当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree related OJ problems
Binary tree related OJ problems
2022-07-05 16:31:00 【m0_ sixty million six hundred and thirty-one thousand three hun】
Catalog
- 1. Preorder traversal of two tree
- 2. Check whether the two subtrees are the same
- 3. The subtree of another tree
- 4. The maximum depth of a binary tree
- 5. Balanced binary trees
- 6. Symmetric binary tree
- 7. The construction of binary tree is traversal
- 8. Recent public ancestor
- 9. Construct binary tree according to preorder and inorder traversal
- 10. Construct a binary tree according to the middle order and post order traversal
- 11. Binary tree creates a string
- 12. Binary tree preorder non recursive traversal implementation
- 13. Implementation of non recursive traversal of order in binary tree
- 14. Binary tree postorder non recursive traversal implementation
- 15. Binary search tree to bidirectional linked list
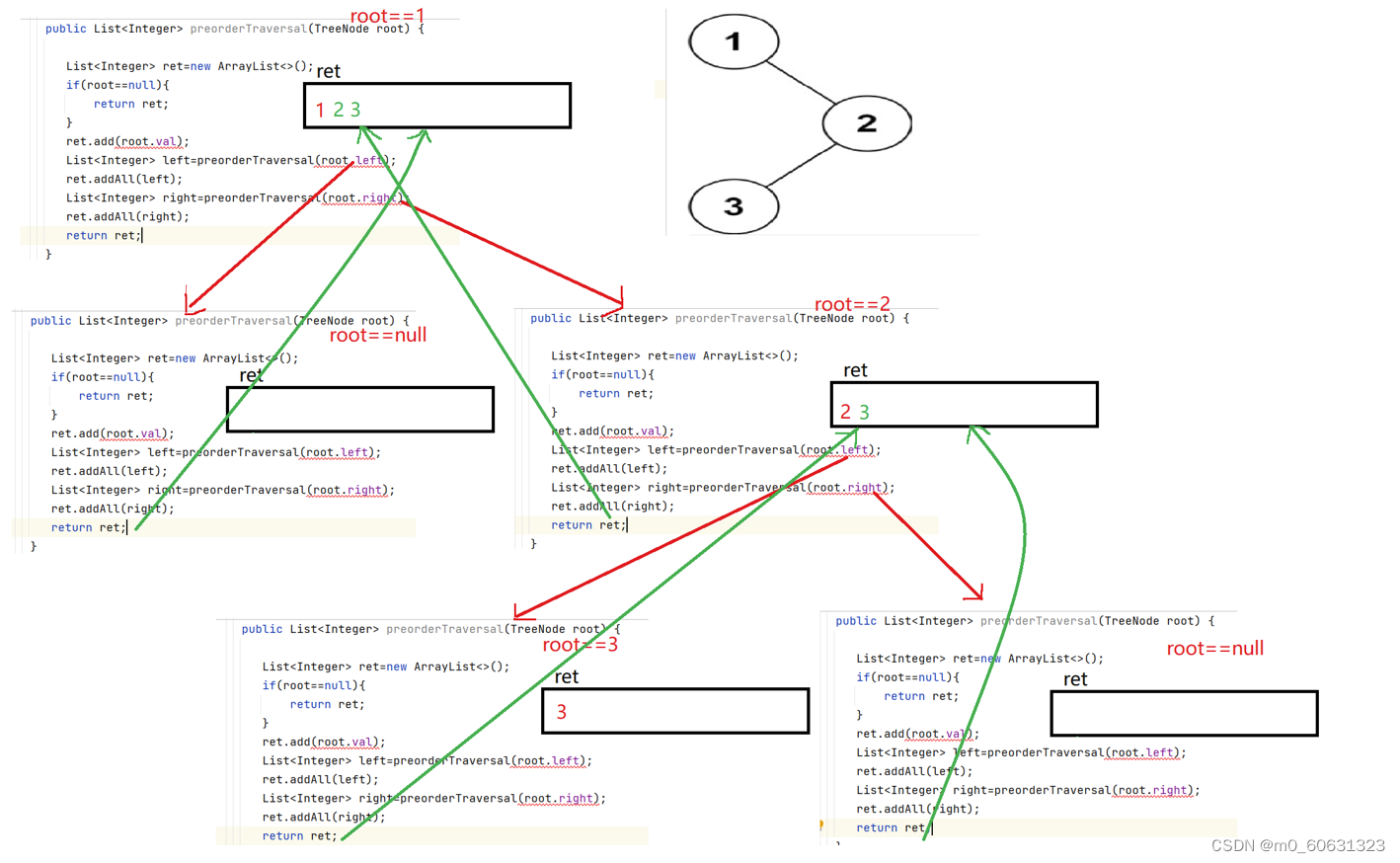
1. Preorder traversal of two tree
Writing a : Sub problem ideas
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null){
return ret;
}
ret.add(root.val);
List<Integer> left=preorderTraversal(root.left);
ret.addAll(left);
List<Integer> right=preorderTraversal(root.right);
ret.addAll(right);
return ret;
}
Write two :
public void process1(List<Integer> list, TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return ;
}
list.add(root.val);
process1(list,root.left);
process1(list,root.right);
}
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new LinkedList<>();
process1(list,root);
return list;
}
2. Check whether the two subtrees are the same
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null){
return true;
}
if(p==null||q==null){
return false;
}
if(p.val==q.val){
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
return false;
}
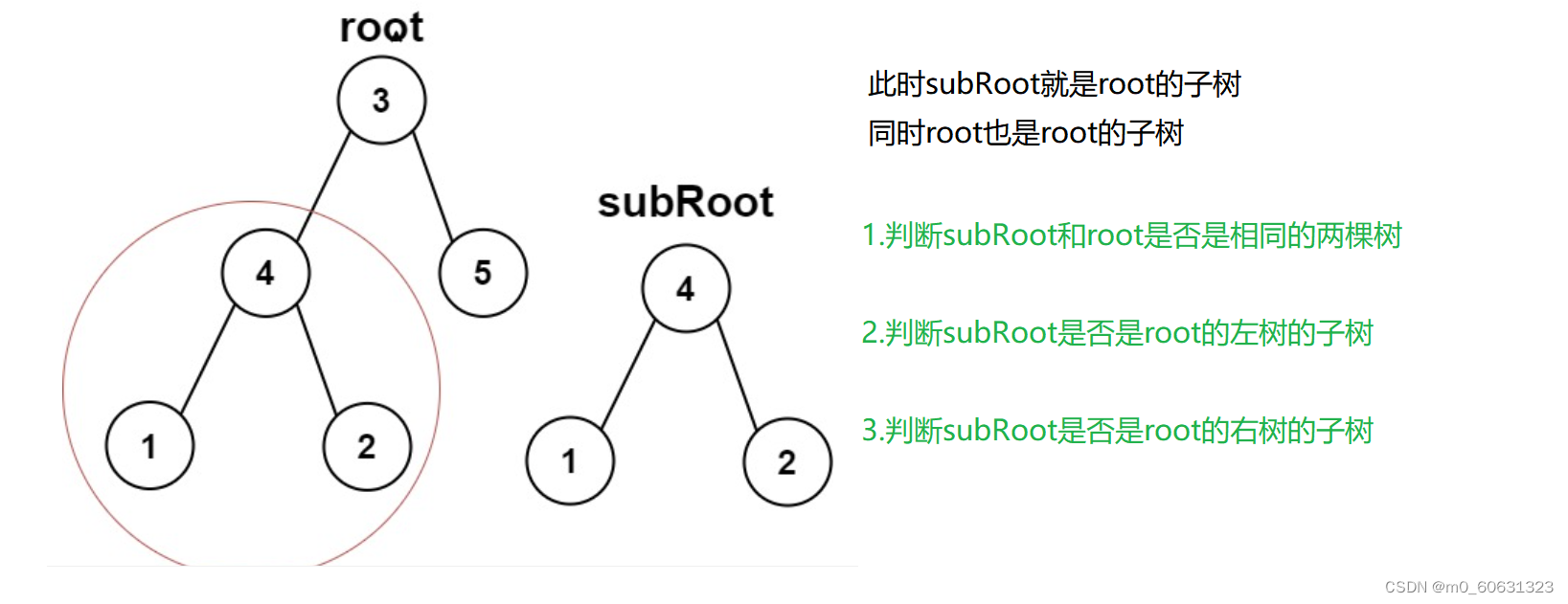
3. The subtree of another tree
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(p==null&&q==null){
return true;
}
if(p==null||q==null){
return false;
}
if(p.val==q.val){
return isSameTree(p.left,q.left) && isSameTree(p.right,q.right);
}
return false;
}
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode root, TreeNode subRoot) {
if(isSameTree(root,subRoot)) return true;
if(root==null) return false;
if(isSubtree(root.left,subRoot)) return true;
if(isSubtree(root.right,subRoot)) return true;
return false;
}
4. The maximum depth of a binary tree
Sub problem ideas :
The maximum depth of a binary tree is equal to : The greater of the maximum depth of the left subtree and the maximum depth of the right subtree plus 1
int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int left=getHeight(root.left);
int right=getHeight(root.right);
return left>right?left+1:right+1;
}
5. Balanced binary trees
5.1 Depth traversal
Traverse each node , See whether the height difference between the left and right subtrees of all nodes is less than or equal to 1
Time complexity O(n^2) Because when finding the height of the left and right subtrees of each node, you have to traverse all nodes of the left and right subtrees
int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int left=getHeight(root.left);
int right=getHeight(root.right);
return left>right?left+1:right+1;
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
int leftH=getHeight(root.left);
int rightH=getHeight(root.right);
return Math.abs(leftH-rightH)<2&&
isBalanced(root.left) &&isBalanced(root.right);
}
5.2 Check the height difference in the process of finding the depth
In the above method, there is a process of repeated calculation , Lead to high time complexity 
int getHeight(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return 0;
}
int left=getHeight(root.left);
int right=getHeight(root.right);
if(left>=0&&right>=0&&Math.abs(left-right)<=1){
return left>right?left+1:right+1;
}else {
return -1;
}
}
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
return getHeight(root)>=0;
}
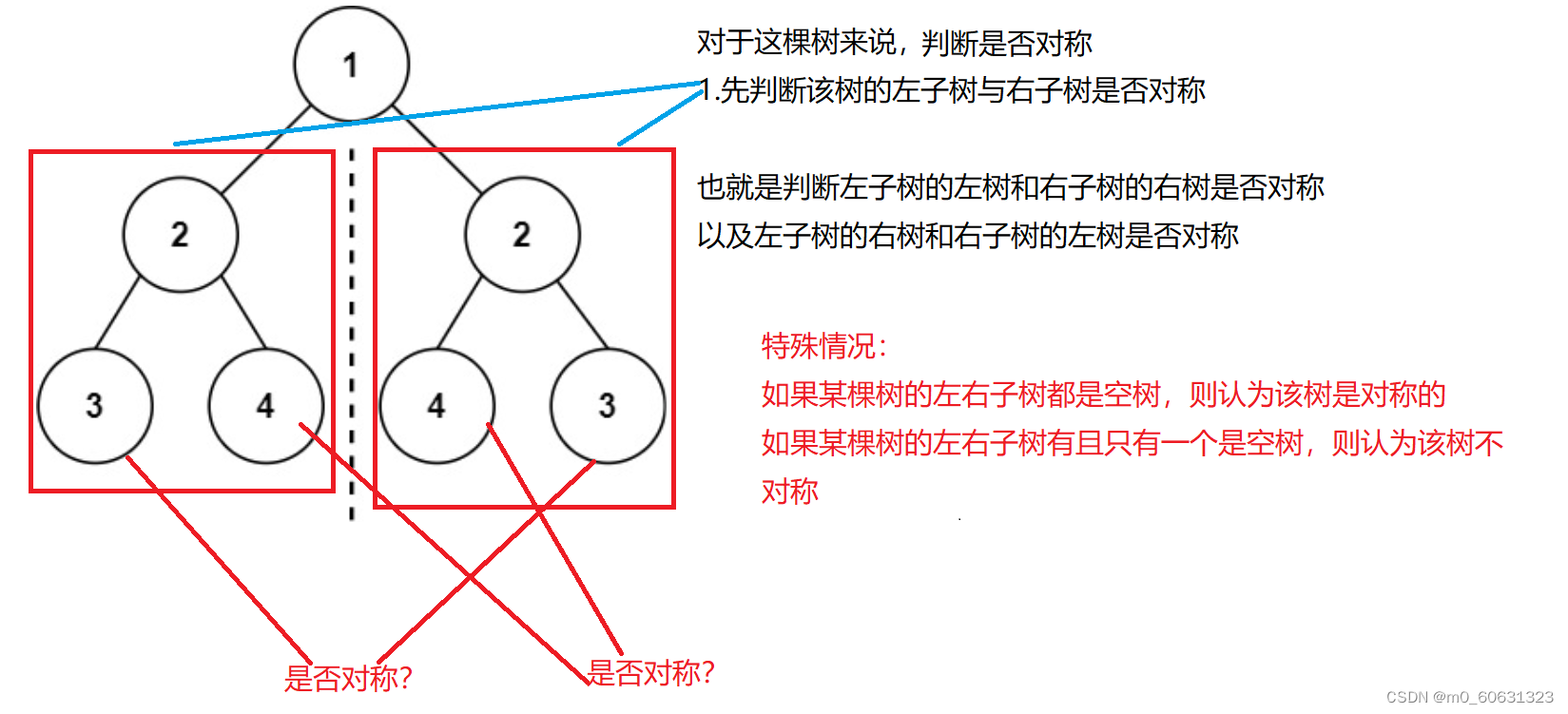
6. Symmetric binary tree
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode left,TreeNode right){
if(left==null&&right==null){
return true;
}
if(left==null||right==null){
return false;
}
if(left.val==right.val){
return isSymmetricChild(left.left,right.right)&&isSymmetricChild(left.right,right.left);
}
return false;
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null) return true;
return isSymmetricChild(root.left,root.right);
}
7. The construction of binary tree is traversal
import java.util.*;
class TreeNode{
char val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
public TreeNode(char val){
this.val=val;
}
}
public class Main {
public static int i=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNextLine()){
String str=scan.nextLine();
TreeNode root=create(str);
inOrder(root);
}
}
public static TreeNode create(String str){
TreeNode root=null;
if(str.charAt(i)!='#'){
root=new TreeNode(str.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left=create(str);
root.right=create(str);
}else {
i++;
}
return root;
}
public static void inOrder(TreeNode root){
if(root==null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val+" ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
}
8. Recent public ancestor
8.1 inspire
If the given tree is a binary search tree , How to find the nearest common ancestor ?
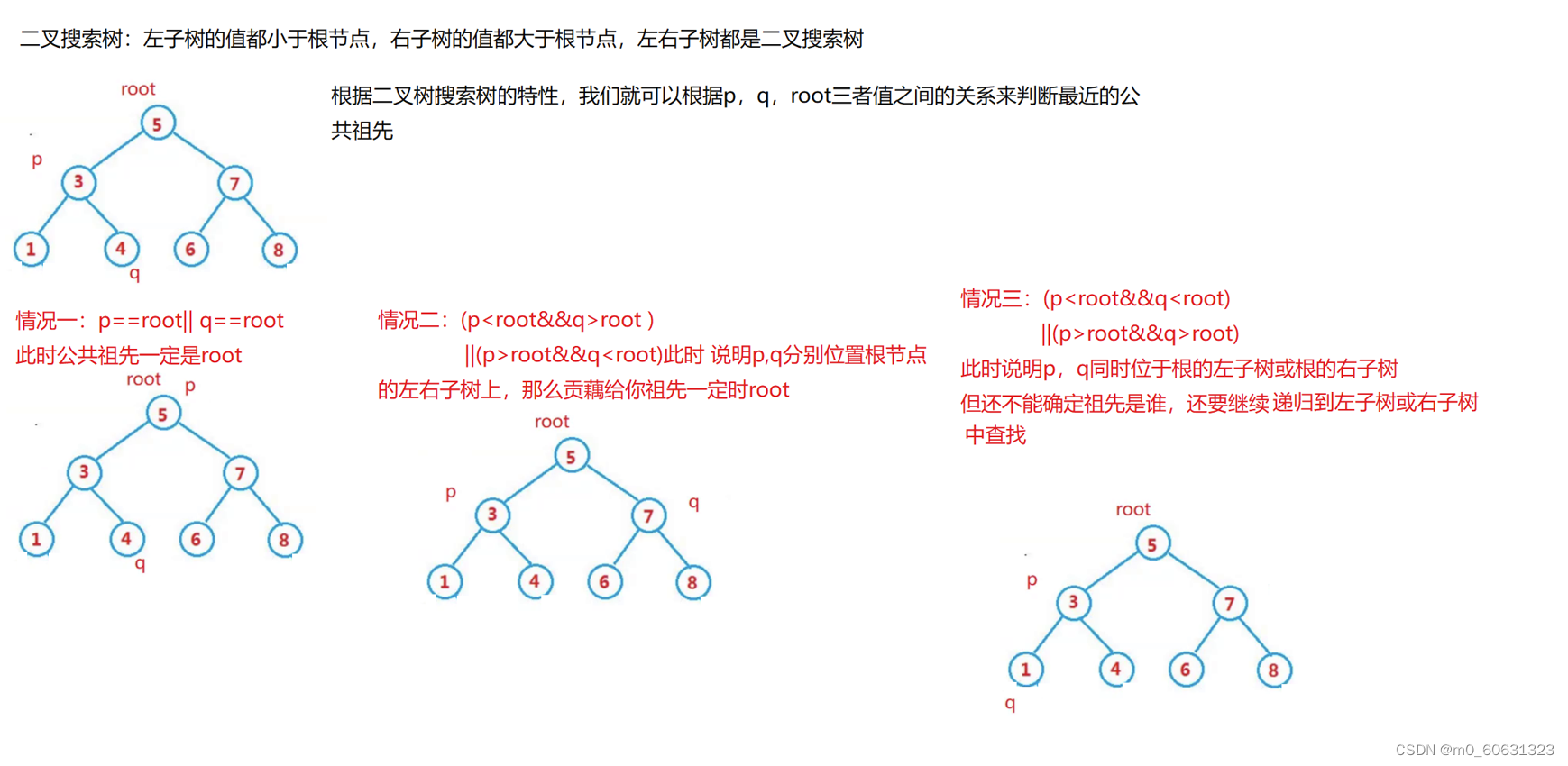
8.2 Method 1 : recursive

public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(root==null){
return null;
}
if(p==root||q==root){
return root;
}
TreeNode leftR=lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q);
TreeNode rightR=lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q);
if(leftR!=null&&rightR!=null){
// Because in the process of recursion, you only encounter p||q==root, Just go back to , If leftR and rightR Not for null, explain p,q It must be on the two subtrees of the root node
return root;
}else if(leftR!=null){
//p,q All in root On the left tree
return leftR;
}else if(rightR!=null){
//p,q All in root On the right tree
return rightR;
}
return null;//p,q Not in order to root On a tree with roots ( During recursion root It will change )
}
8.3 Method 2 : Utilization stack
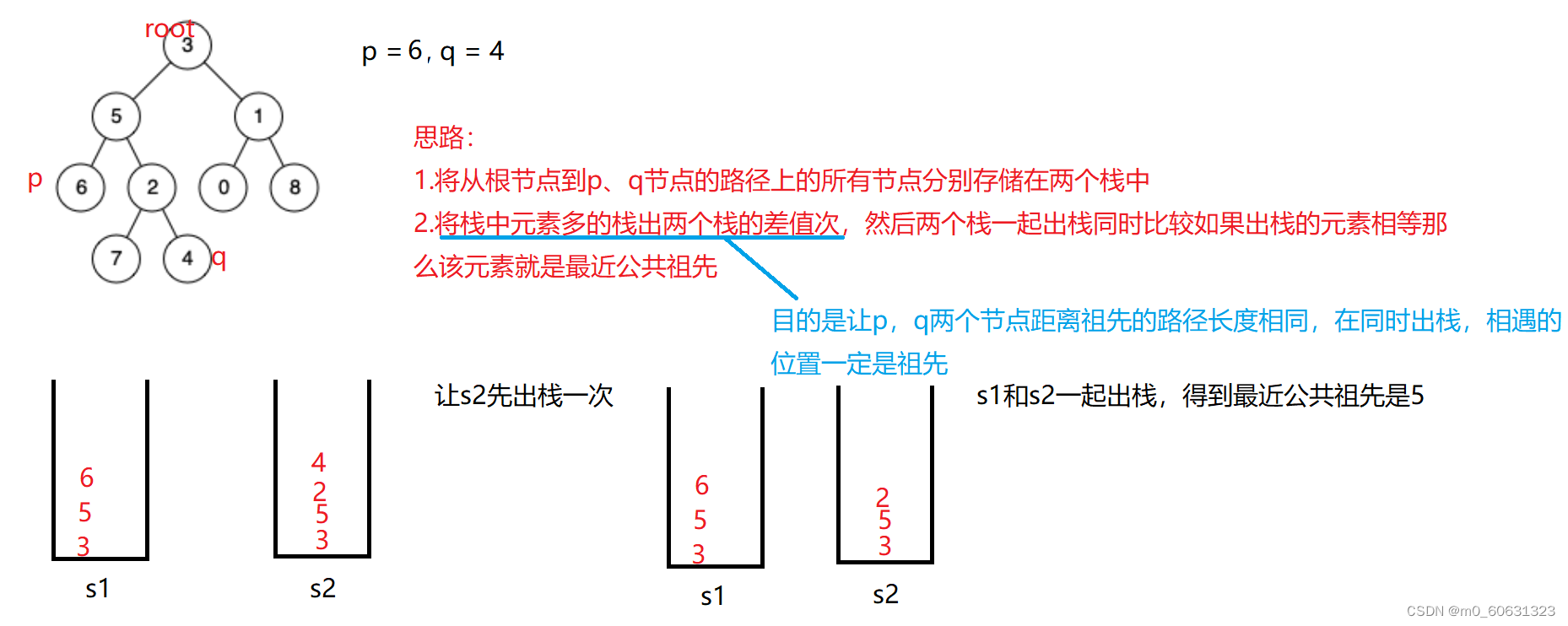
In this way , The most important step is how to move from the root node to p
,q All nodes on the path of are stored in the stack 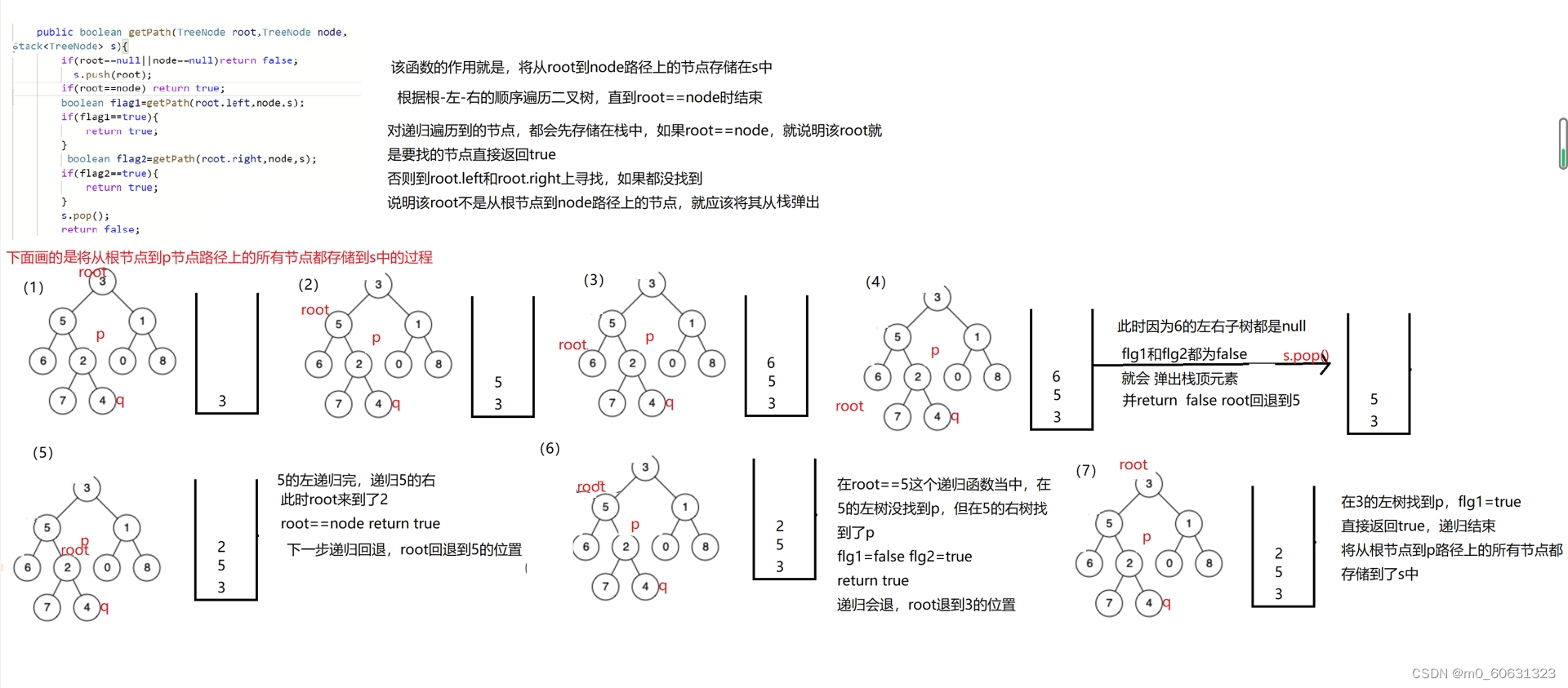
public boolean getPath(TreeNode root,TreeNode node,Stack<TreeNode> s){
if(root==null||node==null)return false;
s.push(root);
if(root==node) return true;
boolean flag1=getPath(root.left,node,s);
if(flag1==true){
return true;
}
boolean flag2=getPath(root.right,node,s);
if(flag2==true){
return true;
}
s.pop();
return false;
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Stack<TreeNode> s1=new Stack<>();
Stack<TreeNode> s2=new Stack<>();
getPath(root,p,s1);
getPath(root,q,s2);
int size1=s1.size();
int size2=s2.size();
if(size1>size2){
int size=size1-size2;
while(size!=0){
s1.pop();
size--;
}
}else {
int size=size2-size1;
while(size!=0){
s2.pop();
size--;
}
}
while(!s1.empty()&&!s2.empty()){
if(s1.peek()==s2.peek()){
return s1.peek();
}else {
s1.pop();
s2.pop();
}
}
return null;
}
9. Construct binary tree according to preorder and inorder traversal
OJ link 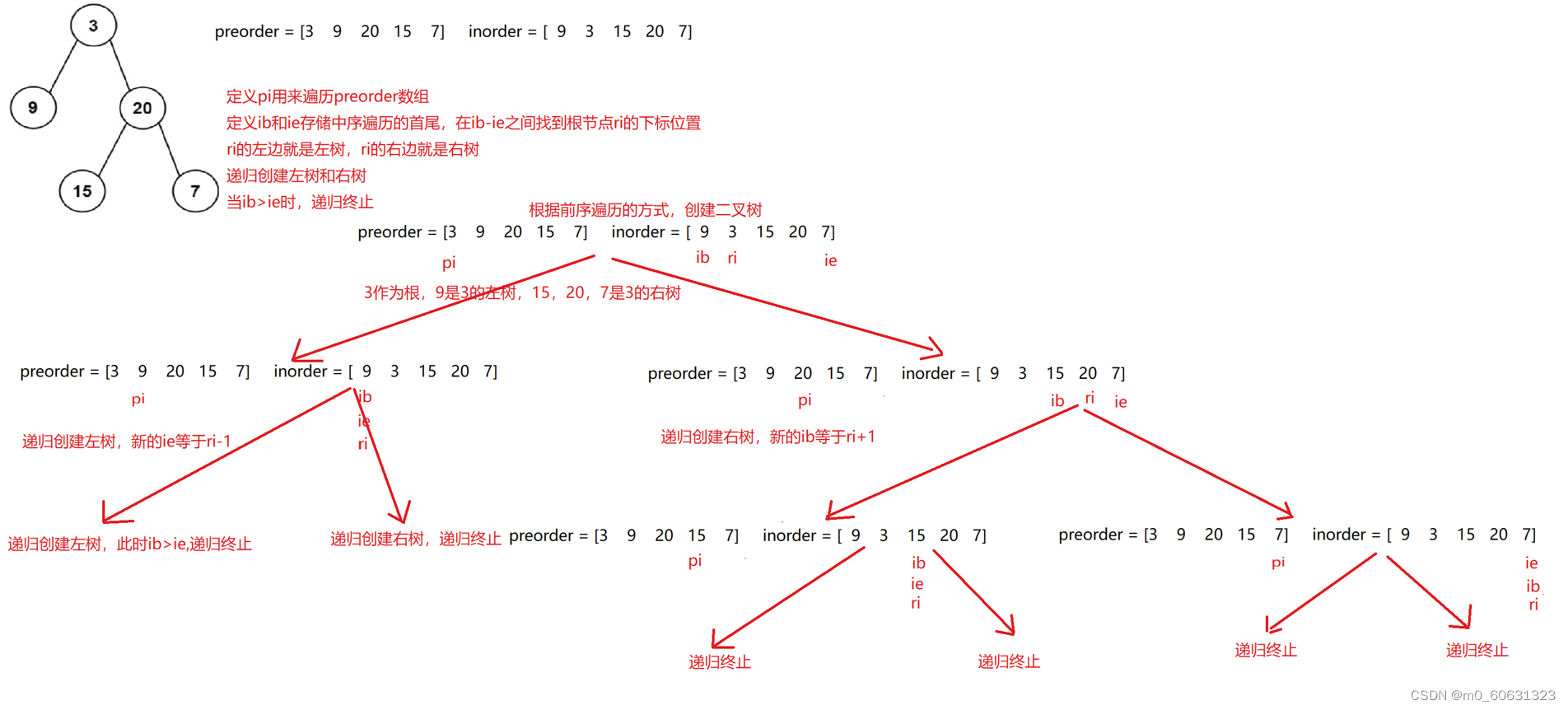
Source code :
int preIndex=0;
private int findInorderRootIndex(int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend,int val){
for(int i=inbegin;i<=inend;i++){
if(inorder[i]==val){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend){
return null; // At this time, there is no left tree or right tree
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
int ri=findInorderRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
preIndex++;
root.left=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,ri-1);
root.right=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,ri+1,inend);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
Be careful :
preIndex To be defined as a global variable , because preIndex The value of is always increasing , If it is defined as a local variable in the process of recursive fallback ,preIndex It will decrease
Optimize : Use HashMap Store the nodes in the middle order traversal and their corresponding subscripts in map in , So I'm looking for ri When subscribing, you don't have to traverse the array in the middle order
int preIndex=0;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
public void RootIndex(int[] inorder){
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
}
public TreeNode buildTreeChild(int[] preorder,int[] inorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend){
return null; // At this time, there is no left tree or right tree
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(preorder[preIndex]);
int ri= map.get(preorder[preIndex]);
// int ri=findInorderRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
preIndex++;
root.left=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,inbegin,ri-1);
root.right=buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,ri+1,inend);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
RootIndex(inorder);
return buildTreeChild(preorder,inorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
10. Construct a binary tree according to the middle order and post order traversal
OJ link
Because it is similar to the previous question , So here is just the difference between the two
difference :
- The order of postorder traversal is left and right roots , So define postIndex, Traverse the array traversed from back to front
- First create the right tree recursively , Then recursively create the left tree
int postIndex=0;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map=new HashMap<>();
public void RootIndex(int[] inorder){
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i],i);
}
}
public TreeNode buildTreeChild1(int[] inorder,int[] postorder,int inbegin,int inend){
if(inbegin>inend){
return null; // At this time, there is no left tree or right tree
}
TreeNode root=new TreeNode(postorder[postIndex]);
int ri= map.get(postorder[postIndex]);
// int ri=findInorderRootIndex(inorder,inbegin,inend,preorder[preIndex]);
postIndex--;
root.right=buildTreeChild1(inorder,postorder,ri+1,inend);
root.left=buildTreeChild1(inorder,postorder,inbegin,ri-1);
return root;
}
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {
RootIndex(inorder);
postIndex=postorder.length-1;
return buildTreeChild1(inorder,postorder,0,inorder.length-1);
}
Be careful :
postIndex To assign a value to a function
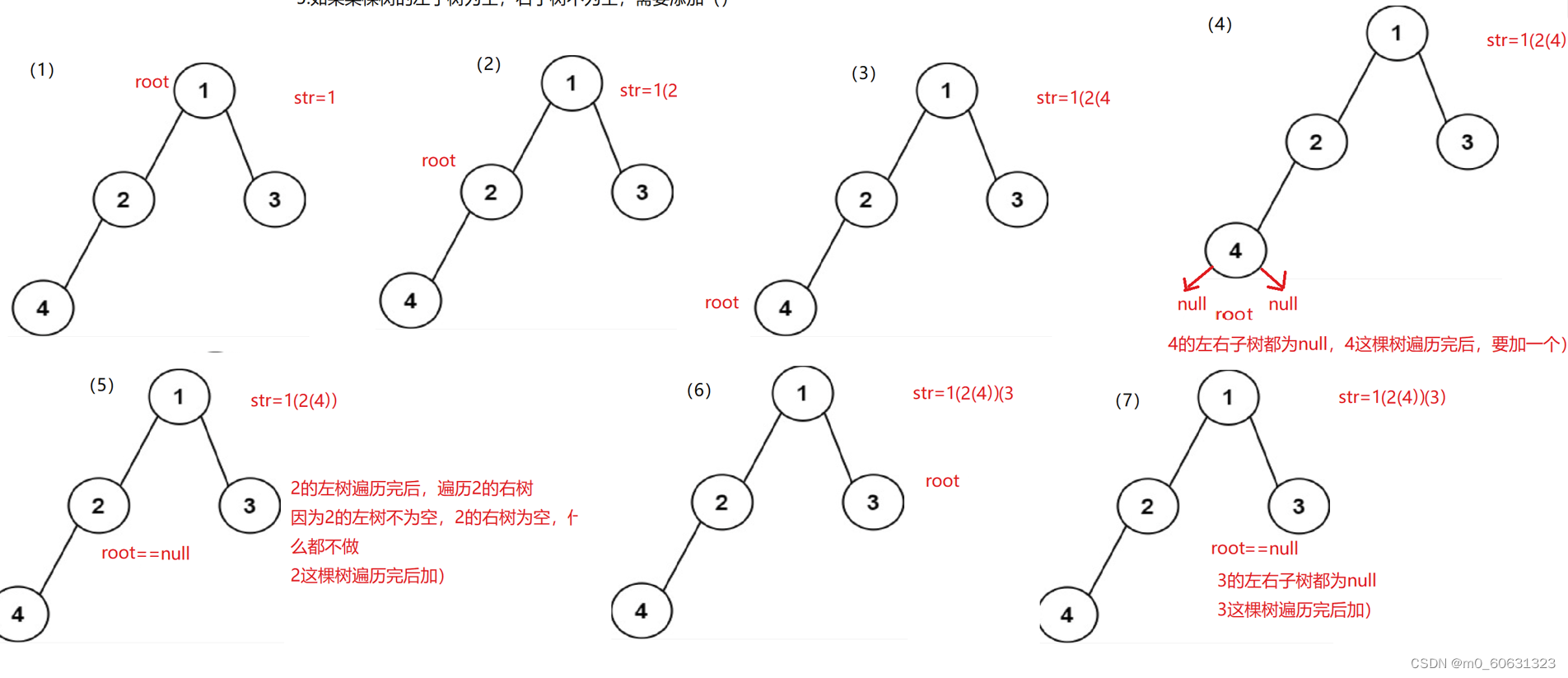
11. Binary tree creates a string
Source code :
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
public String tree2str(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return sb.substring(1, sb.length() - 1);
// The outermost layer does not need to be added ()
}
void dfs(TreeNode root) {
sb.append("(");
sb.append(root.val);
if (root.left != null) dfs(root.left);
else if (root.right != null) sb.append("()");
if (root.right != null) dfs(root.right);
sb.append(")");
}
12. Binary tree preorder non recursive traversal implementation
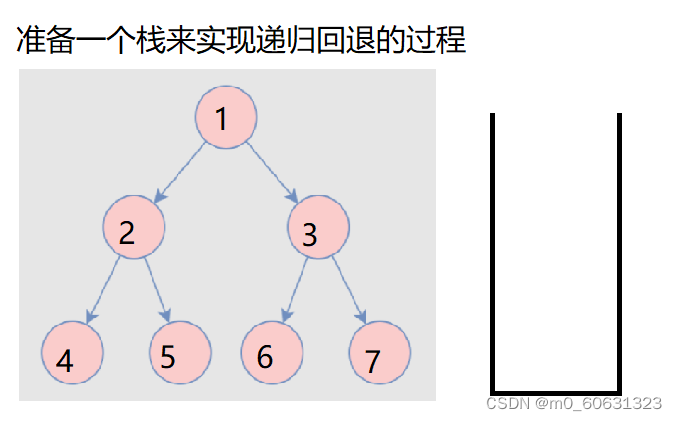
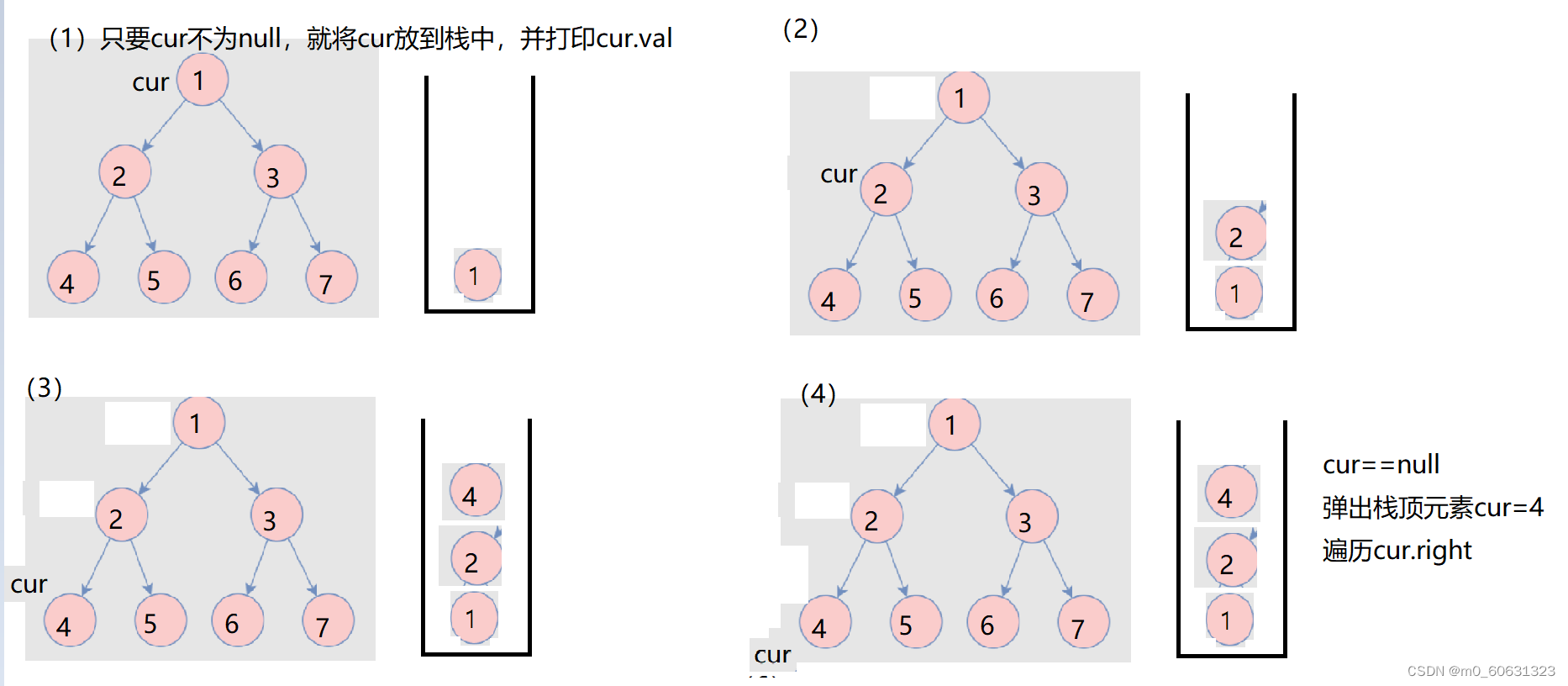
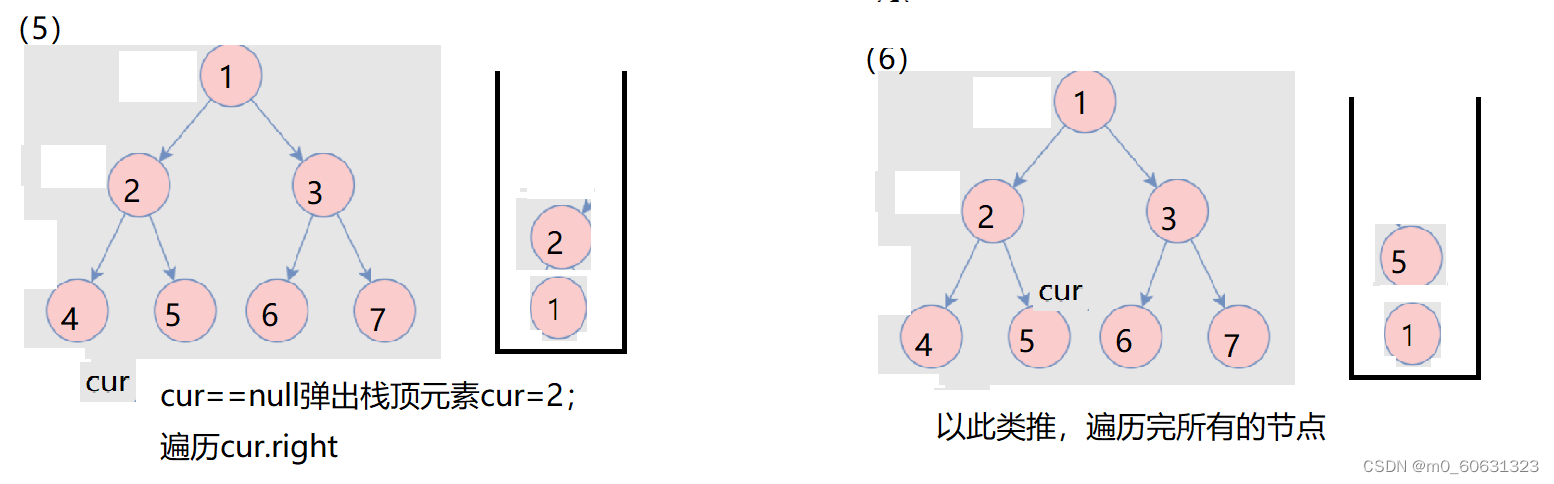
Source code :
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
if(root==null) return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while (cur!=null||!stack.empty()){
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
list.add(cur.val);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
cur=top.right;
}
return list;
}
13. Implementation of non recursive traversal of order in binary tree
In general, it is similar to the previous question :
Just adjust the position of the print element statement
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Stack<TreeNode> stack=new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur=root;
while (cur!=null||!stack.empty()){
while (cur!=null){
stack.push(cur);
cur=cur.left;
}
TreeNode top=stack.pop();
list.add(top.val);
cur=top.right;
}
return list;
}
14. Binary tree postorder non recursive traversal implementation
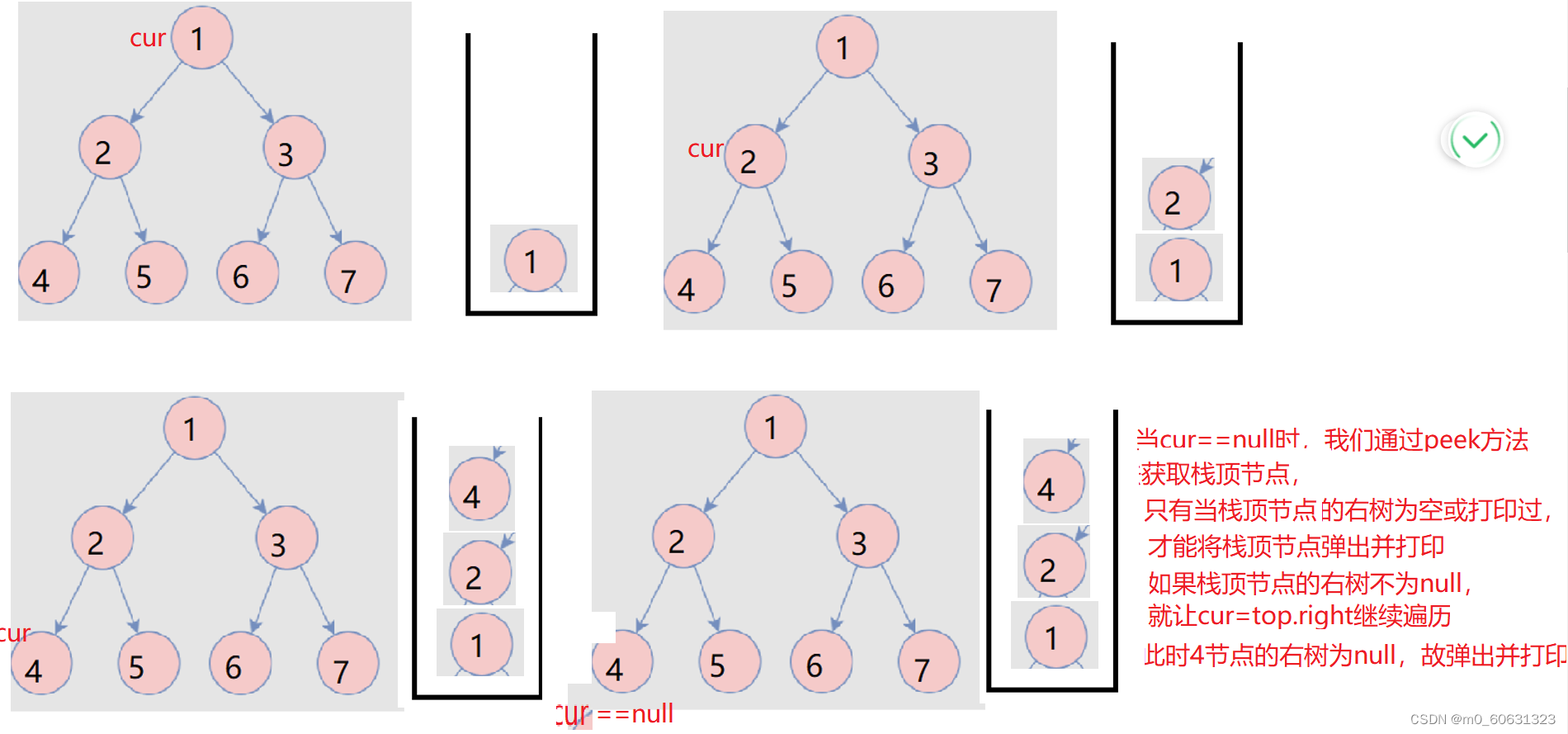
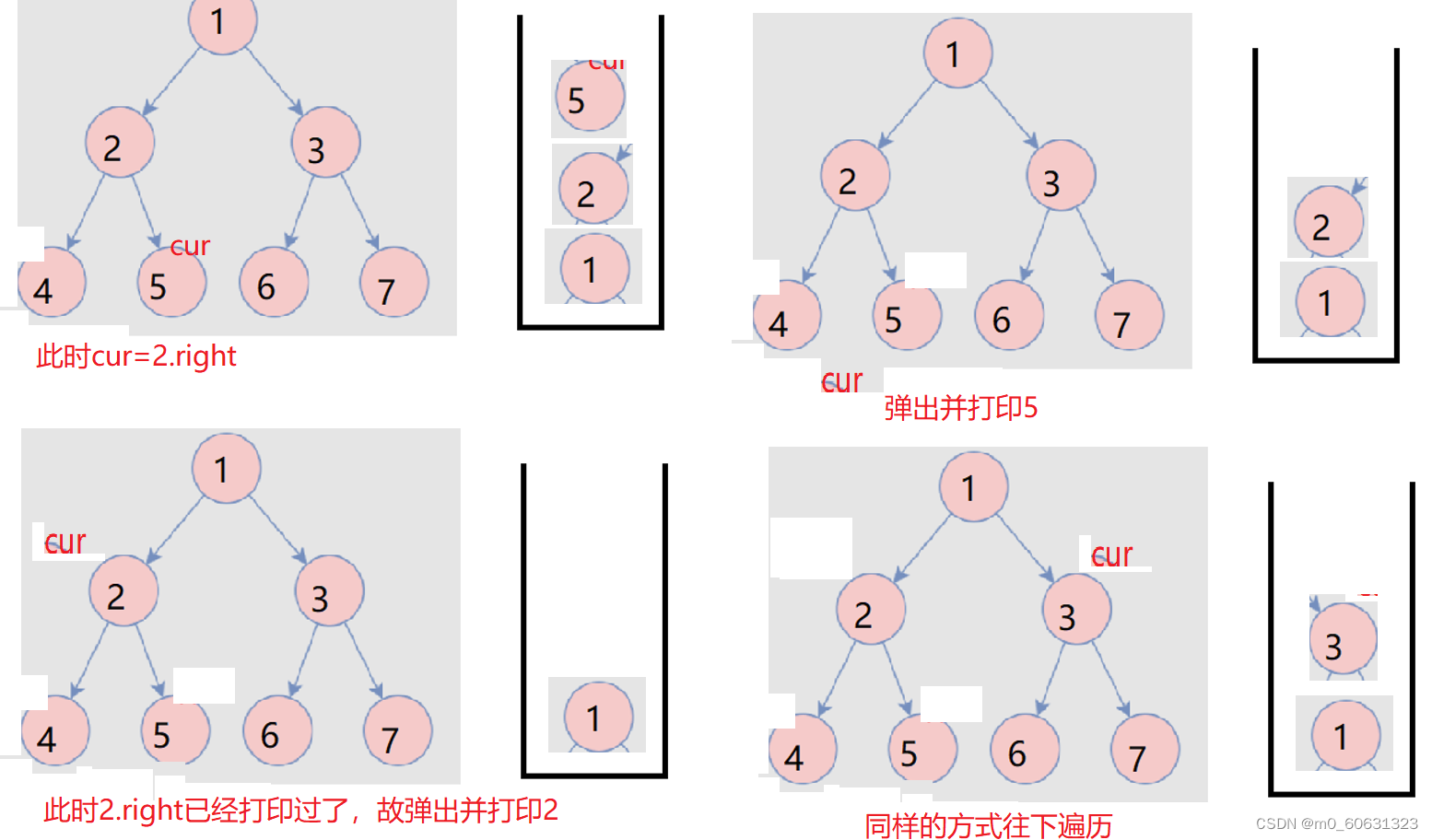
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return list;
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();
TreeNode cur = root;
TreeNode prev=null;
while (cur != null || !stack.empty()) {
while (cur != null) {
stack.push(cur);
cur = cur.left;
}
TreeNode top = stack.peek();
if (top.right == null||top.right==prev) {
list.add(top.val);
stack.pop();
prev=top;
} else {
cur = top.right;
}
}
return list;
}
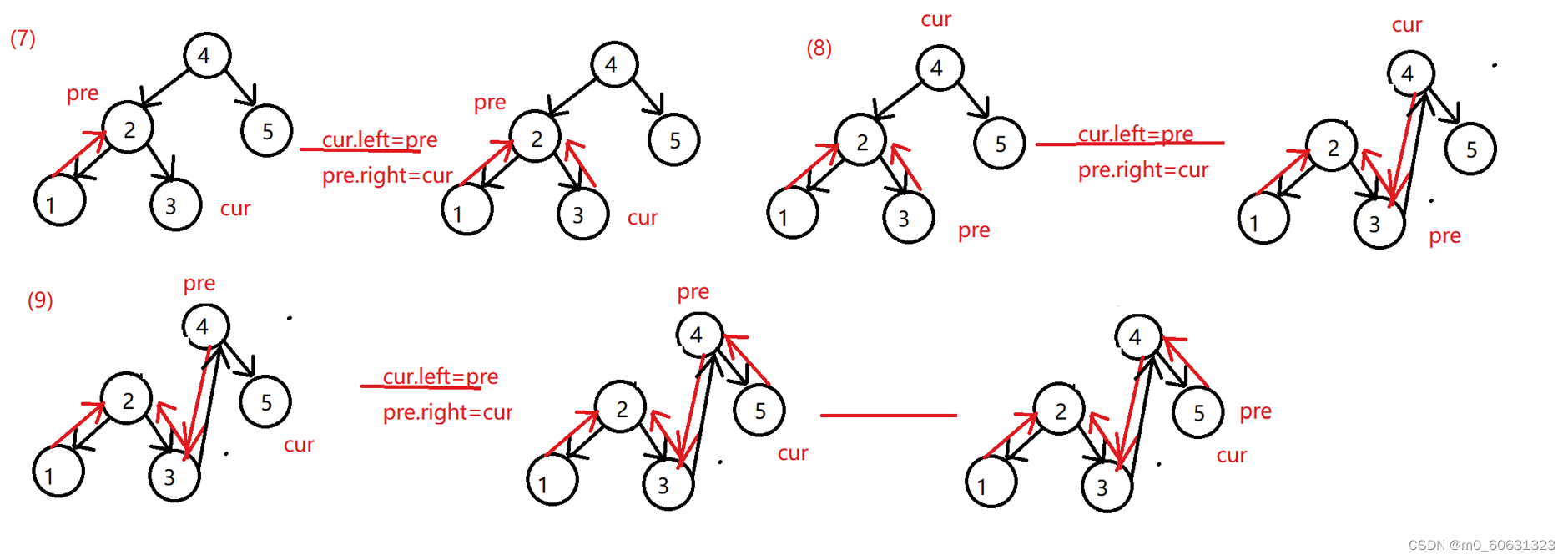
15. Binary search tree to bidirectional linked list
OJ link
Process decomposition diagram of code execution :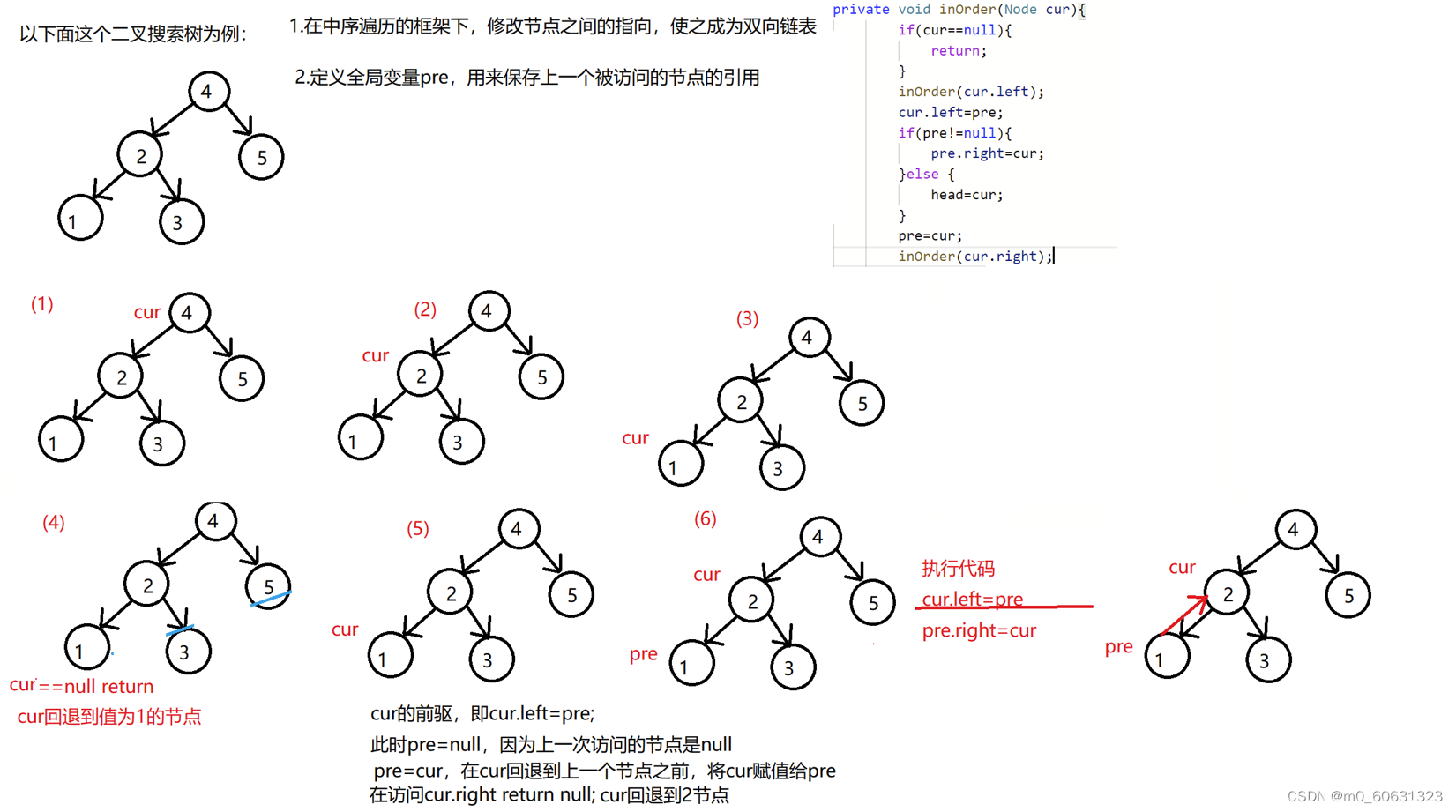
Node pre=null;
Node head=null;
public Node treeToDoublyList(Node pRootOfTree) {
if(pRootOfTree==null){
return null;
}
inOrder(pRootOfTree);
head.left=pre;
pre.right=head;
return head;
}
private void inOrder(Node cur){
if(cur==null){
return;
}
inOrder(cur.left);
cur.left=pre;
if(pre!=null){
pre.right=cur;
}else {
head=cur;
}
pre=cur;
inOrder(cur.right);
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

2020-2022两周年创作纪念日
CISP-PTE之SQL注入(二次注入的应用)

Accès aux données - intégration du cadre d'entité
ES6 drill down - ES6 generator function
vulnhub-FirstBlood
Seaborn draws 11 histograms
PSPNet | 语义分割及场景分析

The visual experience has been comprehensively upgraded, and Howell group and Intel Evo 3.0 have jointly accelerated the reform of the PC industry

Five common negotiation strategies of consulting companies and how to safeguard their own interests

Global Data Center released DC brain system, enabling intelligent operation and management through science and technology
随机推荐
數據訪問 - EntityFramework集成
vulnhub-FirstBlood
Cartoon: what is blue-green deployment?
Enterprise backup software Veritas NetBackup (NBU) 8.1.1 installation and deployment of server
[js] 技巧 简化if 判空
解决CMakeList find_package找不到Qt5,找不到ECM
[vulnerability warning] cve-2022-26134 conflict Remote Code Execution Vulnerability POC verification and repair process
Summary of methods for finding intersection of ordered linked list sets
后台系统发送验证码功能
Flet教程之 12 Stack 重叠组建图文混合 基础入门(教程含源码)
《21天精通TypeScript-3》-安装搭建TypeScript开发环境.md
国泰君安网上开户安全吗
Cs231n notes (medium) -- applicable to 0 Foundation
Global Data Center released DC brain system, enabling intelligent operation and management through science and technology
Flet教程之 09 NavigationRail 基础入门(教程含源码)
OneForAll安装使用
《MongoDB入门教程》第04篇 MongoDB客户端
移动办公时如何使用frp内网穿透+teamviewer方式快速连入家中内网主机
Seaborn draws 11 histograms
【刷题篇】有效的数独