当前位置:网站首页>Advanced concurrent programming series 9 (lock interface analysis)
Advanced concurrent programming series 9 (lock interface analysis)
2020-11-07 18:55:00 【yhhitall】
1. Test you
A lot of friends are getting started java In concurrent programming , When it comes to thread safety control , It must be right synchronized Key words are very familiar .synchronized Keyword means synchronous locking , I'm using , You have to wait until I'm finished .
For example Advanced Concurrent Programming Series 7 ( Introduction to lock ) This article , We are right. add_i Variable increment operation , Synchronous locking is the same , Give Way add_i Variables at the same time , It will only be operated by one thread , So thread safety .
/**
* addI Method , Realization add_i Variables operate on themselves
*/
public synchronized static void addI(){
add_i ++;
}
So to speak , You may have questions : since synchronized Keywords can be locked , Ensure thread safety . that java Why did the designer of juc The lock interface is provided in the package Lock, as well as Lock How about the implementation of the interface ? It's not just Yoga 、 He Shengliang ? Not good. , Do you want to repeat the story of Zhou Yu and Kong Ming !
It's not , Although there are synchronized keyword , We said there would be more Lock Interfaces and implementations are not redundant , So, let's talk about it together .
The reason why there is synchronized keyword , We need to provide Lock Interface , It is mainly based on the following factors :
-
synchronized Synchronous locking is internally controlled by jdk control , Fair lock . Practical application , Sometimes we need fair locks , But it can't . One sentence summary : inflexible
-
synchronized Synchronous locking is internally controlled by jdk control , Non interruptible . It's more domineering to use , Once the thread that acquired the lock is not finished , The outside can't be manipulated , Non interruptible lock acquisition thread . One sentence summary : inflexible
-
synchronized Synchronous locking is internally controlled by jdk control , Unable to get lock status , It's a thread A After getting the lock , Then the thread that needs the same lock BCD Can only be blocked waiting , Not flexible enough to use . For example, you can't thread A After getting the lock , Threads B To try to get the lock , If the lock cannot be acquired , Threads B You can do something else , You don't have to wait here . One sentence summary : inflexible
You can see , To sum up, we are interested in synchronized The impression of keywords is : inflexible . Here we need to pay attention to , Some friends are talking about synchronized keyword , And Lock When the lock is different , From the perspective of performance , In fact, from jdk1.6 in the future ,jvm Lock optimization is implemented internally , There is almost no difference in performance between the two . The main difference is still synchronized inflexible .
Then let's take a look at , in the light of synchronized Inflexible places ,Lock What solutions does the interface provide :
-
synchronized Lock is unfair lock .Lock Interface common implementation class ReentrantLock, When constructing a lock object , We can specify to construct fair locks , Or unfair lock , Implement on-demand construction
-
synchronized A lock is a non interruptible lock .Lock The interface provides lockInterruptibly() Method , Support interrupt operation
-
synchronized Lock cannot be locked .Lock The interface provides tryLock() Method , Used to return the lock state . If the thread A Lock has been acquired , So thread B adopt tryLock Attempt to acquire lock , You don't need to be blocked
-
in addition Lock Implementation class of interface , Through the read-write lock ReentrantReadWriteLock Read lock in class ReadLock, The shared lock is implemented . The so-called shared lock read lock , That is, everyone is reading operation , Don't be too outspoken , You can read , I can read , Reading is the real reading .
Through the above about Lock Description of the interface , Are you more and more in love with Lock Lock the interface , Yes, I think it is . So next , Let's see Lock Interface design , And basic usage .
2. Case study
2.1.Lock Interface source code
Through the analysis above , I think we'll all be curious ,Lock How the interface is designed , What capabilities does it need to provide us ? Right , Let's try to think about it :
-
Need a lock operation , So there should be a way to lock :lock
-
When the task is completed , A lock release operation is required , So there should be a way to release the lock :unlock
-
According to our above and synchronized contrast ,Lock Need to support getting lock state , If an attempt to acquire a lock fails , No need to block threads , So there should be an attempt to acquire a lock method :tryLock
-
According to our above and synchronized contrast ,Lock Interrupt operations need to support , Therefore, there should be a lock method that supports interrupt operations :lockInterruptibly
-
The above should be what we can intuitively think of Lock Basic ability , in fact Lock Interfaces are implemented through different implementation classes , Provides more powerful capabilities . We will gradually show through the case , For the moment, you don't need to care too much about
Let's take a look ,Lock Interface source screenshot , Besides looking at the pictures , I suggest you open jdk Source code , Have a look Lock Interface source code , There are very detailed source code comments , It's a great way to learn .
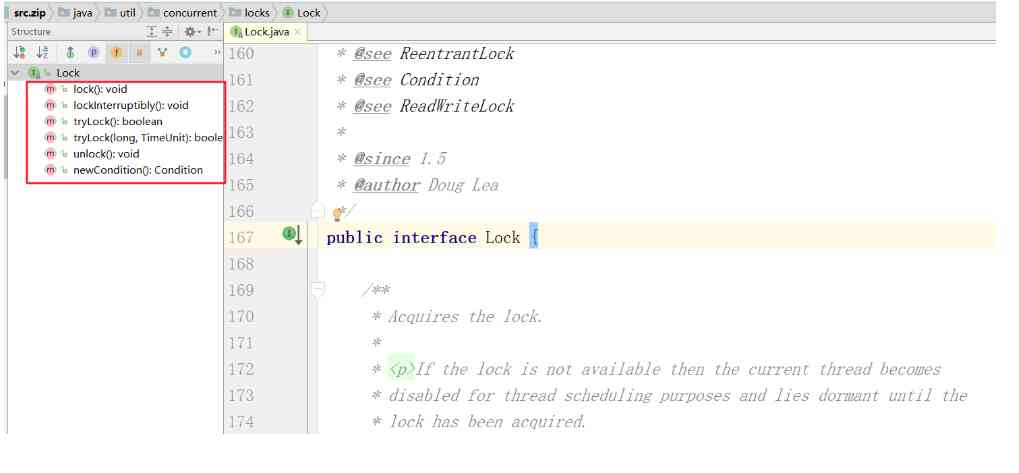
2.2.Lock Interface programming templates
In your application , If it's through synchronized Keyword lock words , You must still have an impression : Use synchronized keyword , We don't need to release the lock , Everything has jvm To control .
But if you choose a more flexible Lock Lock mode , Remember to : Matching release lock operation , Don't just give birth to 、 If you don't care about it, it's troublesome , So what's waiting for you is deadLock( Deadlock ) 了 .
Next, I'll give you a generic Lock Locks use templates , You need to pay attention to try{...}finally{...} Sentence block .
Here we will not expand the actual use case for the moment , Practical application cases , We'll put it in the next one to learn with you .
/**
* addI Method , Realization add_i Variables operate on themselves
* adopt Lock Lock
*/
public static void addI(){
// Lock
lock.lock();
try{
// Business operations
add_i ++;
}finally{
// Release the lock
lock.unlock();
}
}
版权声明
本文为[yhhitall]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
带你深入了解 GitLab CI/CD 原理及流程

7.Swarm搭建集群

Nanjing logo design and production, guide VI system design

Tips for Mac novices

What should be considered in the promotion plan outside the station?
Opencv computer vision learning (10) -- image transform (Fourier transform, high pass filter, low pass filter)

And how to solve the conflict between pop-up menu and pop-up menu

三步轻松理解Kerberos协议

嘉宾专访|2020 PostgreSQL亚洲大会中文分论坛:岳彩波

课堂练习
随机推荐
Didi's distributed ID generator (tinyid), easy to use
Nanjing logo design and production, guide VI system design
Python3 operating gitlab
Three steps to understand Kerberos Protocol easily
How to write plug-in code of small program mall system? How to use code to check whether the plug-in is successfully added?
PHP后门隐藏技巧
7. Swarm builds clusters
2020-11-06: go, let's talk about the scheduler.
HandlerMethodArgumentResolver使用和原理
Knowledge competition of garbage classification
confd
In simple terms, the large front-end framework angular6 practical course (angular6 node.js 、keystonejs、
Analysis of the original code of [QT] qthread
测试攻城狮必备技能点!一文带你解读DevOps下的测试技术
Mate 40系列发布 搭载华为运动健康服务带来健康数字生活
ImageMagick - add watermark
OpenCV計算機視覺學習(10)——影象變換(傅立葉變換,高通濾波,低通濾波)
条形码识别性能低,如何优化Dynamsoft Barcode Reader解码性能
带你深入了解 GitLab CI/CD 原理及流程
Dynamsoft barcode reader v7.5!