当前位置:网站首页>Teacher wangshuyao's notes on operations research 04 fundamentals of linear algebra
Teacher wangshuyao's notes on operations research 04 fundamentals of linear algebra
2022-07-29 06:52:00 【three billion seventy-seven million four hundred and ninety-one】
The first 4 speak Fundamentals of linear algebra
Linear algebra is through a series of means “ Toss about ” Equations , Extract the system information .
The purpose of linear algebra
Solve a system of linear equations ( The degree of the linear equation, that is, the unknown number, is 1 The equation of ).
Steps of solving linear equations
- Judge whether there is a solution
- How to solve
- How to express solutions
Some classical ideas of linear algebra and analytic geometry
For binary linear equations { a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 = b 2 \left\{\begin{array}{l}a_{11} x_{1}+a_{12} x_{2}=b_{1} \\ a_{21} x_{1}+a_{22} x_{2}=b_{2}\end{array}\right. { a11x1+a12x2=b1a21x1+a22x2=b2, The two equations of this system represent two straight lines in space . If two lines intersect , The equations have solutions , And the solution of the equations is the intersection of two straight lines ; And if two straight lines are parallel , The equations have no solution , When the coefficients of two straight lines are proportional, they are parallel .
For ternary linear equations { a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + a 13 x 3 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + a 23 x 3 = b 2 \left\{\begin{array}{l}a_{11} x_{1}+a_{12} x_{2}+a_{13} x_{3}=b_{1} \\ a_{21} x_{1}+a_{22} x_{2}+a_{23} x_{3}=b_{2}\end{array}\right. { a11x1+a12x2+a13x3=b1a21x1+a22x2+a23x3=b2, The two equations of the system of equations represent two planes in space . If two planes intersect , Then the line where two planes intersect is the solution of the equations , The equations have infinite solutions . If two planes are parallel , The equations have no solution , When the two plane coefficients are proportional, they are parallel .
For ternary linear equations { a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + a 13 x 3 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + a 23 x 3 = b 2 a 31 x 1 + a 32 x 2 + a 33 x 3 = b 3 \left\{\begin{array}{l}a_{11} x_{1}+a_{12} x_{2}+a_{13} x_{3}=b_{1} \\ a_{21} x_{1}+a_{22} x_{2}+a_{23} x_{3}=b_{2}\\ a_{31} x_{1}+a_{32} x_{2}+a_{33} x_{3}=b_{3}\end{array}\right. ⎩⎨⎧a11x1+a12x2+a13x3=b1a21x1+a22x2+a23x3=b2a31x1+a32x2+a33x3=b3, The three equations of the system of equations represent three planes in space . Three planes can intersect at the same point , The same point is the unique solution of these three equations ; They can also intersect on the same line , This is the case of infinite solutions ; At least two planes can also coincide and intersect with the third plane ( Including the case that three planes coincide ), This is also the case of infinite solutions ; Of course , At least one plane does not intersect with other planes ( For example, the three planes are parallel to each other , Or when two planes are recombined and parallel to the third plane ), Or the intersection lines of the three planes neither coincide nor intersect at the same point , Then this is no solution .
Methodology of solving linear equations
Inspired by the solution of low dimensional linear equations , More generally , about n n n A system of elementary linear equations { a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 + a 13 x 3 + ⋯ + a 1 n x n = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 + a 23 x 3 + ⋯ + a 2 n x n = b 2 … a n 1 x 1 + a n 2 x 2 + a n 3 x 3 + ⋯ + a n n x n = b n \left\{\begin{array}{l}a_{11} x_{1}+a_{12} x_{2}+a_{13} x_{3}+\dots+a_{1n} x_{n}=b_{1} \\ a_{21} x_{1}+a_{22} x_{2}+a_{23} x_{3}+\dots+a_{2n} x_{n}=b_{2}\\\dots\\ a_{n1} x_{1}+a_{n2} x_{2}+a_{n3} x_{3}+\dots+a_{nn} x_{n}=b_{n}\end{array}\right. ⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧a11x1+a12x2+a13x3+⋯+a1nxn=b1a21x1+a22x2+a23x3+⋯+a2nxn=b2…an1x1+an2x2+an3x3+⋯+annxn=bn, To solve a system of equations , The core idea is to extract the system information of these equations , Then use the elimination method to solve the equations . Using matrix and matrix multiplication in linear algebra , The system information of the equations can be well extracted .
matrix
How to treat matrix
For binary linear equations { a 11 x 1 + a 12 x 2 = b 1 a 21 x 1 + a 22 x 2 = b 2 \left\{\begin{array}{l}a_{11} x_{1}+a_{12} x_{2}=b_{1} \\ a_{21} x_{1}+a_{22} x_{2}=b_{2}\end{array}\right. { a11x1+a12x2=b1a21x1+a22x2=b2, The coefficient matrix is [ a 11 a 12 a 21 a 22 ] \begin{bmatrix} a_{11}& a_{12}\\ a_{21}& a_{22} \end{bmatrix} [a11a21a12a22], To judge whether the linear equations have solutions , Only one row vector of its coefficient matrix needs to be judged ( Or column vectors ) Whether it can be used by another row vector ( Or column vectors ) Linear representation .
about n n n Meta linear equations are similar , To judge whether the linear equations have solutions , Only one row vector of its coefficient matrix needs to be judged ( Or column vectors ) Whether it can be used by the remaining row vectors ( Or column vectors ) Linear representation . Replace all vectors that can be linearly represented by the remaining vectors with 0, The number of vectors that cannot be linearly represented by the remaining vectors is the rank of the matrix , It represents the essential attribute of matrix . Then we can discuss the solution of linear equations according to the rank of the matrix , For details, please refer to the relevant knowledge in linear algebra .
The solution of matrix rank
You can do elementary row transformation on the matrix , Reduce it to a stepped matrix and find the rank of the matrix .
For shapes like n × m n\times m n×m The rank of the matrix of R ≤ m i n ( n , m ) R\le min(n,m) R≤min(n,m).
The basis of a matrix
According to the rank of the matrix R R R Find one in the matrix R R R Order is not 0 The determinant of ( At least one such determinant can be found ), Arrange the elements in the determinant in order into a matrix , This matrix is a base of the original matrix .
The matrix of the inverse
Finding the inverse of a matrix
Find the inverse matrix with elementary row transformation . The matrix ( A , E ) (A,E) (A,E) Perform elementary line transformation , Make it into a ( E , B ) (E,B) (E,B), be B B B Namely A A A The inverse matrix A − 1 A^{-1} A−1.
Properties of matrix inverse
A ⋅ A − 1 = E A\cdot A^{-1}=E A⋅A−1=E
determinant
What are the ranks
Determinant is an algorithm , and + 、 − +、- +、− similar , You can calculate a number . Of course, determinant can also be regarded as a number .
Geometric meaning of determinant
For determinants ∣ a 1 a 2 b 1 b 2 ∣ \begin{vmatrix} a_1& a_2\\ b_1& b_2 \end{vmatrix} ∣∣∣∣a1b1a2b2∣∣∣∣, The corresponding matrix is [ a 1 a 2 b 1 b 2 ] \begin{bmatrix} a_{1}& a_{2}\\ b_{1}& b_{2} \end{bmatrix} [a1b1a2b2], Its row vector α 1 = \alpha_1= α1= [ a 1 a 2 ] \begin{bmatrix} a_{1}& a_{2}\end{bmatrix} [a1a2], α 2 = \alpha_2= α2= [ b 1 b 2 ] \begin{bmatrix} b_{1}& b_{2}\end{bmatrix} [b1b2], Draw these two vectors in the figure below .
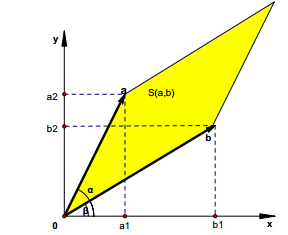
You can find the area of the Yellow parallelogram in the figure S = − a b s i n ( α − β ) S=-absin(\alpha-\beta) S=−absin(α−β), The meaning of each symbol is shown in the figure . In addition, the clockwise area is negative , Counterclockwise area is positive , This is a directed area , Because the picture is clockwise , So there is also a minus sign in front , Is the actual area . Then simplify it to S = a 1 b 2 − a 2 b 1 S=a_1b_2-a_2b_1 S=a1b2−a2b1.
Sum up , The geometric meaning of second-order determinant is the area of parallelogram .
The geometric meaning of the third-order determinant is the volume of the parallelepiped .
n n n The geometric meaning of order determinant is n n n Volume of dimensional hypercube .
therefore , If the value of determinant is 0, Then the corresponding matrix has redundant ( Not independent ) Vector ; conversely , Then the corresponding matrix is full rank .
summary
The purpose of linear algebra is to solve linear equations , It can be cleverly combined with analytic geometry .
Information can be extracted from the coefficients of linear equations , Build it into a matrix , And the unknown number is also expressed as a matrix , We can use matrix multiplication to express linear equations .
Independent in the matrix ( Linearly independent ) The number of vectors is the rank of the matrix , It reflects the essential attribute of matrix .
According to the rank of the matrix R R R Find one in the matrix R R R Order is not 0 The determinant of , Arrange the elements in the determinant in order into a matrix , This matrix is a base of the original matrix .
Determinant is an algorithm , Its geometric meaning is the area of a parallelogram composed of two vectors ( Take the second-order determinant as an example ).
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Hongke | uses jesd204 serial interface to bridge analog and digital worlds at high speed

Understanding of access, hybrid and trunk modes

王树尧老师运筹学课程笔记 10 线性规划与单纯形法(关于检测数与退化的讨论)

AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(AQS) 之共享锁源码浅读

Loss function -- cross entropy loss function

MySQL: what happens in the bufferpool when you crud? Ten pictures can make it clear

有用网站

CNN-卷积神经网络

JMM memory model concept

Shallow reading of shared lock source code of abstractqueuedsynchronizer (AQS)
随机推荐
软件定义边界SDP
SS command details
10种常见的软件架构模式
JVM之垃圾回收机制(GC)
ss命令详解
吴恩达老师机器学习课程笔记 04 多元线性回归
5g service interface and reference point
MQTT服务器搭建以及使用MQTT.fx测试
吴恩达老师机器学习课程笔记 03 线性代数回顾
How to use SFTP command to access SFTP server on the development board
JMM 内存模型概念
王树尧老师运筹学课程笔记 01 导学与绪论
Understanding of access, hybrid and trunk modes
成长为架构师途中的一些思考
王树尧老师运筹学课程笔记 07 线性规划与单纯形法(标准型、基、基解、基可行解、可行基)
Apisik health check test
量子机器学习中的安全性问题
Computer right mouse click always turn around what's going on
王树尧老师运筹学课程笔记 06 线性规划与单纯形法(几何意义)
Hongke shares | how to test and verify complex FPGA designs (1) -- entity or block oriented simulation