当前位置:网站首页>Map collection
Map collection
2022-06-30 12:08:00 【Timely】
Catalog
One 、 characteristic
disorder , Key value pair , Bonds cannot be repeated , Values can be repeated , Key repetition covers , No inheritance Collection Interface
Two 、 Capacity expansion
Capacity expansion : Initial capacity 16, Load factor 0.75, Expansion increment 1 times
3、 ... and 、 Traverse
Prepare the data
private Map<String, Object>map=new HashMap<String, Object>();
@Before
public void setup() {
map.put("1", " mouse ");
map.put("1", " The computer ");
map.put("2", " Fan ");
map.put("3", " a bag ");
map.put("4", " speech ");
map.putIfAbsent("1", "aaa");// If missing, add
}
* Get all the keys first Set aggregate , Re traversal ( Get value by key )
@Test
public void test01() {
Iterator<String>it=map.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String key = it.next();
System.out.println(map.get(key));
}
}
The renderings are as follows :

* Take out and save all Entry Of Set, Then traverse this Set that will do
@Test
public void test02() {
Iterator<Entry<String, Object>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Entry e=it.next();
System.out.println("key = "+ e.getKey() +" value ="+ e.getValue());
}
}The renderings are as follows :

Four 、 Realization
HashMap
HashMap The thread of is not safe , But most commonly used , Fast . The internal array is used to store data .
First, let's understand Execution process
When we went to map Inside put Element time , We will first check whether the array exists . If it doesn't exist , A default length of 16 Array of . The array does not store elements directly , But through a series of operations , By giving key Get key Position in the array , This array is called a bucket ( Calculate the number of buckets the node is in ). The element pointed to by the bucket in the figure is Node node (Node the truth is that Entry<k,v>). Each time an element is added, it is calculated , If there is no element , A node will be declared to be put in , If the stored elements are the same, they will be overwritten , conversely , Will be added down through the linked list ( New element above , The original element goes down ).
How to get value ? Let's calculate first , adopt key Find the bucket where the element is located , If it is a linked list , Then you can find the elements by traversing the linked list .

When there are many elements , The above method needs to traverse all the time , There are shortcomings . Use binary tree to search , Iterate through the conditions of the element , You don't need to traverse the linked list .

Let's take a look at the structure The basic principle
First of all to Map Inside put value , If found to be empty , Generate a new empty , According to key Of hush Value calculates the corresponding subscript in the array . If there is no value in the array, a new node is generated , If it is worth it, judge the generated node , If more than 8, Convert to red black tree to save node information , No more than 8 Save the information to the linked list .

Be careful : The green part in the flow chart is JDK8 New processing logic , Aimed at Table[i] Medium Node The number of nodes is greater than 8 when , Improve search speed through red and black trees .
HashTable
HashTable Thread safe but not commonly used
public void test03() {
Map<Integer, Object>table=new Hashtable<Integer, Object>();
table.put(1, " Zhang San ");
table.put(2, " Li Si ");
table.put(3, " Wang Wu ");
table.put(4, " Lao Liu ");
Iterator<Integer> it = table.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key=it.next();
System.out.println(table.get(key));
}
}ConcurrentHashMap
Thread safety , Than HashTable High performance
public void test04() {
Map<Integer, Object>cmap=new ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Object>();
cmap.put(1, " Zhang San ");
cmap.put(2, " Li Si ");
cmap.put(3, " Wang Wu ");
cmap.put(4, " Lao Liu ");
Iterator<Integer> it = cmap.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key=it.next();
System.out.println(cmap.get(key));
}
}TreeMap
key Values are sorted in a certain order , The performance is better when adding or getting elements HashMap slow , This is because the internal red black tree needs to be maintained , Used to guarantee key Order of values .
public void test05() {
Map<Integer, Object>tmap=new TreeMap<Integer, Object>();
tmap.put(1, " Zhang San ");
tmap.put(2, " Li Si ");
tmap.put(3, " Wang Wu ");
tmap.put(4, " Lao Liu ");
Iterator<Integer> it = tmap.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key=it.next();
System.out.println(tmap.get(key));
}
}key The default value is ascending , If you want to sort in descending order, you can use a comparator ( use key Compare )
public void test05() {
Map<Integer, Object>tmap=new TreeMap<Integer, Object>(new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
return o2-o1;
}
});
tmap.put(1, " Zhang San ");
tmap.put(2, " Li Si ");
tmap.put(3, " Wang Wu ");
tmap.put(4, " Lao Liu ");
Iterator<Integer> it = tmap.keySet().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
int key=it.next();
System.out.println(tmap.get(key));
}
}The renderings are as follows :

LinkedHashMap
Inherit HashMap,LinkedHashMap Is ordered , And the default is the insertion order , When we want to store in order key-value when , You need to use LinkedHashMap 了
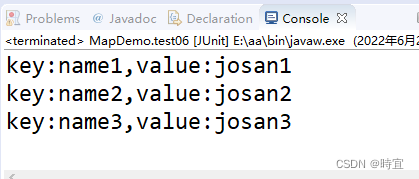
public void test06() {
Map<String, String> linkedHashMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
linkedHashMap.put("name1", "josan1");
linkedHashMap.put("name2", "josan2");
linkedHashMap.put("name3", "josan3");
Set<Entry<String, String>> set = linkedHashMap.entrySet();
Iterator<Entry<String, String>> iterator = set.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Entry entry = iterator.next();
String key = (String) entry.getKey();
String value = (String) entry.getValue();
System.out.println("key:" + key + ",value:" + value);
}
}The effect is as follows :
边栏推荐
- Object mapping - mapping Mapster
- [pattern recognition]
- 网络营销之四大误解
- 1020. 飞地的数量
- go-zero微服务实战系列(八、如何处理每秒上万次的下单请求)
- Paper interpretation (AGC) attributed graph clustering via adaptive graph revolution
- OpenMLDB Meetup No.4 会议纪要
- R语言ggplot2可视化:gganimate包基于transition_time函数创建动态散点图动画(gif)
- Biological network analysis using deep learning
- 【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】深入了解Deployment(八)
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
Installing onnx is very slow. Use Tsinghua image
How can c write an SQL parser
【模式识别大作业】
Object mapping - mapping Mapster
Lucene full text search toolkit learning notes summary
Shutter 007 input field from zero
移除无效的括号[用数组模拟栈]
R language ggplot2 visualization: use ggplot2 to visualize the scatter diagram and use scale_ color_ viridis_ D function specifies the color scheme of data points
NoSQL——Redis的配置与优化
【云原生 | Kubernetes篇】深入了解Deployment(八)
论文解读(AGC)《Attributed Graph Clustering via Adaptive Graph Convolution》
【LeetCode】15、三数之和
Embedded sig | multi OS hybrid deployment framework
治数如治水,数据治理和数据创新难在哪?
Analysis of KOA - onion model
200. number of islands
WebView, Scrollview sliding conflict correction
Beego development blog system learning (II)
Flutter 从零开始 007 输入框
695.最大岛屿面积









