当前位置:网站首页>IO model review
IO model review
2022-07-07 10:26:00 【Zong_ 0915】
IO Model review
Preface
This piece of ice river teacher's article , Do a review .
One . IO The basic concept of
First of all, what is IO: It involves the process of data migration between computer core and other devices , Namely IO. For example, disk IO:
- Input : Read data from disk to memory .
- Output : Write data in memory to disk .
And the operating system initiates once IO The operation generally includes two stages :
- IO call : The application process goes to Operating system kernel A call .
- IO perform : Operating system kernel complete IO operation .
among ,IO The implementation stage is divided into two stages :
- Data preparation stage : Kernel wait I/O The device is ready for data .
- Copy data phase : Copy data from kernel buffer to user process buffer .
Pictured :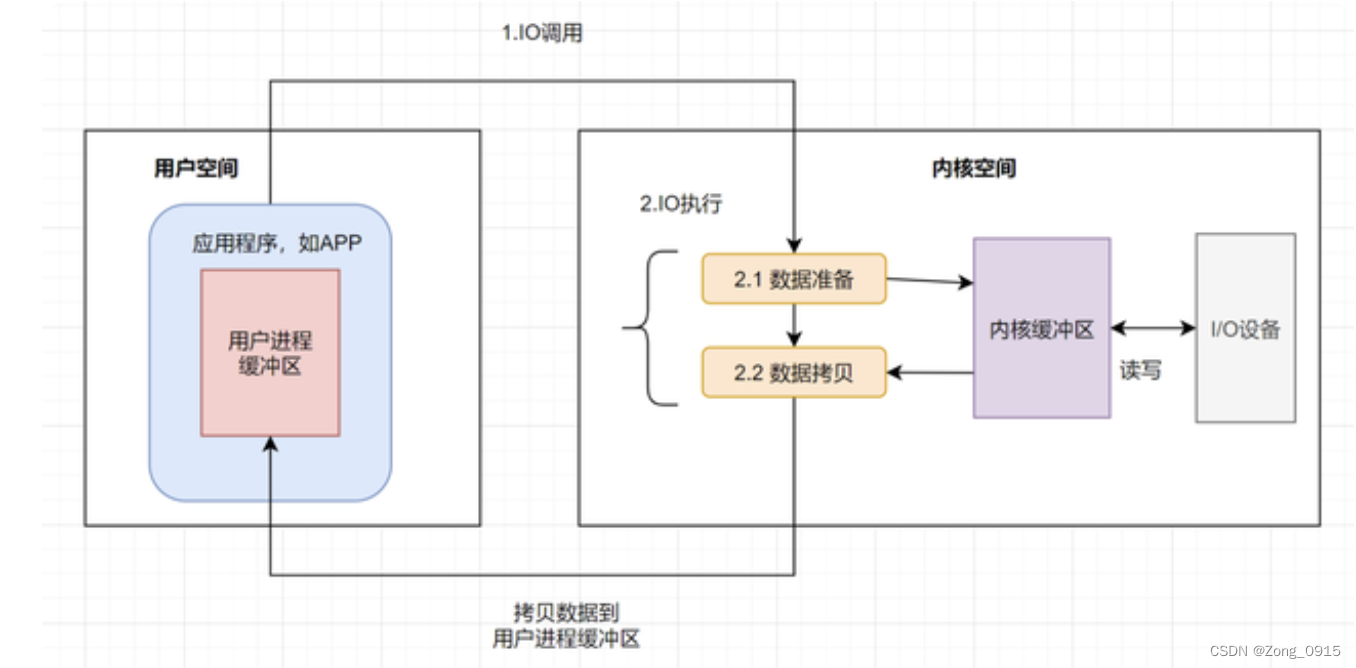
Two . IO Model
IO There are five types of models :
2.1 Blocking type IO(BIO)
Application process initiation IO call , however Kernel data is not ready . therefore The application process has been blocking and waiting , Until the kernel data is ready .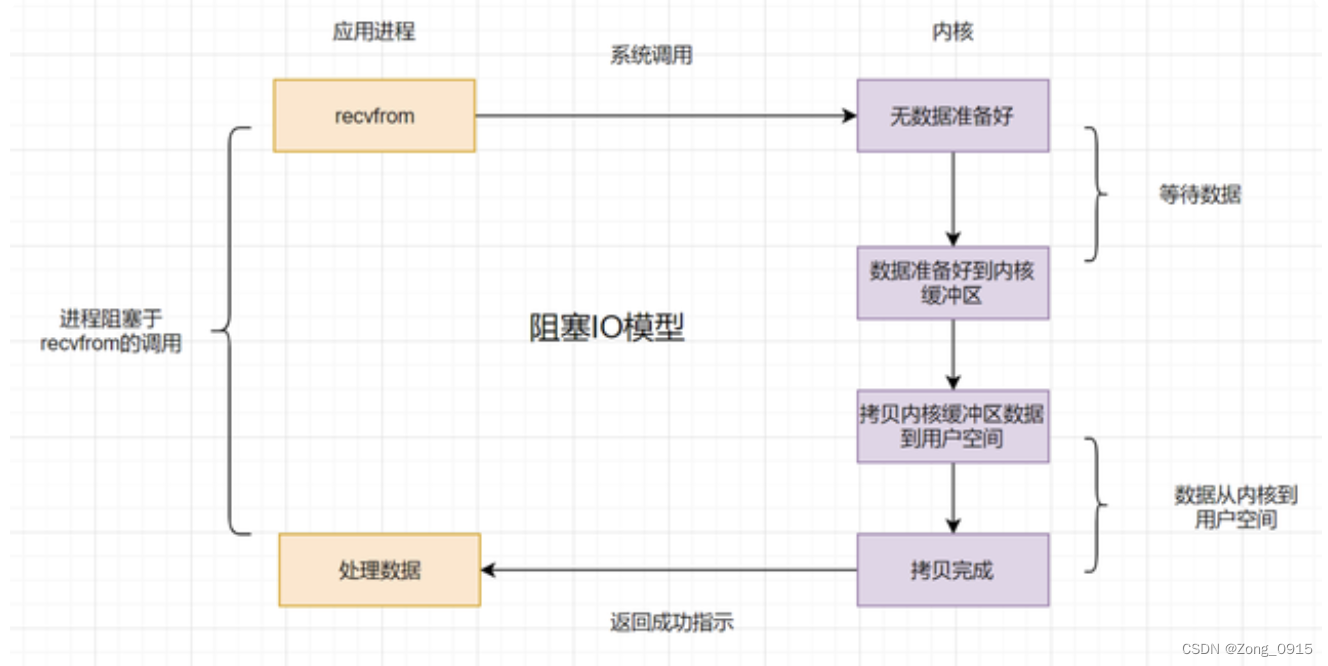
shortcoming : If the kernel data is never ready , Then the user process will always be blocked , Waste performance .
2.2 Non-blocking type IO(NIO)
In view of the blocking IO The shortcomings of , On its basis , If the kernel data is not ready , Non-blocking type IO Meeting First, return the error message to the user process , Make it unnecessary to wait , Then request by polling .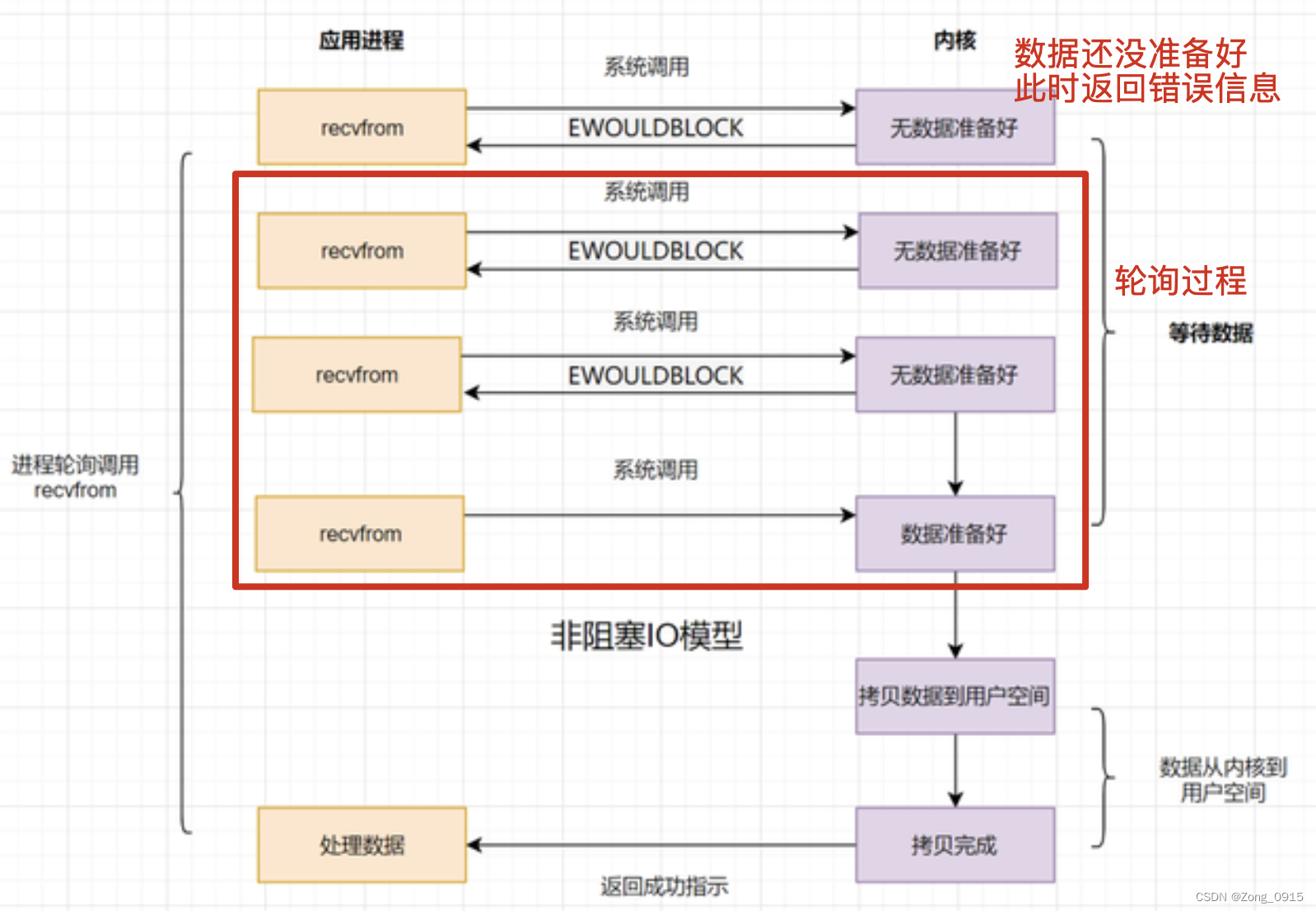 advantage : Compared with blocking IO, Users don't have to wait , It will not enter the blocking state because the kernel data is not ready .
advantage : Compared with blocking IO, Users don't have to wait , It will not enter the blocking state because the kernel data is not ready .
shortcoming : Frequent polling , Lead to frequent system calls , Consume a lot of CPU resources .
2.3 IO Multiplexing (BIO)
Since frequent polling leads to CPU It costs a lot . Let the kernel data be ready , Actively notify the application to make system calls . That is to say IO Multiplexing .
Concept : File descriptor (File Descriptor)
The file descriptor is a non negative integer . When opening an existing file or creating a new file , The kernel returns a file descriptor . Reading and writing files also need to use file descriptors to specify the files to be read and written .
IO The core idea of reuse model : The system provides us with a class of functions , They can monitor multiple at the same time fd The operation of , ren Which one returns kernel data ready , The application process then initiates a system call . Be careful , Here, the application process is still required to initiate system calls .
IO There are three ways of multiplexing :select、poll、epoll.
2.3.1 select
The application process can pass select function , Come on Monitor multiple at the same time fd, stay select Function monitoring fd In the process of , As long as any data state is ready .select It will return to the readable state , At this time, the application process will initiate a request to read kernel data . Pictured :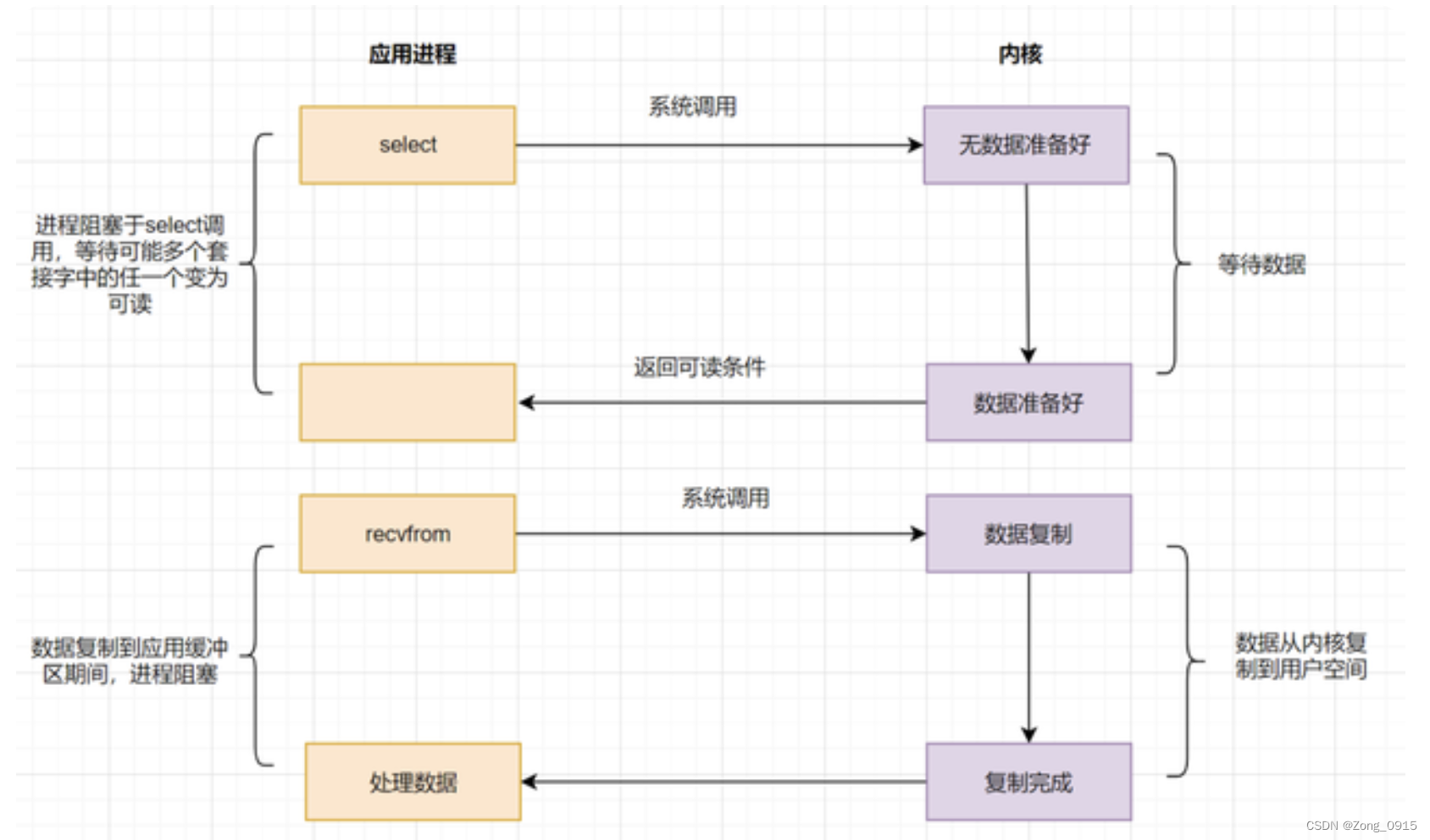
Drawbacks as follows :
- Monitoring IO The maximum number of connections has an upper limit .
selectWhen the function returns , By traversingfdaggregate , Find ready descriptorfd.( namely Traverse all streams )
2.3.2 poll
Whereas select Disadvantages of the way , It came up. poll. Compared with the former ,poll It solves the problem of limiting the number of connections . however poll You still need to traverse the file descriptor to get the ready socket.
2.3.3 epoll
So in order to solve the problem select and poll The problem is , And then there is IO Multiplexing (epoll) Model , Use event driven to realize :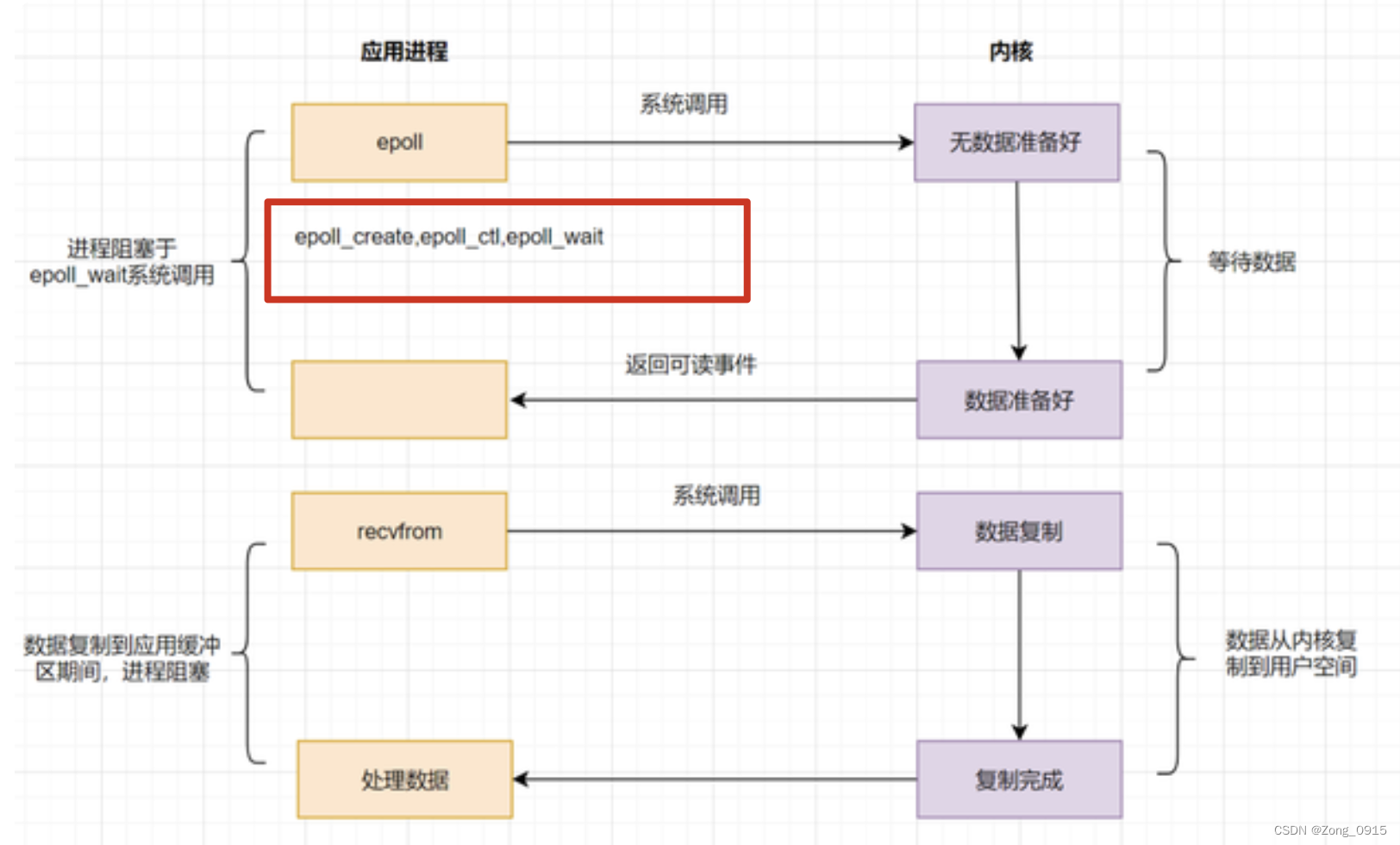
Looks like select There is no difference in the flow chart , Add some words here :
epollFirst, throughepoll_ctl()Function to register a file descriptor .- Once based on a
fdWhen it's ready , The kernel uses a callback mechanism , Quickly activate thisfd. - When the process calls
epoll_wait()I'll be informed when . By adopting Listen for event callbacks Mechanism to Avoid traversing all text descriptors .
although IO Multiplexing this way for non blocking IO, There is no need to make frequent calls , But through callback . But when the process calls epoll_wait() when , It can still be blocked .
Important things are to be repeated for 3 times , Multiplexing IO It still is : Synchronous blocking ! Synchronous blocking ! Synchronous blocking !
Therefore, we hope to have such a function in design ( I think it would be better to understand this way ):
- Multiplexing IO, Although you can specify the corresponding IO flow . Avoid traversing all IO.
- Although the results are obtained through callback , But the process of waiting for the result , It needs blocking to wait .
- Therefore, the design hopes that the user process can not wait , Do something else first . Wait for the callback result , I can feel it again .
Then comes the signal drive IO Model .
2.4 Signal driven IO(NIO)
On the basis of multiplexing . Send a signal to the kernel . At this time, the application process does not need to be blocked , You can do other things . When the kernel data is ready , Re pass SIGIO Signal the application process . Once the process gets the signal , Immediately call to get kernel data . Pictured :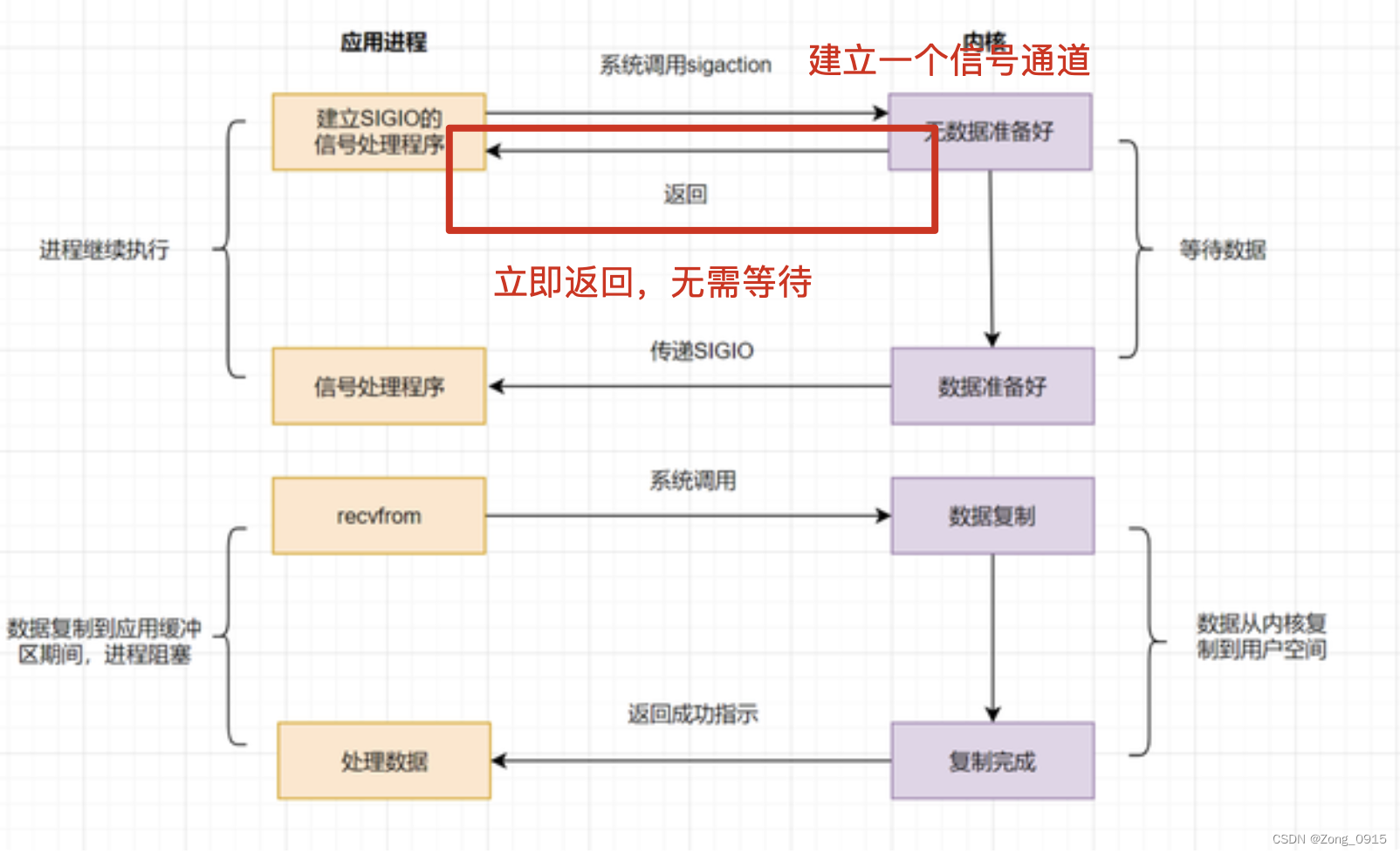
Of course , The data status inquiry process here is asynchronous, right , But the data replication part , It is still synchronously blocked , Therefore, the whole signal drives IO The process of is not asynchronous .
2.5 asynchronous IO(AIO)
You only need to send a request to the kernel once , All operations of data status inquiry and data copy can be completed , And don't block waiting for results .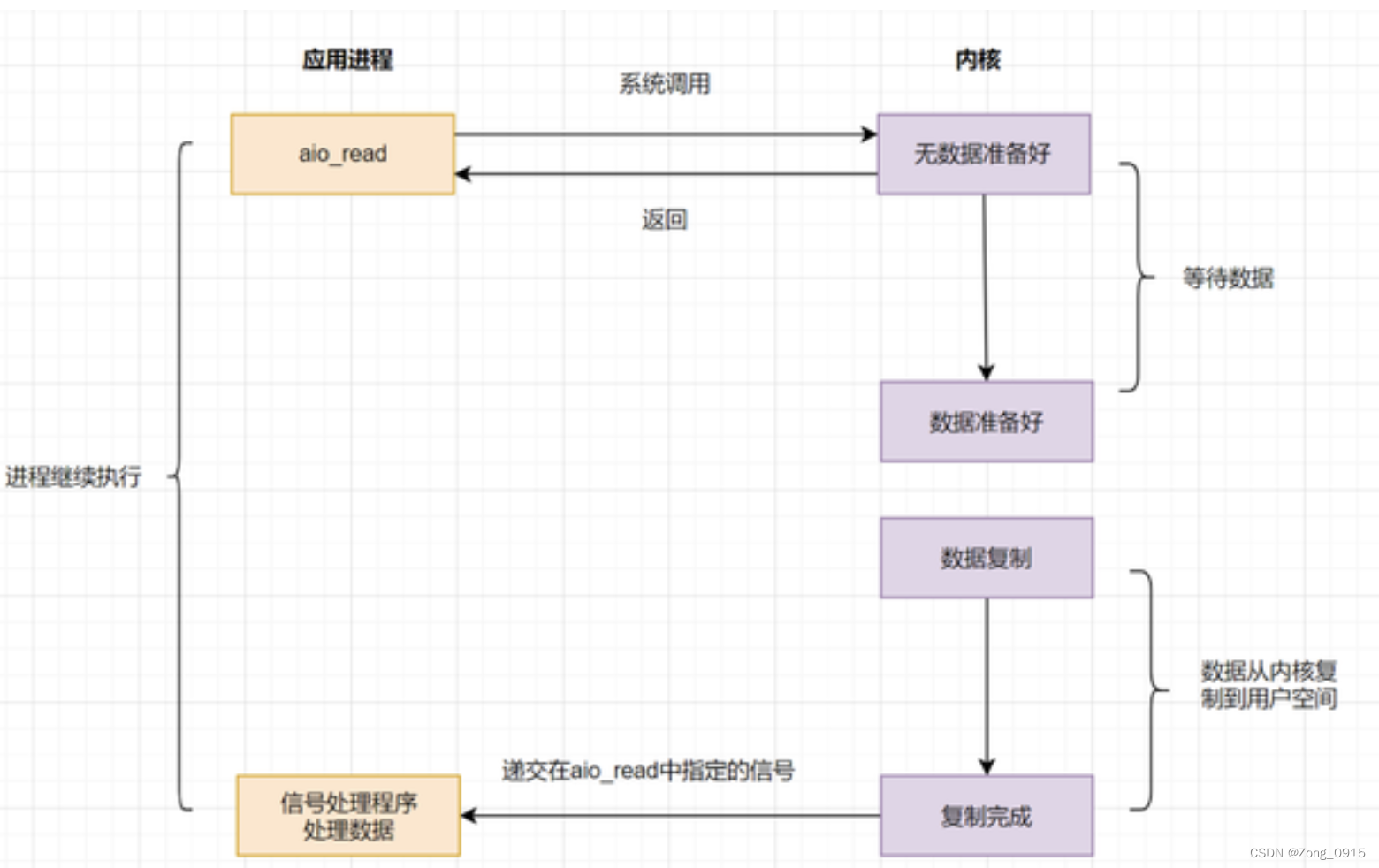
Here's the explanation BIO、NIO、AIO:
- Synchronous blocking (
blocking-IO) abbreviationBIO. - Synchronous nonblocking (
non-blocking-IO) abbreviationNIO. - Asynchronous non-blocking (
asynchronous-non-blocking-IO) abbreviationAIO.
3、 ... and . summary
3.1 select、poll、epoll The three difference *
| Comparative study | select | poll | epoll |
|---|---|---|---|
| Underlying data structure | Array | Linked list | Red and black trees + Double linked list |
| Get ready fd The way | Traverse all of | Traverse all of | Event callback |
| The complexity of the event | O(n) | O(n) | O(1) |
| maximum connection | 1024(Linux) | unlimited | unlimited |
fd Data copy mode | Every time you call select, We need to fd Copy from user space to kernel space | Every time you call poll, We need to fd Copy from user space to kernel space | Through memory mapping (mmap), There is no need to make frequent copies fd, At a time can be . |
3.2 Five kinds IO Model
| IO Model | Blocked state | sync |
|---|---|---|
| Blocking type IO | Blocking | Sync |
| Non-blocking type IO | Non blocking | Sync |
| IO Multiplexing | Blocking | Sync |
| Signal driven IO | Non blocking | Sync |
| asynchronous IO | Non blocking | asynchronous |
Blocking , The concept of non blocking distinguishes : It can be simply understood as whether you need to do something to get a reply immediately , If you cannot get a return immediately , Need to wait , That's blocking . Prefer whether to respond immediately .
Sync , The concept of asynchrony : You always do one thing before you do another , Whether it takes time to wait , This is synchronization . Otherwise, it is asynchronous . I prefer whether I can do two things in parallel .
Then look back at the table above :
Non-blocking type IO The explanation in this respect :
- Non blocking : Because user processes can get results immediately ( It may be the data that the end user wants , It may also be an error message ).
- Sync : Because the data replication phase is always executed after the data query phase .
IO Explanation of multiplexing :
- Blocking : The user process needs to wait for the callback result to return . The process is blocked .
- Sync : Because the data replication phase is always executed after the data query phase .
Signal driven IO The explanation in this respect :
- Non blocking : The user process can get the return immediately in the data query stage .
- Sync : You need to wait for the kernel to send a signal , Express
fdeureka . Let the user process getfd, Then the user process initiates a request for data copy .
asynchronous IO The explanation in this respect :
- Non blocking : Users can also get results immediately .
- asynchronous : The whole data waiting and copying operation are handed over to the operating system , Not users , Users do not need to block waiting .
In the end, it can be found that , For these five IO Model , The difference between asynchronous and synchronous is nothing more than :
- Sync : The data waiting and copying process is divided into two stages , Initiated by the application process . It needs to be initiated twice .
- asynchronous : The data waiting and copying operations are handed over to the operating system . The application process can initiate a request .
边栏推荐
- 基于HPC场景的集群任务调度系统LSF/SGE/Slurm/PBS
- 2022.7.6DAY598
- This article explains the complex relationship between MCU, arm, muc, DSP, FPGA and embedded system
- Study summary of postgraduate entrance examination in July
- ORM model -- associated fields, abstract model classes
- 1324:【例6.6】整数区间
- Learning records - high precision addition and multiplication
- PDF文档签名指南
- ISP、IAP、ICP、JTAG、SWD的编程特点
- Inno setup packaging and signing Guide
猜你喜欢
AHB bus in stm32_ Apb2 bus_ Apb1 bus what are these
Serial communication relay Modbus communication host computer debugging software tool project development case

柏拉图和他的三个弟子的故事:如何寻找幸福?如何寻找理想伴侣?
How to cancel automatic saving of changes in sqlyog database
【二开】【JeecgBoot】修改分页参数
This article explains the complex relationship between MCU, arm, muc, DSP, FPGA and embedded system
![[sword finger offer] 42 Stack push in and pop-up sequence](/img/f4/eb69981163683c5b36f17992a87b3e.png)
[sword finger offer] 42 Stack push in and pop-up sequence

STM32中AHB总线_APB2总线_APB1总线这些是什么
基于gis三维可视化技术的智慧城市建设
XML configuration file parsing and modeling
随机推荐
Chris LATTNER, the father of llvm: why should we rebuild AI infrastructure software
BigDecimal数值比较
A small problem of bit field and symbol expansion
Slurm资源管理与作业调度系统安装配置
Guid主键
P1223 排队接水/1319:【例6.1】排队接水
柏拉图和他的三个弟子的故事:如何寻找幸福?如何寻找理想伴侣?
OpenGL glLightfv 函数的应用以及光源的相关知识
Adb 实用命令(网络包、日志、调优相关)
Inno setup packaging and signing Guide
555电路详解
Study summary of postgraduate entrance examination in September
Trajectory planning for multi-robot systems: Methods and applications 综述阅读笔记
Programming features of ISP, IAP, ICP, JTAG and SWD
PDF文档签名指南
Encrypt and decrypt stored procedures (SQL 2008/sql 2012)
Learning records - high precision addition and multiplication
table宽度比tbody宽度大4px
Talking about the return format in the log, encapsulation format handling, exception handling
1324:【例6.6】整数区间