当前位置:网站首页>PI control of three-phase grid connected inverter - off grid mode
PI control of three-phase grid connected inverter - off grid mode
2022-07-02 09:38:00 【Quikk】
Three phase grid connected inverter is off grid PI control
Off grid control of three-phase grid connected inverter
The basic difference between inverter parallel and off grid control
When the three-phase grid connected inverter is connected to the grid , Its main function is to transmit electric energy to the large power grid . At this time, the system parallel node voltage is Big grid clamping , Therefore, it is only necessary to control the inverter to output the current that meets the power requirements , Control objectives can be achieved , Therefore, the grid connected inverter in this state is generally equivalent to Current source .
When the three-phase grid connected inverter is off grid , Its main function is to output the voltage that meets the load operation conditions , Current system System output current All by load Self parameters decision . Therefore, the grid connected inverter in this state is generally equivalent to Voltage source .
Basic topology of off grid inverter
The following figure shows the inverter topology in the off grid state , Here we use pure resistance instead of pure resistive load :

Take the direction of the inverter pointing to the load current as the positive direction of the current reference , In the picture i a i_{a} ia The direction indicated is positive .
{ U a − L d i a d t − i a R − U C a = 0 U b − L d i b d t − i b R − U C b = 0 U c − L d i c d t − i c R − U C c = 0 C d u C a d t = i a − i g a C d u C b d t = i b − i g b C d u C c d t = i c − i g c (1) \left\{ \begin{matrix}{} U_a-L\frac{di_a}{dt}-i_aR-U_{Ca}=0\\ U_b-L\frac{di_b}{dt}-i_bR-U_{Cb}=0\\ U_c-L\frac{di_c}{dt}-i_cR-U_{Cc}=0\\ C\frac{du_{Ca}}{dt}=i_a-i_{ga}\\ C\frac{du_{Cb}}{dt}=i_b-i_{gb}\\ C\frac{du_{Cc}}{dt}=i_c-i_{gc}\\ \end{matrix} \right.\tag{1} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧Ua−Ldtdia−iaR−UCa=0Ub−Ldtdib−ibR−UCb=0Uc−Ldtdic−icR−UCc=0CdtduCa=ia−igaCdtduCb=ib−igbCdtduCc=ic−igc(1)
You can get :
{ d i a d t = 1 L U a − R L i a − 1 L U C a d i b d t = 1 L U b − R L i b − 1 L U C b d i c d t = 1 L U c − R L i c − 1 L U C c d u C a d t = 1 C i a − 1 C i g a d u C b d t = 1 C i b − 1 C i g b d u C c d t = 1 C i c − 1 C i g c (2) \left\{ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}=\frac{1}{L}U_a-\frac{R}{L}i_a-\frac{1}{L}U_{Ca}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}=\frac{1}{L}U_b-\frac{R}{L}i_b-\frac{1}{L}U_{Cb}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt}=\frac{1}{L}U_c-\frac{R}{L}i_c-\frac{1}{L}U_{Cc}\\ \frac{du_{Ca}}{dt}=\frac{1}{C}i_a-\frac{1}{C}i_{ga}\\ \frac{du_{Cb}}{dt}=\frac{1}{C}i_b-\frac{1}{C}i_{gb}\\ \frac{du_{Cc}}{dt}=\frac{1}{C}i_c-\frac{1}{C}i_{gc}\\ \end{matrix} \right.\tag{2} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧dtdia=L1Ua−LRia−L1UCadtdib=L1Ub−LRib−L1UCbdtdic=L1Uc−LRic−L1UCcdtduCa=C1ia−C1igadtduCb=C1ib−C1igbdtduCc=C1ic−C1igc(2)
In the form of a matrix :
{ [ d i a d t d i b d t d i c d t ] = 1 L [ U a U b U c ] − R L [ i a i b i c ] − 1 L [ U C a U C b U C c ] [ d U C a d t d U C b d t d U C c d t ] = 1 C [ i a i b i c ] − 1 C [ i g a i g b i g c ] (3) \left\{ \begin{matrix}{} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt} \end{matrix} \right]= \frac{1}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_a\\ U_b\\ U_c\\ \end{matrix} \right]- \frac{R}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c\\ \end{matrix} \right]- \frac{1}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{Ca}\\ U_{Cb}\\ U_{Cc}\\ \end{matrix} \right]\\ \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{dU_{Ca}}{dt}\\ \frac{dU_{Cb}}{dt}\\ \frac{dU_{Cc}}{dt} \end{matrix} \right]= \frac{1}{C} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c\\ \end{matrix} \right]- \frac{1}{C} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{ga}\\ i_{gb}\\ i_{gc}\\ \end{matrix} \right] \end{matrix} \right.\tag{3} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧⎣⎡dtdiadtdibdtdic⎦⎤=L1⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤−LR⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤−L1⎣⎡UCaUCbUCc⎦⎤⎣⎡dtdUCadtdUCbdtdUCc⎦⎤=C1⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤−C1⎣⎡igaigbigc⎦⎤(3)
α β \alpha\beta αβ Inverter equation in coordinate system
And the known abc- α β \alpha\beta αβ The positive and inverse transformation matrix is :
[ U α U β U 0 ] = T a b c − α β [ U a U b U c ] = 2 3 × [ 1 − 1 2 − 1 2 0 3 2 − 3 2 1 1 1 ] [ U a U b U c ] (4) \left[ \begin {matrix}{} U_\alpha\\ U_\beta\\ U_0 \end{matrix} \right] = T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin {matrix} U_a\\ U_b\\ U_c \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{2}{3}\times \left[ \begin {matrix} 1 & -\frac{1}{2} & -\frac{1}{2}\\ 0 & \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & -\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\\ 1 & 1 & 1 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin {matrix} U_a\\ U_b\\ U_c \end{matrix} \right]\tag{4} ⎣⎡UαUβU0⎦⎤=Tabc−αβ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤=32×⎣⎡101−21231−21−231⎦⎤⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤(4)
[ U a U b U c ] = T α β − a b c [ U α U β U 0 ] = [ 1 0 1 2 − 1 2 3 2 1 2 − 1 2 − 3 2 1 2 ] [ U α U β U 0 ] (5) \left[ \begin {matrix}{} U_a\\ U_b\\ U_c \end{matrix} \right]= T_{\alpha\beta-abc} \left[ \begin {matrix} U_{\alpha}\\ U_{\beta}\\ U_0 \end{matrix} \right]= \left[ \begin {matrix} 1 & 0 & \frac{1}{2}\\ -\frac{1}{2} & \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & \frac{1}{2}\\ -\frac{1}{2} & -\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} & \frac{1}{2} \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin {matrix} U_{\alpha}\\ U_{\beta}\\ U_0 \end{matrix} \right]\tag{5} ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤=Tαβ−abc⎣⎡UαUβU0⎦⎤=⎣⎢⎡1−21−21023−23212121⎦⎥⎤⎣⎡UαUβU0⎦⎤(5)
Here we add 0 The axis is to make the transformation matrix into a square matrix , It is conducive to the inversion , actually 0 Axis No participation Control operation uses .
fitting (3) Multiply both sides at the same time T a b c − α β T_{abc-\alpha\beta} Tabc−αβ The inverter equation can be transformed to α β \alpha\beta αβ In coordinate system , Available :
T a b c − α β [ d i a d t d i b d t d i c d t ] = 1 L T a b c − α β [ U a U b U c ] − R L T a b c − α β [ i a i b i c ] − 1 L T a b c − α β [ U C a U C b U C c ] \begin{matrix}{} T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt} \end{matrix} \right]= \frac{1}{L} T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_a\\ U_b\\ U_c\\ \end{matrix} \right]- \frac{R}{L} T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c\\ \end{matrix} \right]- \frac{1}{L} T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{Ca}\\ U_{Cb}\\ U_{Cc}\\ \end{matrix} \right]\\ \end{matrix}{} Tabc−αβ⎣⎡dtdiadtdibdtdic⎦⎤=L1Tabc−αβ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤−LRTabc−αβ⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤−L1Tabc−αβ⎣⎡UCaUCbUCc⎦⎤
Note here that only
[ U α U β U 0 ] = T a b c − α β [ U a U b U c ] \left[ \begin {matrix}{} U_\alpha\\ U_\beta\\ U_0 \end{matrix} \right]= T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin {matrix} U_a\\ U_b\\ U_c \end{matrix} \right] ⎣⎡UαUβU0⎦⎤=Tabc−αβ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤
therefore T a b c − α β [ d i a d t d i b d t d i c d t ] T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] Tabc−αβ⎣⎡dtdiadtdibdtdic⎦⎤ It needs to be calculated separately , The calculation process is as follows :
[ i α i β i 0 ] ′ = ( T a b c − α β [ i a i b i c ] ) ′ = ( T a b c − α β ) ′ [ i a i b i c ] + ( T a b c − α β ) [ d i a d t d i b d t d i c d t ] \left[ \begin {matrix}{} i_\alpha\\ i_\beta\\ i_0 \end{matrix} \right]' = (T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin {matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c \end{matrix} \right])' = (T_{abc-\alpha\beta})' \left[ \begin {matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c \end{matrix} \right] + (T_{abc-\alpha\beta}) \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] ⎣⎡iαiβi0⎦⎤′=(Tabc−αβ⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤)′=(Tabc−αβ)′⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤+(Tabc−αβ)⎣⎡dtdiadtdibdtdic⎦⎤
therefore
T a b c − α β [ d i a d t d i b d t d i c d t ] = ( T a b c − α β [ i a i b i c ] ) ′ − ( T a b c − α β ) ′ [ i a i b i c ] T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] = (T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin {matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c \end{matrix} \right])' - (T_{abc-\alpha\beta})' \left[ \begin {matrix}{} i_a\\ i_b\\ i_c \end{matrix} \right] Tabc−αβ⎣⎡dtdiadtdibdtdic⎦⎤=(Tabc−αβ⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤)′−(Tabc−αβ)′⎣⎡iaibic⎦⎤
and ( T a b c − α β ) (T_{abc-\alpha\beta}) (Tabc−αβ) Is a constant matrix , therefore
( T a b c − α β ) ′ = 0 (T_{abc-\alpha\beta})'=0 (Tabc−αβ)′=0
therefore :
T a b c − α β [ d i a d t d i b d t d i c d t ] = [ d i α d t d i β d t d i 0 d t ] T_{abc-\alpha\beta} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_a}{dt}\\ \frac{di_b}{dt}\\ \frac{di_c}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{\alpha}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{\beta}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_0}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] Tabc−αβ⎣⎡dtdiadtdibdtdic⎦⎤=⎣⎡dtdiαdtdiβdtdi0⎦⎤
The same can be :
{ [ d i α d t d i β d t d i 0 d t ] = 1 L [ U α U β U 0 ] − R L [ i α i β i 0 ] − 1 L [ U C α U C β U C 0 ] [ d U C α d t d U C β d t d U C 0 d t ] = 1 C [ i α i β i 0 ] − 1 C [ i g α i g β i g 0 ] (6) \left\{ \begin{matrix}{} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{\alpha}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{\beta}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_0}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{\alpha}\\ U_{\beta}\\ U_0\\ \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{R}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{\alpha}\\ i_{\beta}\\ i_0\\ \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{1}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{C\alpha}\\ U_{C\beta}\\ U_{C0}\\ \end{matrix} \right]\\ \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{dU_{C\alpha}}{dt}\\ \frac{dU_{C\beta}}{dt}\\ \frac{dU_{C0}}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{C} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{\alpha}\\ i_{\beta}\\ i_0\\ \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{1}{C} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{g\alpha}\\ i_{g\beta}\\ i_{g0}\\ \end{matrix} \right] \end{matrix} \right.\tag{6} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧⎣⎡dtdiαdtdiβdtdi0⎦⎤=L1⎣⎡UαUβU0⎦⎤−LR⎣⎡iαiβi0⎦⎤−L1⎣⎡UCαUCβUC0⎦⎤⎣⎡dtdUCαdtdUCβdtdUC0⎦⎤=C1⎣⎡iαiβi0⎦⎤−C1⎣⎡igαigβig0⎦⎤(6)
dq Inverter equation in coordinate system
And the known α β \alpha\beta αβ-dq The positive and inverse transformation matrix is :
[ U d U q ] = T α β − d q [ U α U β ] = [ c o s φ s i n φ − s i n φ c o s φ ] [ U α U β ] \left[ \begin {matrix}{} U_d\\ U_q\\ \end{matrix} \right] = T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin {matrix} U_\alpha\\ U_\beta\\ \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin {matrix} cos\varphi & sin\varphi \\ -sin\varphi & cos\varphi \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin {matrix} U_\alpha\\ U_\beta\\ \end{matrix} \right] [UdUq]=Tαβ−dq[UαUβ]=[cosφ−sinφsinφcosφ][UαUβ]
[ U α U β ] = T d q − α β U d U q = [ c o s φ − s i n φ s i n φ c o s φ ] [ U d U q ] \left[ \begin {matrix}{} U_\alpha\\ U_\beta\\ \end{matrix} \right] = T_{dq-\alpha\beta} \begin {matrix} U_d\\ U_q\\ \end{matrix} = \left[ \begin {matrix} cos\varphi & -sin\varphi \\ sin\varphi & cos\varphi \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin {matrix} U_d\\ U_q\\ \end{matrix} \right] [UαUβ]=Tdq−αβUdUq=[cosφsinφ−sinφcosφ][UdUq]
Put the above α β \alpha\beta αβ Remove the inverter equation in coordinates 0 Axis equation , And multiply it by the transformation matrix T α β − d q T_{\alpha\beta-dq} Tαβ−dq Available :
T α β − d q [ d i α d t d i β d t ] = 1 L T α β − d q [ U α U β ] − R L T α β − d q [ i α i β ] − 1 L T α β − d q [ U C α U C β ] T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{\alpha}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{\beta}}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{L} T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{\alpha}\\ U_{\beta} \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{R}{L} T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{\alpha}\\ i_{\beta} \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{1}{L} T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{C\alpha}\\ U_{C\beta}\\ \end{matrix} \right]\\ Tαβ−dq[dtdiαdtdiβ]=L1Tαβ−dq[UαUβ]−LRTαβ−dq[iαiβ]−L1Tαβ−dq[UCαUCβ]
The same process as above , Need to find T α β − d q [ d i α d t d i β d t ] T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{\alpha}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{\beta}}{dt}\end{matrix} \right] Tαβ−dq[dtdiαdtdiβ], here φ = ω t \varphi=\omega t φ=ωt , ( T α β − d q ) ′ (T_{\alpha\beta-dq})' (Tαβ−dq)′ No more for 0.
( T α β − d q ) ′ = [ − ω s i n φ ω c o s φ − ω c o s φ − ω s i n φ ] (T_{\alpha\beta-dq})' = \left[ \begin{matrix}{} -\omega sin \varphi & \omega cos \varphi\\ -\omega cos \varphi & -\omega sin \varphi \end{matrix} \right] (Tαβ−dq)′=[−ωsinφ−ωcosφωcosφ−ωsinφ]
T α β − d q [ d i α d t d i β d t ] = = [ d i d d t d i q d t ] − [ − ω s i n φ ω c o s φ − ω c o s φ − ω s i n φ ] [ i α i β ] = [ − ω s i n φ ω c o s φ − ω c o s φ − ω s i n φ ] ( T α β − d q ) − 1 [ i d i q ] = [ − ω s i n φ ω c o s φ − ω c o s φ − ω s i n φ ] ( T α β − d q ) − 1 [ i d i q ] = ω [ 0 1 − 1 0 ] [ i d i q ] T_{\alpha\beta-dq} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{\alpha}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{\beta}}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] == \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{d}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{q}}{dt} \end{matrix} \right] - \left[ \begin{matrix}{} -\omega sin \varphi & \omega cos \varphi\\ -\omega cos \varphi & -\omega sin \varphi \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{\alpha}\\ i_{\beta} \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix}{} -\omega sin \varphi & \omega cos \varphi\\ -\omega cos \varphi & -\omega sin \varphi \end{matrix} \right] (T_{\alpha\beta-dq})^{-1} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{d}\\ i_{q} \end{matrix} \right]\\ = \left[ \begin{matrix}{} -\omega sin \varphi & \omega cos \varphi\\ -\omega cos \varphi & -\omega sin \varphi \end{matrix} \right] (T_{\alpha\beta-dq})^{-1} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{d}\\ i_{q} \end{matrix} \right] = \omega \left[ \begin{matrix}{} 0 & 1 \\ -1 & 0 \end{matrix} \right] \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{d}\\ i_{q} \end{matrix} \right] Tαβ−dq[dtdiαdtdiβ]==[dtdiddtdiq]−[−ωsinφ−ωcosφωcosφ−ωsinφ][iαiβ]=[−ωsinφ−ωcosφωcosφ−ωsinφ](Tαβ−dq)−1[idiq]=[−ωsinφ−ωcosφωcosφ−ωsinφ](Tαβ−dq)−1[idiq]=ω[0−110][idiq]
Substituting into the system equation, we can get dq The inverter equation in the coordinate system is :
{ [ d i d d t d i q d t ] = 1 L [ U d U q ] − R L [ i d i q ] − 1 L [ U C d U C q ] + ω [ i q − i d ] [ d U C d d t d U C q d t ] = 1 C [ i d i q ] − 1 C [ i g d i g q ] + ω [ U C q − U C d ] (7) \left \{ \begin{matrix}{} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{di_{d}}{dt}\\ \frac{di_{q}}{dt}\\ \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{d}\\ U_{q}\\ \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{R}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{d}\\ i_{q}\\ \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{1}{L} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{Cd}\\ U_{Cq}\\ \end{matrix} \right] + \omega \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{q}\\ -i_{d}\\ \end{matrix} \right] \\ \left[ \begin{matrix}{} \frac{dU_{Cd}}{dt}\\ \frac{dU_{Cq}}{dt}\\ \end{matrix} \right] = \frac{1}{C} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{d}\\ i_{q}\\ \end{matrix} \right] - \frac{1}{C} \left[ \begin{matrix}{} i_{gd}\\ i_{gq}\\ \end{matrix} \right] +\omega \left[ \begin{matrix}{} U_{Cq}\\ -U_{Cd}\\ \end{matrix} \right] \\ \end{matrix} \right.\tag{7} ⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧[dtdiddtdiq]=L1[UdUq]−LR[idiq]−L1[UCdUCq]+ω[iq−id][dtdUCddtdUCq]=C1[idiq]−C1[igdigq]+ω[UCq−UCd](7)
At this point, you can find the system d The existence of the axis equation is related to q Phenomenon of shaft coupling , Therefore, it is necessary to control the system accurately dq Shaft decoupling .
fitting (7) Laplace transform can get :
{ i d = i g d + s C U C d − ω C U C q i q = i g q + s C U C q + ω C U C d U d = ( s L + R ) i d + U C d − ω L i q U q = ( s L + R ) i q + U C q + ω L i d (8) \left\{ \begin{matrix}{} i_d = i_{gd}+sCU_{Cd}-\omega CU_{Cq}\\ i_q = i_{gq}+sCU_{Cq}+\omega CU_{Cd}\\ U_d = (sL+R)i_{d}+U_{Cd}-\omega Li_{q}\\ U_q = (sL+R)i_{q}+U_{Cq}+\omega Li_{d}\\ \end{matrix} \right.\tag{8} ⎩⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎧id=igd+sCUCd−ωCUCqiq=igq+sCUCq+ωCUCdUd=(sL+R)id+UCd−ωLiqUq=(sL+R)iq+UCq+ωLid(8)
Usage (8) The following block diagram can be drawn .

According to the inverter body model, double PI Control schematic diagram , Because by Combine after decoupling PI controller Precise control can be achieved .
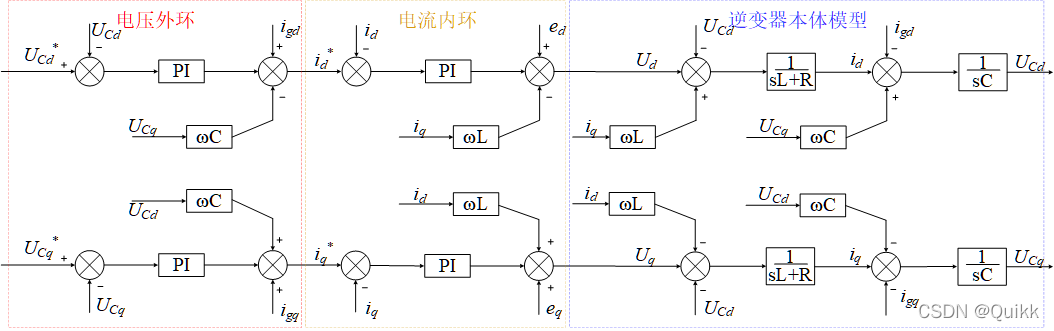
Grid connected inverter PI Controller constant value tracking
about PI controller
G ( s ) = K P ( 1 + K i s ) = K P s + K P K i s G ( j ω ) = K P j ω + K P K i j ω G_{(s)}=K_P(1+\frac{K_i}{s})=\frac{K_Ps+K_PK_i}{s}\\ G(j\omega) = \frac{K_Pj\omega+K_PK_i}{j\omega} \\ G(s)=KP(1+sKi)=sKPs+KPKiG(jω)=jωKPjω+KPKi
therefore :
G ( j 0 ) = K P j 0 + K P K i j 0 = ∞ G(j0) = \frac{K_Pj0+K_PK_i}{j0} = \infty \\ G(j0)=j0KPj0+KPKi=∞
At this time, the closed-loop transmittal is :
A = G ( j 0 ) 1 + G ( j 0 ) = 1 A=\frac{G_{(j0)} }{1+G_{(j0)}} = 1 A=1+G(j0)G(j0)=1
therefore PI The controller pair frequency is 0 The signal of ( DC signal ) Can achieve Tracking without static error ! Therefore, in the above process, the inverter control model needs to be transformed to dq Axis , because dq Transformation is based on PLL The output voltage angle is transformed , So the three-phase current is dq In coordinate system (d The shaft component is the current amplitude ,q The axis component is zero ). Decoupling is to eliminate other shaft pairs PI The impact of control .
Simulation results
SPWM Modulation signal :
Output line voltage ( Before filter ):
Load side phase voltage (0.1s Grid connection ,0.8s Given power step ):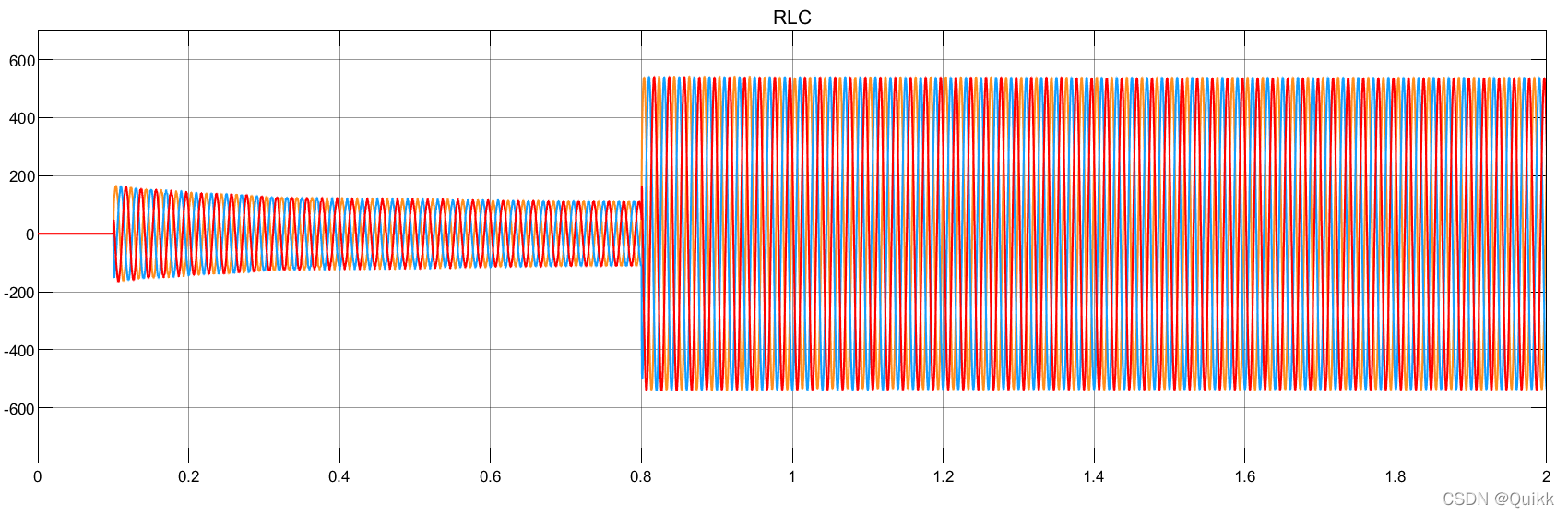
Output power :
simulation model : Model links
边栏推荐
- Safety production early warning system software - Download safety production app software
- Microservice practice | fuse hytrix initial experience
- C语言之分草莓
- 个人经历&&博客现状
- Chrome用户脚本管理器-Tampermonkey 油猴
- Oracle modify database character set
- MySQL error: unblock with mysqladmin flush hosts
- hystrix 实现请求合并
- 分享一篇博客(水一篇博客)
- MySQL multi column in operation
猜你喜欢
FragmentTabHost实现房贷计算器界面

Read Day6 30 minutes before going to bed every day_ Day6_ Date_ Calendar_ LocalDate_ TimeStamp_ LocalTime

QT QLabel样式设置

Fragmenttabhost implements the interface of housing loan calculator
2837xd 代码生成——StateFlow(4)
微服务实战|手把手教你开发负载均衡组件
YOLO物体识别,生成数据用到的工具
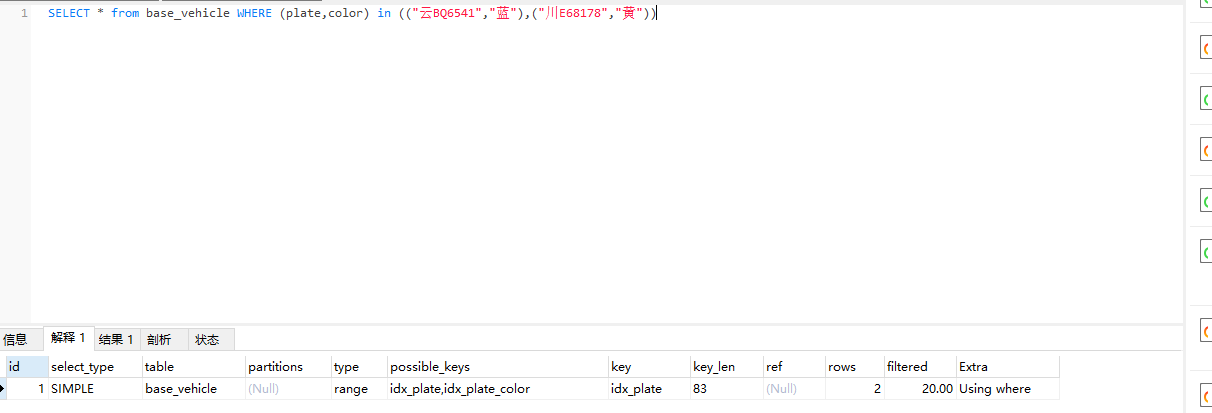
Mysql 多列IN操作
Micro service practice | introduction and practice of zuul, a micro service gateway
Chrome浏览器标签管理插件–OneTab
随机推荐
微服务实战|微服务网关Zuul入门与实战
Oracle modifies tablespace names and data files
Customize redis connection pool
每天睡觉前30分钟阅读_day4_Files
C语言之判断直角三角形
Knowledge points are very detailed (code is annotated) number structure (C language) -- Chapter 3, stack and queue
MySQL multi column in operation
c语言编程题
三相并网逆变器PI控制——离网模式
QT信号槽总结-connect函数错误用法
Matplotlib swordsman - a stylist who can draw without tools and code
tinyxml2 读取和修改文件
idea查看字节码配置
cmake的命令-官方文档
Chrome浏览器标签管理插件–OneTab
Chrome video download Plug-in – video downloader for Chrome
Number structure (C language) -- Chapter 4, compressed storage of matrices (Part 2)
每天睡觉前30分钟阅读_day3_Files
C语言之分草莓
Elastic Stack之Beats(Filebeat、Metricbeat)、Kibana、Logstash教程