当前位置:网站首页>Combined search /dfs solution - leetcode daily question - number of 1020 enclaves
Combined search /dfs solution - leetcode daily question - number of 1020 enclaves
2022-07-06 09:46:00 【C+++++++++++++++++++】
List of articles
Title Description
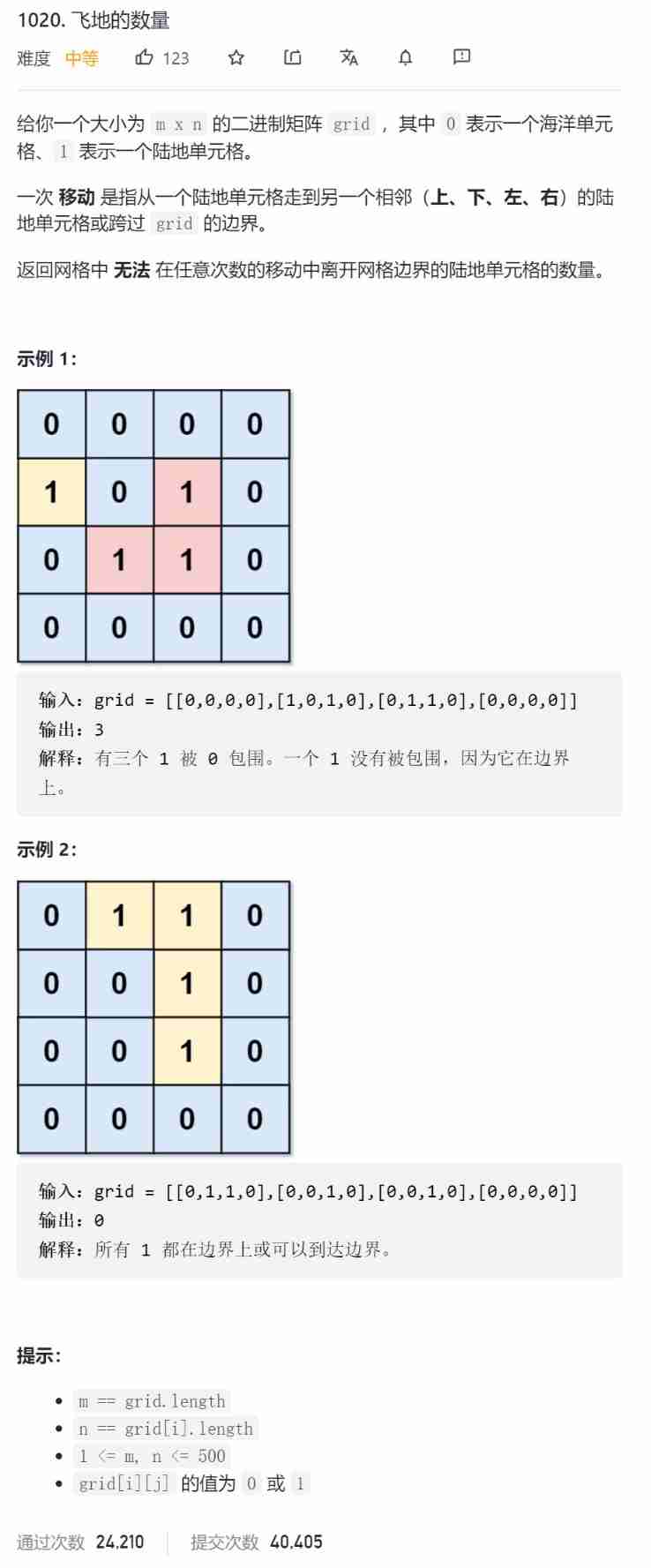
title
One 、 Take the boundary value as the object to search and solve
At the beginning, I soon thought of using more violent direct dfs Deep search , And then it's over time .
Pay attention to this question because 1 Whether it can be extended to the whole border is valid by judging from outside 1 So we need to be clever , It should be based on all boundaries 1 For the object, first put all that can be exceeded 1 I found out , Then the rest 1 That's the answer .
Two 、 And look up the set and merge + Whether the border attribute is updated
Create a query set , Use a one-dimensional array to store all the elements of a two-dimensional array , At the same time, a one-dimensional array is added to determine whether the boundary is contiguous , Every time merge During the operation, it is necessary to judge whether the merge operation and the border update should be performed at the same time .
First use and search set merge be-all 1, Then judge whether it is contiguous one by one .
Solution code
dfs Method :
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> dirs = {
{
-1, 0}, {
1, 0}, {
0, -1}, {
0, 1}};
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
this->m = grid.size();
this->n = grid[0].size();
this->visited = vector<vector<bool>>(m, vector<bool>(n, false));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
dfs(grid, i, 0);
dfs(grid, i, n - 1);
}
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
dfs(grid, 0, j);
dfs(grid, m - 1, j);
}
int enclaves = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i][j]) {
enclaves++;
}
}
}
return enclaves;
}
void dfs(const vector<vector<int>> & grid, int row, int col) {
if (row < 0 || row >= m || col < 0 || col >= n || grid[row][col] == 0 || visited[row][col]) {
return;
}
visited[row][col] = true;
for (auto & dir : dirs) {
dfs(grid, row + dir[0], col + dir[1]);
}
}
private:
int m, n;
vector<vector<bool>> visited;
};
And look up the collection method :
// This parallel search set is well written
class UnionFind {
public:
UnionFind(const vector<vector<int>> & grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
this->parent = vector<int>(m * n); // The connection relationship between storage and collection
this->onEdge = vector<bool>(m * n, false);// The key to finding whether there is a boundary element
this->rank = vector<int>(m * n);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
// Update and search the set according to the transmitted two-dimensional array , Simultaneous updating onEdge The boundary element is true
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
int index = i * n + j;
parent[index] = index;
if (i == 0 || i == m - 1 || j == 0 || j == n - 1) {
onEdge[index] = true;
}
}
}
}
}
int find(int i) {
if (parent[i] != i) {
parent[i] = find(parent[i]);
}
return parent[i];
}
void uni(int x, int y) {
int rootx = find(x);
int rooty = find(y);
if (rootx != rooty) {
if (rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) {
// Here, it is treated as rank optimization
parent[rooty] = rootx;
onEdge[rootx] = onEdge[rootx] | onEdge[rooty];// Each time the elements are merged, the relationship between this pile and the boundary is updated
} else if (rank[rootx] < rank[rooty]) {
parent[rootx] = rooty;
onEdge[rooty] = onEdge[rooty] | onEdge[rootx];
} else {
parent[rooty] = rootx;
onEdge[rootx] = onEdge[rootx] | onEdge[rooty];
rank[rootx]++;
}
}
}
bool isOnEdge(int i) {
return onEdge[find(i)];
}
private:
vector<int> parent; // And the necessary of search set
vector<bool> onEdge; // Judge whether it borders
vector<int> rank; // By rank
};
class Solution {
public:
int numEnclaves(vector<vector<int>>& grid) {
int m = grid.size(), n = grid[0].size();
UnionFind uf(grid);
// First of all 1 Connect , Then judge whether it borders
// Because the cycle is from top to bottom , From left to right , Therefore, the left and up directions do not need to be considered
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
int index = i * n + j;
if (j + 1 < n && grid[i][j + 1] == 1) {
uf.uni(index, index + 1);
}
if (i + 1 < m && grid[i + 1][j] == 1) {
uf.uni(index, index + n);
}
}
}
}
// Judge this 1 Whether it borders the border
int enclaves = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < m - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n - 1; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 1 && !uf.isOnEdge(i * n + j)) {
enclaves++;
}
}
}
return enclaves;
}
};
边栏推荐
- Global and Chinese markets for modular storage area network (SAN) solutions 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- MapReduce instance (IX): reduce end join
- Global and Chinese market of electric pruners 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- 大学C语言入门到底怎么学才可以走捷径
- CAPL 脚本打印函数 write ,writeEx ,writeLineEx ,writeToLog ,writeToLogEx ,writeDbgLevel 你真的分的清楚什么情况下用哪个吗?
- Summary of May training - from a Guang
- MapReduce working mechanism
- MapReduce instance (V): secondary sorting
- Global and Chinese market for annunciator panels 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- 英雄联盟轮播图手动轮播
猜你喜欢
基于B/S的网上零食销售系统的设计与实现(附:源码 论文 Sql文件)

Popularization of security knowledge - twelve moves to protect mobile phones from network attacks
What are the models of data modeling

Programmation défensive en langage C dans le développement intégré

Elk project monitoring platform deployment + deployment of detailed use (II)

Mapreduce实例(八):Map端join
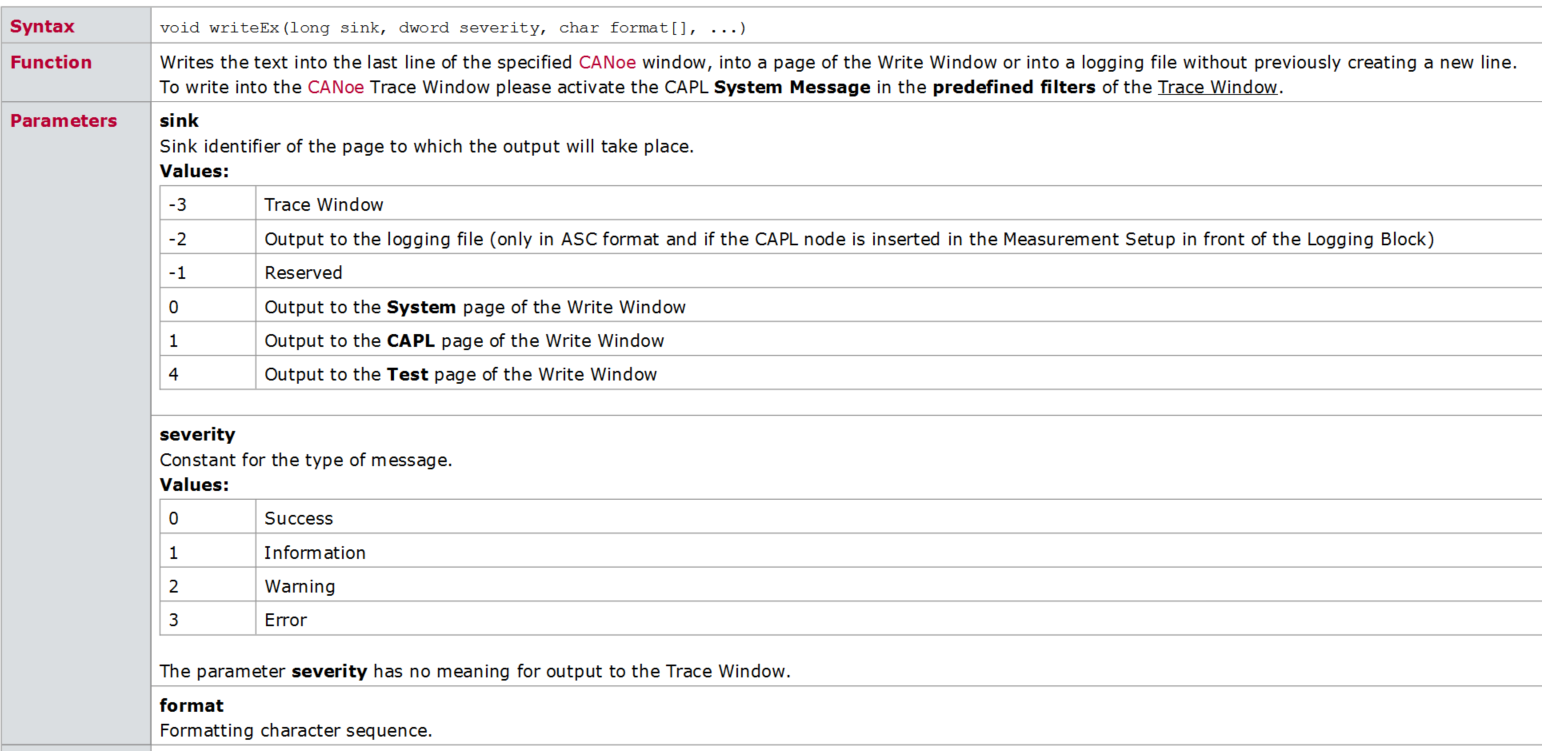
CAPL 脚本打印函数 write ,writeEx ,writeLineEx ,writeToLog ,writeToLogEx ,writeDbgLevel 你真的分的清楚什么情况下用哪个吗?

嵌入式开发中的防御性C语言编程
Design and implementation of film and television creation forum based on b/s (attached: source code paper SQL file project deployment tutorial)
Counter attack of noodles: redis asked 52 questions in a series, with detailed pictures and pictures. Now the interview is stable
随机推荐
I2C summary (single host and multi host)
Global and Chinese market of electric pruners 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Global and Chinese market of AVR series microcontrollers 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Elk project monitoring platform deployment + deployment of detailed use (II)
Vs All comments and uncomments
Lua script of redis
Hero League rotation map automatic rotation
硬件工程师的真实前途我说出来可能你们不信
嵌入式开发中的防御性C语言编程
Global and Chinese market of electronic tubes 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
大学想要选择学习自动化专业,可以看什么书去提前了解?
Learning SCM is of great help to society
Release of the sample chapter of "uncover the secrets of asp.net core 6 framework" [200 pages /5 chapters]
Interview shock 62: what are the precautions for group by?
018.有效的回文
为拿 Offer,“闭关修炼,相信努力必成大器
Why is 51+ assembly in college SCM class? Why not come directly to STM32
Global and Chinese market of bank smart cards 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
Libuv thread
Nc17 longest palindrome substring