当前位置:网站首页>代码重构:面向单元测试
代码重构:面向单元测试
2022-08-03 23:22:00 【阿里云云栖号】

作 者 | 杜沁园(悬衡)
重构代码时,我们常常纠结于这样的问题:
需要进一步抽象吗?会不会导致过度设计?
如果需要进一步抽象的话,如何进行抽象呢?有什么通用的步骤或者法则吗?
不可测试的代码
代码不够简洁?
不好维护?
不符合个人习惯?
过度设计,不好理解?
“单测很容易书写,很容易就全覆盖了”,那么这就是可测试的代码;
“虽然能写得出来,但是费了老大劲,使用了各种框架和技巧,才覆盖完全”,那么这就是可测试性比较差的代码;
“完全不知道如何下手写”,那么这就是不可测试的代码;
public void producerConsumer() {
BlockingQueue<Integer> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
Thread producerThread = new Thread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
blockingQueue.add(i + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100));
}
});
Thread consumerThread = new Thread(() -> {
try {
while (true) {
Integer result = blockingQueue.take();
System.out.println(result);
}
} catch (InterruptedException ignore) {
}
});
producerThread.start();
consumerThread.start();
}
生产者:将 0-9 的每个数字,分别加上 [0,100) 的随机数后通过阻塞队列传递给消费者;
消费者:从阻塞队列中获取数字并打印;
需要测试的逻辑位于异步线程中,对于它什么时候执行?什么时候执行完?都是不可控的;
逻辑中含有随机数;
消费者直接将数据输出到标准输出中,在不同环境中无法确定这里的行为是什么,有可能是输出到了屏幕上,也可能是被重定向到了文件中;
可测试意味着什么?
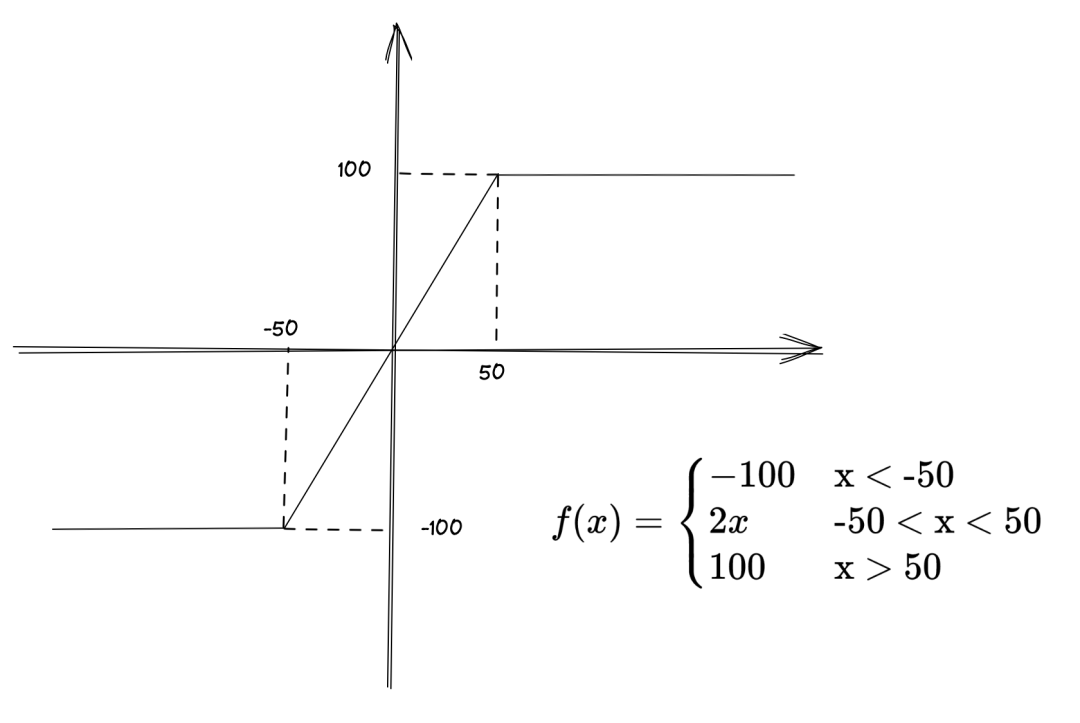
<-50
f(-51) == -100
[-50, 50]
f(-25) == -50
f(25) == 50
>50
f(51) == 100
边界情况
f(-50) == -100
f(50) == 100
每一个分段其实就是代码中的一个条件分支,用例的分支覆盖率达到了 100%;
像 2x 这样的逻辑运算,通过几个合适的采样点就可以保证正确性;
边界条件的覆盖,就像是分段函数的转折点;
函数的返回值只和参数有关,只要参数确定,返回值就是唯一确定的
代码中含有远程调用,无法确定这次调用是否会成功;
含有随机数生成逻辑,导致行为不确定;
执行结果和当前日期有关,比如只有工作日的早上,闹钟才会响起;
public int f() {
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100) + 1;
}
public Supplier<Integer> g(Supplier<Integer> integerSupplier) {
return () -> integerSupplier.get() + 1;
}
public void testG() {
Supplier<Integer> result = g(() -> 1);
assert result.get() == 2;
}
public int g2(Supplier<Integer> integerSupplier) {
return integerSupplier.get() + 1;
}
因为这个例子比较简单,“可测试” 带来的收益看起来没有那么高,真实业务中的逻辑一般比 +1 要复杂多了,此时如果能构建有效的测试将是非常有益的。
面向单测的重构
第一轮重构
我们本章回到开头的生产者消费者的例子,用上一章学习到的知识对它进行重构。
public <T> void producerConsumerInner(Consumer<Consumer<T>> producer,
Consumer<Supplier<T>> consumer) {
BlockingQueue<T> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> producer.accept(blockingQueue::add)).start();
new Thread(() -> consumer.accept(() -> {
try {
return blockingQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
})).start();
}
public <T> void producerConsumerInner(Executor executor,
Consumer<Consumer<T>> producer,
Consumer<Supplier<T>> consumer) {
BlockingQueue<T> blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
executor.execute(() -> producer.accept(blockingQueue::add));
executor.execute(() -> consumer.accept(() -> {
try {
return blockingQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}));
}
private void testProducerConsumerInner() {
producerConsumerInner(Runnable::run,
(Consumer<Consumer<Integer>>) producer -> {
producer.accept(1);
producer.accept(2);
},
consumer -> {
assert consumer.get() == 1;
assert consumer.get() == 2;
});
}
public abstract class ProducerConsumer<T> {
private final Executor executor;
private final BlockingQueue<T> blockingQueue;
public ProducerConsumer(Executor executor) {
this.executor = executor;
this.blockingQueue = new LinkedBlockingQueue<>();
}
public void start() {
executor.execute(this::produce);
executor.execute(this::consume);
}
abstract void produce();
abstract void consume();
protected void produceInner(T item) {
blockingQueue.add(item);
}
protected T consumeInner() {
try {
return blockingQueue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
private void testProducerConsumerAbCls() {
new ProducerConsumer<Integer>(Runnable::run) {
@Override
void produce() {
produceInner(1);
produceInner(2);
}
@Override
void consume() {
assert consumeInner() == 1;
assert consumeInner() == 2;
}
}.start();
}
很显然这种测试无法验证多线程运行的情况,但我故意这么做的,这部分单元测试的主要目的是验证逻辑的正确性,只有先验证逻辑上的正确性,再去测试并发才比较有意义,在逻辑存在问题的情况下就去测试并发,只会让问题隐藏得更深,难以排查。一般开源项目中会有专门的单元测试去测试并发,但是因为其编写代价比较大,运行时间比较长,数量会远少于逻辑测试。
public void producerConsumer() {
new ProducerConsumer<Integer>(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2)) {
@Override
void produce() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
produceInner(i + ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100));
}
}
@Override
void consume() {
while (true) {
Integer result = consumeInner();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}.start();
}
随机数生成逻辑
打印逻辑
public class NumberProducerConsumer extends ProducerConsumer<Integer> {
private final Supplier<Integer> numberGenerator;
private final Consumer<Integer> numberConsumer;
public NumberProducerConsumer(Executor executor,
Supplier<Integer> numberGenerator,
Consumer<Integer> numberConsumer) {
super(executor);
this.numberGenerator = numberGenerator;
this.numberConsumer = numberConsumer;
}
@Override
void produce() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
produceInner(i + numberGenerator.get());
}
}
@Override
void consume() {
while (true) {
Integer result = consumeInner();
numberConsumer.accept(result);
}
}
}
private void testProducerConsumerInner2() {
AtomicInteger expectI = new AtomicInteger();
producerConsumerInner2(Runnable::run, () -> 0, i -> {
assert i == expectI.getAndIncrement();
});
assert expectI.get() == 10;
}
public void producerConsumer() {
new NumberProducerConsumer(Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2),
() -> ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(100),
System.out::println).start();
}
单元测试的边界
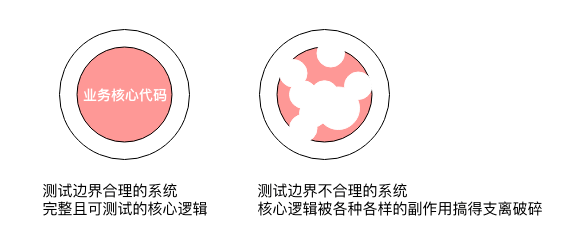
重构的工作流
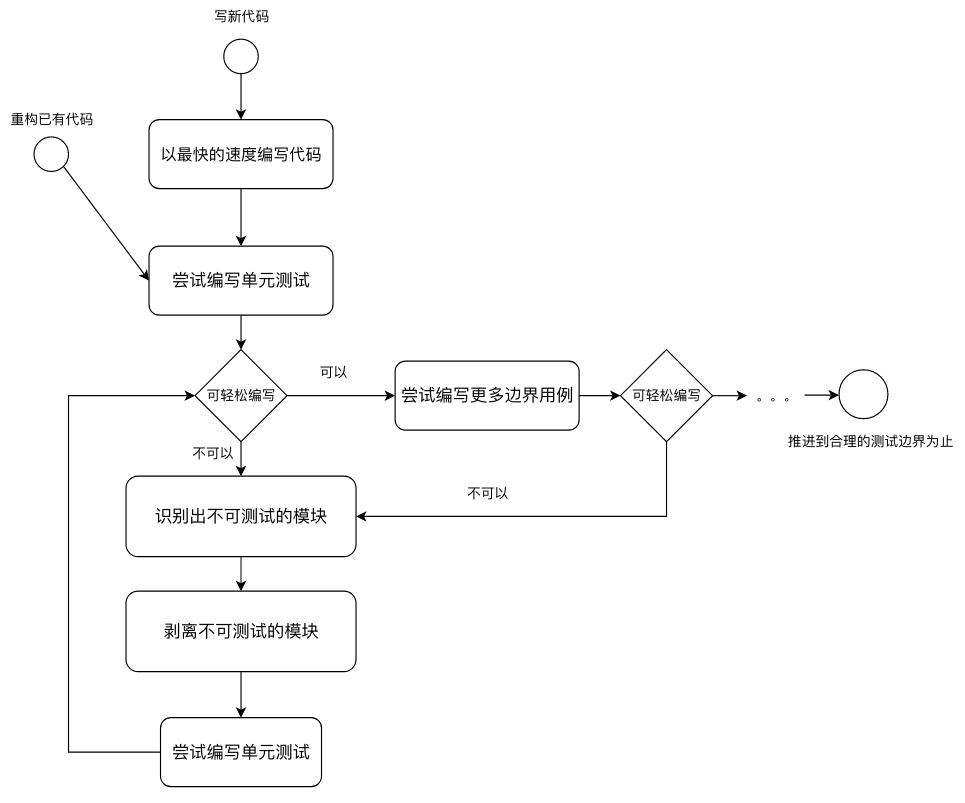
过度设计
和 TDD 的区别
红灯:写用例,运行,无法通过用例
绿灯:用最快最脏的代码让测试通过
重构:将代码重构得更加优雅
代码结构尚未完全确定,出入口尚未明确,即使提前写了单元测试,后面大概率也要修改
产品一句话需求,外加对系统不够熟悉,用例很难在开发之前写好
业务实例 - 导出系统重构
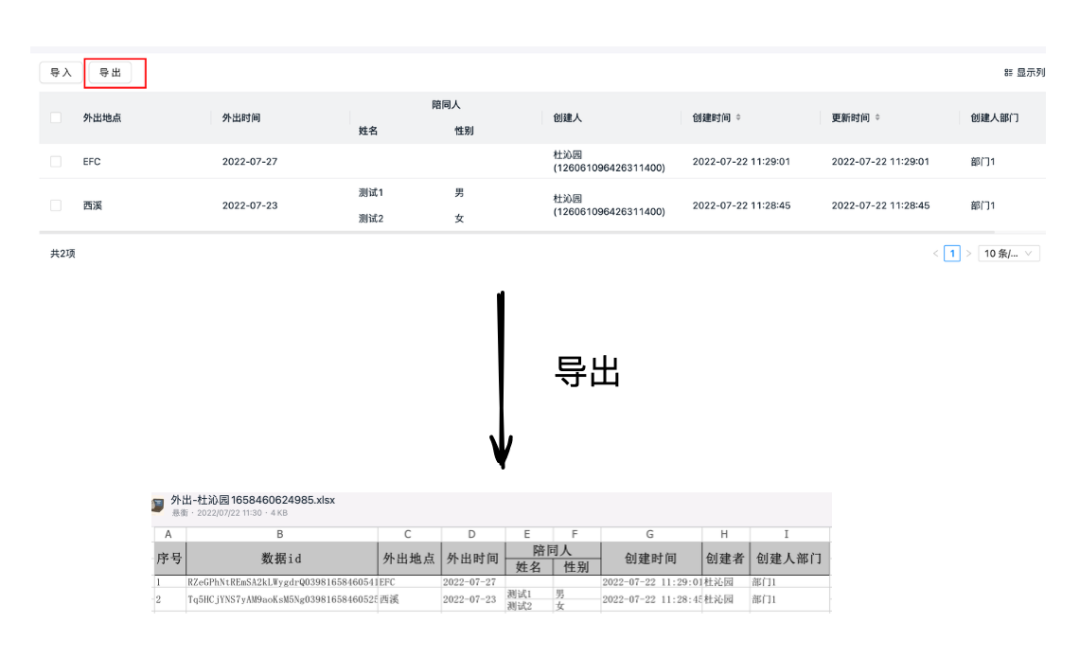
启动一个线程,在内存中异步生成 Excel
上传 Excel 到钉盘/oss
发消息给用户

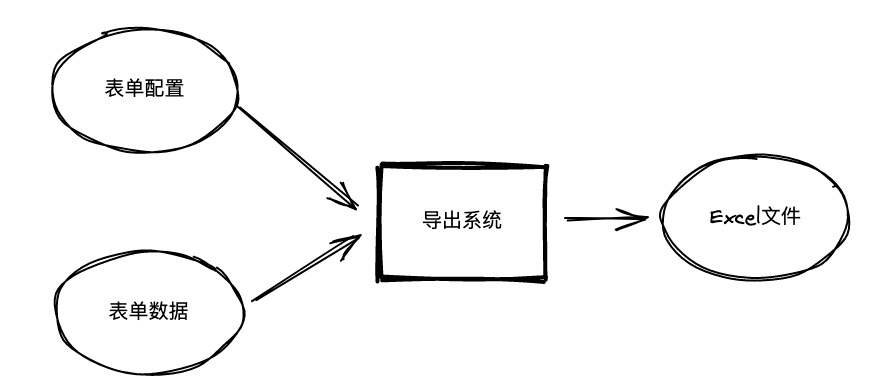
异步执行导致不可测试:抽出一个同步的函数;
大量使用 Spring Bean 导致逻辑割裂:将逻辑放到普通的 Java 类或者静态方法中;
表单数据,流程与用户的相关信息查询是远程调用,含有副作用:通过高阶函数将这些副作用抽出去;
导入状态落入数据库,也是一个副作用:同样通过高阶函数将其抽象出去;
public byte[] export(FormConfig config, DataService dataService, ExportStatusStore statusStore) {
//... 省略具体逻辑, 其中包括所有可测试的逻辑, 包括表单数据转换,excel 生成
}
config:数据,表单配置信息,含有哪些控件,以及控件的配置
dataService: 函数,用于批量分页查询表单数据的副作用
public interface DataService {
PageList<FormData> batchGet(String formId, Long cursor, int pageSize);
}
public interface ExportStatusStore {
/**
* 将状态切换为 RUNNING
*/
void runningStatus();
/**
* 将状态置为 finish
* @param fileId 文件 id
*/
void finishStatus(Long fileId);
/**
* 将状态置为 error
* @param errMsg 错误信息
*/
void errorStatus(String errMsg);
}
public void testExport() {
// 这里的 export 就是刚刚展示的导出测试边界
byte[] excelBytes = export(new FormConfig(), new LocalDataService(),
new LocalStatusStore());
assertExcelContent(excelBytes, Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList("序号", "表格", "表格", "表格", "创建时间", "创建者"),
Arrays.asList("序号", "物品编号", "物品名称", "xxx", "创建时间", "创建者"),
Arrays.asList("1", "22", "火车", "而非", "2020-10-11 00:00:00", "悬衡")
));
}
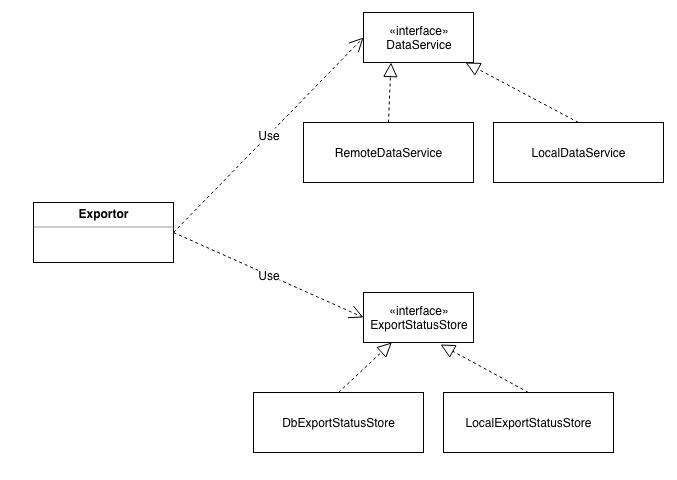
通过 DataService 的抽象,系统可以支持多种数据源导出,比如来自搜索,或者来自 db 的,只要传入不同的 DataService 实现即可,完全不需要改动和性逻辑;
ExportStatusStore 的抽象,让系统有能力使用不同的状态存储,虽然目前使用的是 db,但是也可以在不改核心逻辑的情况下轻松切换成 tair 等其他中间件;
单元测试的局限性
一种可灰度的接口迁移方案
千万级可观测数据采集器 - iLogtail 代码完整开源
全链路压测:影子库与影子表之争
全链路灰度在数据库上我们是怎么做的?
企业上云|数字化转型经验分享
阿里云主长春:助力“专精特新”,数字科技陪伴企业成长
云钉低代码新模式、新能力、新机遇
推文科技:AI 解决方案助力内容出海
三星堆奇幻之旅:只有云计算才能带来的体验
不止能上路,更能做好服务:自动驾驶产品规模化的问题定义
自动驾驶,未来的移动智能载体?
如何提出关键问题
支撑10万人同时在线互动,是实现元宇宙的基本前提?
边栏推荐
- 完全二叉树问题
- node连接mysql数据库报错:Client does not support authentication protocol requested by server
- RSS订阅微信公众号初探-feed43
- SolidEdge ST8安装教程
- Zilliz 2023 秋季校园招聘正式启动!
- Software testing is seriously involution, how to improve your competitiveness?
- Unity2021发布WebGL雾效消失问题
- 图论-虚拟节点分层建图
- Zilliz 2023 Fall Campus Recruitment Officially Launched!
- Another MySQL masterpiece published by Glacier (send the book at the end of the article)!!
猜你喜欢

云平台建设解决方案

数据分析知识点搜集(纯粹的搜集)
Fluorescein-PEG-CLS,胆固醇-聚乙二醇-荧光素科研试剂
Shell编程之循环语句与函数

Zilliz 2023 Fall Campus Recruitment Officially Launched!
用栈实现队列
牛客2022 暑期多校3 H Hacker(SAM + 线段树查询区间内部最大子段和)
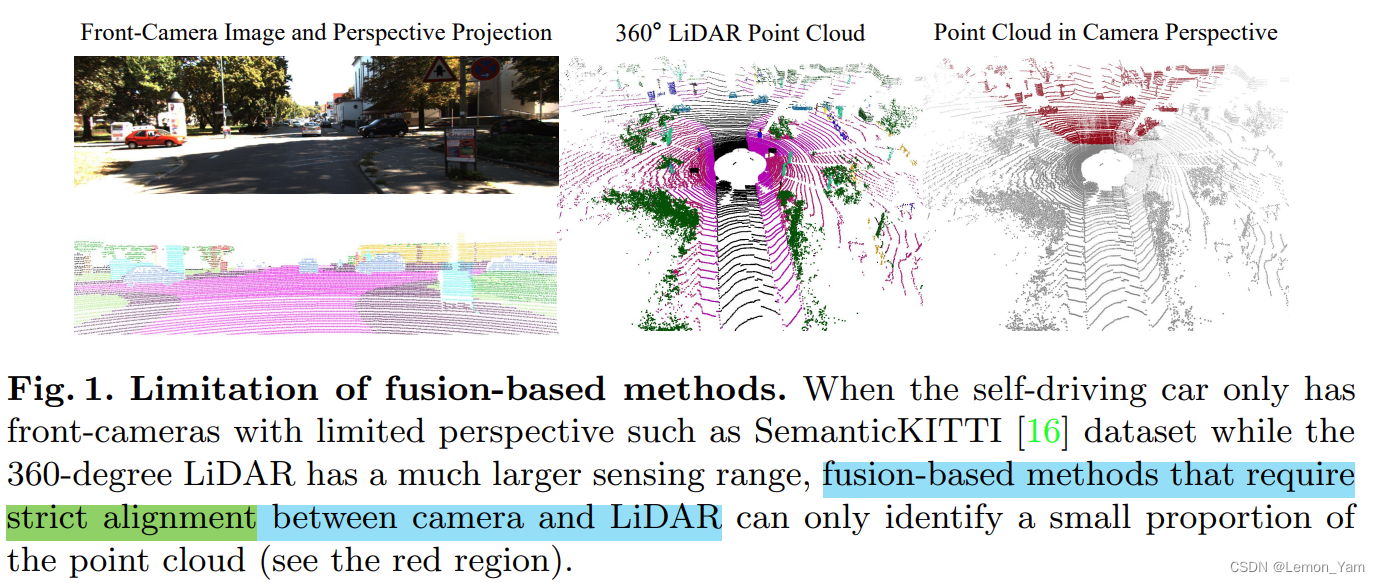
3D Semantic Segmentation - 2DPASS
Click the icon in Canvas App to generate PDF and save it to Dataverse
rosbridge-WSL2 && carla-win11
随机推荐
win10系统下yolov5-V6.1版本的tensorrt部署细节教程及bug修改
Creo 9.0创建几何点
ML's yellowbrick: A case of interpretability (threshold map) for LoR logistic regression model using yellowbrick based on whether Titanic was rescued or not based on the two-class prediction dataset
Testng listener
禾匠编译错误记录
Quickly build a website with static files
如何创建一个Web项目
【LeetCode】最长回文子序列(动态规划)
JS获得URL超链接的参数值
【LeetCode】最长公共子序列(动态规划)
获国际权威认可 | 云扩科技入选《RPA全球市场格局报告,Q3 2022》
关于IDO预售系统开发技术讲解丨浅谈IDO预售合约系统开发原理分析
websocket多线程发送消息报错TEXT_PARTIAL_WRITING--自旋锁替换synchronized独占锁的使用案例
Fluorescein-PEG-CLS, cholesterol-polyethylene glycol-fluorescein scientific research reagent
RPA助力商超订单自动化!
Network basic learning series four (network layer, data link layer and some other important protocols or technologies)
云平台建设解决方案
射频芯片(RFIC)的协议之5G及其调制
生成器版和查看器版有什么区别?
【深度学习】基于tensorflow的服装图像分类训练(数据集:Fashion-MNIST)