当前位置:网站首页>多边形等分
多边形等分
2022-08-05 05:16:00 【staHuri】
多边形等分思路
前提条件
- 封闭面,不可以有空洞
解题思路
- 封闭面中随机构造点
- 利用 k-means 分组(在此方法中设置分组数量 簇数)
- 计算每一个簇的质心
- 利用质心绘制 voronoi 泰森多边形
- 利用封闭面切割泰森多边形
注
本文中判断点是否在面中利用了 这篇文章
实现
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import shapefile as shp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from scipy.spatial import Voronoi, voronoi_plot_2d
def isPoiWithinPoly(poi, poly):
""" 判断是否在面内 :param poi: [x,y] :param poly: [ [ [x1,y1],[x2,y2],[] ] ] :return: boolean """
sinsc = 0
for epoly in poly:
for i in range(len(epoly) - 1):
s_poi = epoly[i]
e_poi = epoly[i + 1]
if isRayIntersectsSegment(poi, s_poi, e_poi):
sinsc += 1
return True if sinsc % 2 == 1 else False
def isRayIntersectsSegment(poi, s_poi, e_poi):
if s_poi[1] == e_poi[1]:
return False
if s_poi[1] > poi[1] and e_poi[1] > poi[1]:
return False
if s_poi[1] < poi[1] and e_poi[1] < poi[1]:
return False
if s_poi[1] == poi[1] and e_poi[1] > poi[1]:
return False
if e_poi[1] == poi[1] and s_poi[1] > poi[1]:
return False
if s_poi[0] < poi[0] and e_poi[1] < poi[1]:
return False
xseg = e_poi[0] - (e_poi[0] - s_poi[0]) * (e_poi[1] - poi[1]) / (e_poi[1] - s_poi[1]) # 求交
if xseg < poi[0]:
return False
return True
# 开始
sf = shp.Reader("浙江省.shp")
plt.figure()
x = None
y = None
# 将SHP中的图形展示到Plots中
for shape in sf.shapeRecords():
for i in range(len(shape.shape.parts)):
i_start = shape.shape.parts[i]
if i == len(shape.shape.parts) - 1:
i_end = len(shape.shape.points)
else:
i_end = shape.shape.parts[i + 1]
x = [i[0] for i in shape.shape.points[i_start:i_end]]
y = [i[1] for i in shape.shape.points[i_start:i_end]]
plt.plot(x, y)
# 获取当前面的最大最小XY
minX = min(x)
maxX = max(x)
minY = min(y)
maxY = max(y)
# 随机生成一定数量的散点 在这个平面内
# step 总共要多少个点
step = 10000
# count 记录当前点数量
count = 1
point_random = []
for i in range(10000):
rx = random.uniform(minX, maxX)
ry = random.uniform(minY, maxY)
if isPoiWithinPoly([rx, ry], [list(zip(x, y))]) and count < step:
count += 1
point_random.append([rx, ry])
# plt.scatter(rx, ry, s=20, c='aqua', alpha=0.5)
print("当前共有", count, "点")
print("随机点", point_random)
# kmean 簇族 分组量
group_size = 10
clf = KMeans(n_clusters=group_size)
cluster_group = clf.fit_predict(point_random)
# 遍历构造新的随机点 + 分组 [x,y,group_id]
point_kmean = []
# 设置颜色集合
cnames = ['black', 'blue', 'red', 'khaki', 'aliceblue', 'antiquewhite', 'aqua', 'aquamarine', 'azure', 'beige',
'bisque', 'blanchedalmond', 'blueviolet', 'brown', 'burlywood', 'cadetblue', 'chartreuse', 'chocolate',
'coral', 'cornflowerblue', 'cornsilk', 'crimson', 'cyan', 'darkblue', 'darkcyan', 'darkgoldenrod', 'darkgray',
'darkgreen', 'darkkhaki', 'darkmagenta', 'darkolivegreen', 'darkorange', 'darkorchid', 'darkred',
'darksalmon', 'darkseagreen', 'darkslateblue', 'darkslategray', 'darkturquoise', 'darkviolet', 'deeppink',
'deepskyblue', 'dimgray', 'dodgerblue', 'firebrick', 'floralwhite', 'forestgreen', 'fuchsia', 'gainsboro',
'ghostwhite', 'gold', 'goldenrod', 'gray', 'green', 'greenyellow', 'honeydew', 'hotpink', 'indianred',
'indigo', 'ivory', 'khaki', 'lavender', 'lavenderblush', 'lawngreen', 'lemonchiffon', 'lightblue',
'lightcoral', 'lightcyan', 'lightgoldenrodyellow', 'lightgreen', 'lightgray', 'lightpink', 'lightsalmon',
'lightseagreen', 'lightskyblue', 'lightslategray', 'lightsteelblue', 'lightyellow', 'lime', 'limegreen',
'linen', 'magenta', 'maroon', 'mediumaquamarine', 'mediumblue', 'mediumorchid', 'mediumpurple',
'mediumseagreen', 'mediumslateblue', 'mediumspringgreen', 'mediumturquoise', 'mediumvioletred',
'midnightblue', 'mintcream', 'mistyrose', 'moccasin', 'navajowhite', 'navy', 'oldlace', 'olive', 'olivedrab',
'orange', 'orangered', 'orchid', 'palegoldenrod', 'palegreen', 'palevioletred', 'papayawhip', 'peachpuff',
'peru', 'pink', 'plum', 'powderblue', 'purple', 'red', 'rosybrown', 'royalblue', 'saddlebrown', 'salmon',
'sandybrown', 'seagreen', 'seashell', 'sienna', 'silver', 'skyblue', 'slateblue', 'slategray', 'snow',
'springgreen', 'steelblue', 'tan', 'teal', 'thistle', 'tomato', 'turquoise', 'violet', 'wheat', 'white',
'whitesmoke', 'yellow', 'yellowgreen']
for point, gp_id in zip(point_random, cluster_group):
point_kmean.append([point, gp_id])
# 放到 plt 中展示
plt.scatter(point[0], point[1], s=5, c=cnames[gp_id], alpha=1)
# 通过 kmean 质心绘制泰森多边形
cluster_center = clf.cluster_centers_
print("质心")
print(cluster_center)
for i in cluster_center:
plt.scatter(i[0], i[1], s=25, c='green', alpha=1)
# 泰森多边形加载到plot上
points = np.array(cluster_center)
vor = Voronoi(points)
voronoi_plot_2d(vor)
for region in vor.regions:
if not -1 in region:
polygon = [vor.vertices[i] for i in region]
plt.fill(*zip(*polygon))
plt.show()
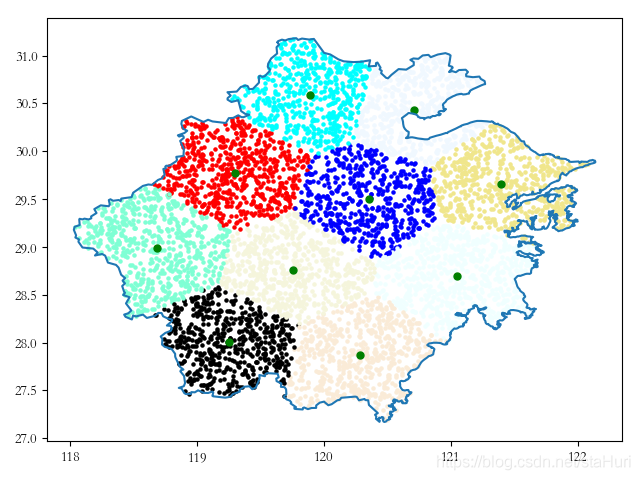
边栏推荐
- 初识机器学习
- 基于Flink CDC实现实时数据采集(二)-Source接口实现
- 【ts】typescript高阶:模版字面量类型
- 基于Flink CDC实现实时数据采集(三)-Function接口实现
- Tensorflow2 与 Pytorch 在张量Tensor基础操作方面的对比整理汇总
- 【Promise高级用法】实现并行和串行API
- SparkML-初探-文本分类
- [Kaggle project actual combat record] Steps and ideas sharing of a picture classification project - taking leaf classification as an example (using Pytorch)
- Oracle压缩表修改字段的处理方法
- 网络信息安全运营方法论 (上)
猜你喜欢
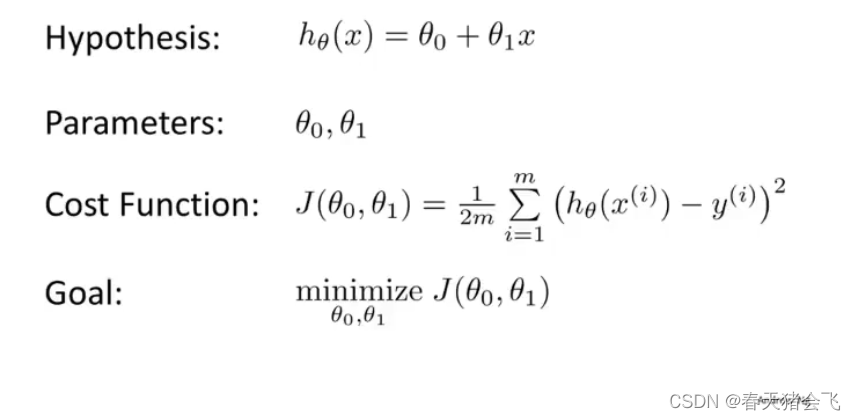
单变量线性回归
Thread handler句柄 IntentServvice handlerThread
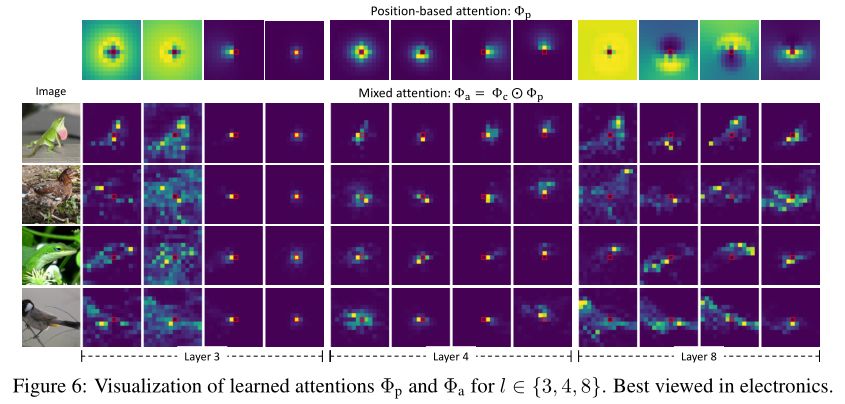
神经网络也能像人类利用外围视觉一样观察图像

MaskDistill - Semantic segmentation without labeled data
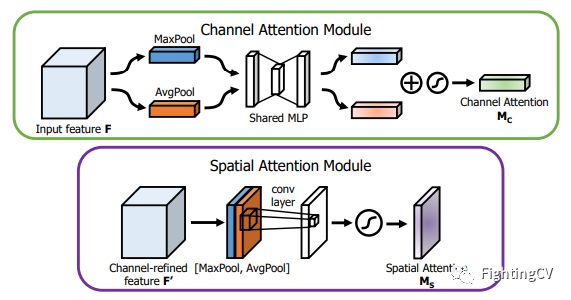
A deep learning code base for Xiaobai, one line of code implements 30+ attention mechanisms.
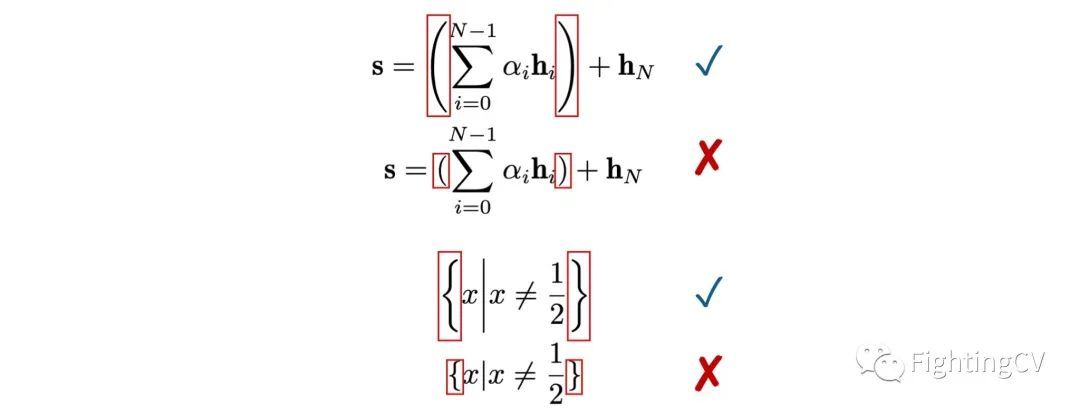
发顶会顶刊论文,你应该这样写作

哥廷根大学提出CLIPSeg,能同时作三个分割任务的模型

IJCAI 2022|边界引导的伪装目标检测模型BGNet
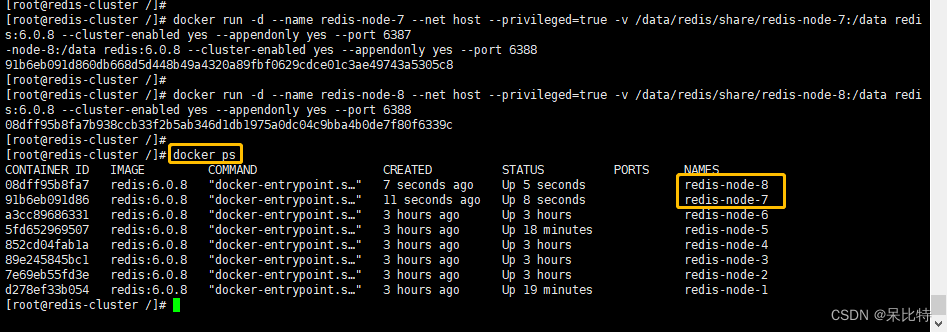
Redis集群(docker版)——从原理到实战超详细
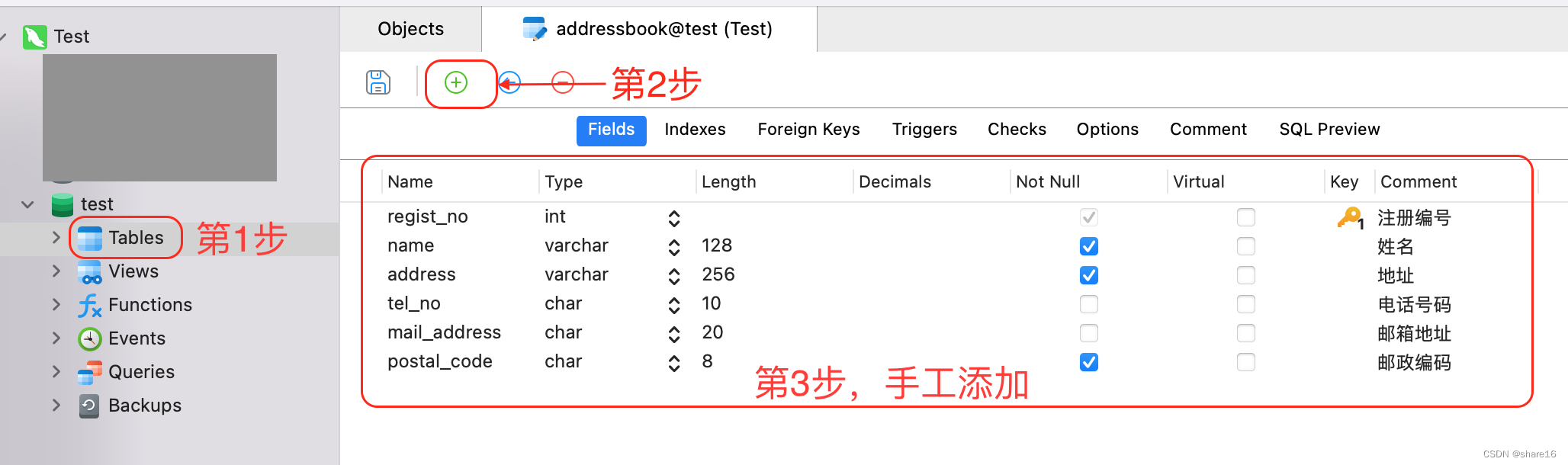
SQL(1) - Add, delete, modify and search
随机推荐
【nodejs】第一章:nodejs架构
OSPF网络类型
【Multisim仿真】直流稳压电源设计报告
[Intensive reading of the paper] R-CNN's Bounding box regression problem is detailed
基于STM32F4的FFT+测频率幅值相位差,波形显示,示波器,时域频域分析相关工程
MSRA proposes extreme masking model ExtreMA for learning instances and distributed visual representations
读论文- pix2pix
【论文精读】ROC和PR曲线的关系(The relationship between Precision-Recall and ROC curves)
初识机器学习
BroadCast Receiver(广播)详解
六步搞定子网划分
C语言联合体union占用空间大小问题
《基于机器视觉的输电线路交叉点在线测量方法及技术方案》论文笔记
Flink Oracle CDC写入到HDFS
Flink和Spark中文乱码问题
AWS 常用服务
【Pytorch学习笔记】11.取Dataset的子集、给Dataset打乱顺序的方法(使用Subset、random_split)
CAN、CAN FD
Detailed explanation of BroadCast Receiver (broadcast)
沁恒MCU从EVT中提取文件建立MounRiver独立工程