当前位置:网站首页>The role of /etc/profile, /etc/bashrc, ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bashrc files
The role of /etc/profile, /etc/bashrc, ~/.bash_profile, ~/.bashrc files
2022-07-31 14:26:00 【Stop losing your hair】
/etc/profile: This file sets the environment information for each user of the system. When the user logs in for the first time, this file is executed.And collect the shell settings from the configuration files in the /etc/profile.d directory.Think of system environment variables.
/etc/bashrc: Execute this file for every user running the bash shell, which is read when the bash shell is opened.
~/.bash_profile: Each user can use this file to enter shell information dedicated to their own use. When the user logs in, this file is executed only once! By default, he sets some environment variables and executes the user's.bashrc file.
~/.bashrc: This file contains bash information specific to your bash shell and is read when logging in and every time a new shell is opened.
~/.bash_logout: This file is executed every time you exit the system (exit the bash shell).
In addition, the variables (global) set in /etc/profile can act on any user, while the variables (local) set in ~/.bashrc can only inherit the variables in /etc/profile, theyIt's a "father-son" relationship.
~/.bash_profile is the interactive, login mode to enter the bash operation
~/.bashrc is the interactive non-login mode to enter the bash operation
Usually the two settings are roughly the same, so usually the former will callthe latter.
Several initialization files of bash - [Ubuntu]
(1) /etc/profile
Global (public) configuration, no matter which user is, the file will be read when logging in.
(2) /ect/bashrc
Ubuntu does not have this file, the corresponding one is /ect/bash.bashrc
It is also a global (public)
When bash is executed, no matter what it ismode, will read this file.
(3) ~/.profile
If bash is executed in login mode, read /.bash_profile, if it does not exist, read /.bash_login, if the first two do not exist, read ~/.profile.
Also, when logging in graphical mode, this file will be read even if /.bash_profile and /.bash_login exist.
(4) ~/.bash_login
If bash is executed in login mode, read /.bash_profile, if it does not exist, read /.bash_login, if the first two do not exist, read ~/.profile.
(5) ~/.bash_profile
Unbutu does not have this file by default, you can create a new one.
This file is read only when bash is executed as login.Usually this configuration file is also configured to read ~/.bashrc.
(6) ~/.bashrc
When bash is executed in non-login form, read this file.If executed in login form, this file will not be read.
(7) ~/.bash_logout
This file will only be read when it is logged out and in the form of longin.That is, when logging out in text mode, this file will be read, and when logging out in graphics mode, this file will not be read.
Here are a few examples on this machine:
When logging in in graphical mode, read sequentially: /etc/profile and ~/.profile
After logging in in graphical mode, when opening a terminal, read in sequence: /etc/bash.bashrc and ~/.bashrc
When logging in in text mode, read in sequence: /etc/bash.bashrc, /etc/profile and ~/.bash_profile
From other users su to this user, there are two cases:
(1) IfWith -l parameter (or - parameter, --login parameter), such as: su -l username, then bash is logged in, it will sequentially read the following configuration files: /etc/bash.bashrc, /etc/profile and ~/.bash_profile.
(2) If there is no -l parameter, then bash is non-login, it will read sequentially: /etc/bash.bashrc and ~/.bashrc
When logging out, or logging out of su user, if it is the longin method, then bash will read: ~/.bash_logout
When executing a custom shell file, if the "bash -l a.sh" method is used, bash will read the line: /etc/profile and ~/.bash_profile, if you use other methods, such as: bash a.sh, ./a.sh, sh a.sh (this does not belong to the bash shell), it will not read any of the above files.
The above example always reads /.bash_profile, if the file does not exist, then reads /.bash_login, if the first two do not exist, reads ~/.profile.
边栏推荐
- Use of C# Assembly
- In the future, the interviewer asks you why it is not recommended to use Select *, please answer him out loud!
- AI cocoa AI frontier introduction (7.31)
- 最近很火的国产接口神器Apipost体验
- UnityShader入门学习(二)——渲染流水线
- Resnet&API
- Shell script classic case: detecting whether a batch of hosts is alive
- LeetCode旋转数组
- The pre-sale of the new Hyundai Paristi is open, and safety and comfort are not lost
- Selenium自动化测试之Selenium IDE
猜你喜欢

技能大赛训练题:ftp 服务攻防与加固
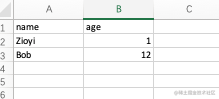
Small test knife: Go reflection helped me convert Excel to Struct

Five dimensions to start MySQL optimization

OAuth2:搭建授权服务器

Sentinel流量控制
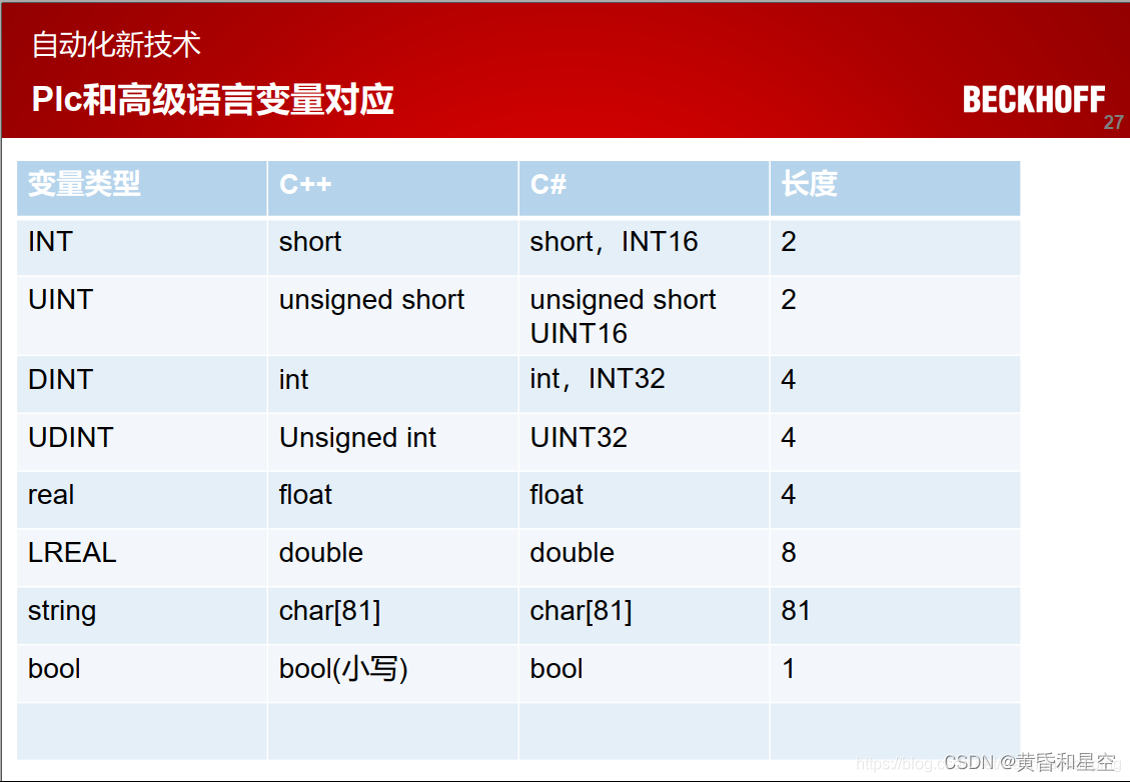
ADS communicate with c #

The paper manual becomes 3D animation in seconds, the latest research of Wu Jiajun of Stanford University, selected for ECCV 2022

IDEA connects to MySQL database and uses data
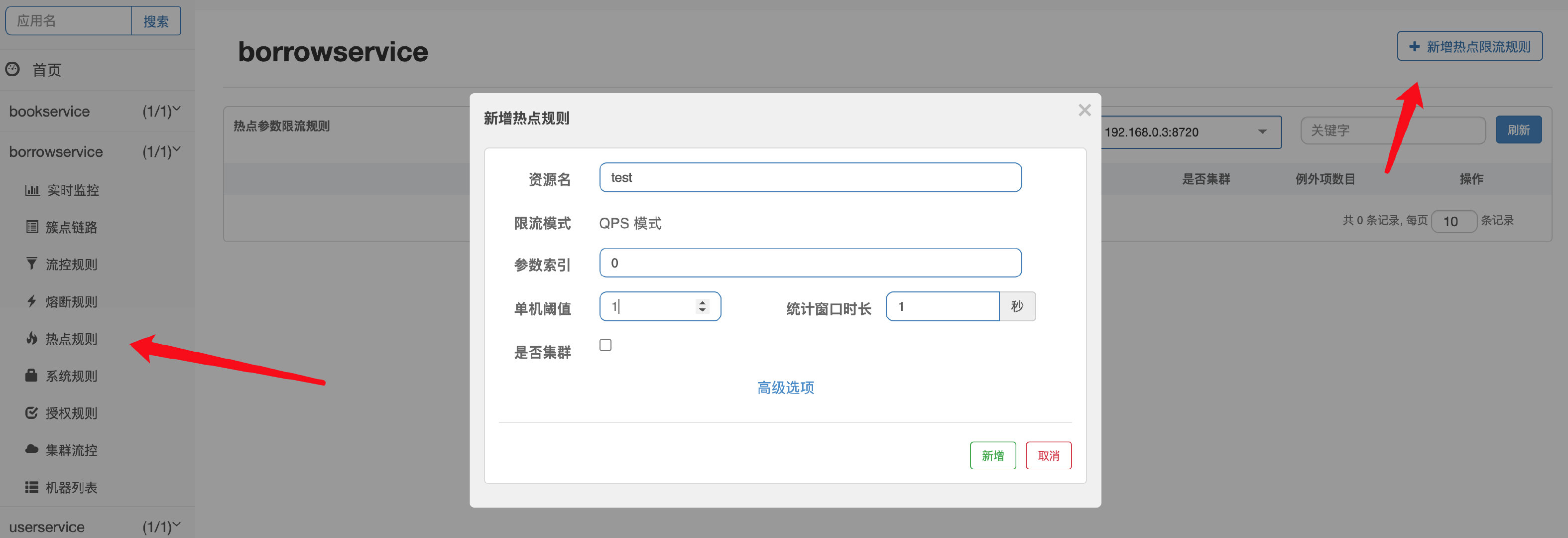
Sentinel热点参数限流

拥塞控制,CDN,端到端
随机推荐
消息队列消息数据存储MySQL表设计
新款现代帕里斯帝预售开启,安全、舒适一个不落
A detailed guide to simulating latency with SQL/JDBC
Buffer 与 拥塞控制
高等数学——常用不定积分公式
自制的数据库安全攻防题,相关靶机自己制作
4.爬虫之Scrapy框架2数据解析&配置参数&数据持久化&提高Scrapy效率
Redis与分布式:主从复制
【Pytorch】torch.argmax()用法
For enterprises in the digital age, data governance is difficult, but it should be done
【redis】发布和订阅消息
el-tooltip的使用
Redis与分布式:集群搭建
leetcode:485.最大连续 1 的个数
三角恒等变换公式
龟速乘【模板】
LeetCode只出现一次的数字
Open Inventor 10.12 Major Improvements - Harmony Edition
The magic of SQL MERGE statement (detailed instructions)
以后面试官问你 为啥不建议使用Select *,请你大声回答他!