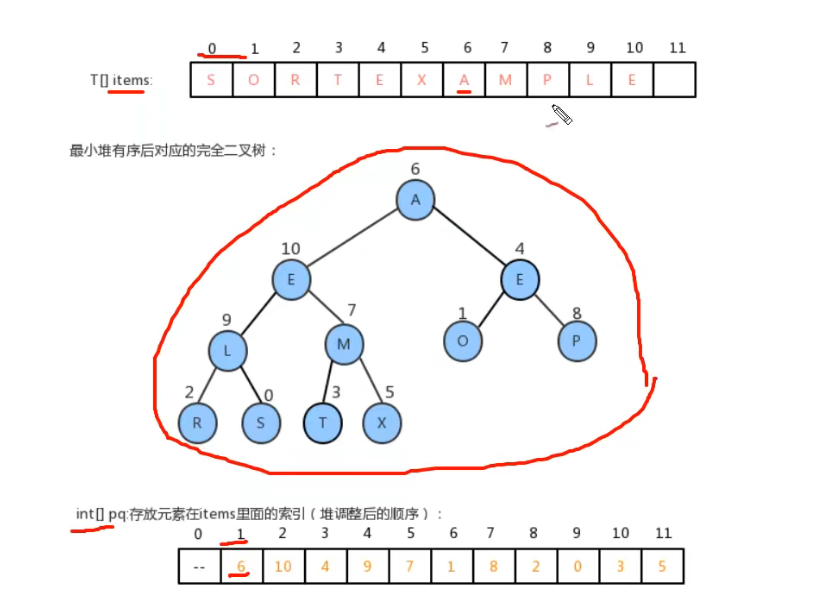
The value of the auxiliary tree is the index of the original array , So if the original array needs to be heap adjusted , You can adjust the auxiliary tree directly , In this way, no matter where the value of the auxiliary tree is adjusted , Its value is constant , According to this value , You can get the value of the original array .
however , There's another problem : If the value of the original array changes , Although I say , The index of this value has not changed , But when you adjust the heap , You need to find the corresponding position of the original value index in the auxiliary tree , for instance , Here the original array changes the index 0 Value s by H, At this time, we need to adjust the heap , according to H The index of 0, Find the value in the auxiliary tree as 0 To adjust the position of . This does not seem to affect the position of the original array value , But the efficiency is low , Because you want to find this 0 Words , You have to traverse the auxiliary tree , Because in the auxiliary tree 0 Is the value , It's not an index . And if the auxiliary tree is large , So the query efficiency is very low , In this way, we will lose more than we gain by exchanging space for time .
therefore , We are going to save an auxiliary tree , Let's call it 2 Number , The previous auxiliary tree is 1 Number . So this 2 The value in the number is saved 1 Index of No , and 2 The index of the number itself will coincide with the index of the original array :
So you see , If it changes S The value of is H, So at this point , You can get the index of this value 0, Go straight to 2 No. to find the corresponding value , This value , It's our index in number one , You can adjust it directly according to this index 2 The number is piled up .
边栏推荐
- Study the Analects of entanglement
- Solution to the occurrence interval (space) of latex manual numbering documents
- TypeScript-类和接口、类和泛型、接口合并现象
- Method summary of creating deep learning model with keras/tensorflow 2.9
- 经典图论,深度优先和广度优先,拓扑,Prim和Krukal,该来温习啦
- TypeScript-键盘映射
- Web design and website planning assignment 13 making video playlists
- Solve cannot import name 'multiheadattention' from 'tensorflow keras. layers‘
- Typescript declaration merge
- Introduction to guava cache usage
猜你喜欢

JS learning basics document Write write a line of text in the page

Solution to the occurrence interval (space) of latex manual numbering documents

torch. meshgrid

How to make hyperlinks in RichTextBox- How can I make a hyperlink work in a RichTextBox?

Solve valueerror: no model found in config file

Web design and website planning assignment 11 game selection form

B+超强树,带你知晓MySQL的底层是怎样的结构

Anaconda+tensorflow most effective summary version (blood and tears summary of 6 reloads)

Typescript header file usage details
![[software tools] screen recording software captura](/img/79/705bb40fc15322243880f3b9864f2b.jpg)
[software tools] screen recording software captura
随机推荐
torch. nn. functional. pad
TypeScript-接口和类型别名异同
盘它!用「飞项」轻松管理各类型项目
Project training - clonemon
Layout of code setting constraintlayout_ constraintDimensionRatio
Web design and website planning assignment 12 online registration form
JS learning basics document Write write a line of text in the page
【1】 Integrated learning: quickly understand Integrated Learning
Typescript interface and type alias similarities and differences
Using flying items to manage by objectives, not being a "headless fly" in the workplace
并查集是什么?你还在为其烦恼?其实就是一个连通图的问题,理解起来没有那么困难
Icml2022 article intéressant
bat 批处理单独环境打包
DAMENG 用户管理
Shell Programming Notes
Jupyter notebook code completion plug-in + Solution
In place reversal of a LinkedList
Difference between threadpooltaskexecutor and ThreadPoolExecutor
How to start participating in the open source community
Typescript keyboard mapping