当前位置:网站首页>Getting Started with Tkinter
Getting Started with Tkinter
2022-07-31 18:59:00 【Zhou radish】
Tkinter 作为 Python 的标准库,是非常流行的 Python GUI 工具,同时也是非常容易学习的,今天我们就来开启 Tkinter 的入门之旅
图形用户界面 (GUI)
图形用户界面 (GUI) 只不过是一个桌面应用程序,可帮助我们与计算机进行交互
像文本编辑器这样的 GUI 应用程序可以创建、读取、更新和删除不同类型的文件
数独、国际象棋和纸牌等应用程序则是游戏版的GUI程序
还有 Google Chrome、Firefox 和 Microsoft Edge 之类的 GUI 应用程序是用来浏览 Internet 的
这些都是我们日常在电脑上使用的一些不同类型的 GUI 应用程序,其实我们通过 Tkinter 也是可以构建简单的类似应用程序的
今天我们作为 GUI 的入门,将创建一个非常简单且漂亮的 GUI 应用程序
用于创建GUI的 Python 库
Python 有大量的第三方类库,对于 GUI 库,主要有以下几种:
Kivy Python QT wxPython Tkinter
其中,Tkinter 是很多学习者和开发者的首选,因为它简单易用而且随 Python 安装自带
Tkinter 基础
下面的图片显示了应用程序是如何在 Tkinter 中实际执行

我们首先导入 Tkinter 模型,接着,我们创建主窗口,在这个窗口中,我们将要执行操作并显示一切视觉效果,接下来我们添加 Widgets,最后我们进入 Main Event Loop
这里有 2 个重要的关键字
Widgets Main Event Loop
事件循环基本上是告诉代码继续显示窗口,直到我们手动关闭它,是在后台无限循环运行的
对于 Widgets 我们后面单独学习
下面一个代码例子,来深入理解下
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
# to rename the title of the window window.title("GUI")
# pack is used to show the object in the window
label = tkinter.Label(window, text = "Hello World!").pack()
window.mainloop()
我们导入 Tkinter 包并定义一个窗口,接着我们可以修改一个窗口标题,每当打开应用程序时,该标题都会显示在标题选项卡上
最后,我们还定义了一个标签,标签只不过是需要在窗口上显示的输出,在例子中是 hello world

Tkinter Widgets
那么到底什么是 Widgets 呢
Widgets 类似于 HTML 中的元素,我们可以在 Tkinter 中找到针对不同类型元素的不同类型的 Widgets
让我们看看 Tkinter 中所有这些 Widgets 的简要介绍
Canvas - Canvas 用于在 GUI 中绘制形状 Button – Button 用于在 Tkinter 中放置按钮 Checkbutton – Checkbutton 用于在应用程序中创建复选按钮 Entry - Entry 用于在 GUI 中创建输入字段 Frame – Frame 在 Tkinter 中用作容器 Label - Label 用于创建单行 Widgets,如文本、图像等 Menu - Menu 用于在 GUI 中创建菜单
下面让我们逐一看一下每个 Widgets 的用法
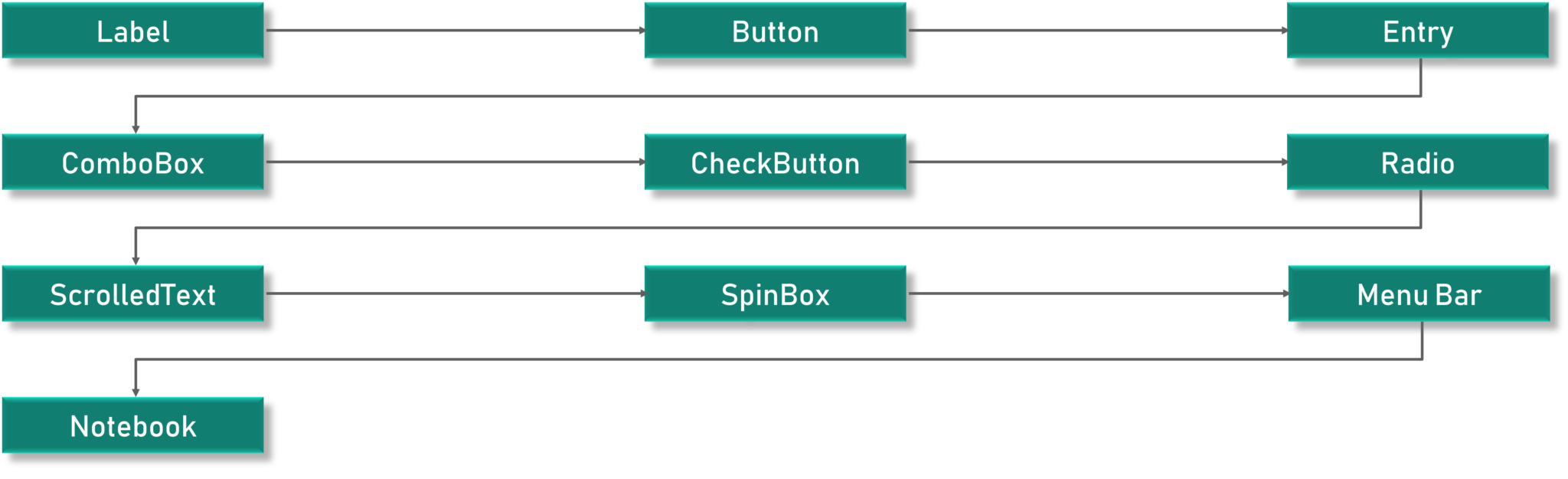
Label
标签用于创建文本和图像以及所有相关的,而且要注意的是,它只能是单行定义
l1 = Label(window, text="萝卜大杂烩!", font=("ArialBold", 50))
l1.grid(column=0, row=0)

还有一个函数 geometry,它基本上用于更改窗口大小并根据我们的要求进行设置
l1 = Label(window, text="萝卜大杂烩!", font=("ArialBold", 50))
window.geometry('350x200')
在这种情况下,我们将其设置为宽 350 像素和高 200 像素
接下来是 button
Button
按钮与标签非常相似,我们创建一个变量并使用 Widgets 语法来定义按钮要表达的内容
window.geometry('350x200')
bt = Button(window, text="Enter")
我们还可以更改按钮或任何其他 Widgets 的前景颜色,使用代码中所示的参数 FG. 同样,也可以使用 BG 属性更改背景颜色
bt = Button(window, text="Enter", bg="orange", fg="red")
bt.grid(column=1, row=0)

我们的前景是定义为红色的文本,背景为橙色
下面来看一下点击按钮的操作
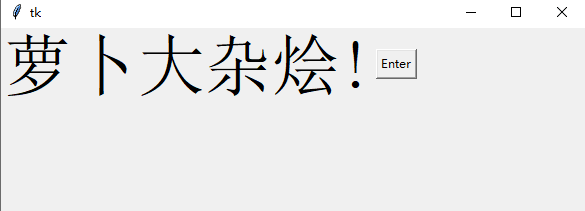
def clicked():
l1.configure(text="按钮被点击了!!")
bt = Button(window, text="Enter", bg="orange", fg="red", command=clicked)
这个我们称之为点击事件,我们需要编写有关单击按钮或触发单击事件时应该发生什么的功能
我们定义了一个名为 clicked 的函数,可以显示一条文本消息,我们在按钮定义中添加一个名为 command 的参数,来调用点击事件
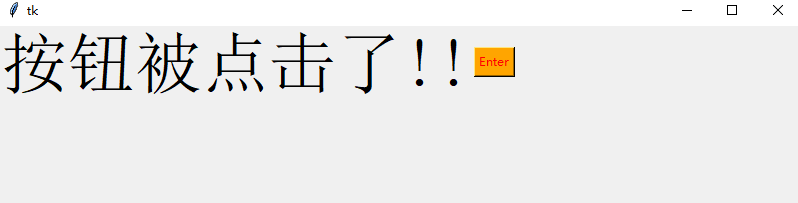
Entry
它用于在 GUI 中创建输入字段以接收文本输入
txt = Entry(window, width=10)
txt.grid(column=1, row=0)
def clicked():
res = "Welcome to " + txt.get()
l1.configure(text=res)
bt = Button(window, text="Enter", bg="orange", fg="red", command=clicked)
在这里,我们使用 Tkinter Entry 类创建一个文本框,grid 定义我们希望窗口小部件位于何处
同时 clicked 函数接收 Entry 的文本信息

Combobox
这是一个带有某些选项的下拉菜单
from tkinter.ttk import *
combo = Combobox(window)
combo['values']= (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, "Text")
combo.current(3)
combo.grid(column=0, row=0)

这样一个下拉菜单就完成了
Checkbutton
复选按钮是非常常用的组件
chk_state = BooleanVar()
chk_state.set (True)
chk = Checkbutton(window, text="Select", var=chk_state)
chk.grid(column=4, row=0)
我们首先创建一个 booleanvar 类型的变量,这是一个 Tkinter 变量
默认情况下,我们将设置状态保持为 true,这代表按钮已经被选中 接下来,我们将 chk_state 传递给 checkbutton 类来为我们设置检查状态

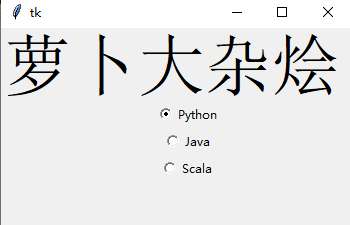
Radio Button
单选按钮也是非常常用的
rad1 = Radiobutton(window, text=Python', value=1)
rad2 = Radiobutton(window, text=Java', value=2)
rad3 = Radiobutton(window, text=Scala', value=3)
rad1.grid(column=0, row=0)
rad2.grid(column=1, row=0)
rad3.grid(column=2, row=0)
在这里,我们使用了不同的参数值,1,2和3,如果它们相同,则会导致冲突并出现错误
它们的文本数据是可以相同,在这里,我们使用了 Python、Java 和 Scala
Scrolled Text
滚动文本组件
scro_txt = scrolledtext.ScrolledText(window, width=40,height=10)
scro_txt.grid(column=0, row=4)
我们指定了窗口的高和宽,否则默认会填充整个 Windiws 窗口
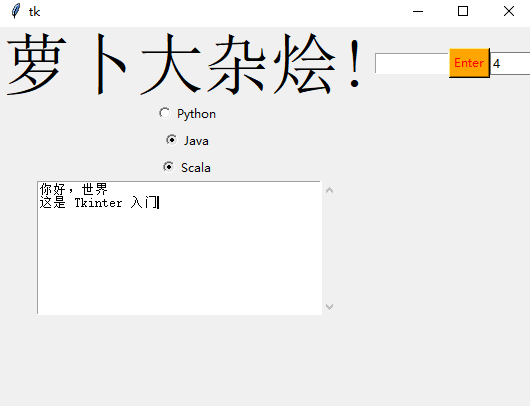
Message Box
消息组件可以方便的弹出提醒消息
def clicked():
messagebox.showinfo('Message title', 'Message content')
btn = Button(window,text=‘ENTER', command=clicked)

SpinBox
Spinbox 也是一个常见的组件,有两个选项卡,存在向上和向下滚动选项卡
pin = Spinbox(window, from_=0, to=100, width=5)
有 3 个参数——from、to 和 width
From – 告诉我们范围的开始和默认值 to – 给我们范围的上限阈值 width 基本上是将 widget 的大小设置为5个字符的空格

Geometry
Tkinter 中的所有 Widgets 都会有一些位置信息,这些度量使得我们可以组织 Widgets 及其父框架、窗口等
Tkinter 具有以下三个布局方式
pack():- 它在块中组织 Widgets,这意味着它占据了整个可用宽度,这是在窗口中显示 Widgets 的标准方法 grid():- 它以类似表格的结构组织 Widgets place():- 它将 Widgets 放置在我们想要的特定位置
组织布局
为了在窗口中安排布局,我们将使用 Frame 类
Frame -- 在窗口中创建分区,我们可以根据需要使用 pack() 方法的侧面参数对齐框架 Button -- 在窗口中创建一个按钮,需要传递几个参数,如文本(按钮的值)、fg(文本的颜色)、bg(背景颜色)
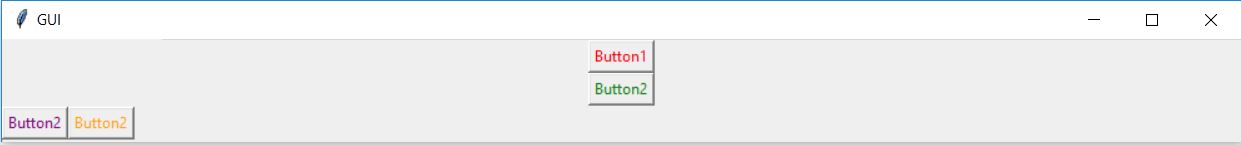
在下面的代码中,我们使用 window、top_frame、bottom_frame 来布局
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating 2 frames TOP and BOTTOM
top_frame = tkinter.Frame(window).pack()
bottom_frame = tkinter.Frame(window).pack(side = "bottom")
# now, create some widgets in the top_frame and bottom_frame
btn1 = tkinter.Button(top_frame, text = "Button1", fg = "red").pack()# 'fg - foreground' is used to color the contents
btn2 = tkinter.Button(top_frame, text = "Button2", fg = "green").pack()# 'text' is used to write the text on the Button
btn3 = tkinter.Button(bottom_frame, text = "Button2", fg = "purple").pack(side = "left")# 'side' is used to align the widgets
btn4 = tkinter.Button(bottom_frame, text = "Button2", fg = "orange").pack(side = "left")
window.mainloop()
再来看一个登录的小栗子
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating 2 text labels and input labels
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Username").grid(row = 0) # this is placed in 0 0
# 'Entry' is used to display the input-field
tkinter.Entry(window).grid(row = 0, column = 1) # this is placed in 0 1
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Password").grid(row = 1) # this is placed in 1 0
tkinter.Entry(window).grid(row = 1, column = 1) # this is placed in 1 1
# 'Checkbutton' is used to create the check buttons
tkinter.Checkbutton(window, text = "Keep Me Logged In").grid(columnspan = 2) # 'columnspan' tells to take the width of 2 columns
# you can also use 'rowspan' in the similar manner
window.mainloop()

下面我们来了解 binding 函数
binding 函数
每当事件发生时调用函数就是绑定函数
在下面的示例中,当单击按钮时,它会调用一个名为 say_hi 的函数. 函数 say_hi 会创建一个带有文本 Hi 的新标签
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating a function called say_hi()
def say_hi():
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Hi").pack()
tkinter.Button(window, text = "Click Me!", command = say_hi).pack() # 'command' is executed when you click the button
# in this above case we're calling the function 'say_hi'.
window.mainloop()

另一种绑定函数的方法是使用事件,事件类似于鼠标移动、鼠标悬停、单击和滚动等等
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# creating a function with an arguments 'event'
def say_hi(event): # you can rename 'event' to anything you want
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Hi").pack()
btn = tkinter.Button(window, text = "Click Me!")
btn.bind("Button-1", say_hi) # 'bind' takes 2 parameters 1st is 'event' 2nd is 'function'
btn.pack()
window.mainloop()
单击事件有 3 种不同的类型,分别是 leftClick、middleClick 和 rightClick
下面的代码将使用对于的文本创建一个新标签
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
#creating 3 different functions for 3 events
def left_click(event):
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Left Click!").pack()
def middle_click(event):
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Middle Click!").pack()
def right_click(event):
tkinter.Label(window, text = "Right Click!").pack()
window.bind("Button-1", left_click)
window.bind("Button-2", middle_click)
window.bind("Button-3", right_click)
window.mainloop()

Images 和 Icons
我们可以使用 PhotoImage 方法添加图像和图标
import tkinter
window = tkinter.Tk()
window.title("GUI")
# taking image from the directory and storing the source in a variable
icon = tkinter.PhotoImage(file = "4.PNG")
# displaying the picture using a 'Label' by passing the 'picture' variriable to 'image' parameter
label = tkinter.Label(window, image = icon)
label.pack()
window.mainloop()
好了,进步的 Tkinter 知识我们都梳理完毕了,下面就完成一个简单的实战项目吧
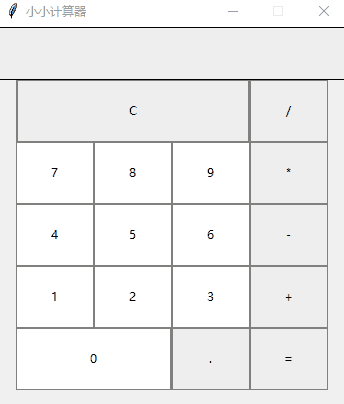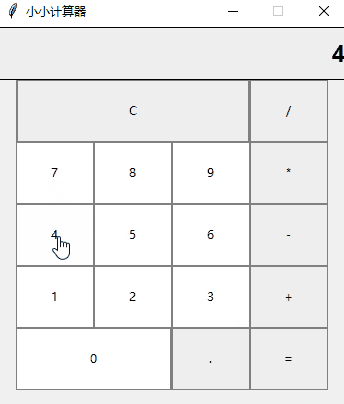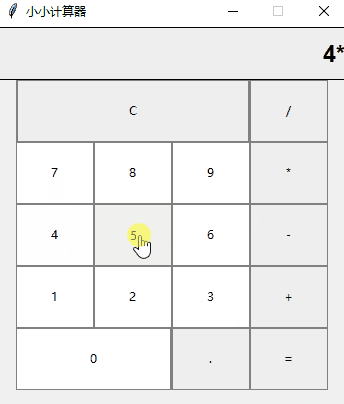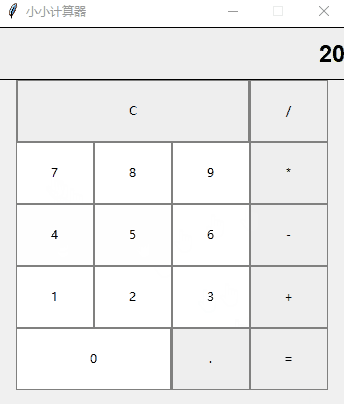
计算器 APP
首先初始化页面
window = Tk()
window.geometry("350x380")
window.resizable(0, 0) # this prevents from resizing the window
window.title("小小计算器")
接下来定义输入数字框
input_text = StringVar()
input_frame = Frame(window, width=312, height=50, bd=0, highlightbackground="black", highlightcolor="black",
highlightthickness=1)
input_frame.pack(side=TOP)
input_field = Entry(input_frame, font=('arial', 18, 'bold'), textvariable=input_text, width=50, bg="#eee", bd=0,
justify=RIGHT)
input_field.grid(row=0, column=0)
input_field.pack(ipady=10)
然后定义按钮方法,我们以清除按钮和除法按钮为例
clear = Button(btns_frame, text="C", fg="black", width=32, height=3, bd=0, bg="#eee", cursor="hand2",
command=lambda: btn_clear()).grid(row=0, column=0, columnspan=3, padx=1, pady=1)
divide = Button(btns_frame, text="/", fg="black", width=10, height=3, bd=0, bg="#eee", cursor="hand2",
command=lambda: btn_click("/")).grid(row=0, column=3, padx=1, pady=1)
最后就是计算equal逻辑
equals = Button(btns_frame, text="=", fg="black", width=10, height=3, bd=0, bg="#eee", cursor="hand2",
command=lambda: btn_equal()).grid(row=4, column=3, padx=1, pady=1)
def btn_equal():
global expression
result = str(eval(expression))
input_text.set(result)
expression = ""
好了,让我看下最终的效果吧,虽然页面很简陋,但是加减乘除这些基本运算还是包含了的
好了,今天的分享就到这里,喜欢就点个赞吧
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

go基础部分学习笔记记录
Combinatorics Notes (6) Associative Algebra of Locally Finite Partially Ordered Sets, Möbius Inversion Formula
useragent在线查找
Kotlin coroutines: continuation, continuation interceptor, scheduler

Introduction to Audio Types and Encoding Formats in Unity

Unity 之 音频类型和编码格式介绍

C# 之 扑克游戏 -- 21点规则介绍和代码实现
flyway的快速入门教程
MySQL---单行函数

如何才能真正的提高自己,成为一名出色的架构师?
随机推荐
Masterless replication system (2) - read and write quorum
Kotlin coroutines: continuation, continuation interceptor, scheduler
Given an ip address, how does the subnet mask calculate the network number (how to get the ip address and subnet mask)
API for JD.com to obtain historical price information of commodities
京东获取商品历史价格信息 API
Concurrency, Timing and Relativity
How programmers learn open source projects, this article tells you
Batch (batch size, full batch, mini batch, online learning), iterations and epochs in deep learning
multithreaded lock
idea中搜索具体的字符内容的快捷方式
如何识别假爬虫?
INeuOS industrial Internet operating system, the equipment operational business and "low code" form development tools
移动web开发02
1161. 最大层内元素和 : 层序遍历运用题
京东按关键字搜索商品 API
中文编码的设置与action方法的返回值
Bika LIMS 开源LIMS集—— SENAITE的使用(检测流程)
matplotlib ax bar color Set the color, transparency, label legend of the ax bar
Apache EventMesh 分布式事件驱动多运行时
Handling write conflicts under multi-master replication (3) - Convergence to a consistent state and custom conflict resolution logic