当前位置:网站首页>Process architecture and process management
Process architecture and process management
2022-06-30 04:25:00 【Tra220123】
One 、 Process control block PCB
task_struct Structure :
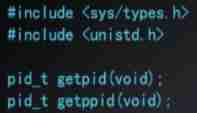
process id: Each process in the system has a unique id, stay c Used in language pid_t Type said , Is a nonnegative integer .
State of process : With operation , Hang up , stop it , Zombies, etc .
Process switch need to save and restore some of the CPU register .
Information describing the virtual address space .
Describe the information of the control terminal .
Current working directory .
umask Mask .
Document descriptor table , Contains a lot of points to file Pointer to structure .
Information related to signals .
user id And groups id.
Control terminal 、session And process groups .
The maximum number of resources a process can use .
Two 、 Process control fork
1.fork effect :
Copy a new process from an existing process , The original process is called the parent process , A new process is called a subprocess .
There are many processes running in the system , These processes are copied one by one from the beginning when there was only one process .
2. stay shell Enter a command to run a program , because shell The process will call after reading the command entered by the user fork F points out a new shell process .


fork Call failure returns -1.
fork Return... In child process 0, Subprocesses can call getpid Function gets its own process id, You can also call getpid Function to get the parent process id.
Use... In the parent process getpid Get your own process id, To get child processes id, Only will fork The return value is recorded !
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
char *msg;
int n;
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0) {
n=6;
while (n > 0) {
printf("child self=%d, parent=%d\n", getpid(), getppid());
sleep(1);
n--;
}
} else {
n = 3;
while (n > 0) {
printf("father self=%d, parent=%d\n", getpid(), getppid());
sleep(1);
n--;
}
}
return 0;
}3. establish 10 Subprocess , And print their pid and ppid?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
char *msg;
int n;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
if (!pid) {
sleep(1);
printf("child[%d], self=%d, parent=%d\n", i, getpid(), getppid());
break;
}
}
return 0;
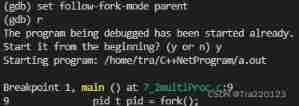
}4.gdb How to debug multiple processes ?

3、 ... and 、exec Family of functions
1. When a process calls a exec Function time , The user space code and data of the process are completely replaced by the new program , Starting from the start routine of the new program .
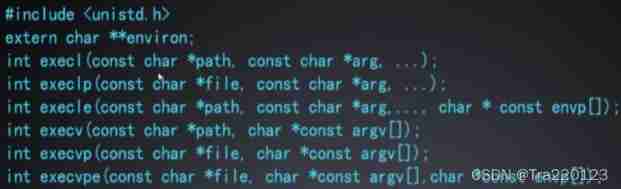
If the call is successful, the new program is loaded and executed from the startup code , Not returning , If there is an error, return -1.
exec Function has only wrong return value but no successful return value .
![]()
exec When the system call executes a new program, it will pass the command line parameters and environment variable table to main function .
And command line arguments argv similar , The environment variable table is also an array of strings .
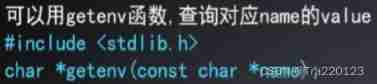
name=value

#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
printf("path value = [%s]\n", getenv("PATH"));
setenv("PATH", "hello", 1);
printf("path value = [%s]\n", getenv("PATH"));
// extern char **environ;
// for (int i = 0; environ[i]; i++) {
// printf("%s\n", environ[i]);
// }
return 0;
}
① No letters p(path) Of exec The first parameter of the function must be the relative path or absolute path of the program , Such as :“/bin/ls” or “./a.out”
② For letters p Function of : If the parameter contains /, Think of it as a pathname . Otherwise, it is regarded as the program name without path , stay PATH Search the directory list of environment variables for this program .
③ In the e(environment) At the end of the exec function , A new environmental scale can be compared with other exec Still use the current environment variables table to execute the new program .
2. Realization exec Family function call commands
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
execlp("ls", "ls", "-a", "-l", NULL);
perror("exec");
exit(1);
return 0;
}#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(void) {
char *arr[] = {"hello", "-a", "-l", NULL};
execvp("ls", arr);
perror("exec");
exit(1);
}3. Realize stream redirection
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
if (argc < 3) {
printf("usage:cmd + inputfile + outputfile\n");
return 1;
}
int fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open read");
exit(1);
}
dup2(fd, 0);
close(fd);
fd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT, 0644);
if (fd < 0) {
perror("open write");
exit(1);
}
dup2(fd, 1);
close(fd);
execl("./upper", "./upper", NULL);
perror("exec");
return 0;
}Four 、wait and waitpid function
1. A process closes all file descriptors on termination , Free up memory allocated in user space , But its PCB Still keep , The kernel holds some information in it :
If it terminates normally, the exit status is saved , If the abnormal termination saves the signal that causes the process to terminate .
Parent process call wait or waitpid Get this information , And then get rid of the process .

The exit status of a process can be in shell Special variables are used in $? see , because shell It's its parent process , When terminated ,shell call wait or waitpid Get its exit status and clear the process completely .
① If a process has terminated , But its parent process has not yet called wait or waitpid Clean it up , The process state at this time is called zombie process . It can be used ps u View process status .
② If you use kill -9 To kill a zombie process : Zombie process still can not kill . But the process of fatherhood can be .
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
if (pid == 0) {
int n = 5;
while (n > 0) {
printf("Is child process\n");
sleep(1);
n--;
}
} else {
int stat_val;
waitpid(pid, &stat_val, 0);
if (WIFEXITED(stat_val)) {
printf("child exited with code: %d\n", WEXITSTATUS(stat_val));
} else if (WIFSIGNALED(stat_val)) {
printf("child terminated abnormally, signal is %d\n %d\n", WTERMSIG(stat_val));
}
}
return 0;
}2. Parent process call wait or waitpid May be :
① Blocking ( All child processes are still running )
② The termination information of the subprocess is returned immediately ( If a subprocess has terminated , Waiting for parent process to read its termination information )
③ Error return immediately ( There are no child processes )
3.wait VS waitpid
If all the child processes of the parent process are running , call wait Will block the parent process , And call waitpid If in options Specified in parameter WNOHANG This allows the parent process to return immediately without blocking 0.
wait Wait for any child process to stop , and waitpid adopt pid Parameter to specify which subprocess to wait for .
5、 ... and 、 Interprocess communication
1.IPC: interProcess communication
Each process has a different user address space , The global variables of any process cannot be seen in another process , So to exchange data between processes, you have to go through the kernel .
Create a buffer in the kernel , process 1 Copy data from user space to kernel buffer , process 2 Read data from the kernel buffer , The mechanism provided by the kernel is called interprocess communication .

2. The Conduit
① Pipe is one of the most basic IPC Mechanism , from pipe Function creation .

call pipe Function to open a buffer in the kernel ( The Conduit ) For communication , There is a read terminal and a write terminal , And then through filedes Parameters are passed out to the user program, two file descriptors .
filedes[0] Point to pipe read end ,filedes[1] Point to the pipe write end



#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int main(void) {
pid_t pid;
int fd[2], n;
char buf[20];
if (pipe(fd) < 0) {
perror("pipe");
exit(1);
}
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
perror("fork");
exit(1);
}
if (pid > 0) {
close(fd[0]);
write(fd[1], "hello pipe\n", 11);
wait(NULL);
} else {
close(fd[1]);
sleep(1);
n = read(fd[0], buf, 20);
write(1, buf, n);
}
return 0;
}② When using pipes, pay attention to the following 4 Special circumstances in ( Suppose it's all blocking I/O operation , No settings O_NONBLOCK sign ):
If all file descriptors pointing to the write end of the pipe are closed , And there are still processes reading data from the read side of the pipeline , After the divine domain data in the pipeline is read , Again read Returns the 0, It's like reading to the end of the file .
If there is a file descriptor pointing to the write end of the pipeline, it is not closed , The process that holds the write end of the pipeline does not write data to the pipeline , At this point, a process reads data from the pipe reader , After the remaining data in the pipeline is read , Again read It will block , The data is not read and returned until there is data readable in the pipeline .
If all file descriptors pointing to the read end of the pipeline are closed , At this point, a process writes to the pipe write, Then the process will receive a signal SIGPIPE, It usually causes the process to terminate abnormally .
If there are file descriptors that point to the read end of the pipeline, they are not closed , The process that holds the read end of the pipeline does not read data from the pipeline , At this point, a process writes data to the write end of the pipe , Then again when the pipe is full write It will block , Only when there is an empty position in the pipeline can the data be written and returned .
#include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/wait.h> int main(void) { pid_t pid; int fd[2], n; char buf[20]; char test[1024]; if (pipe(fd) < 0) { perror("pipe"); exit(1); } pid = fork(); if (pid < 0) { perror("fork"); exit(1); } if (pid > 0) { close(fd[0]); for (int i = 0; i< 100; i++) { write(fd[1], test, 1024); printf("i=%d\n", i); } wait(NULL); } else { close(fd[1]); sleep(10); } return 0; }
边栏推荐
- JS generator
- 基于海康EhomeDemo工具排查公网部署出现的视频播放异常问题
- FortiGate performs DNAT mapping, and intranet users cannot normally access the mapping
- 01 backpack, dynamic planning
- Fair lock and unfair lock
- Detailed explanation of network layer
- An error occurs when sqlyog imports the database. Please help solve it!
- 什么是光耦电路,实际使用中应该注意些什么?
- Error Nova missingauthplugin: an auth plugin is required to determine endpoint URL
- FortiGate firewall configuration link detection link monitor and status query
猜你喜欢

Threejs realizes the simulation of river, surface flow, pipe flow and sea surface

进程间通信之匿名管道

Troubleshoot abnormal video playback problems in public network deployment based on Haikang ehomedemo tool
![[cloud native] AI cloud development platform - Introduction to AI model foundry (developers can experience AI training model for free)](/img/08/b390810d457af5e4470d9743b01ca1.png)
[cloud native] AI cloud development platform - Introduction to AI model foundry (developers can experience AI training model for free)

How to use div boxes to simulate line triangles

Imile uses Zadig's multi cloud environment to deploy thousands of times a week to continuously deliver global business across clouds and regions
![Blue Bridge Cup: magic cube rotation [Vocational group]](/img/ba/aeae2744f3aaa1052b5af452f990e2.jpg)
Blue Bridge Cup: magic cube rotation [Vocational group]

How the FortiGate firewall rejects a port by using the local in policy policy

输入输出及中断技术——微机第六章学习笔记

What is an optocoupler circuit and what should be paid attention to in actual use?
随机推荐
A solution to the problem of "couldn't open file /mnt/repodata/repomd.xml"
win10系统使用浏览器下载后,内容无故移动或删除
Error in conditional filter (if) syntax in sum function in SQL Server2005
Find the interface and add parameters to the form
OneNote production schedule
Input / output and interrupt technology -- microcomputer Chapter 6 learning notes
SQL append field
Refers to the difference between IP and *ip at output
Sql语句遇到的错误,求解
The same node code will cause duplicate data
输入输出及中断技术——微机第六章学习笔记
FortiGate firewall modifies the default timeout of a session
Pig-Latin (UVA492)
Threejs realizes the simulation of river, surface flow, pipe flow and sea surface
Share an example of a simple MapReduce method using a virtual machine
Qt Creator 8 Beta2发布
SQL error caused by entity class: Oracle "ora-00904" error: possible case of invalid identifier
487-3279(POJ1002)
El upload upload file (manual upload, automatic upload, upload progress)
7-3 single source shortest circuit for strange play upgrade