当前位置:网站首页>[JVM] [Chapter 17] [garbage collector]
[JVM] [Chapter 17] [garbage collector]
2022-07-06 05:28:00 【Why can't you even speak clearly】
Garbage collector
- 1、GC Classification and performance indicators
- 2、 Overview of different garbage collectors
- 3、Serial Recyclers : Serial recycler
- 4、ParNew Recyclers : Parallel recycling
- 5、Parallel Recyclers : Throughput priority
- 6、CMS Recyclers : Low latency
- 7. G1 Recyclers : Regionalized generational
- 8. Garbage collector summary
- 9. GC Log analysis (*)
- 10 The new development of garbage collector
1、GC Classification and performance indicators
1.1、 Garbage collector overview and classification
Overview of garbage collector
- The garbage collector is not specified too much in the specification , It can be made by different manufacturers 、 Different versions JVM To achieve .
- because JDK The version of is in the process of high-speed iteration , therefore Java So far, it has derived a lot of GC edition .
- Analyze the garbage collector from different angles , Can be GC There are different types .
Java New features in different versions
- Grammar level :Lambda expression 、switch、 Automatic unpacking and packing 、enum
- API level :Stream API、 New date time 、Optional、String、 Collections framework
- Bottom level optimization :JVM Optimize 、GC The change of 、 Meta space 、 Static domain 、 String constant pool position change
Garbage collector classification
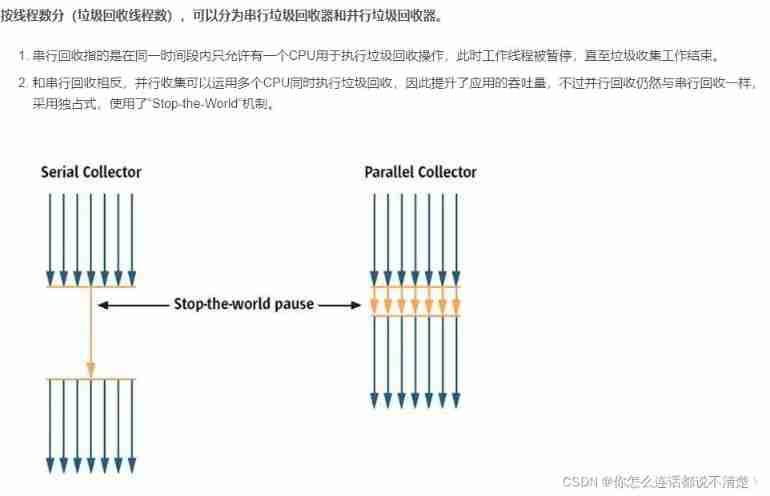

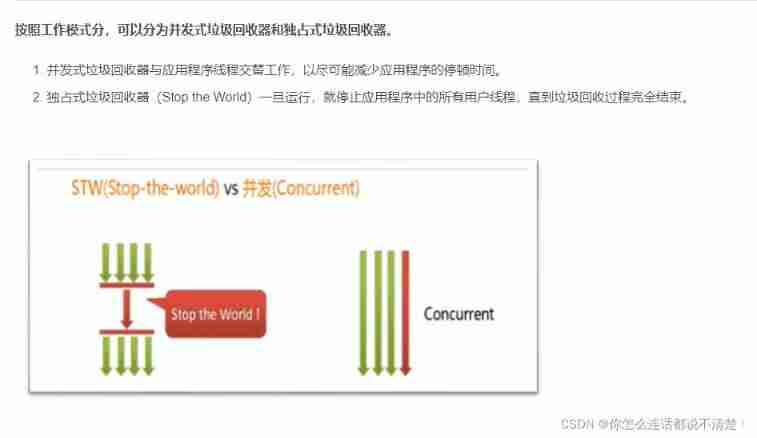

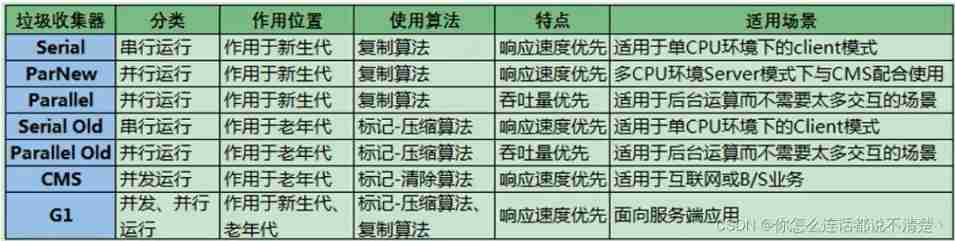
By working memory range , It can also be divided into the younger generation garbage collector and the older generation garbage collector .
1.2、 assessment GC Performance index of
throughput : The percentage of time spent running user code in total runtime ( Total operation time = The running time of the program + Time of memory recovery )
Garbage collection expenses : Throughput complement , The ratio of the time spent in garbage collection to the total running time .
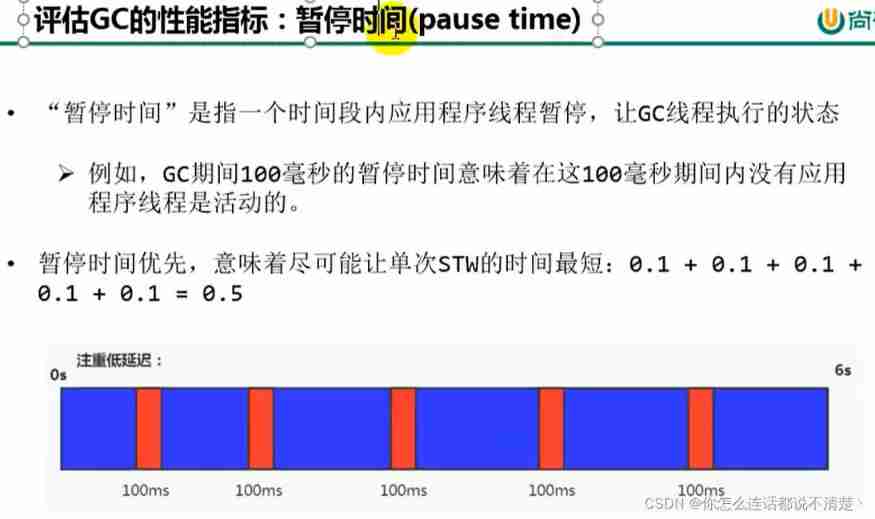
Pause time : When performing garbage collection , The time when the program's worker thread is suspended .
Collection frequency : Relative to the execution of the application , Frequency of collection operations .
Memory footprint :Java The amount of memory the heap occupies .
Fast : The time from the birth of an object to its recycling .
throughput 、 Pause time 、 Memory footprint these three together constitute a “ Impossible Triangle ”. The overall performance of the three will be better and better with the progress of technology . A good collector usually satisfies at most two of them at the same time .
Of the three , Pause time is becoming more and more important . Because with the development of hardware , More memory is more and more tolerable , The improvement of hardware performance also helps to reduce the impact of collector runtime on the application , That is, the throughput is improved . and Memory expansion , It has a negative effect on delay .
Simply speaking , Because memory is not worth money , There are two main points :
- throughput
- Pause time
assessment GC Performance index of : throughput (throughput)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=172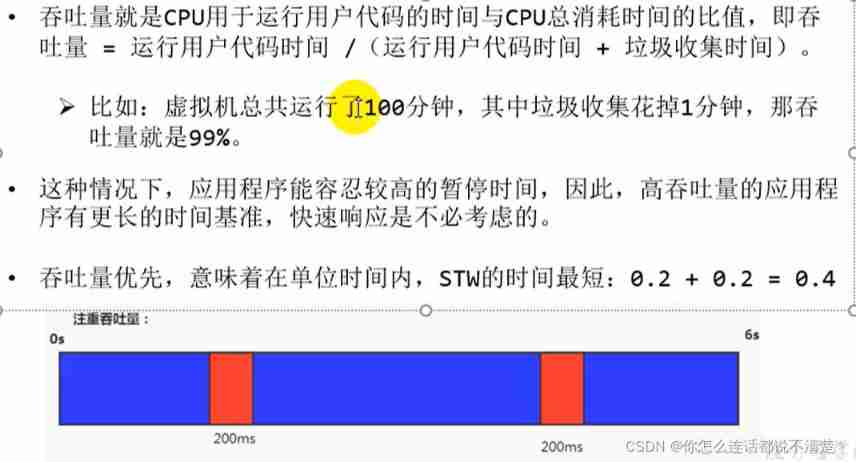
assessment GC Performance index of : Pause time (pause time)
contrast
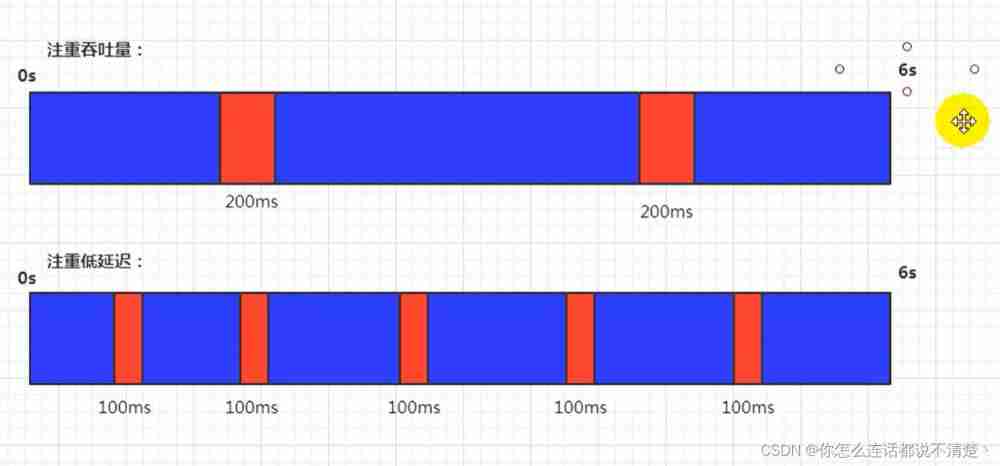
throughput : Eat a lot , Run more ;
Low latency : Eat less , Eat frequently , Less running ;


2、 Overview of different garbage collectors
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=173&spm_id_from=pageDriver
- The garbage collection mechanism is Java Your signature ability , Greatly improved development efficiency . This, of course, is also the focus of the interview .
- GC Garbage collectors are and JVM In one continuous line , It is and JVM Use it together , In different usage scenarios, the corresponding collectors are also different
- that ,Java What are the common garbage collectors ?
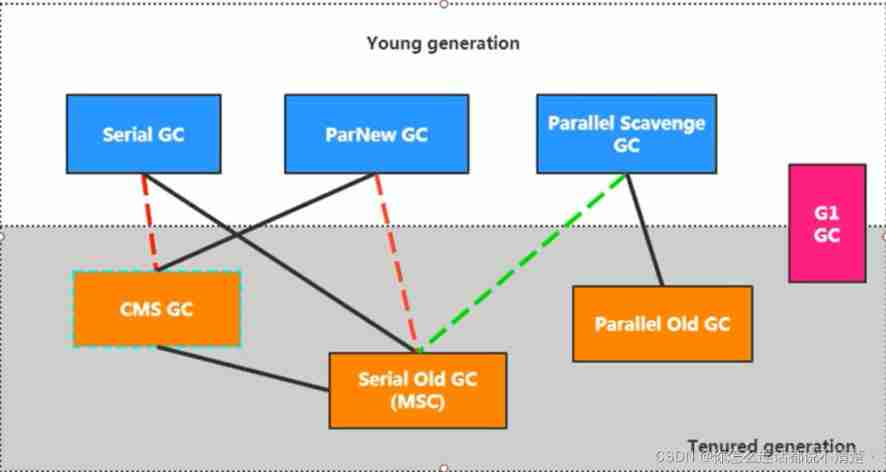
2.1、 Garbage collector history

7 A classic garbage collector
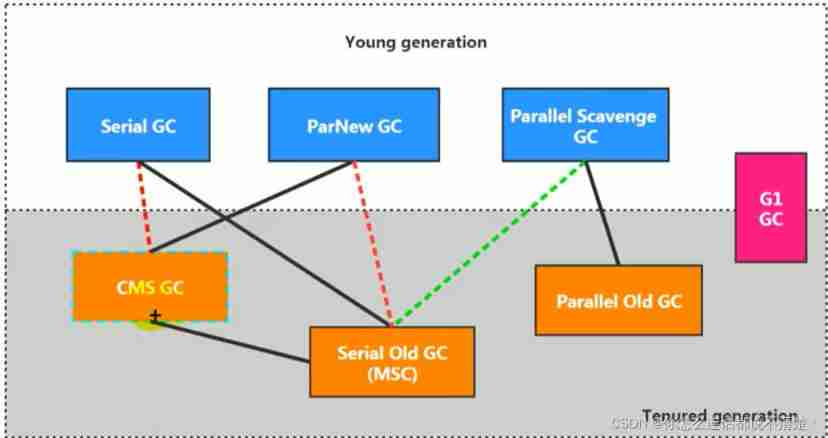
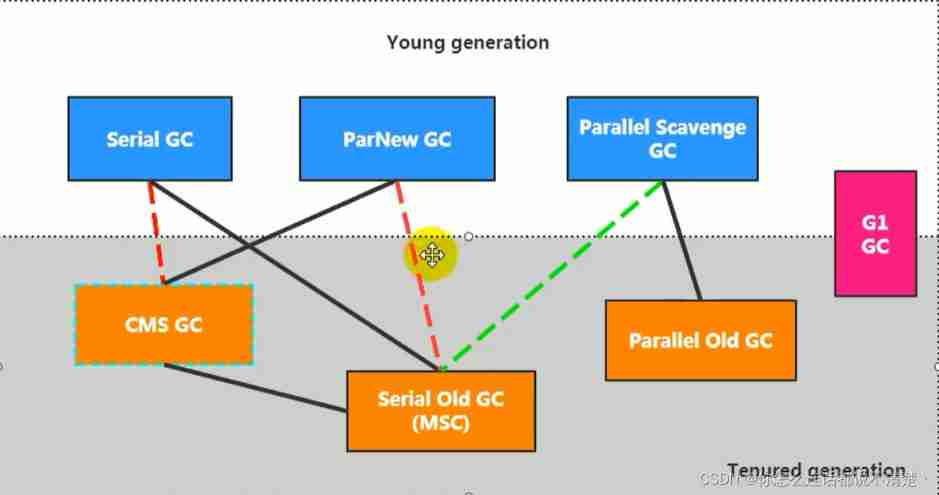
2.2、 The relationship between recyclers and garbage generation
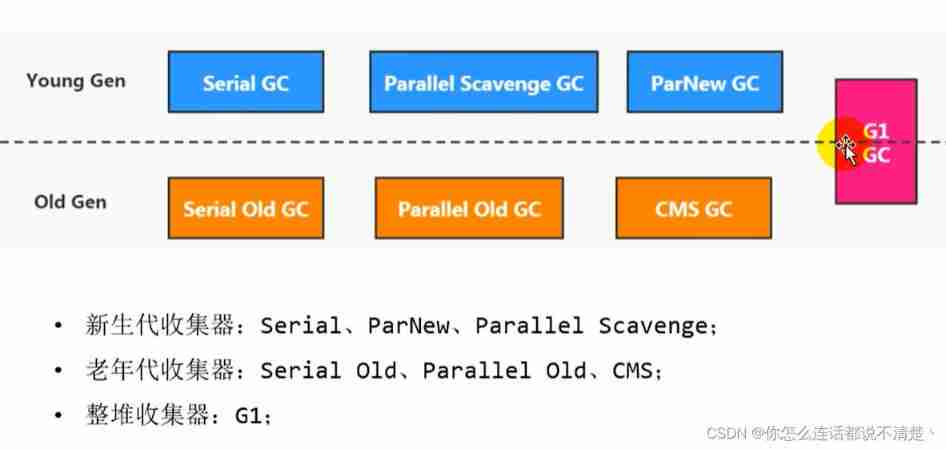
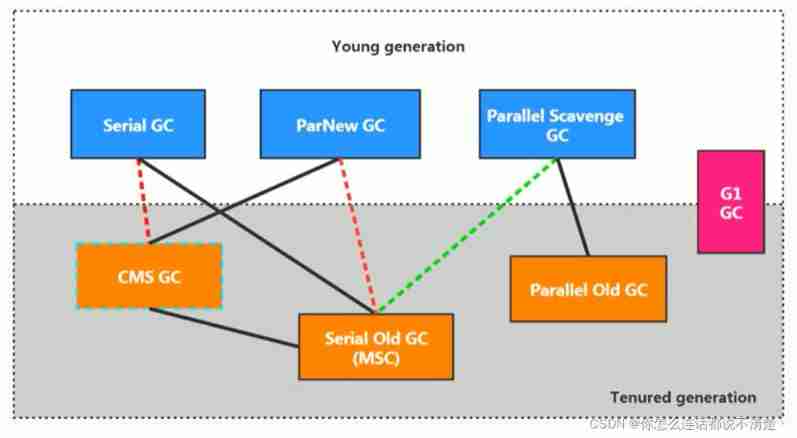
There is a connection between the two collectors , It shows that they can be used together :
Serial/Serial old
Serial/CMS
ParNew/Serial Old
ParNew/CMS
Parallel Scavenge/Serial Old
Parallel Scavenge
Parallel Old、G1;
among Serial Old As CMS appear "Concurrent Mode Failure" A failed backup plan .
( Red dotted line ) Because of the cost of maintenance and compatibility testing , stay JDK 8 When will Serial+CMS、ParNew+Serial Old These two combinations are declared obsolete (JEP173), And in JDK9 The support for these combinations has been completely removed from (JEP214), namely : remove .
( Dotted green line )JDK14 in : Abandoning Parallel Scavenge and Serial Old GC Combine (JEP366)
( Cyan dotted line )JDK14 in : Delete CMS Garbage collector (JEP363)

2.3、 See the default garbage collector
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=175
Set up -XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags see
- stay JDK 8 Next , Set up JVM Parameters
-XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags
Program printouts :-XX:+UseParallelGC Use use ParallelGC ,ParallelGC Default and Parallel Old Binding uses
-XX:InitialHeapSize=266620736
-XX:MaxHeapSize=4265931776
-XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags
-XX:+UseCompressedClassPointers
-XX:+UseCompressedOops
-XX:-UseLargePagesIndividualAllocation
-XX:+UseParallelGC
View through command line instructions
Command line command
jps
jinfo -flag UseParallelGC process id
jinfo -flag UseParallelOldGC process id
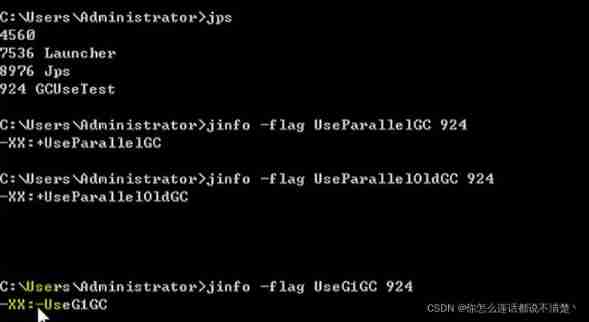
JDK 8 By default ParallelGC and ParallelOldGC The combination of
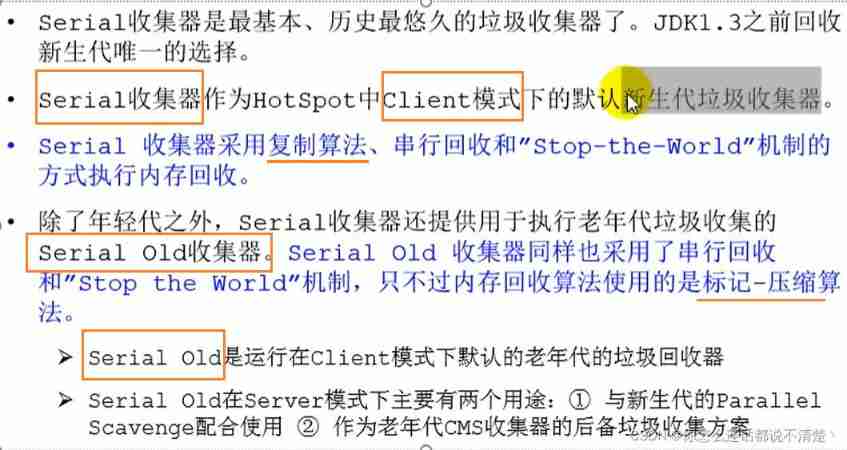
3、Serial Recyclers : Serial recycler
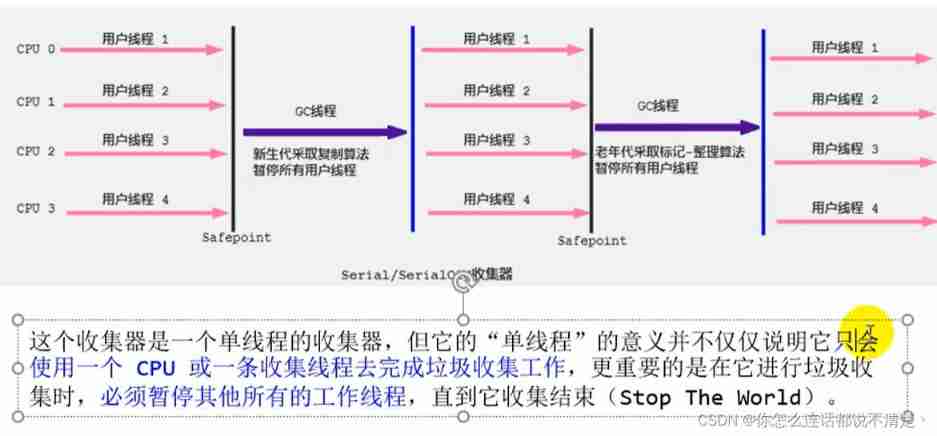


4、ParNew Recyclers : Parallel recycling

- We can only deal with the new generation
- Copy algorithm
- Parallel recycling
- stop-the world
parallel or Serial
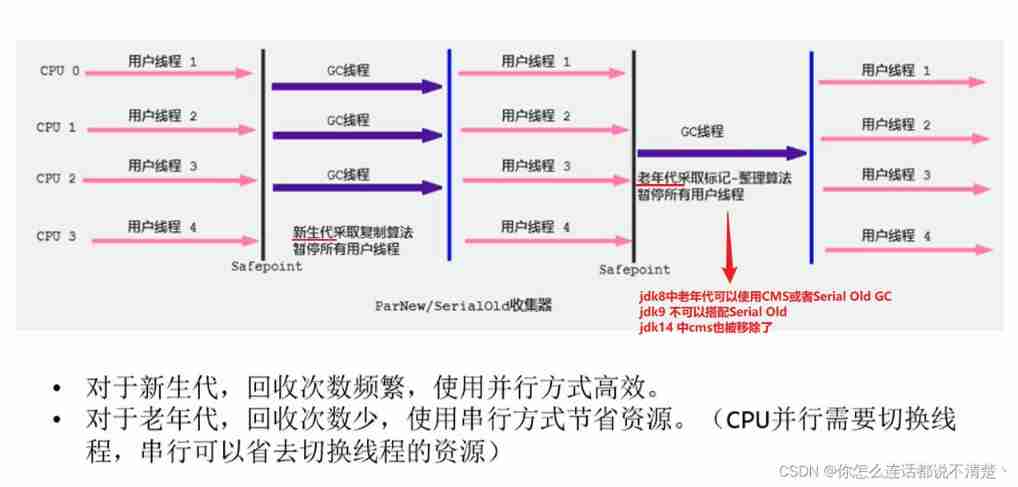
ParNew And Serial Compare

Use

5、Parallel Recyclers : Throughput priority
Parallel and ParNew
Parallel Scavenge The collector and ParNew The collector It also uses Copy algorithm 、 Parallel recycling and "Stop the World" Mechanism .
that Parallel Whether the emergence of collectors is unnecessary ?
(1) and ParNew Collectors are different ,Parallel Scavenge The goal of the collector is to achieve a Controllable throughput (Throughput), It's also known as a throughput first garbage collector
(2) Adaptive adjustment strategy It's also Parallel Scavenge And ParNew An important difference .
Adaptive adjustment strategy :jvm Performance monitoring during operation , Dynamically adjust memory allocation , To suit the throughput first Or low latency
High throughput can be used efficiently CPU Time , Complete the operation task of the program as soon as possible , It is mainly suitable for tasks that are operated in the background without much interaction . therefore , It is commonly used in server environments . for example , Those execution Batch processing 、 The order processing 、 Payment of wages 、 Applications for Scientific Computing .
Parallel Old In combination with
Parallel The collector JDK1.6 Provides for the implementation of garbage collection for the elderly Parallel Old The collector , In place of the old days Serial Old The collector ( without Parallel Old , In the old days, it can only be used Serial Old Serial recovery , There are all new generations Parallel 了 , It shows that the server performance is good , There is no need to use inefficient Serial Old).
Parallel Old The collector uses Mark - Compress Algorithm , But it's also based on Parallel recycling and "Stop-the-World" Mechanism .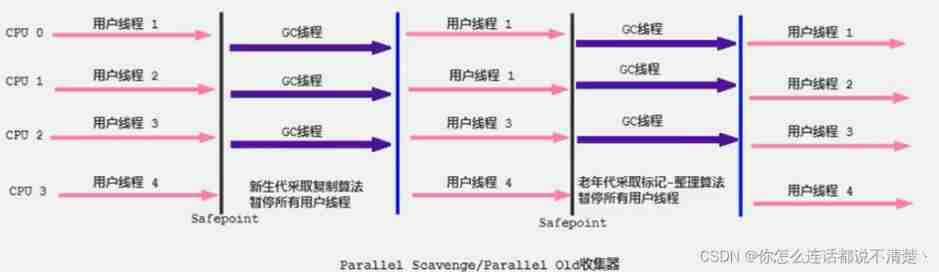

Parallel Recycler parameter settings

The third is cpu The core number

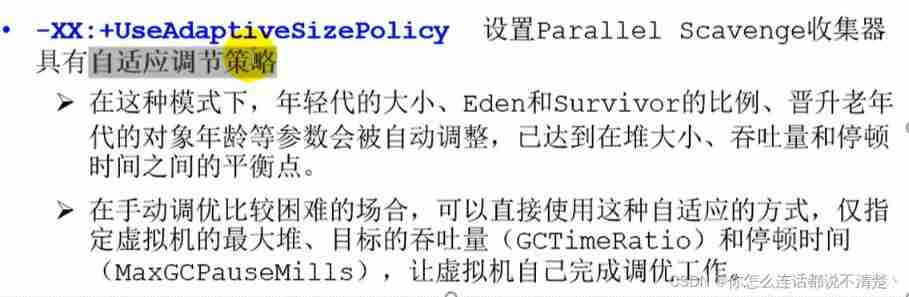
Default on ;
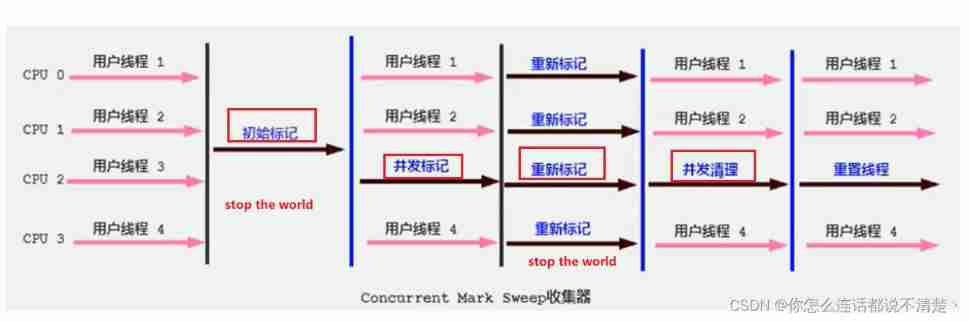
6、CMS Recyclers : Low latency
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=182&spm_id_from=pageDriver

working principle
CMS Characteristics and disadvantages
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=183&spm_id_from=pageDriver
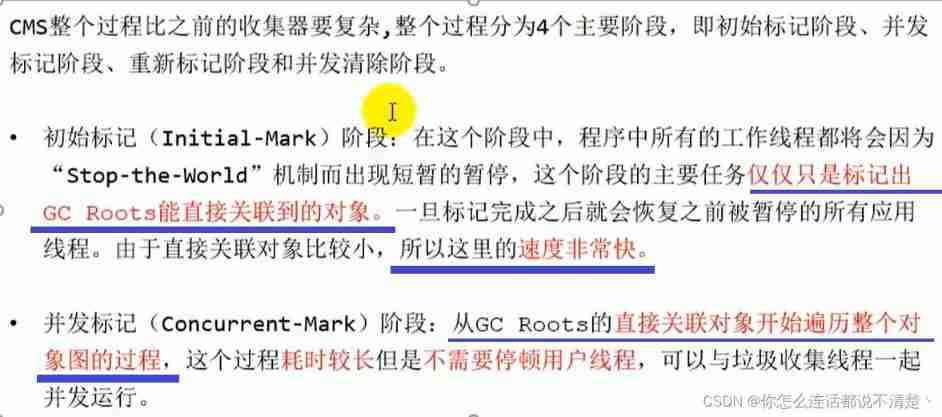
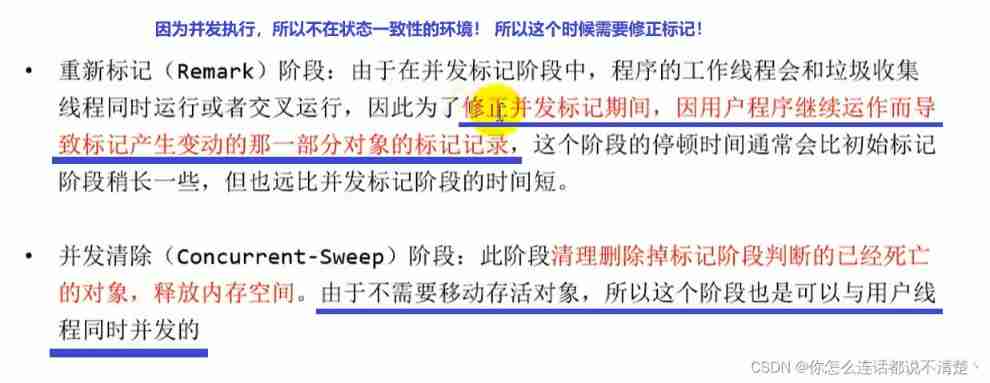
Even though CMS The collector uses concurrent recycling ( Non exclusive ), But in It still needs to be executed in the two stages of initialization marking and re marking “Stop-the-World” Mechanism to suspend worker threads in a program , But the pause won't be long , Therefore, it can be said that all the current garbage collectors can't be done, and there is no need at all “Stop-the-World”, Just shorten the pause as much as possible .
Because the most time-consuming phase of concurrent tagging and concurrent cleanup does not need to suspend work , So the overall recycling is low pause . in addition , Since the user thread is not interrupted during the garbage collection phase , So in CMS In the process of recycling , You should also make sure that the application user thread has enough memory available .
therefore ,CMS Collectors can't wait until the old days are almost completely full to collect like other collectors , But when the heap memory utilization reaches a certain threshold , And we started recycling , To make sure that the application is CMS There is still enough space to support the application running in the working process .
If CMS The memory reserved during running cannot meet the needs of the program , There will be one “Concurrent Mode Failure” Failure , At this point the virtual machine will initiate the backup plan : The occasional Serial old Collector to redo old garbage collection , That's a long pause .
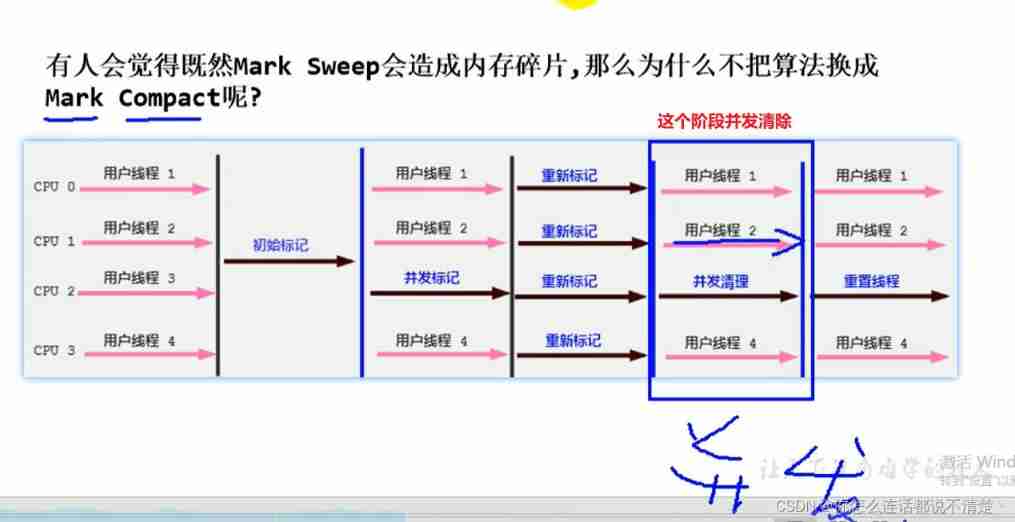
CMS The collector's garbage collection algorithm uses Tag clearing algorithm , This means that after every memory recycle , Because the memory space occupied by the useless object of memory recycling is very likely to be some discontinuous memory blocks , Inevitably, there will be some memory fragmentation . that CMS When allocating memory space for new objects , You will not be able to use pointer collisions (Bump the Pointer) technology , Only the free list can be selected (Free List) Perform memory allocation .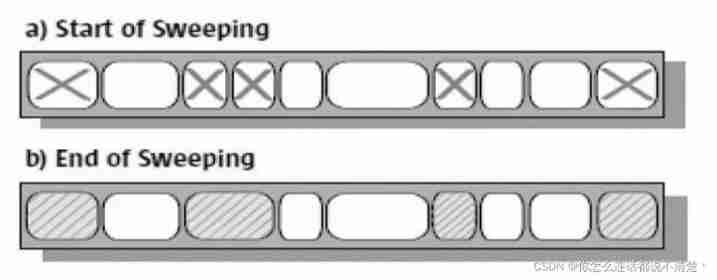
summary
6.5、CMS Parameter configuration


CMS Summary
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=185&spm_id_from=pageDriver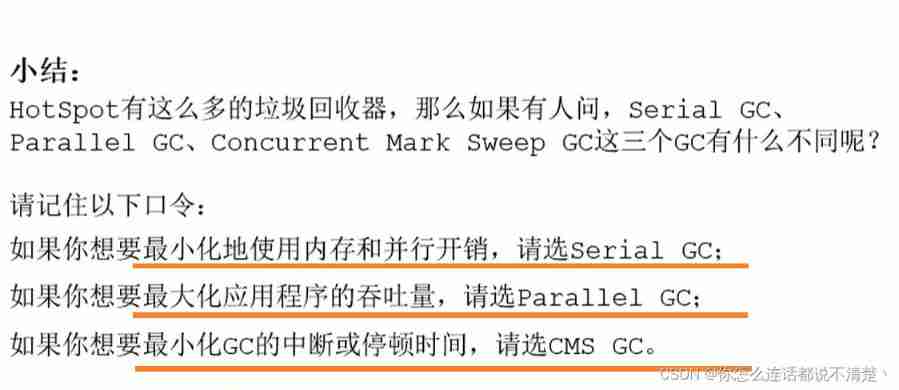

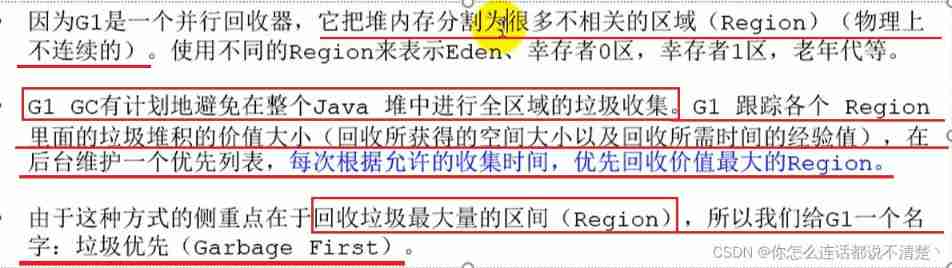
7. G1 Recyclers : Regionalized generational
7.1 know G1
Full function collector : The throughput should be as high as possible within the controllable range of delay 
Why call G1?

7.2 G1 Advantages and disadvantages
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=187&spm_id_from=pageDriver
(1) Both parallel and concurrent
- parallel :G1 During recycling , There can be multiple GC Threads work at the same time , Make effective use of the advantages of multi-core ; However, during this period, the user thread will STW
- Concurrent :G1 Threads have the ability to execute alternately with user threads ,G1 Part of the work during recycling can be performed simultaneously with the user thread ; therefore , There is no complete blocking of the application during the entire recycle phase ;
(2) Generational collection
G1 It will also distinguish between the new generation and the old generation ; There are still new generations Eden and Survivor District ;
Divide the space into several areas (region), These areas are logically attributed to the younger generation and the older generation ; From the perspective of heap structure ,G1 Does not require Eden District 、 The younger generation 、 The old age is continuous , Nor insist on fixed size and quantity ;
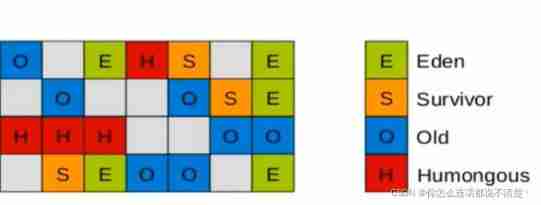
G1 A garbage collector takes into account both the new generation and the old generation ; Other garbage collectors either work in the younger generation , Or work in the elderly
(2) Spatial integration ability
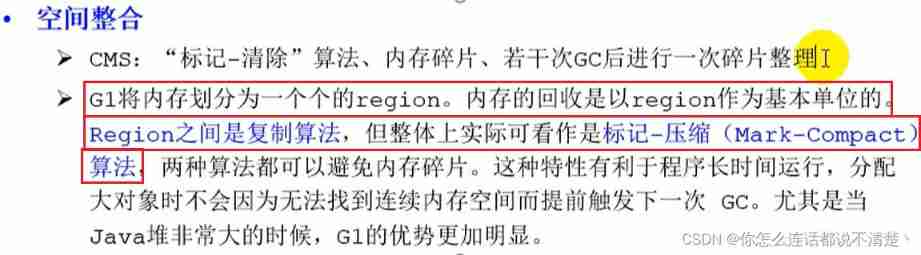
(4) Predictable pause time model

- With region, It is equivalent to subdividing generations ! The recycling area is smaller
- Which areas to recycle ?=> region Garbage value ranking
- real time : You must GC complete ; Soft real time : A small amount of error is allowed
shortcoming

7.3 G1 Parameter setting
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=188&spm_id_from=pageDriver

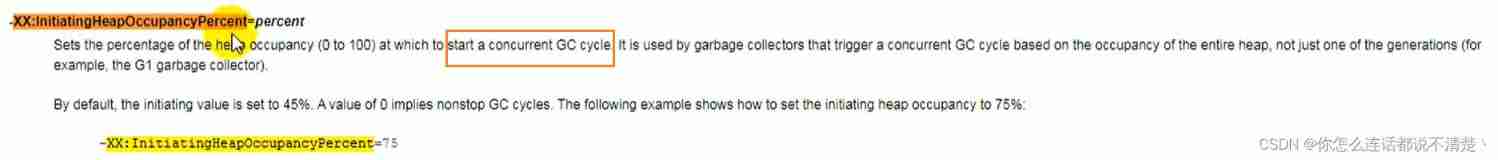
7.4 G1 Use scenarios
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=189&spm_id_from=pageDriver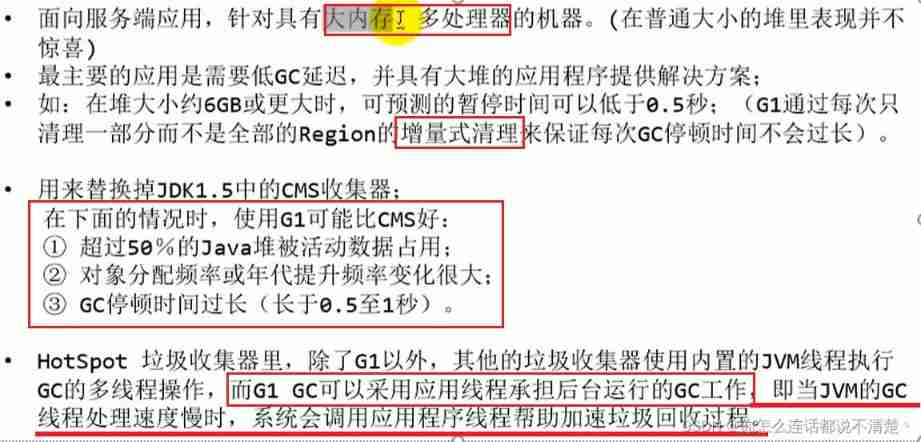
7.5 Region Introduce

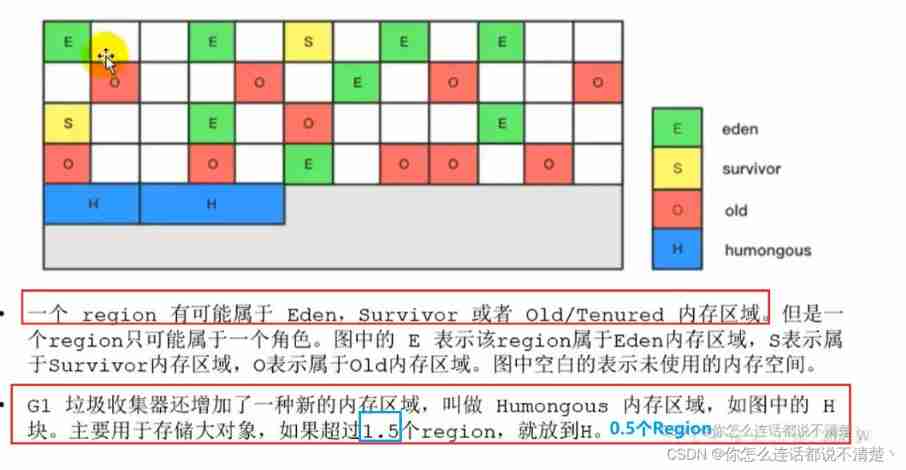

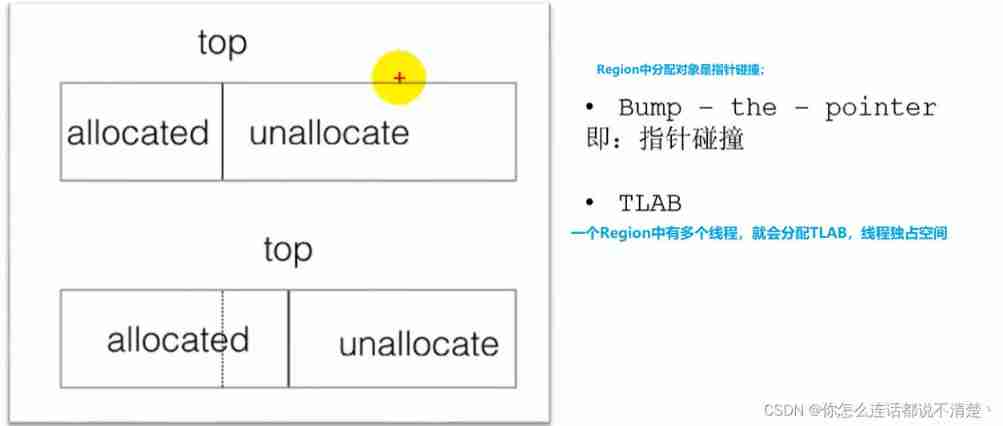
7.6 G1 Garbage collection process
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=191

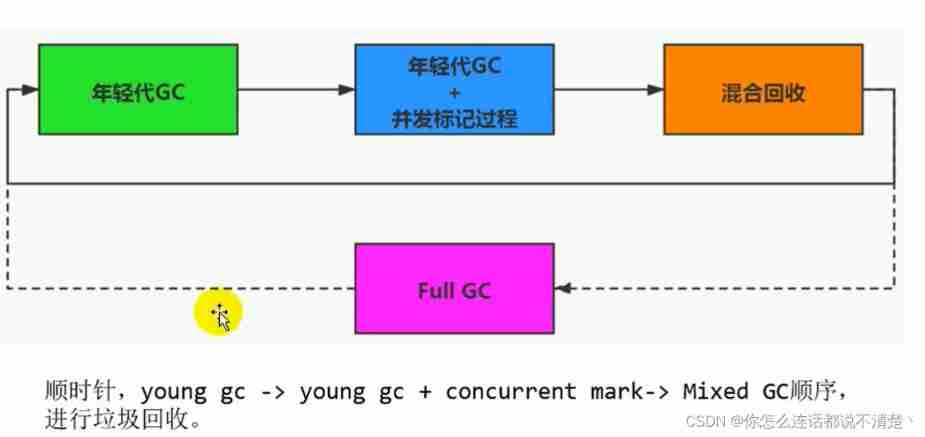

G1 Recycler garbage collection process :Remembered Set( Memory set )
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=193
The problem of an object being referenced by different regions
Problem description :
One Region It can't be isolated , One Region Objects in can be arbitrarily Region Object reference in , When judging the survival of an object , Is it necessary to scan the whole Java Only by stacking can we ensure accuracy ?
- In other generational collectors , There are also such problems ( and G1 More prominent , because G1 It's mainly for a lot of )
- Recycling the new generation also has to scan the older generation at the same time ? In this way, it will reduce Minor GC The efficiency of
resolvent :
No matter what G1 Or other generational collectors ,JVM Is to use Remembered Set To avoid global scanning ;
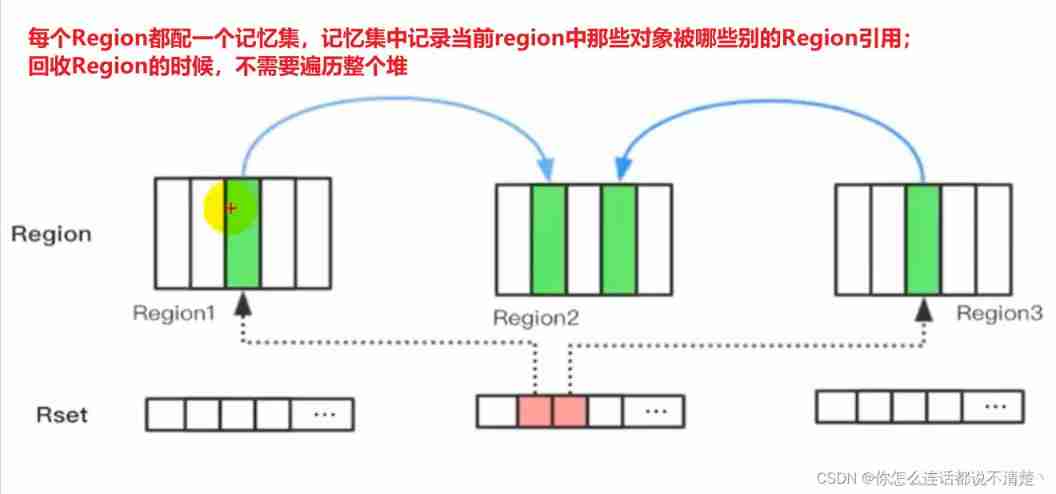
Every Region There is a corresponding Remembered Set
Every time I go to Region Write a Reference Type data ( object ) when , There will be a Write Barrier Temporarily interrupt the operation , Then check whether the object to be written is different from the data referencing the object Region( Other collectors : Whether the new generation objects are referenced );
- If different , adopt CardTable Record the relevant reference information to where the reference points to the object Region Corresponding Remembered Set in ;
- When it comes to garbage collection , stay GC The enumeration range of the root node is added with Remembered Set; To ensure that there is no global scan , There will be no omission .(RS The middle is also counted GC Roots Within reach )
A few words summarize
- It's recycling Region when , In order not to scan the whole heap , Introduced Remembered Set
- Remembered Set Recorded the current Region Which object in is referenced by
- This is going on Region Replication time , Don't scan the whole heap , Just go to Remembered Set There's a reference to the current Region The object of
- Region After copying , modify Remembered Set The reference of the object in
G1 The younger generation GC

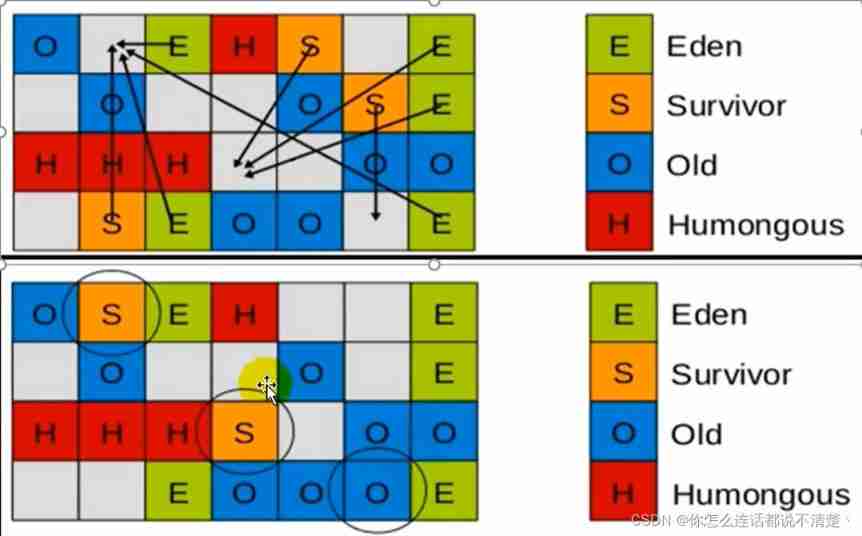
Recycling process :
The first stage , Scan the root ( look for GC Roots)
- Root means static The object that the variable points to , Local variables on the chain of executing method calls, etc .
- Root reference together with RSet The external reference of the record serves as the entry to scan the surviving object .
The second stage , to update RSet( Guarantee RSet accuracy )
- Handle dirty card queue( See remarks ) Medium card, to update RSet.
- After this stage is completed ,RSet It can accurately reflect the reference of the old age to the object in the memory segment .
The third stage , Handle RSet
- Identify objects that are directed by older generation objects Eden Objects in the , These are pointed at Eden Objects in are considered to be living objects .
The fourth stage , copy object .
- This stage , The object tree is traversed ,Eden The surviving objects in the segment will be copied to Survivor Empty memory segments ,Survivor The objects that live in the memory segment of the
- If the age does not reach the threshold , Age will increase 1, Reaching the threshold will be copied to Old Empty memory segments .
If Survivor Space is not enough ,Eden Part of the data in space will be directly promoted to the old space .
The fifth stage , Handling references
- Handle Soft,Weak,Phantom,Final,JNI Weak Etc . Final Eden Space data is empty ,GC Stop working , The objects in the target memory are continuously stored , There are no fragments , So the copy process can achieve the effect of memory collation , Reduce debris .
remarks :
- Reference assignment statements for applications oldObject.field=new Object(),JVM Special operations are performed before and after to dirty card queue Join a queue that holds object reference information card.
- When the younger generation recycled ,G1 Would be right Dirty Card Queue All of the card To deal with , To update RSet, Guarantee RSet Reflect the reference relationship in real time .
Then why not update directly at the reference assignment statement RSet Well ?
- The design here is Young GC Update when RSet, It's for performance ,RSet Thread synchronization is required for processing , It's going to cost a lot , With queues, performance is much better .
G1 Concurrent marking process

G1 Mixed recycling process
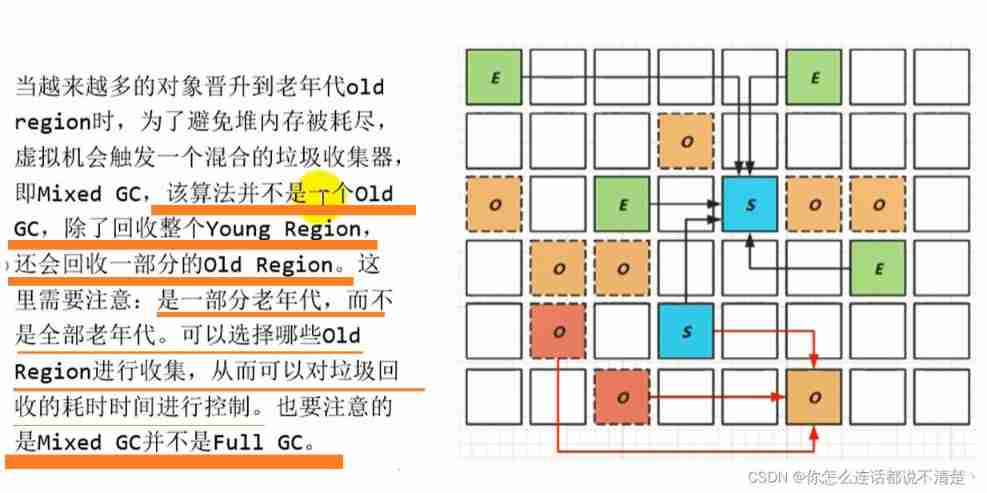
Details of mixed recycling

G1 Recycling optional process four :Full GC
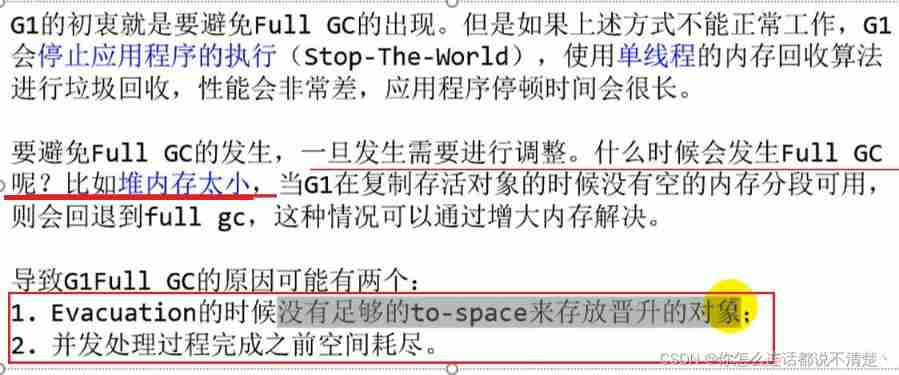
G1 Replenishment of the recycler
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=194
- from Oracle Information from the official can be obtained , Recycling phase (Evacuation) In fact, I have thought about designing concurrent execution with user programs , But it's a complicated thing to do , in consideration of G1 Just part of it Region, Pause time is user controllable , So it's not urgent to achieve , And I chose to put this feature in G1 Then came the low latency garbage collector ( namely ZGC) in .
- in addition , Also considering G1 Not just for low latency , Pausing user threads can maximize the efficiency of garbage collection , In order to ensure the throughput, we chose the implementation scheme of completely suspending user threads .
G1 Optimization suggestions for recyclers
8. Garbage collector summary
end JDK1.8, Altogether 7 Different garbage collectors . Each garbage collector has its own characteristics , In specific use , We need to choose different garbage collectors according to the specific situation .
GC Development stage : Seria l=> Parallel( parallel )=> CMS( Concurrent )=> G1 => ZGC
Different manufacturers 、 There is a big gap in the implementation of different versions of virtual machines .HotSpot Virtual machine in JDK7/8 All collectors and combinations are shown in the figure below ( Update to JDK14)
How to choose a garbage collector

About the interview

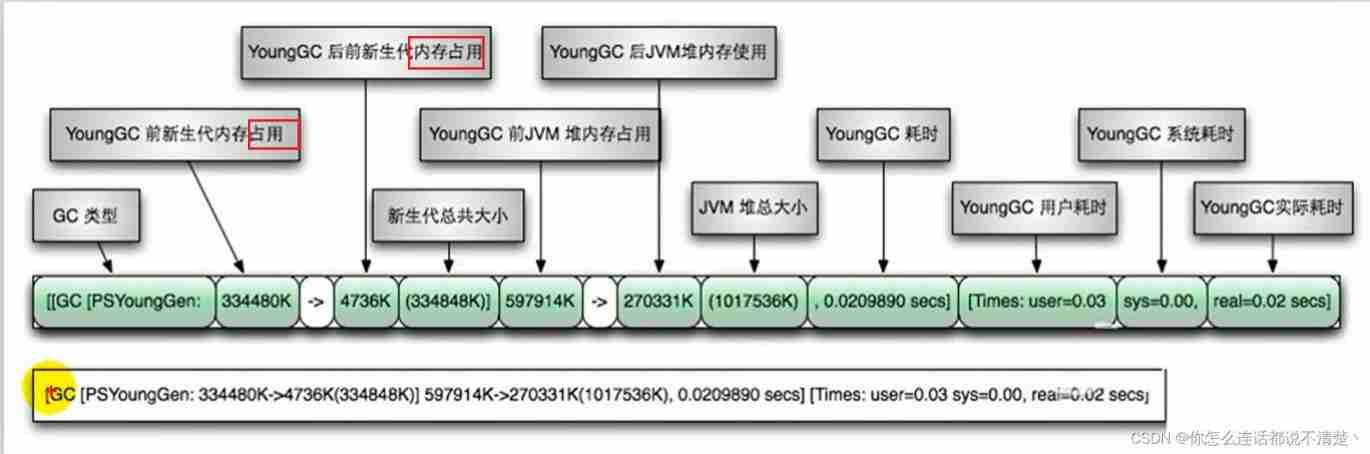
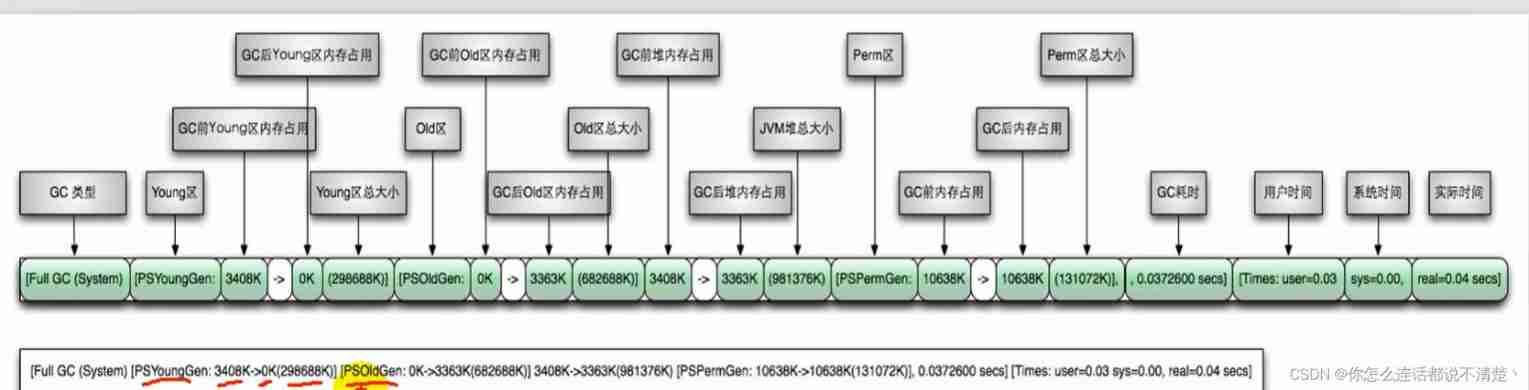
9. GC Log analysis (*)
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=196&spm_id_from=pageDriver
GC Log parameter settings
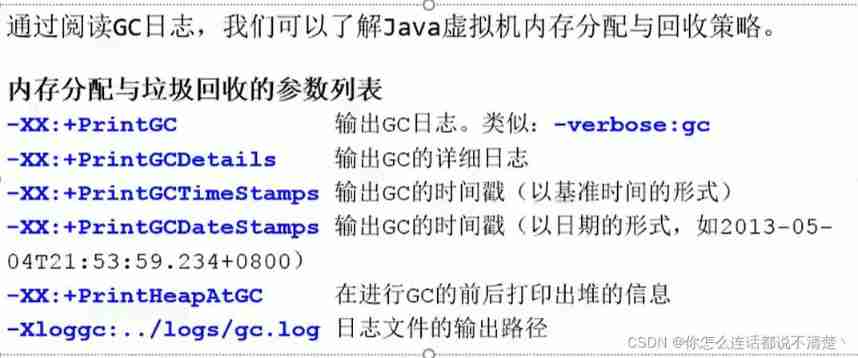
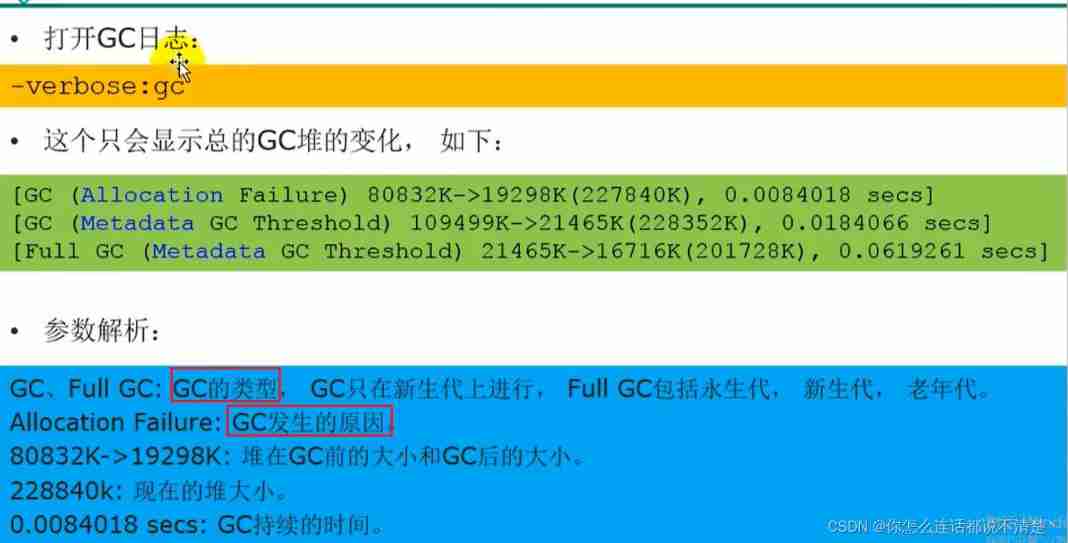
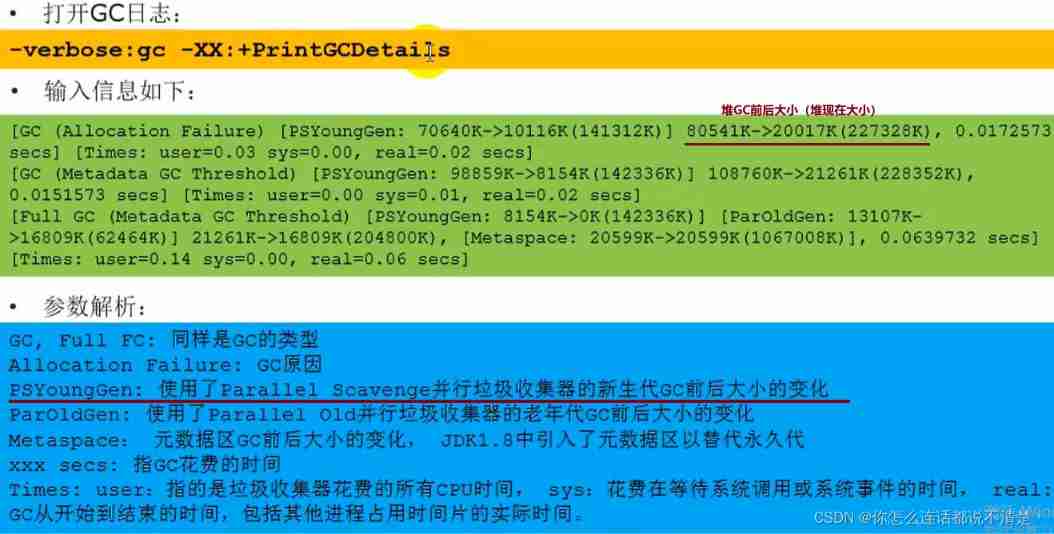
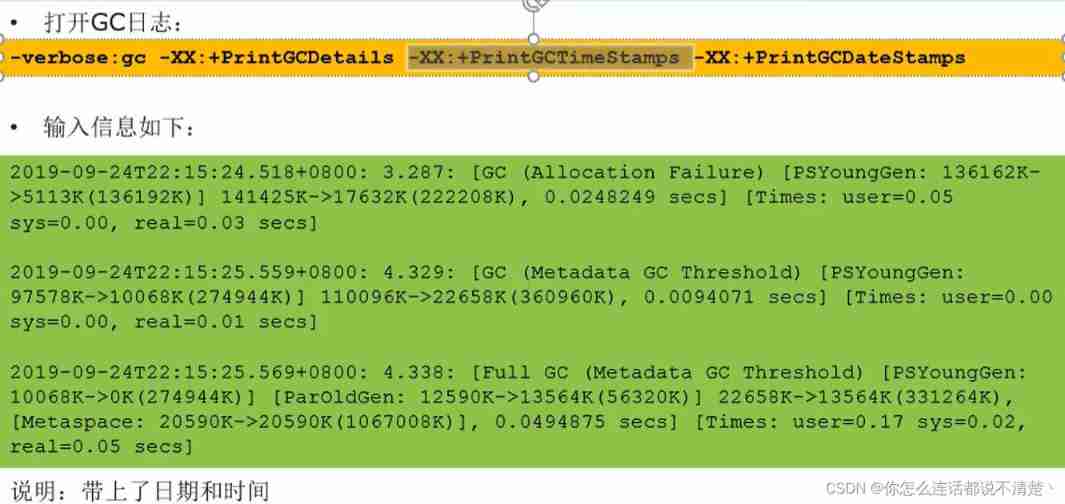
GC Log supplement
YounGC
Full GC
GC Log practice
/** * stay jdk7 and jdk8 Respectively * -verbose:gc -Xms20M -Xmx20M Pile up 20m * -Xmn10M The new generation 10m * -XX:+PrintGCDetails * -XX:SurvivorRatio=8 The new generation 8:1:1 * -XX:+UseSerialGC * * @author shkstart [email protected] * @create 2020 0:12 */
public class GCLogTest1 {
private static final int _1MB = 1024 * 1024;
public static void testAllocation() {
byte[] allocation1, allocation2, allocation3, allocation4;
allocation1 = new byte[2 * _1MB];
allocation2 = new byte[2 * _1MB];
allocation3 = new byte[2 * _1MB];
allocation4 = new byte[4 * _1MB];
}
public static void main(String[] agrs) {
testAllocation();
}
}
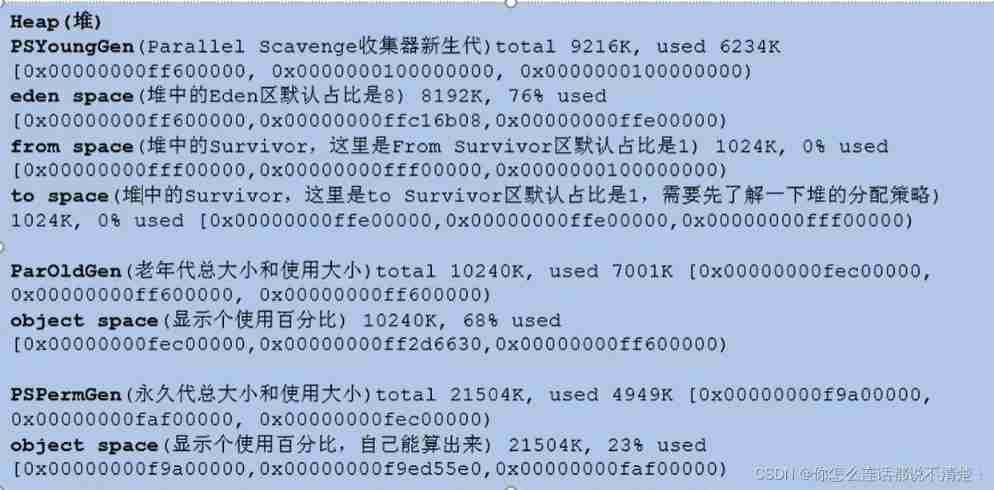
JDK7 Situation in
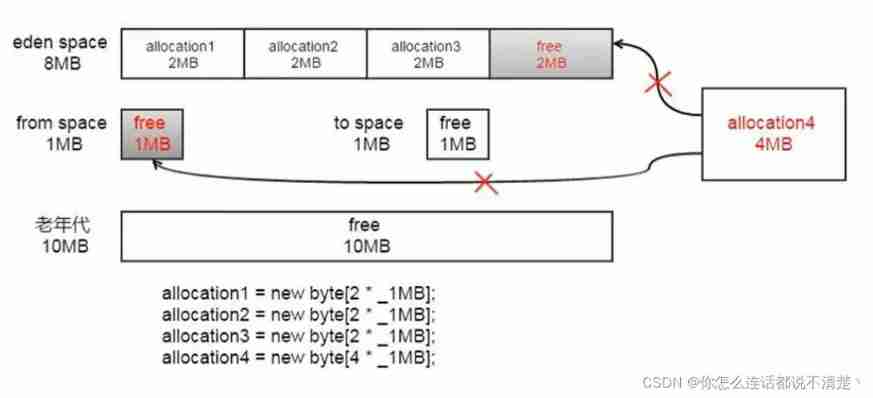
- First of all, we will 3 individual 2M The array of is stored in Eden District , And then back 4M After the array of , Will not be able to store , because Eden All that's left is 2M There's more space left , Then there will be a Young GC operation
- YoungGC Will change the original Eden Area content , Store in Survivor District , however Survivor There's no room for it , Then it will go straight to Old District
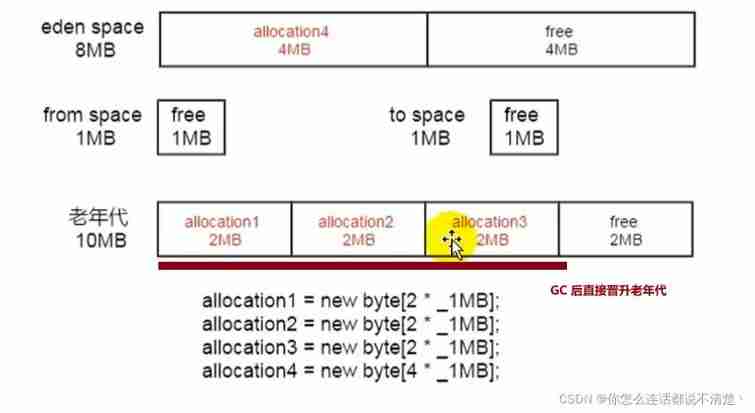

JDK8 Situation in
And JDK7 The difference is ,JDK8 Direct determination 4M Is a large object , It's directly connected to the senior district

Common log analysis tools
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=199&spm_id_from=pageDriver
10 The new development of garbage collector
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PJ411n7xZ?p=200
Looking back at the past

Looking forward to the future

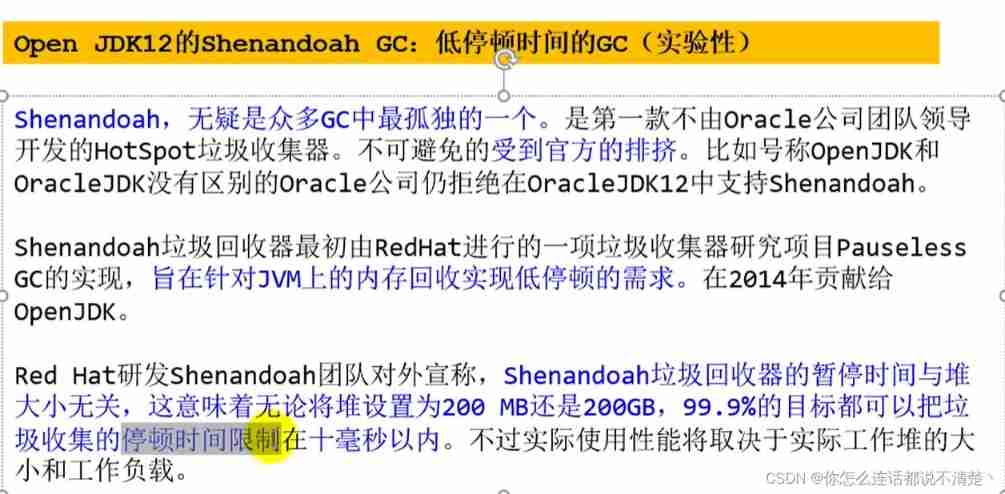
Shenandoah GC
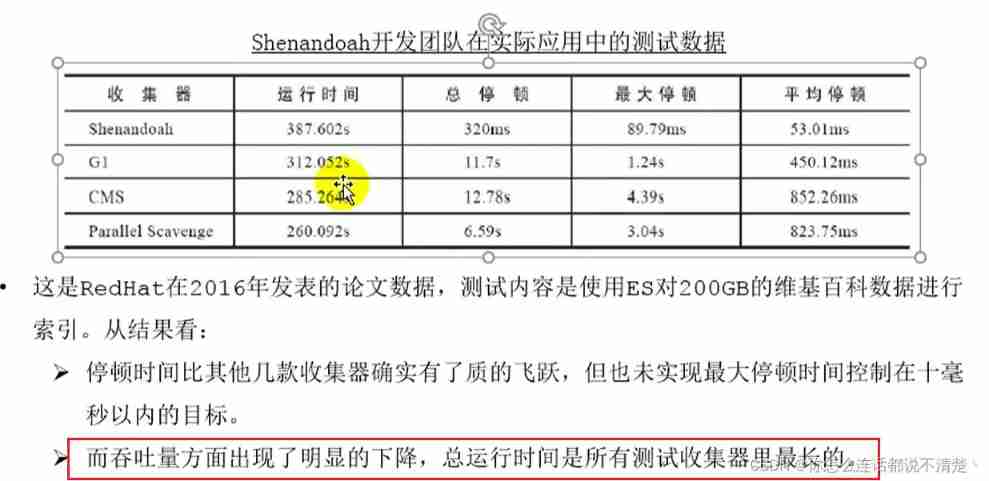
Revolutionary ZGC

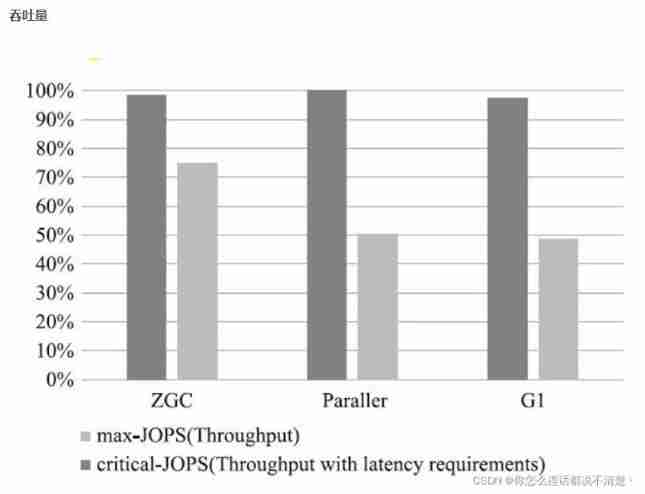
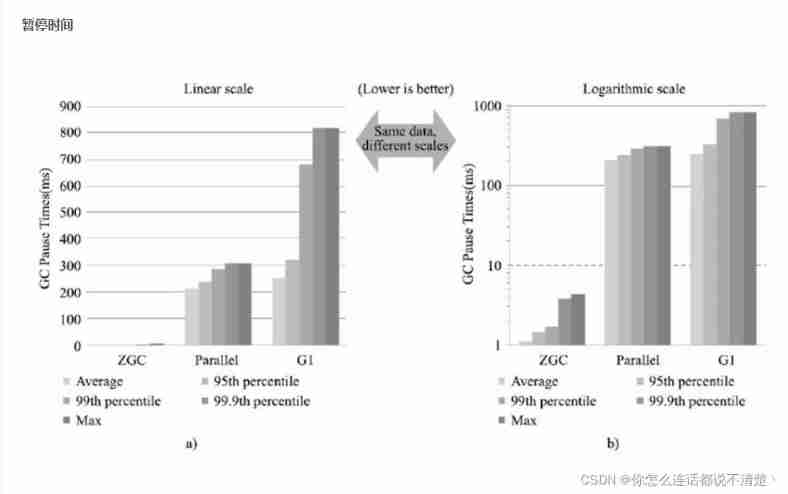
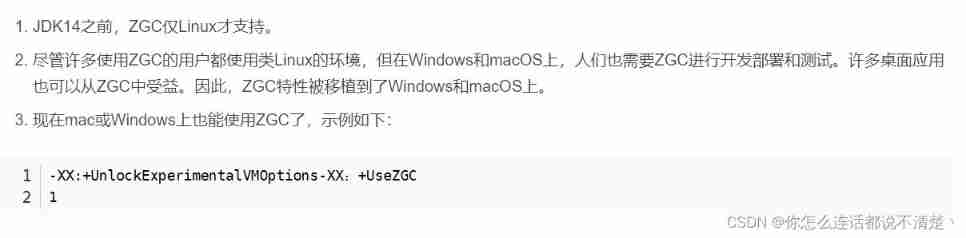
JDK14 New specific :ZGC
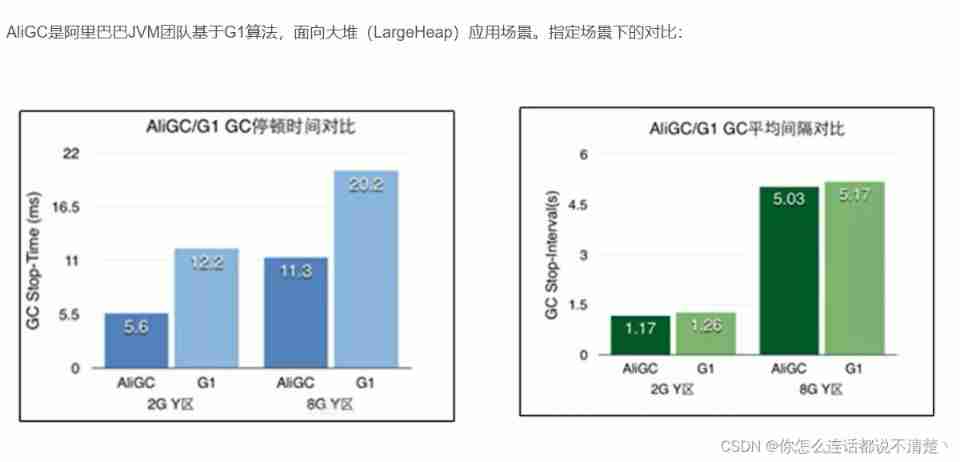
For a lot of AliGC
边栏推荐
- [mask requirements of OSPF and Isis in multi access network]
- 03. Login of development blog project
- [leetcode16] the sum of the nearest three numbers (double pointer)
- 用StopWatch 统计代码耗时
- 毕业设计游戏商城
- Idea one key guide package
- Easy to understand I2C protocol
- Easy to understand IIC protocol explanation
- UCF(暑期团队赛二)
- Realize a binary read-write address book
猜你喜欢
Codeforces Round #804 (Div. 2) Editorial(A-B)
Modbus protocol communication exception

C Advanced - data storage (Part 1)
初识CDN
flutter 实现一个有加载动画的按钮(loadingButton)
Simple understanding of interpreters and compilers

Building intelligent gray-scale data system from 0 to 1: Taking vivo game center as an example
Pointer classic written test questions

Ad20 is set with through-hole direct connection copper sheet, and the bonding pad is cross connected
Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 71_ Unomi
随机推荐
Building intelligent gray-scale data system from 0 to 1: Taking vivo game center as an example
[QNX Hypervisor 2.2用户手册]6.3.3 使用共享内存(shmem)虚拟设备
The ECU of 21 Audi q5l 45tfsi brushes is upgraded to master special adjustment, and the horsepower is safely and stably increased to 305 horsepower
LeetCode_ String inversion_ Simple_ 557. Reverse word III in string
Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 73_ Webmin
[detailed explanation of Huawei machine test] check whether there is a digital combination that meets the conditions
[effective Objective-C] - memory management
03. 开发博客项目之登录
Vulhub vulnerability recurrence 69_ Tiki Wiki
[untitled]
【torch】|torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_
[machine learning notes] univariate linear regression principle, formula and code implementation
改善Jpopup以实现动态控制disable
Summary of deep learning tuning tricks
Pointer classic written test questions
Summary of redis basic knowledge points
Fluent implements a loadingbutton with loading animation
Tetris
Easy to understand I2C protocol
毕业设计游戏商城