当前位置:网站首页>基于OpenGL的冰川与火鸟(光照计算模型、视景体、粒子系统)
基于OpenGL的冰川与火鸟(光照计算模型、视景体、粒子系统)
2022-08-02 18:47:00 【biyezuopinvip】
目录
一、 项目简介 3
- 功能与操作简介 3
- 代码简介 3
- 与课程设计要求的对应 4
二、 场景实现 4 - 冰川 4
- 太阳与时间变化 5
- 天空 6
- 雾效 6
- 风 6
三、 粒子系统 7 - 粒子生成器 7
- 雪 7
- 雨 8
- 火鸟 8
- 火 10
四、 交互控制 10 - 相机 10
- 角色 11
- 其余交互的实现 12
五、 辅助功能 13 - Loader.h 13
- Mesh.h 13
- Shader_m.h 13
六、 外部辅助与库 13 - 核心模式,GLFW与GLAD 13
- GLM 13
- Learn OpenGL 13
- Blender 14
- Stb_image 14
- Mmsystem.h 14
七、项目感想 14
一、项目简介
1.功能与操作简介
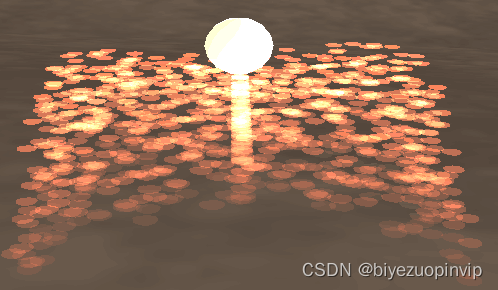
本项目搭建了一个冰川场景。
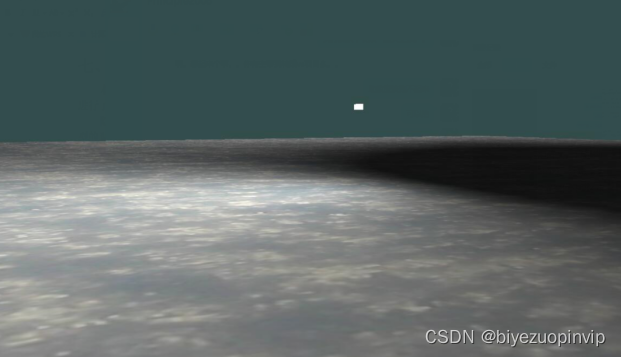
场景中包括冰面、天空。拥有白天、夜晚、黄昏/黎明三个时间段,雨、雪、暴风、雾等天气。
场景中有一只火鸟,以及一些散落在地图上的火焰。火鸟接近蓝色的火焰,可将其引爆,之后火焰变为红色,然后在一段时间后变回蓝色。
使用者可以控制火鸟的移动、视角的转换、时间变化快慢、天气切换等。
使用鼠标控制视角,滚轮放大和缩小。
使用WS控制火鸟沿当前视角方向前进,AD控制火鸟转向。
使用数字键切换天气:
1:晴天
2:雨天
3:无风雪天
4:暴风雪
使用+、-改变时间变化速度
(由于以上均为粘滞键,按键有事需要长按才能生效)
2.代码简介
使用了OpenGL的核心模式,并利用了一些外部的库与代码。与头文件同名的vs文件为模型对应的顶点着色器,fs为片段着色器。
CG.cpp:主函数,包括了创建窗口,创建、绘制场景中的所有物体,控制系统风力,接受用户输入,控制天气等功能。
Camera.h:响应用户鼠标的滚轮和移动事件,转换视角。同时根据绑定的物体的运动状态修改相机的位置与方向。
Character.h:响应用户的键盘WASD输入,改变角色的运动状态。同时控制角色(火鸟)的翅膀挥动、粒子效果等。
Fire.h:控制场景中的火苗的属性。检测与主角的距离,控制火苗爆炸。
Floor.h:创建冰川地形。
Fog.h:控制雾的范围与变化。
Light.h:控制太阳的属性、移动。
Loader.h:读入模型。
Mesh.h:将读入的模型与VAO、VBO绑定,加载纹理。
Particle.h:粒子生成器,根据输入的各种属性生成粒子。
Rain.h / Snow.h:控制雨、雪粒子系统。
Sky.h:控制天空的属性。
Shader_m.h:加载着色器。
Stb_image.h:读入图片作为纹理。
Glad.c:在运行时查找opengl函数的具体位置。
最后三个文件为直接从外部导入,未作修改。此外,还使用了glfw、glm等库(详见“外部辅助与库”)。
3.与课程设计要求的对应
(1)场景建模及渲染,场景添加光照,光照可交互控制(20分,按照场景复杂度、渲染效果等评分)
场景使用blender建模。尝试外部模型导入,但效果不好于是放弃。渲染有太阳与天空的渲染、雾效的渲染等。
场景中太阳、火焰、火鸟均有光照。
光照的交互控制:可控制时间变化快慢、与火焰交互可以改变火焰光照的强度、颜色。
(2)设计实现粒子系统特效,粒子运动有物理仿真,可实时切换粒子系统中的粒子三维模型(30分,按照粒子系统的特效复杂度、计算模型、算法效率等评分)
粒子系统有雨、雪、火焰、火鸟翅膀。
雨、雪、火焰与场景中的风有物理关系,粒子的位置、速度、加速度均使用了物理学规律。
可在控制天气转换的时候,实时切换粒子系统中的粒子三维模型。
(3)粒子的三维模型的光照、纹理映射(20分,按照粒子的视觉外观实现方法的复杂度、实现效果评分)
粒子使用三维模型,雪粒子与场景中光源有光照计算。火粒子考虑到计算效率,在生成器的位置设置了光源营造例子发光的效果。
火粒子、雪粒子均有纹理映射。
(4)设计实现粒子系统的交互控制(20分,根据交互方式的新颖、自然和交互响应评分)
使用者可以控制火鸟的移动、视角的转换、时间变化快慢、天气切换等。
本文来转载自:http://www.biyezuopin.vip/onews.asp?id=16550
#pragma once
#ifndef CAMERA_H
#define CAMERA_H
#include <glad/glad.h>
#include <glm/glm.hpp>
#include <glm/gtc/matrix_transform.hpp>
#include <vector>
// Defines several possible options for camera movement. Used as abstraction to stay away from window-system specific input methods
/*enum Camera_Movement { FORWARD, BACKWARD, LEFT, RIGHT };*/
// Default camera values
const float YAW = -90.0f;
const float PITCH = 0.0f;
//const float SPEED = 2.5f;
const float SENSITIVTY = 0.1f;
const float ZOOM = 45.0f;
// An abstract camera class that processes input and calculates the corresponding Eular Angles, Vectors and Matrices for use in OpenGL
class Camera
{
public:
// Camera Attributes
glm::vec3 Position;
glm::vec3 Front;
glm::vec3 Up;
glm::vec3 Right;
glm::vec3 WorldUp;
// Eular Angles
float Yaw;
float Pitch;
// Camera options
//float MovementSpeed;
float MouseSensitivity;
float Zoom;
// Constructor with vectors
Camera(glm::vec3 position = glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f), glm::vec3 up = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f), float yaw = YAW, float pitch = PITCH) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = position;
WorldUp = up;
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
// Constructor with scalar values
Camera(float posX, float posY, float posZ, float upX, float upY, float upZ, float yaw, float pitch) : Front(glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -1.0f)), MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = glm::vec3(posX, posY, posZ);
WorldUp = glm::vec3(upX, upY, upZ);
Yaw = yaw;
Pitch = pitch;
updateCameraVectors();
}
Camera(Character c) : MouseSensitivity(SENSITIVTY), Zoom(ZOOM)
{
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - c.GetDirection().x * 3.0f,c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - c.GetDirection().z * 3.0f);
WorldUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
Front = glm::normalize(-Position + c.GetPosition() * 3.0f); //dst - src
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp));
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
Yaw = -90.0f;
//std::cout << Yaw;
Pitch = -atan(1.0f / 3.0f) * 180.0f / Pi;
}
// Returns the view matrix calculated using Eular Angles and the LookAt Matrix
glm::mat4 GetViewMatrix()
{
return glm::lookAt(Position, Position + Front, Up);
}
// Processes input received from any keyboard-like input system. Accepts input parameter in the form of camera defined ENUM (to abstract it from windowing systems)
/* void ProcessKeyboard(Camera_Movement direction, float deltaTime) { float velocity = MovementSpeed * deltaTime; if (direction == FORWARD) Position += Front * velocity; if (direction == BACKWARD) Position -= Front * velocity; if (direction == LEFT) Position -= Right * velocity; if (direction == RIGHT) Position += Right * velocity; }*/
// Processes input received from a mouse input system. Expects the offset value in both the x and y direction.
void ProcessMouseMovement(float xoffset, float yoffset, Character c, GLboolean constrainPitch = true)
{
//std::cout << Front.x << std::endl;
xoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
yoffset *= MouseSensitivity;
Yaw += xoffset;
Pitch += yoffset;
// Make sure that when pitch is out of bounds, screen doesn't get flipped
if (constrainPitch)
{
if (Pitch > 89.0f)
Pitch = 89.0f;
if (Pitch < -89.0f)
Pitch = -89.0f;
}
// Update Front, Right and Up Vectors using the updated Eular angles
//Pitch = -atan(2.0f / 1.0f) * 180.0f / Pi;
updateCameraVectors();
float angle = atan(Front.z / Front.x);
if (Front.x < 0) angle -= Pi;
//else if (Direction.x < 0 && cameraDir.x > 0)angle += pi;
float x = cos(angle);
float z = sin(angle);
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - x * 3.0f, c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - z * 3.0f);
}
// Processes input received from a mouse scroll-wheel event. Only requires input on the vertical wheel-axis
void ProcessMouseScroll(float yoffset)
{
if (Zoom >= 1.0f && Zoom <= 45.0f)
Zoom -= yoffset;
if (Zoom <= 1.0f)
Zoom = 1.0f;
if (Zoom >= 45.0f)
Zoom = 45.0f;
}
void MoveCameraByCharacter(Character c) {
//std::cout << c.GetDirection().x*c.GetDirection().x + c.GetDirection().z + c.GetDirection().z << std::endl;
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - c.GetDirection().x * 3.0f, c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - c.GetDirection().z * 3.0f);
//double endAngle = atan((double)c.GetDirection().z / (double)c.GetDirection().x);
//double startAngle = atan((double)Front.z / (double)Front.x);
//std::cout << Xstart << " i " << Ystart << " j " << Xend << " x " << Yend << " y " << std::endl;
//防止180跳变
//if (Front.x > 0 && c.GetDirection().x < 0) endAngle += pi;
//else if (Front.x < 0 && c.GetDirection().x > 0)endAngle += pi;
//Direction = cameraDir;
//Yaw -= endAngle * 180.0f / Pi - startAngle * 180.0f / Pi;
//updateCameraVectors();
//std::cout << Yaw << std::endl;
//Front = c.GetDirection();
//WorldUp = glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);
//Front = glm::normalize(-Position + c.GetPosition()); //dst - src
//Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp));
//Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
//Yaw = 0.0f;
//std::cout << Yaw;
//Pitch = -atan(2.0f / 1.0f) * 180.0f / Pi;
}
void RotateCameraByCharacter(Character c, bool isleft) {
Position = glm::vec3(c.GetPosition().x - c.GetDirection().x * 3.0f, c.GetPosition().y + 1.0f, c.GetPosition().z - c.GetDirection().z * 3.0f);
if(isleft)
Yaw -= c.rotateAcce;
else
Yaw += c.rotateAcce;
updateCameraVectors();
Front = glm::vec3(c.GetDirection().x * sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y), Front.y, c.GetDirection().z * sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y));
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, glm::vec3(0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f))); // Normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
glm::vec3 GetHorizDir() {
return glm::vec3(Front.x* sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y), 0, Front.z* sqrt(1 - Front.y * Front.y));
}
private:
// Calculates the front vector from the Camera's (updated) Eular Angles
void updateCameraVectors()
{
// Calculate the new Front vector
glm::vec3 front;
front.x = cos(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.y = sin(glm::radians(Pitch));
front.z = sin(glm::radians(Yaw)) * cos(glm::radians(Pitch));
Front = glm::normalize(front);
// Also re-calculate the Right and Up vector
Right = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Front, WorldUp)); // Normalize the vectors, because their length gets closer to 0 the more you look up or down which results in slower movement.
Up = glm::normalize(glm::cross(Right, Front));
}
};
#endif




边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

荐号 | 当一个人不联系你,不拉黑你,原因只有一个……!
【C语言刷题】Leetcode203——移除链表元素
How can services start smoothly under tens of millions of QPS
EasyCVR平台通过国标GB28181接入柯达NVR显示注册失败,该如何解决?
动态折线图,制作原来是这么简单
3年半测试经验,20K我都没有,看来是时候跳槽了
What is the use of IT assets management software
ETH Zurich重磅综述 | 人脸-素描合成:一个新的挑战
博云入选 Gartner 中国 DevOps 代表厂商

香农与信息论三大定律
随机推荐
小姐姐面试蚂蚁金服被虐经历,心疼...
浅谈一下pyd文件的逆向
有哪些好用的实时网络流量监控软件
备战无人机配送:互联网派To C、技术派To B
MYSQL关键字执行顺序?
How can services start smoothly under tens of millions of QPS
洛谷P4316 绿豆蛙的归宿
JVM内存和垃圾回收-03.运行时数据区概述及线程
Sentinel vs Hystrix 限流对比,到底怎么选?
Win11dll文件缺失怎么修复?Win11系统dll文件丢失的解决方法
【动态规划专项训练】基础篇
想通过FC连接RDS mysql。是不是将FC服务角色添加rds权限后,就可以通过地址,端口建连了呢
AtomicInteger详解
连续三次 | 灵雀云入选Gartner中国ICT技术成熟度曲线报告
仿制药的未来商机--个人研发的体会
注释
codeforces:E. Add Modulo 10【状态压缩 + 找规律】
互联网寒冬,挚友7面阿里,终获Offer
Why young people are snapping up domestic iPhone, because it is much cheaper and more populist
[论文分享] VideoFlow: A Flow-Based Generative Model for Video