当前位置:网站首页>矩阵分解与梯度下降
矩阵分解与梯度下降
2022-07-29 05:27:00 【yc_ZZ】
目录
1、矩阵分解(矩阵乘法回顾)
2、梯度下降
3、矩阵算法推导
4、python代码实现
1、矩阵分解
①为何学习矩阵分解
 矩阵算法就是将用户和产品矩阵中的数据,分解成两个矩阵(用User矩阵和Item矩阵),两个矩阵相乘得到的结果就是预测评分。
矩阵算法就是将用户和产品矩阵中的数据,分解成两个矩阵(用User矩阵和Item矩阵),两个矩阵相乘得到的结果就是预测评分。
矩阵分解就是把原来的大矩阵,近似的分解成小矩阵的乘积,在实际推荐计算时不再使用大矩阵,而是使用分解得到的两个小矩阵
具体来说就是,假设用户物品的评分矩阵A是m乘n维,即一共有m个用户,n个物品.通过一套算法转化为两个矩阵U和V,矩阵U的维度是m乘k,矩阵V的维度是n乘k。
就如同我们现在需要学习的推荐系统,这里面有缺失得评分,我们需要通过矩阵分解,算出这个缺失得评分

我们的目的就是运用已知得评分来算出未知的评分
②回顾矩阵乘法
大写字母表示矩阵,小写字母表示具体的值
矩阵乘法有条件是第一个矩阵的列与第二个矩阵的行数相等

2、梯度下降
梯度下降通俗解释:如同一个人想要下山,不知道怎么下山。于是决定走一步算一步,也就是每次沿着当前位置最陡峭最易下山的方向前进一小步,然后继续沿下一个位置最陡方向前进一小步。这样一步一步走下去,一直走到觉得我们已经到了山脚



通俗理解是首先带入初始位置,然后算出该点的导数,带入一步一步修改新的位置,再进行迭代,直到斜率小于等于参数。相当于找到了最小值

3、矩阵算法推导
使用梯度下降方法获得修正的p和q分量:

根据负梯度的方向更新变量:

最后再不停迭代直到算法最终收敛
3、python代码
import numpy as np
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 定义矩阵分解函数
def Matrix_decomposition(R, P, Q, N, M, K, alpha=0.0002, beta=0.02):
Q = Q.T # Q 矩阵转置
loss_list = [] # 存储每次迭代计算的 loss 值
for step in range(5000):
# 更新 R^
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if R[i][j] != 0:
# 计算损失函数
error = R[i][j]
for k in range(K):
error -= P[i][k] * Q[k][j]
# 优化 P,Q 矩阵的元素
for k in range(K):
P[i][k] = P[i][k] + alpha * (2 * error * Q[k][j] - beta * P[i][k])
Q[k][j] = Q[k][j] + alpha * (2 * error * P[i][k] - beta * Q[k][j])
loss = 0.0
# 计算每一次迭代后的 loss 大小,就是原来 R 矩阵里面每个非缺失值跟预测值的平方损失
for i in range(N):
for j in range(M):
if R[i][j] != 0:
# 计算 loss 公式加号的左边
data = 0
for k in range(K):
data = data + P[i][k] * Q[k][j]
loss = loss + math.pow(R[i][j] - data, 2)
# 得到完整 loss 值
for k in range(K):
loss = loss + beta / 2 * (P[i][k] * P[i][k] + Q[k][j] * Q[k][j])
loss_list.append(loss)
plt.scatter(step, loss)
# 输出 loss 值
if (step + 1) % 1000 == 0:
print("loss={:}".format(loss))
# 判断
if loss < 0.001:
print(loss)
break
plt.show()
return P, Q
if __name__ == "__main__":
N = 5
M = 4
K = 5
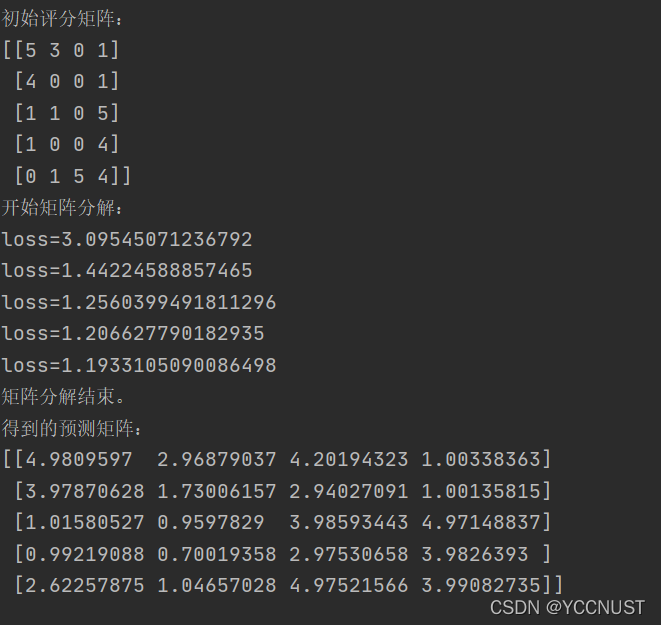
R = np.array([[5, 3, 0, 1],
[4, 0, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 5],
[1, 0, 0, 4],
[0, 1, 5, 4]]) # N=5,M=4
print("初始评分矩阵:")
print(R)
# 定义 P 和 Q 矩阵
P = np.random.rand(N, K) # N=5,K=2
Q = np.random.rand(M, K) # M=4,K=2
print("开始矩阵分解:")
P, Q = Matrix_decomposition(R, P, Q, N, M, K)
print("矩阵分解结束。")
print("得到的预测矩阵:")
print(np.dot(P, Q))结果输出
边栏推荐
- 注解(Annotation)
- day02_ Basic grammar
- Hongke shares | how to test and verify complex FPGA designs (1) -- entity or block oriented simulation
- 5G控制面协议之N2接口
- 有用网站
- 5G服务化接口和参考点
- day03_ 2_ task
- Floating point square root of vivado IP core floating point
- NLP word segmentation
- STP spanning tree principle and example of election rules
猜你喜欢

注解(Annotation)

Hongke education you want to enter the field of TSN? Hongke teaches you how to build TSN test system

CDM—码分复用(简单易懂)

3、 Wide area communication network

成长为架构师途中的一些思考

为什么5G N2接口控制面使用SCTP协议?

Joint use skills of joiner.on and stream().Map

day12_多线程

CNN convolutional neural network

FIR filter design (1) -- using the FDATool toolbox of MATLAB to design FIR filter parameters
随机推荐
ss命令详解
8、 Network security
4、 LAN and man
Inventory | major network security events of global key information infrastructure
find命令详解(文章最后运维最常用操作)
How to pre circumvent the vulnerabilities of unsafe third-party components?
NLP-分词
Design of IIR filter based on FPGA
Traffic characteristics of webshell management tools
Solution for website being suspended
Hongke shares | testing and verifying complex FPGA design (2) -- how to perform global oriented simulation in IP core
Case supplement, ATM
Hongke education you want to enter the field of TSN? Hongke teaches you how to build TSN test system
Leetcode刷题记录
day04_数组
vmstat 内存消耗查询
基于噪声伪标签和对抗性学习的医学图像分割注释有效学习
9、 Networking technology
LDAP简述及统一认证说明
如何在开发板上使用sftp命令访问sftp-server
