当前位置:网站首页>Method (common method), method execution memory analysis, method overloading mechanism, method recursion
Method (common method), method execution memory analysis, method overloading mechanism, method recursion
2022-06-11 09:19:00 【lwj_ 07】
One 、 Method
The following procedure does not use " Method " What are the disadvantages of the analysis ? Code redundancy
The same code is written three times ( But the data involved in summation is different each time ) The code is not reused .
belong java There is such a mechanism in the language :
- A function code only needs to be written once
- Use this feature , Just pass specific data to this function
- This function returns a final result .*** Methods are defined in class bodies , Multiple methods can be defined in a class , Methods are written in no order , Be free to . !!! However, methods cannot be defined in the method body !!!!!!!
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// demand 1: Calculation 10+20 And And output the result 【 function : Calculate two int The sum of type data 】
int a=10;
int b=20;
int c=a+b;
System.out.println(c);
// demand 2: Calculation 30+40 And And output the result 【 function : Calculate two int The sum of type data 】
int d=30;
int e=40;
int f=d+e;
System.out.println(f);
// demand 3: Calculation 50+60 And And output the result 【 function : Calculate two int The sum of type data 】
int g=50;
int h=60;
int i=g+h;
System.out.println(i);
}
} About java Methods in language :
1、 How to define methods , Grammatical structure :【 List of modifiers 】 Return value type Method name { List of formal parameters }{
Method body ;
}2、 Explain the above grammatical structure :
2.1、 About modifier list
* optional , It's not necessary
* At present, it is uniformly written as :public static
* Method in the modifier list “ Yes static keyword ” Words , How to call this method ?
- Class name . Method name ( List of actual parameters );
2.2、 return type
* What is the return value ?
One way is to complete a specific function , After the end of this function, most of them need
Return the final result , The execution result may be a specific existing data , And this concrete deposit
The data in is the return value .
* return type ?
The return value is a specific data , There are types of data , What needs to be specified here is return
The specific type of the return value .
* What types can be specified for the return value types ?
java Either type can , Including basic data types and all reference data types .* Return value ?
return value ; And ask for " value " The data type of must be the same as “ Method 's return value type ” Agreement .
The return value type is void When , In the method body You can't ( use ) To write "return value ;" In this way
sentence . But be aware that you can write "return;" Such a statement .
Just have return Keyword statement execution ,return The method where the statement is located ends .【 No JVM end , yes return End of method 】
* List of formal parameters : It's called formal parameter for short
Parameter is a local variable :int a; double b; float c;

The code framework is as follows
public class A // The car factory
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Call this method
}
// Define a method
// A workshop
public static int sumInt(int a, int b){
}
}Simple code demonstration
public class A
{
// The main method needs to be written in such a fixed way , This is the entry to the program .
public static void main(String[] args){
// Call at the entry of the program ( Can be called many times )
A.sumInt(10,20); // The type of formal parameter list is int type
}
// List of modifiers :public static
// return type : void
// Method name : sumInt
// List of formal parameters : (int a, int b)
public static void sumInt(int a, int b){
int c =a+b;
System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c);
}
}Methods are not always called main Among the methods , Among other methods . As long as it is where the program can be executed , Can call other methods .
Code demonstration :
public class A
{
public static void dosome(int a,int b){
int c =a-b;
System.out.println(a+"-"+b+"="+c);
A.sumInt(10,20); // Call again sumInt Method
}
// Main method program entry
public static void main(String[] args){
A.dosome(60,50); // First call dosome Method
System.out.println("hello world!"); // The final output hello world!
}
public static void sumInt(int a, int b){
int c =a+b;
System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+c);
}
}Output results :

When a method is called, the number of actual parameters and formal parameters should be the same , The data type corresponds to the same . When types are different, corresponding automatic type conversion is required
The code is shown as follows :
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
A.sumLong(10L,20L);
// There is an automatic type conversion int--->long ( Small capacity to large capacity )
A.sumLong(10,20);
// Compile error 3.0 by double type ( The large capacity )
//A.sumLong(3.0,20);
A.sumLong((int)(3.0),20); // Add a translator ( Accuracy will be lost )
}
public static void sumLong(long a,long b){
System.out.println(a+"+"+b+"="+(a+b));
}
}The return value type of the method is not void When .
The return value type is not void When :
It is required that the method must be 100% implemented "return value ;" Such a statement to complete the return value .
Without this statement, the compiler will report an error .
demand :
Please define and implement a method , This method can calculate two int Quotient of type data ,
The final calculation result is required to be returned to the caller
Code demonstration 1:( The case where the return value is not received is as follows )
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
A.divide(30,10); // At this point, the program can run after calling But no return value is received
}
public static int divide(int a,int b){
//int c =a/b;
//return c; // The value returned c Must be and return value type int The same type
// In case of inconsistency, an error will be reported
// For example, the error types are (return; return true; return Values of other data types ;)
return a/b;
}
}Generally, calling other people's methods will receive the data in the method , The received data code is as follows :
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Variable reception is adopted : The variable must be consistent with the data type of the return value
// First reception :
int i=A.divide(30,10);
System.out.println(i);
// Second reception :
long x=A.divide(30,10); // In integer type : Small capacity to large capacity
System.out.println(x);
// The third type of reception :
System.out.println(A.divide(30,10));
}
public static int divide(int a,int b){
return a/b;
}
}thorough return sentence
thorough return sentence
* with return Keywords java Statement as long as the execution , End of method execution .
* stay " Same scope " among ,return No code can be written below the statement , because
For this code will never execute , So compilation error .
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
// Successful reception
int i=A.m();
System.out.println(i);
*/
// Report errors : hold m As a variable
//System.out.println(A.m);
// success
System.out.println(A.m());
}
public static int m(){
/*
int a=10;
if (a>3) // Report errors : Missing return statement Because the compiler only knows to judge a>3 I don't know. false still true
// If it is false Words It's in int There is no return statement in the return value type So wrong reporting .
// That is, there is no guarantee return 1; Be carried out 100% .
{
return 1;
}
*/
// Compile successfully Because if the compiler judges a>3 by false When Can also else Output the return statement return 0;
int a=10;
if (a>3)
{
return 1;
// You can't write code here , Compile error , because return The statement cannot be accessed below
//System.out.println("hello world!");
}
else{
// Compile successfully : When a<=3 The statement can be accessed when
System.out.println("hello world!");
return 0;
// Empathy The statement cannot be accessed
//System.out.println("hello world!");
}
// You can also rewrite the code with ternary operators
//return 10>3? 1:0;
}
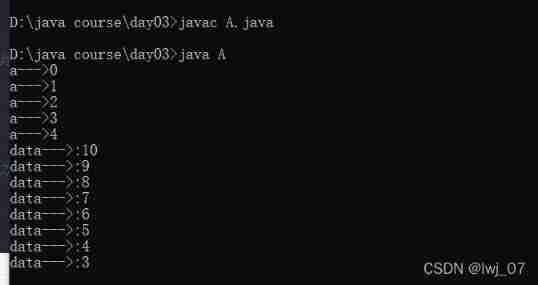
}When the return type is void In the method of “return;” sentence . "return;" Statement appears when the return value is void The main purpose of this method is to end the current method .
Code demonstration :
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
A.m();
for (int i=10;i>1 ;i-- )
{
if (i==2)
{
return;
}
System.out.println("data--->:"+i);
}
// Will not be executed i==2 when return; Has terminated main() Method
System.out.println("junker");
}
public static void m(){
/*
Compile error : Incompatible types : Unexpected return value ( For methods with empty result type , Cannot return value )
return 10;
*/
for (int a=0;a<=10 ;a++ )
{
if (a==5)
{
return; // return effect : It's not the end for loop , Is termination m() Method .
}
System.out.println("a--->"+a);
}
// Will not be executed a==5 when return; Has terminated m() Method
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}
return; and break; The difference between
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
A.m();
}
public static void m(){
/*
Compile error : Incompatible types : Unexpected return value ( For methods with empty result type , Cannot return value )
return 10;
*/
for (int a=0;a<=10 ;a++ )
{
if (a==5)
{
return; // return effect : It's not the end for loop , Is termination m() Method .
//break; // What ends is for loop
}
System.out.println("a--->"+a);
}
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
} 
a key !!!
Method is in the process of execution , stay JVM How is the memory allocated in ? How memory changes ?
/*
Method is in the process of execution , stay JVM How is the memory allocated in ? How memory changes ?
1、 Method only defines and does not call , It's not going to be implemented , And in JVM The method will not be assigned " Operation " Of memory space .
2、 stay JVM There are three main memory spaces in the memory partition :
* Method area memory 【 Method area 】
* Heap memory 【 Heap area 】
* Stack memory 【 The stack area 】
3、 About " Stack " data structure :
* Stack :stack, It's a data structure
* Data structure reflects the storage form of data
* As a programmer, you need to be proficient in : data structure + Algorithm
4、 Where does the method code fragment exist ? When the method is executed, where is the memory of the execution process allocated ?
* Method code snippets Belong to .class A part of a bytecode file , The bytecode file is loaded when the class ,
Put it In the method area . therefore JVM The three main memory spaces in the Method area memory first has
data . Stored code snippets .* Although there is only one code fragment in the method area memory , But it can be Repeated calls to .
Every time this method is called , The method needs to be assigned a separate venue , stay Stack memory allocation .5、 Method at the moment of call , This method will be allocated memory space , Will occur in the stack Stack pressing action ,
After method execution , All memory allocated for the method is freed , This happens Play stack action .
* Pressing stack : Allocate memory to the method
* Bomb stack : Free the memory space of this method
6、 The local variable is in " Method body " In a statement , Local variable runtime memory is allocated in the stack .
*/
Image analysis and description of stack


Method to perform memory analysis
public class A {
public static void main(String[] args){
int a =10;
int b =20;
int retValue =sumInt(a,b);
System.out.println("retValue>>>:"+retValue);
}
public static int sumInt(int i,int j){
int result = i+j;
int num =3;
int retValue = divide(result,num);
return retValue;
}
public static int divide(int x,int y){
int z=x/y;
return z;
}
}
Two 、 Method overloading
The following code does not use " Method overload mechanism ", Don't use overload, Analysis of the shortcomings of the program ?
1、sumInt,sumLong,sumDouble Although the methods have different functions , But the function is similar . It's all about summation .
Methods with similar functions in the following programs , They have three different names , This is for programmers , call
The method is inconvenient , Programmers need to remember more methods , To complete the call 【 inconvenient 】
2、 The code is not beautiful .Is there such a mechanism :
The function is different , however “ Functions are similar ” Can make the programmer more convenient .
Method overload mechanism :Overload
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
int result1 =sumInt(1,2);
System.out.println(result1);
long result2 =sumLong(1L,2L);
System.out.println(result2);
double result3 =sumDouble(1.0,2.0);
System.out.println(result3);
}
public static int sumInt(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
public static long sumLong(long a,long b){
//long c =a+b;
//return c;
return a+b; // a+b by long type
}
public static double sumDouble(double a,double b){
return a+b;
}
}
Experience the benefits of the following method overloading :( The two results are the same advantage : No more method names , At this point, the distinguishing method no longer depends on the method name , It depends on the data type of the parameter .)
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
// Calling a method is like using a method
// Different types of parameters , The method to be called is also different
// At this point, the distinguishing method no longer depends on the method name , It depends on the data type of the parameter .
System.out.println(sum(1,2));
System.out.println(sum(1L,2L));
System.out.println(sum(1.0,2.0));
}
// The following three methods constitute the method overloading mechanism
// sum Method name
public static int sum(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
// sum Method name
public static long sum(long a,long b){
return a+b;
}
// sum Method name
public static double sum(double a,double b){
return a+b;
}
}Enhance understanding of method overloading mechanisms
Method overloading :
1、 Method overloading is also called :overload
2、 When to consider using method overloading ?
* When the functions are similar Try to make the method names the same .
【 But the function is different / When it's different It is very likely to make the method name different 】
3、 What conditions are satisfied to constitute a method overload ?
* In the same class
* Same method name
* Different parameter list :
The quantity is different or Different order or Different types
4、 Method overloading has something to do with , It has nothing to do with ?
* Method overload and method name + Parameter list related
* Method overloading has nothing to do with the return value type
* Method overloading has nothing to do with the modifier list
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
m1();
m1(1);
m2(2,2.0);
m2(2.0,2);
m3(3);
m3(3.0);
}
// The following two methods constitute overloads as follows :
// The number of parameter lists varies :
public static void m1(){}
public static void m1(int a){}
// The parameter order is different :
public static void m2(int a,double b){}
public static void m2(double a,int b){}
// Different parameter types :
public static void m3(int x){}
public static void m3(double y){}
/*
Compile error : Neither of the following methods constitutes a method overload , It is the method repetition that has occurred
public static void m4(int a,int b){}
public static void m4(int b,int a){}
Compile error :
public static void m5(){}
public static int m5(){
return 1;
}
Compile error :
void y(){}
public static void y(){}
*/
}The error results are as follows :

Application of method overloading :
You can customize a package

Then call directly

give the result as follows :

3、 ... and 、 recursive ******
About recursive calls to methods
1、 What is recursion ?
The method itself calls itself .
2、 Recursion is memory intensive , Recursive algorithms should not be used when they are not used .
3、 An error occurred while the following program was running 【 It's not unusual , It's a mistake Error】:
java.lang.StackOverflowError
Stack memory overflow error .
An error cannot be undone , There is only one result , Namely JVM Stop working .
4、 Recursion must have an end condition , If there is no end condition, a stack memory overflow error will occur .
5、 Recursion, even if it has an end condition , Even if the end condition is correct , Stack memory overflow errors can also occur , Because recursion is too deep .
public class A
{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("main begin");
doSome();
System.out.println("main over");
}
// The following code snippet is only one
// But it can be called repeatedly , And just call doSome Method will allocate a new memory space in the stack memory .
public static void doSome(){
System.out.println("doSome begin");
doSome(); // This line of code doesn't end The following code is not executable .
System.out.println("doSome over");
}
}Running results :

Do not use recursion seek 1~N And
public class A
{
/*
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
int sum=0;
for (int a=1;a<=4 ;a++ )
{
sum+=a;
}
System.out.println("sum:"+sum);
*/
// Calculated above 1~4 And It is used when there is no learning method
// After learning the method, you should learn to use the method to complete the code
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(sumInt(4));
}
// Define a method separately , It's a stand-alone feature , Can finish 1~N Sum of
public static int sumInt(int n){
int sum =0;
for (int a=1;a<=n ;a++ )
{
sum+=a;
}
return sum;
}
}边栏推荐
- [share] how do enterprises carry out implementation planning?
- 【分享】企业如何进行施行规划?
- 86. separate linked list
- CUMT learning diary - theoretical analysis of uCOSII - Textbook of Renzhe Edition
- Error [error] input tesnor exceeded available data range [neuralnetwork (3)] [error] input tensor '0' (0)
- Kubelet error getting node help
- 报错RuntimeError: BlobReader error: The version of imported blob doesn‘t match graph_transformer
- Complexity analysis of matrix inversion operation (complexity analysis of inverse matrix)
- Fabric.js 動態設置字號大小
- When the enterprise makes a decision, which part should lead the ERP project?
猜你喜欢

MSF evasion模块的使用

openstack详解(二十三)——Neutron其他配置、数据库初始化与服务启动
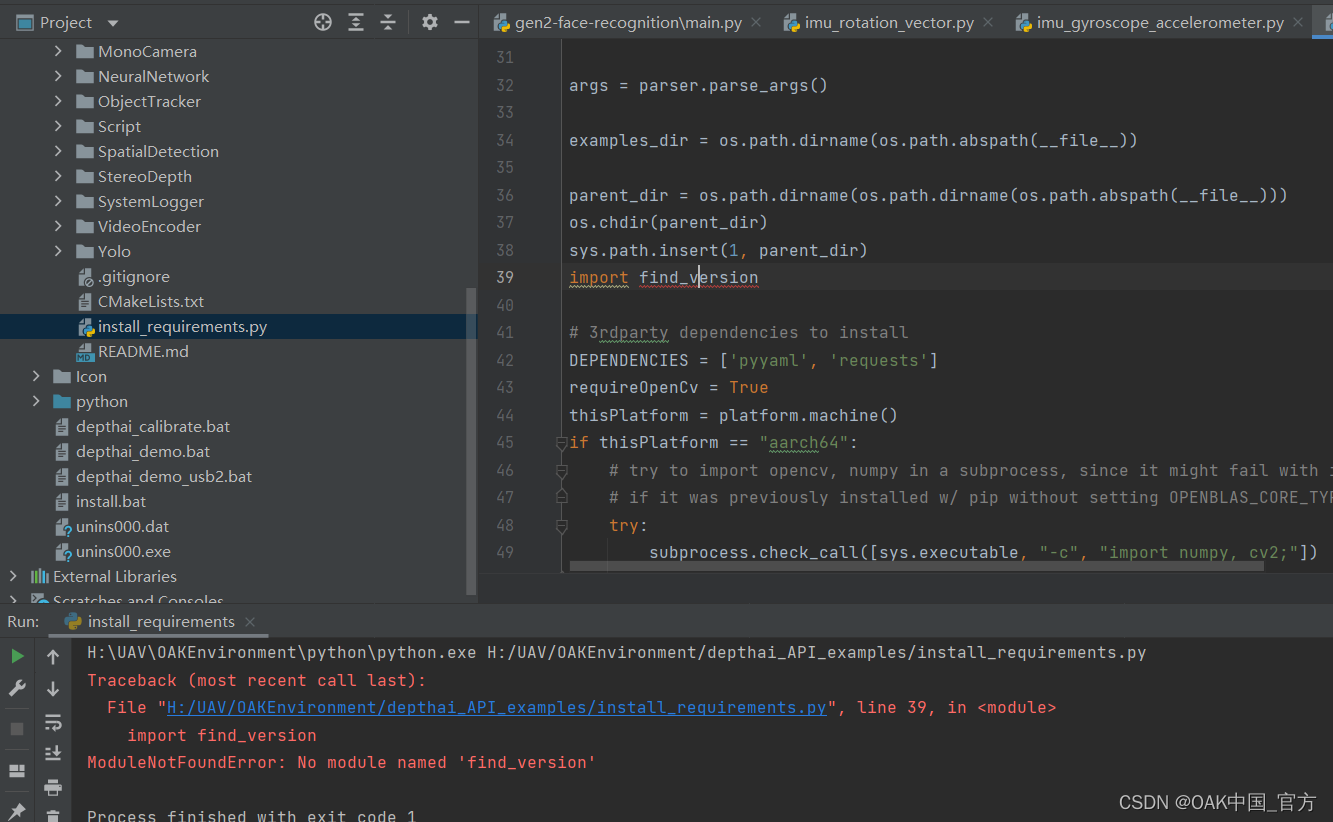
报错ModularNotFoundError: No module named ‘find_version’

报错Output image is bigger(1228800B) than maximum frame size specified in properties(1048576B)

山东大学增强现实实验四

Opencv CEO teaches you to use oak (IV): create complex pipelines
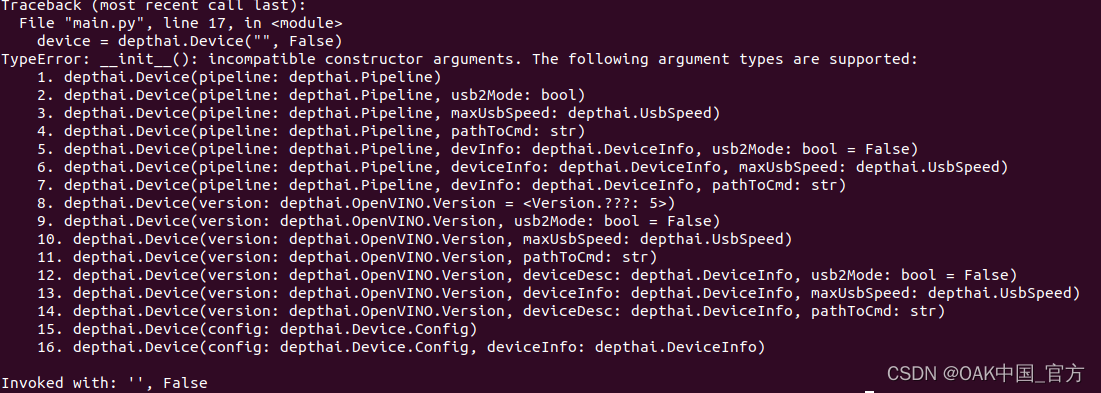
Device = depthai Device(““, False) TypeError: _init_(): incompatible constructor arguments.

ArcGIS 10.9.1 地质、气象体元数据处理及服务发布调用

Type-C蓝牙音箱单口可充可OTG方案

Type-C扩展坞自适应供电专利维权案例
随机推荐
1721. exchange nodes in the linked list
1854. 人口最多的年份
Redis source code analysis hash object (z\u hash)
报错Version mismatch between installed depthai lib and the required one by the scrip.
【方案设计】基于单片机开发的家用血氧仪方案
Tissu. JS définit dynamiquement la taille de la police
PD chip ga670-10 for OTG while charging
Résumé de la méthode d'examen des mathématiques
Openstack explanation (XXIII) -- other configurations, database initialization and service startup of neutron
Type-C扩展坞自适应供电专利维权案例
Do you know these advantages of ERP system?
MSF adds back door to normal program
MSF基于SMB的信息收集
实现边充边OTG的PD芯片GA670-10
[FAQ for novices on the road] about data visualization
Type-C蓝牙音箱单口可充可OTG方案
MySQL startup error "bind on tcp/ip port: address already in use"
Automation operation and maintenance articles collection
市场上的服装ERP体系到底是哪些类型?
Erreur de démarrage MySQL "BIND on TCP / IP Port: Address already in use"