当前位置:网站首页>专业课-代码题记录
专业课-代码题记录
2022-06-26 06:48:00 【作用太大了销夜】
目录
将一个正整数分解质因数 讲义P25
示例:
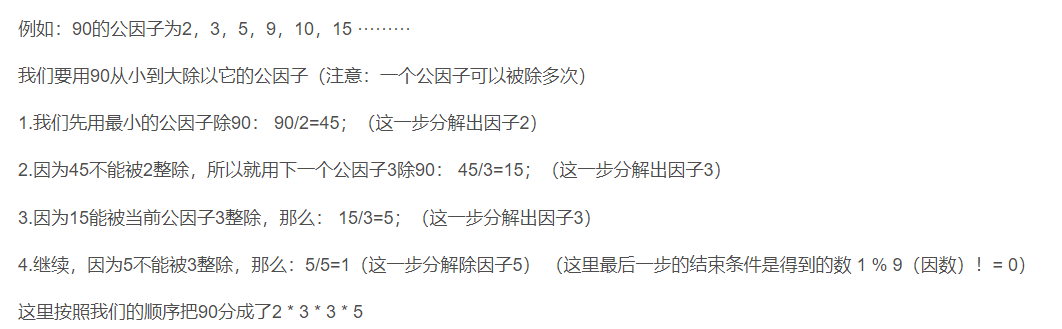

int main()
{
int i, n;
cout << "请输入一个数:";
cin >> n;
cout << n << " = ";
//为什么需要i++?比i小的数难道不能是新的n的质因子吗?
//答案是不会,因为如果比i小的数如果是n的质因子,那早就已经被分解掉了
//实际上在这个算法中,被分解的质因子是从小到大递增的
for (i = 2; i < n; i++)
{
while (n != i) //若n == i,则n的质因数就是n本身
{
//这里不需要判断i是否为质数,因为根据这个算法的特性,在遇到i之前,n中关于i的因数都已经被分解掉了,
//在遇到6之前必定已经将这个6分解为了2*33,在遇到9之前必定已经将9分解为了3*3
//因此这里的i一定是个质数
if (n % i == 0) //若i是质因数,则打印i
{
cout << i << " * ";
n = n / i;
}
else break; //若不能被i整除,则考虑i + 1
}
}
cout << n; //打印最后一个质因数,也就是当n == i时的质因数
return 0;
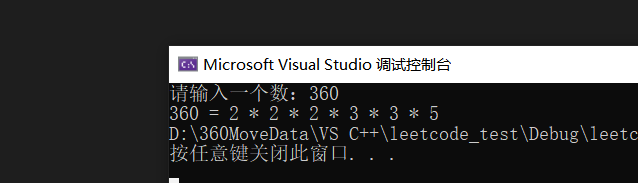
}打印如下:

辗转相除法 讲义P30
非递归写法:
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
int r;
while (b != 0)
{
r = a % b;
a = b;
b = r;
}
return a;
}更为简便的递归写法:
int gcd(int a, int b)
{
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}给出年月日,计算该日是该年的第几天 讲义P32
按讲义上的写法来的,主要是在于数据的健壮性判断十分繁琐
/*
非整百年:能被4整除的为闰年。
整百年:能被400整除的是闰年。
*/
int is_leapyear(int year)
{
if (year % 400 == 0 || year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0)
{
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
//判断该日是今年的第几天
int whichday(int year, int month, int day)
{
int mon[13] = { 0, 31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31 };
mon[2] = is_leapyear(year); //如果是闰年,二月份就加1天
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < month; i++)
{
count += mon[i];
}
count += day;
return count;
}
int main()
{
int year, month, day;
cout << "请输入年份" << endl;
while (1)
{
cin >> year;
if (year < 0)
{
cout << "月份必须非负,请重新输入" << endl;
continue;
}
break;
}
cout << "请输入月份" << endl;
while (1)
{
cin >> month;
if (month < 1 || month > 12)
{
cout << "月份必须在1到12之间" << endl;
continue;
}
break;
}
cout << "请输入天数" << endl;
while (1)
{
cin >> day;
if (day < 1)
{
cout << "天数不能小于1" << endl;
continue;
}
if (month == 1 || month == 3 || month == 5 || month == 7 || month == 8 || month == 10 || month == 12)
{
if (day > 31)
{
cout << "您输入的天数大于" << month << "月的最大天数" << endl;
continue;
}
}
else if (month == 2)
{
if (is_leapyear(year) == 1 && day > 29) //如果是闰年的话
{
cout << "您输入的天数大于" << month << "月的最大天数" << endl;
continue;
}
else if (is_leapyear(year) == 0 && day > 28) //如果不是闰年的话
{
cout << "您输入的天数大于" << month << "月的最大天数" << endl;
continue;
}
}
else
{
if (day > 30)
{
cout << "您输入的天数大于" << month << "月的最大天数" << endl;
continue;
}
}
break;
}
printf("%d年%d月%d日是该年的第%d天", year, month, day, whichday(year, month, day));
return 0;
}
进制转换讲解 讲义P56
打印集合M的前面100个最小数 讲义P59

讲义上的代码写得不好,于是在网上搜到了这一种很有意思的写法,该写法采用了归并排序的思想:
该题的难点在于很难确定最小的n个数到底是哪n个数,现在我们假设可以将int型的y和z看成两个"数组",y记录的是 2 * a[0] + 1、 2 * a[1] + 1、 2 * a[2] + 1....,z记录的是 3 * a[0] + 1、 3 * a[1] + 1、 3 * a[2] + 1....,只要a是个递增数组,y和z也都是递增"数组",之后就可以利用归并排序的思想,每次对比y和z的大小,选取较小值入a数组,然后更新y或z的值。
int main()
{
int a[100];
a[0] = 1;
int i = 0, j = 0; //i为y"数组"的指针,j为z"数组"的指针
int y = 3, z = 4; //y"数组"的首元素为2 * a[0] + 1 = 3,z"数组"的首元素为3 * a[0] + 1 = 4
//类似归并排序
for (int k = 0; k < 100; k++)
{
if (y < z)
{
a[k] = y;
y = 2 * a[i] + 1; //y"数组"移动到下一个元素
i++;
}
else if (y == z) //由于集合的互异性,所以当出现两边的值相等时只取一个,两边的"数组"都移动
{
a[k] = y;
y = 2 * a[i] + 1;
i++;
z = 3 * a[j] + 1;
j++;
}
else
{
a[k] = z;
z = 3 * a[j] + 1; //z"数组"移动到下一个元素
j++;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
if (i % 10 == 0) cout << endl;
printf("%4d ", a[i]);
}
return 0;
}打印结果如下:

输入正整数n,打印集合的所有子集 讲义P61
居然用到了位运算,是我掌握较为薄弱的一个方法。
对于数字0 ~ n-1而言,在一个子集每个数字有两种状态:存在和不存在,于是所有状态的组合就是所有的子集了,并且可知输入的正整数为n,子集的个数共有2 ^ n个。
根据上述,我们可以采用二进制数来代表所有的子集,1表示存在,0表示不存在。
例如输入3,则子集的总数为2^3 = 8个,集合为{0, 1, 2}。而二进制数也有8个,例如 001对应子集{2},010对应子集{1},011对应子集{1, 2}。
void powerset(int n)
{
int m = pow(2, n); //共有2^n种子集,对应2^n个二进制数
int* subset = new int[n]; //记录子集
int len; //记录每次生成的子集的长度
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) //大循环,遍历2^个二进制数,确定2^n种子集
{
len = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) //遍历数字0 ~ n-1,检查每个数字是否存在于当前子集中
{
int tmp = 1 << j; //将1左移j位,用tmp来检查第j个数字是否存在于当前子集中
if (i & tmp)
{
subset[len++] = j; //若存在则记录
}
}
cout << "{";
for (int j = 0; j < len; j++)
{
cout << subset[j];
if (j < len - 1) cout << ", ";
}
cout << "}" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
powerset(n);
return 0;
}输出如下:

求所有元素个数为M的子集 讲义P67
这道题用讲义上的位运算写法有点麻烦,可以直接用dfs来写。这里我直接让原集合中的元素都是1 ~ N - 1了。
int subset[100];
//N是集合中的元素个数,M表示要求元素个数为M的子集
//cur数组用于保存当前子集中的元素,len为cur数组中当前的元素个数
//index表示当前循环需要从下标为index的元素开始遍历
//每调用一次dfs函数,会确定当前子集中len位置的元素
void dfs(int cur[], int len, int M, int index, int N)
{
//如果当前子集中的元素个数为M,打印
if (len == M)
{
cout << "{";
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++)
{
cout << cur[i];
if (i < len - 1) cout << ", ";
}
cout << "}" << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < N; i++)
{
cur[len] = subset[i];
dfs(cur, len + 1, M, i + 1, N);
}
}
int main()
{
int N, M;
cin >> N >> M;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
subset[i] = i + 1;
}
int cur[100];
dfs(cur, 0, M, 0, N);
return 0;
}输出如下:

关于dfs函数中的遍历我原先写的是这样:
for (int i = index; i < N; i++)
{
//选取
cur[len] = subset[i];
dfs(cur, len + 1, M, i + 1, N);
//不选取
dfs(cur, len, M, i + 1, N);
}对于cur[i],分为选取和不选取两种情况,但是这样会导致相同的子集重复打印,例如集合{1,2,3},如果按照上面这种写法,会重复打印子集{2,3}两次。
而下面这种正确的这种写法,其作用可以理解为每次调用dfs函数时,确定子集中len位置的元素,即每次确定cur[len]的值,这样一来可以保证在位置0~M - 1上,每个位置的元素不会重复出现
for (int i = index; i < N; i++)
{
cur[len] = subset[i];
dfs(cur, len + 1, M, i + 1, N);
}实现任意两个不同进制非负整数之间的转换 讲义P68
这道题要求能够输入多组测试数据,先了解一下c++中如何输入多组数据:
int a;
string s;
while (cin >> a >> s)
{
cout << a << " " << s << endl;
}利用while循环和cin即可,只要输入的a是int型、s是string型,就能够不断循环、不断输入下去。但是如果输入的a不是int型,或者输入的s不是string型,while循环就会中断。
回到该题,实现代码如下:
int main()
{
int a, b;
string n;
//多组的测试数据,将a进制的整数n转换为b进制
while (cin >> a >> n >> b)
{
cout << a << "进制:" << n << endl;
int ten = 0; //存储10进制数
//先将a进制转换为10进制
for (int i = 0; i <= n.size() - 1; i++)
{
int x = 0; //记录该位数字
if ('0' <= n[i] && n[i] <= '9')
{
x = n[i] - '0';
}
else if ('a' <= n[i] && n[i] <= 'z')
{
x = n[i] - 'a' + 10;
}
else if ('A' <= n[i] && n[i] <= 'Z')
{
x = n[i] - 'A' + 10;
}
ten = ten * a + x; //这个地方就类似于10进制中的ten * 10 + x
}
cout << "10进制:" << ten << endl;
//再将10进制转换为b进制
string ans;
while (ten > 0)
{
char ch;
int x = ten % b; //记录该位数字
ch = x < 10 ? x + '0' : x - 10 + 'A';
ans = ch + ans;
ten /= b;
}
cout << b << "进制:" << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}结果如下:

与网站上所给的结果相同:

交换两个向量的位置 讲义P80
边栏推荐
- Experience the new features of Milvus 2.0 together
- Container with the most water
- JS download pictures
- Spark3.3.0 source code compilation supplement - Crazy certificate problem
- Decision tree learning notes
- Analyse d'un problème classique
- 【图像分割】基于最大主曲率实现视网膜眼底图像中的血管提取附matlab代码
- STM 32 uses cube to generate Tim to trigger ADC and transmit through DMA
- SecureCRT运行SparkShell 删除键出现乱码的解法
- [micro service series] protocol buffer dynamic analysis
猜你喜欢
Pytorch uses multi GPU parallel training and its principle and precautions

【yolov4】基于yolov4深度学习网络目标检测MATLAB仿真

浅析一道经典题

海量日志采集工具——Flume
New generation engineers teach you how to play with alluxio + ml (Part 1)

寶塔服務器搭建及數據庫遠程連接
Alarm operation and Maintenance Center | build an efficient and accurate alarm collaborative processing system

【golang】time相关

On a classical problem

Kotlin compose state recovery remembersaveable and remember
随机推荐
屏幕共享推荐
遇到女司机业余开滴滴,日入500!
[digital signal processing] basic sequence (unit step sequence | relationship between unit step sequence and unit pulse sequence | rectangular sequence | relationship between rectangular sequence and
Vulnerability discovery - API interface service vulnerability probe type utilization and repair
Differences, advantages and disadvantages between synchronous communication and asynchronous communication
PyTorch搭建CNN-LSTM混合模型实现多变量多步长时间序列预测(负荷预测)
寶塔服務器搭建及數據庫遠程連接
Top down transformation method
Research Report on market development prospect and investment strategy of China's water soluble film industry 2022-2027
Get the first and last days of the current month, and the first and last days of the previous month
SHOW语句用法补充
Customer Stories | Netease spring breeze: the "spring breeze" of the fun industry, reaching out to all areas through in-depth interaction
Pytorch uses multi GPU parallel training and its principle and precautions
What is deadlock
Web technology sharing | webrtc recording video stream
Go学习笔记1.3-变量的数据类型篇
浏览器的四大内核:Trident,Gecko,Webkit,Blink
同步通信和异步通信的区别以及优缺点
SparseArray
Requirement analysis of personal blog system

