当前位置:网站首页>Study diary: February 14th, 2022
Study diary: February 14th, 2022
2022-07-03 20:56:00 【Chen Jia on the weekend】
Today's first question
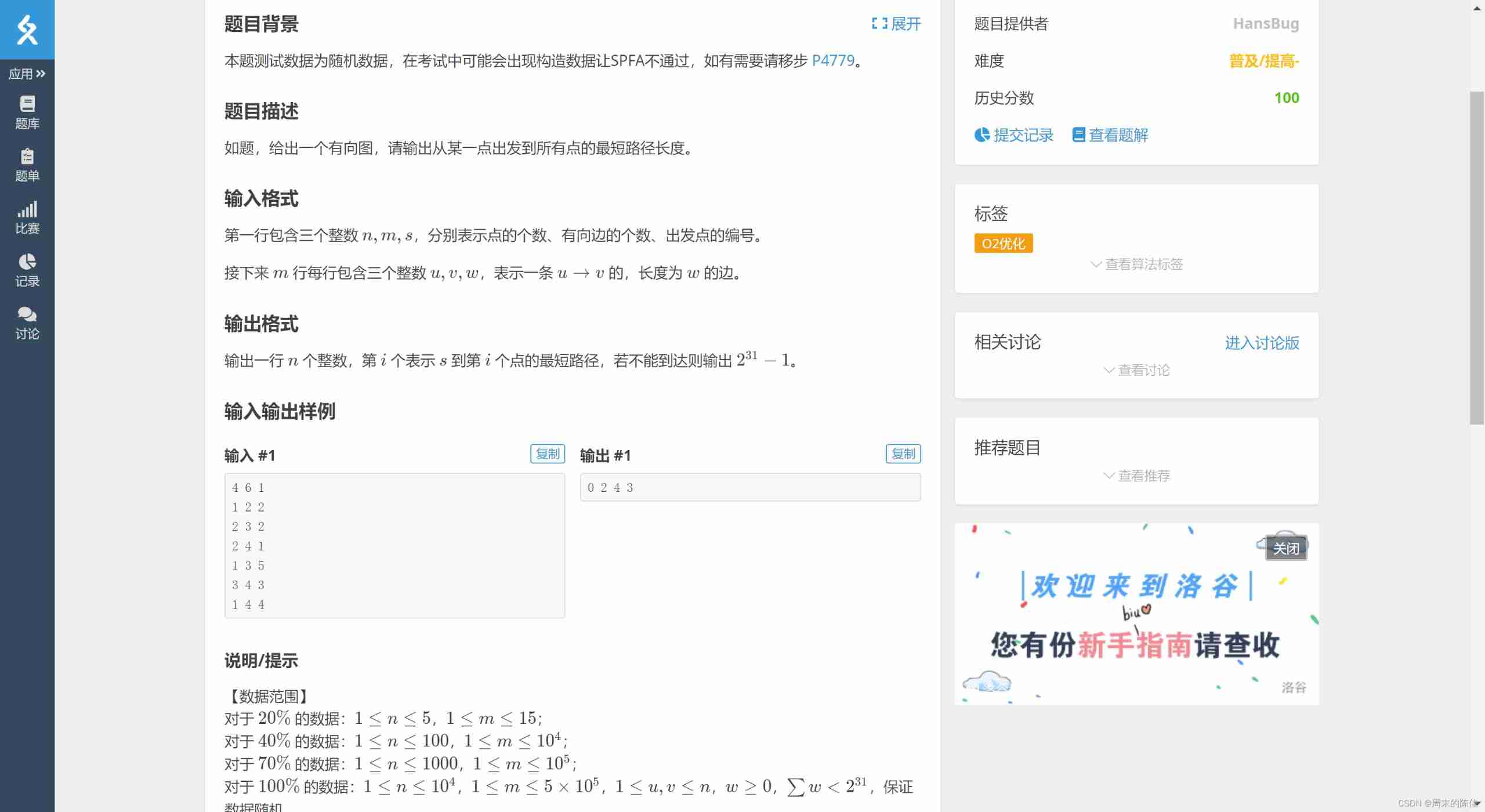
I don't know how long it tortured me , I also asked several students
The first is the storage of data .
The method used is chain forward star
The principle is similar to linked list method and adjacency list
4 6 1 1 2 2 2 3 2 2 4 1 1 3 5 3 4 3 1 4 4
Borrow the data in the title
First we define a structure
among to Store his destination
length Storage distance
next Store other nodes adjacent to it
Then define an array head
First, the first data 1 2 2
For the first structure, his to=2,length=2,next=【1】=0( When next by 0 It indicates that there are no adjacent nodes )
head[1]=1
Second data 2 3 2
For the second structure to=3,length=2,next=head【2】=0
head【2】=2
Third data 2 4 1
For the third structure to=4,length=1,next=head【2】=2
head【2】=3
Fourth data 1 3 5
For the fourth structure to=3,length=5,next=head【1】=1
head【1】=4
The fifth data 3 4 3
For the fifth structure to=4,length=3,next=head【3】=0;
head【3】=5
The sixth data 1 4 4
For the sixth structure to=4,length=4,next=head【4】=0;
head【4】=6;
The storage structure is similar to this

The same effect can be achieved by using linked lists
I first used a linked list
Then is the method of traversing the shortest path

Take the figure given in the title as an example
First of all, let's start from the starting point
from 1 We can achieve 2,3,4
We also build an array to store the shortest path
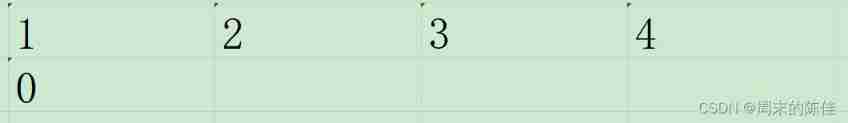
because 1-1 No need to move , So the distance is 0
At first, we can start from 1-2,3,4
So we get a new table

Then choose the shortest distance from the following table, that is 2
From the node 2 Set out to get to 3 and 4
Because what we require is the slave node 1 The shortest distance to each node ,
Let's suppose we start from 2 Transfer to 3 and 4 The distance needed is 4 and 3
It is obviously closer than the principle , So we update the form

Then from the next 3 and 4 Choose the shortest path 3, adopt 3 We can go to 4, But the distance needed is 8 Farther than the original distance , So don't change
Final selection 4, node 4 Cannot reach any node , So the final answer is
0 2 4 3
The code is as follows
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long long Max=2147483647;
int point,side,start;
long long result[1000000];
long long book[1000000];
struct Data
{
int to;
int length;
int next;
}data[1000000];
int head[1000000];
int top=0;
int add(int a,int b,int c)
{
top++;
data[top].to=b;
data[top].length=c;
data[top].next=head[a];
head[a]=top;
return 0;
}
int finding(int start)
{
for(int i=1;i<=point ;i++)
{
result[i]=Max;
book[i]=0;
}
result[start]=0;
int present=start;
while(book[present]==0)
{
book[present]=1;
long long mining=Max;
for(int i=head[present];i;i=data[i].next)
{
if(book[data[i].to]==0)
if(result[data[i].to]>result[present]+data[i].length)
result[data[i].to]=result[present]+data[i].length;
}
for(int i=1;i<=point;i++)
{
if(book[i]==0)
if(result[i]<mining)
{
mining=result[i];
present=i;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
cin>>point>>side>>start;
for(int i=1;i<=side;i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
add(a,b,c);
}
finding(start);
for(int i=1;i<=point ;i++)
cout<<result[i]<<' ';
}This topic has tortured me all day
A total of submitted me 20 Time
Second question

The solution of this problem feels like brute force cracking
AHA algorithm also introduces this algorithm .
In particular, the title also gives the corresponding relationship
We also build such an array data
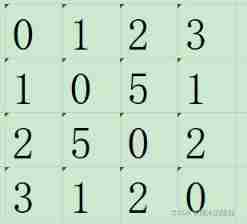
The corresponding relationship among them , for instance data【1】【3】=1
explain 1 To 3 The degree of danger is 1
We from 1-3 There are two ways, one is directly from 1-3, Another is through the intermediate node 2
from 1 To 2 Until then 3 First, the risk of passing through the intermediate node is data【1】【2】+data【2】【3】=7. Obviously, the danger is higher , If we encounter a less dangerous one, we will exchange ,
If we want to go from 2-1 The danger level of direct arrival is 5
From the node 3 The way around is data【2】【3】+data【3】【1】=3
Less dangerous , So we put data【2】【1】 become 3; Through such comparison and transformation , Optimize all routes
The final code implementation is as follows
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int point[1000];
int data[10004][10004];
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
cin>>point[i];
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
cin>>data[i][j];
}
}
int count=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
{
// Choose a better route
if(data[j][k]>data[j][i]+data[i][k])
{
data[j][k]=data[j][i]+data[i][k];
}
}
}
}
// Take the corresponding route according to the obtained optimal route
for(int i=2;i<=m;i++)
{
count+=data[point[i-1]][point[i]];
}
cout<<count;
}The algorithm used is Floyd Algorithm
Three of them are mainly used for loop , The first represents the transit node , The lower two layers are different nodes
Finally, it is better to pass the node or not , Choose the best route , Finally get the solution
The third question
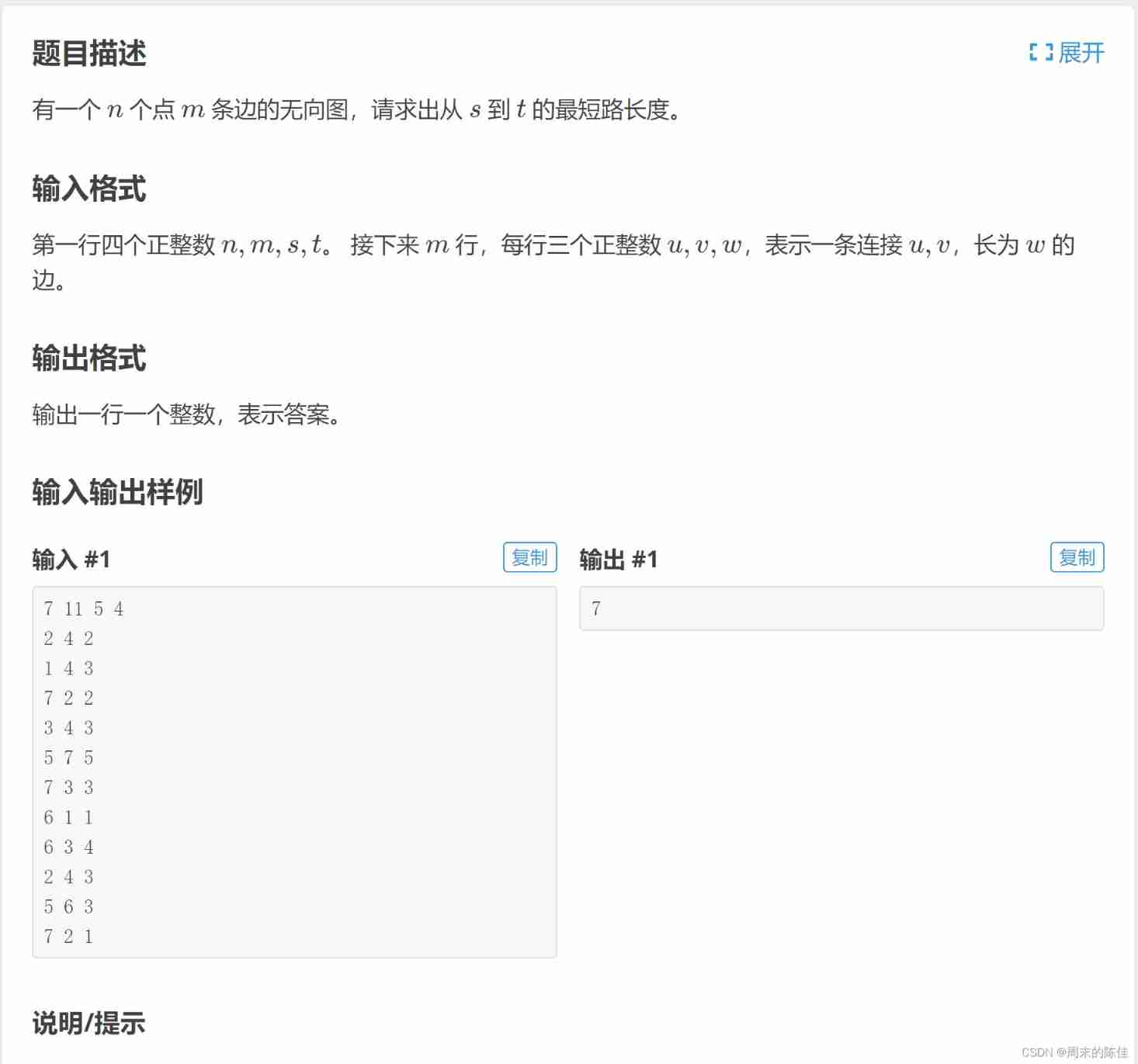
If you remove the end point from the title and change the undirected graph into a directed graph, it will be exactly the same as the first question I wrote today
The key point is simply output result【 a key 】 That's all right. ,
What should we do when a directed graph becomes an undirected graph .
It's also very simple .
A directed graph is one that can only pass , You can't come back
An undirected graph is one that can pass , You can come back again .
Then we can add a return route based on the digraph
So I also directly modify the code of the second question a little
The final code is as follows
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long long Max=2147483647;
int point,side,start;
int ending;
long long result[1000000];
long long book[1000000];
struct Data
{
int to;
int length;
int next;
}data[1000000];
int head[1000000];
int top=0;
int add(int a,int b,int c)
{
top++;
data[top].to=b;
data[top].length=c;
data[top].next=head[a];
head[a]=top;
return 0;
}
int finding(int start)
{
for(int i=1;i<=point ;i++)
{
result[i]=Max;
book[i]=0;
}
result[start]=0;
int present=start;
while(book[present]==0)
{
book[present]=1;
long long mining=Max;
for(int i=head[present];i;i=data[i].next)
{
if(book[data[i].to]==0)
if(result[data[i].to]>result[present]+data[i].length)
result[data[i].to]=result[present]+data[i].length;
}
for(int i=1;i<=point;i++)
{
if(book[i]==0)
if(result[i]<mining)
{
mining=result[i];
present=i;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
cin>>point>>side>>start>>ending;
for(int i=1;i<=side;i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
add(a,b,c);
add(b,a,c);
}
finding(start);
cout<<result[ending];
}The core code and central idea have basically not changed
Fourth question
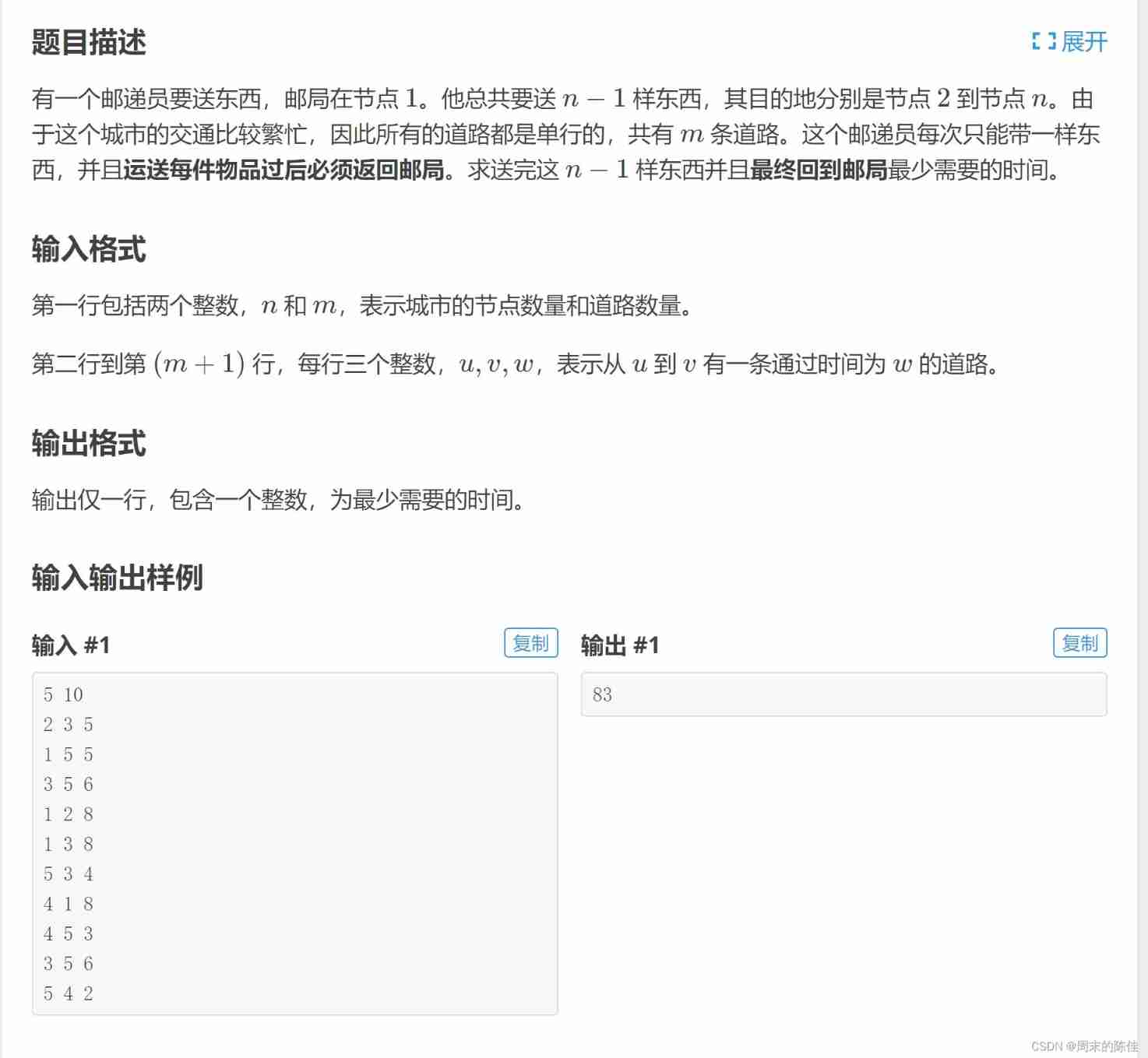
This question is also a variant of the Pirates of the Caribbean
It's just a little troublesome , There are going and coming back
If yes data[i][j] If it comes back data[j][i]
The final code is as follows
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n,m;
int data[1003][1003];
int main()
{
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++)
{
data[i][j]=99999999;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
int a,b,c;
cin>>a>>b>>c;
data[a][b]=min(data[a][b],c);
}
long long count=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
for(int k=1;k<=n;k++)
{
if(data[j][k]>data[j][i]+data[i][k])
{
data[j][k]=data[j][i]+data[i][k];
}
}
}
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
count+=data[1][i]+data[i][1];
}
cout<<count;
}Among them, we need to think about repeating edges a little , It may be a road and a path , Choose the shortest way
边栏推荐
- 同花顺开户注册安全靠谱吗?有没有风险的?
- Use of CMD command
- APEC industry +: father of the king of the ox mill, industrial Internet "king of the ox mill anti-wear faction" Valentine's Day greetings | Asia Pacific Economic media | ChinaBrand
- String and+
- 鹏城杯 WEB_WP
- [postgresql]postgresql custom function returns an instance of table type
- Link aggregation based on team mechanism
- 一台服务器最大并发 tcp 连接数多少?65535?
- thrift go
- Thread, thread stack, method stack, the difference of creating thread
猜你喜欢
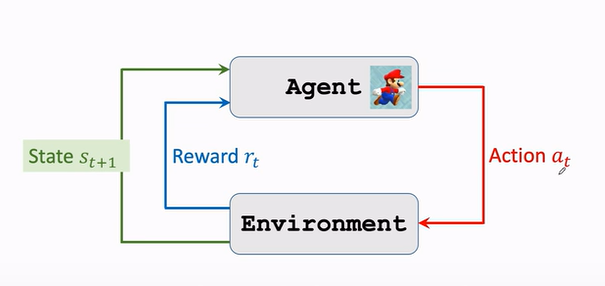
Apprentissage intensif - notes d'apprentissage 1 | concepts de base

In 2021, the global revenue of syphilis rapid detection kits was about US $608.1 million, and it is expected to reach US $712.9 million in 2028

MDM mass data synchronization test verification

如临现场的视觉感染力,NBA决赛直播还能这样看?

运维各常用命令总结

Memory analyzer (MAT)

18、 MySQL -- index

Nmap and masscan have their own advantages and disadvantages. The basic commands are often mixed to increase output

鹏城杯 WEB_WP
JS three families
随机推荐
Do you really know how old you are?
Interval product of zhinai sauce (prefix product + inverse element)
[Yugong series] February 2022 Net architecture class 004 ABP vNext used in WPF project
"Actbert" Baidu & Sydney University of technology proposed actbert to learn the global and local video text representation, which is effective in five video text tasks
Set, weakset, map, weakmap in ES6
阻塞非阻塞和同步异步的区分 参考一些书籍
Basic preprocessing and data enhancement of image data
内存分析器 (MAT)
Day6 merge two ordered arrays
Apprentissage intensif - notes d'apprentissage 1 | concepts de base
不同业务场景该如何选择缓存的读写策略?
Test changes in Devops mode -- learning and thinking
Basic number theory -- Chinese remainder theorem
jvm jni 及 pvm pybind11 大批量数据传输及优化
Read the root directory of the folder, write txt and generate random samples
Based on laravel 5.5\5.6\5 X solution to the failure of installing laravel ide helper
Hcie security Day11: preliminarily learn the concepts of firewall dual machine hot standby and vgmp
Operate BOM objects (key)
Hcie security Day10: six experiments to understand VRRP and reliability
Q&A:Transformer, Bert, ELMO, GPT, VIT