当前位置:网站首页>How MySQL executes query statements
How MySQL executes query statements
2022-07-27 07:11:00 【adrninistrat0r】
1. Preface
The following for MySQL The main steps of executing query statements are analyzed , Connection optimization is not involved 、 Sorting optimization and so on .
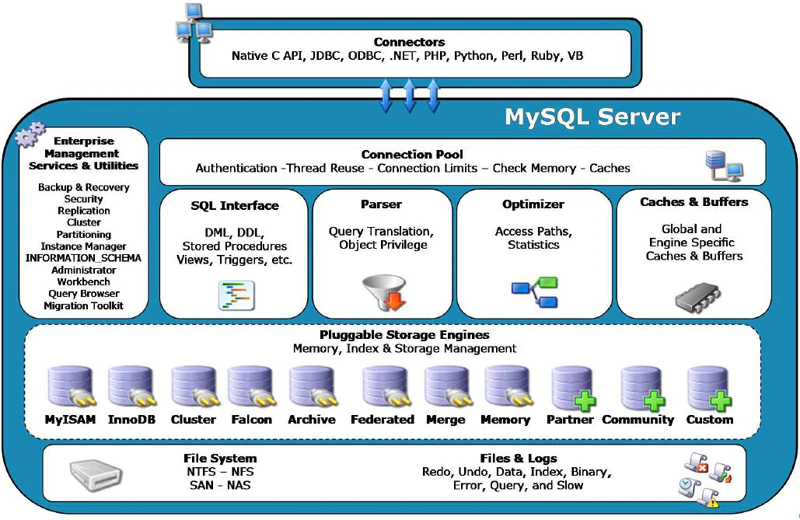
2. MySQL Server architecture
In understanding MySQL How to execute a query statement before , The first thing to understand is MySQL The server (MySQL Server) framework .
MySQL The schematic diagram of server architecture is as follows :
picture source : https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/articles/javase/figure2-large-145676.jpg .
picture source : 《High Performance MySQL, 3rd Edition》 .

MySQL The schematic diagram of module overview is shown below :
picture source : 《Understanding MySQL Internals》 .

The query execution engine is not shown in the above diagram (Query Execution Engine), It is explained in the following content .
2.1. MySQL The relationship between server layer and storage engine
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/storage-engines.html .
Storage engine (Storage engine) It is used to deal with different table types SQL Operation of the MySQL Components .InnoDB It is the default and most common storage engine .
MySQL The server uses a pluggable storage engine architecture , Enable the storage engine to run in MySQL Server load or unload .
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/pluggable-storage-common-layer.html .
MySQL Pluggable storage engines are MySQL Components in the database server , Responsible for executing the actual data of the database I/O operation , And enable and implement certain feature sets for specific application requirements .
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/mysqld.html .
mysqld, Also known as MySQL The server , Is in MySQL The main program that completes most of the work in the facility .MySQL The server is responsible for MySQL Manage access to data directories . The data directory is also the default location for storing other information ( For example, log files and status files ).
When MySQL When the server starts , Will listen for network connections from client programs , And manage access to the database on behalf of these clients .
MySQL The server also has a set of system variables , These variables will be MySQL The operation of the server is affected when it is running .MySQL The server also has a set of state variables , These variables provide information about MySQL Information about server operation .
3. MySQL Query statement execution process
Please refer to 《High Performance MySQL, 3rd Edition》.
towards MySQL( The server ) When sending query statement ,MySQL Follow the steps below :
(MySQL) The client will SQL The statement is sent to (MySQL) The server ;
The server checks the query cache . If hit , Return the stored results from the cache ; otherwise , take SQL Statement is passed to the next step ;
Server pair SQL To analyze 、 Preprocessing , And optimize SQL Execute plan for query ;
The query execution engine calls the storage engine API To implement the plan ;
The server sends the results to the client .
The execution steps of query statements are shown in the following figure :

You can see the steps of query statement execution , The following will be covered :
MySQL client / Server protocol
The query cache
Parser and preprocessor
Optimizer
Query execution engine
Returns the result to the client
3.1. MySQL client / Server protocol
MySQL client / Server protocol (The MySQL Client/Server Protocol) It's half duplex , This means at any given time ,MySQL Servers can send or receive messages , But you cannot send or receive messages at the same time . This also means that there is no way to shorten the message .
The above agreement makes MySQL Communication becomes simple and fast , But there are also limitations in some aspects . This means that there is no flow control ; Once a party sends a message , The other party must get the whole message before responding .
3.2. The query cache
Before parsing the query , If query caching is enabled (Query Cache),MySQL The query will be checked in the query cache . This operation is a case sensitive hash lookup . If the query is different from similar queries in the cache , Even if there is only one byte difference , It won't match , Query processing will enter the next stage .
Reference resources https://mysqlserverteam.com/mysql-8-0-retiring-support-for-the-query-cache/ .
from MySQL 8.0 Start , Query caching is no longer supported .
Even though MySQL Query Cache Designed to improve performance , But it has serious scalability problems , And it's easy to be a serious bottleneck .
from MySQL 5.6 rise , Query caching is disabled by default , Because it is well known that it cannot scale with high throughput workloads on multi-core computers .
Suppose scalability can be improved , The limiting factor of query cache is , Because only queries that hit the cache will be improved ; It is unlikely to improve the predictability of performance . For user oriented systems , Reducing performance differences is usually more important than increasing throughput peaks .
When the cache is close to the client , Caching can bring the greatest benefits .
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/query-cache-in-select.html , Specify SQL_CACHE, When the query cache is available , The query results can be cached ; Specify SQL_NO_CACHE,MySQL The server will not use the query cache .
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/query-cache-configuration.html 、
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/server-system-variables.html .
Whether the query cache is enabled is determined by the system variable query_cache_size And query_cache_type decision . When query_cache_size by 0, or query_cache_type When it is off , The query cache will be closed .
query_cache_size The default value is 1M,query_cache_type The default is off . Query cache is off by default .
Reference resources https://mariadb.com/kb/en/server-system-variables .
stay MariaDB in , Greater than or equal to 10.1.7 Version of query_cache_size The default value is 1M,query_cache_type The default is off ; Less than or equal to 10.1.6 Version of query_cache_size The default value is 0,query_cache_type The default is enabled . That is, query cache is turned off by default .
3.3. Query optimization process
In the next step of the query step , Will SQL Query is transformed into query execution engine (query execution engine) Processing execution plan (execution plan). There are several sub steps : analysis , Preprocessing and optimization .
3.3.1. Parser and preprocessor
First ,MySQL The parser (parser ) Decompose the query , And build “ The parse tree ”(parse tree). Parser usage MySQL Of SQL Syntax to interpret and validate queries .
then , The preprocessor (preprocessor ) Other semantics that cannot be parsed by the parser will be checked in the result parsing tree .
Next , The preprocessor checks the permissions . This is usually very fast , Unless the server has a lot of permissions .
3.3.2. Optimizer
Parse tree is currently valid , Available to the optimizer (optimizer ) Convert it into a query execution plan . Queries can usually be executed in many different ways , And produce the same result . The job of the optimizer is to find the best option .
MySQL Use a cost based optimizer , This means that it will try to predict the cost of various implementation plans , And choose the lowest cost implementation plan .
MySQL Query optimizer is a very complex software , It uses many optimizations to transform queries into execution plans .
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/internals/en/optimizer-definitions.html , The narrow definition of optimizer is : The optimizer is a set of routines , decision DMBS What execution path to use when executing queries .
Reference resources 《Understanding MySQL Internals》,MySQL The optimizer of has the following important tasks :
Determine which index keys can be used to retrieve records from the table , And choose the best index key for each table ;
For each table , Determine whether a full table scan is better than reading through an index key . If there are many records matching the key value , The advantage of reading through the index key will be reduced , And full table scanning will become faster ;
When there are multiple tables in the query , Determine the order in which tables are joined ;
rewrite (rewrite)WHERE Clause to eliminate invalid code , Reduce unnecessary calculations , And change constraints if possible , So that the index key can be used ;
Delete unused tables from the connection ;
Determines whether the index key is available for ORDER BY and GROUP BY;
Try replacing the outer connection with the inner connection ;
Try simplifying subqueries , And determine how far its results can be cached ;
Merge views ( Expand the View reference to a macro ).
3.3.2.1. Table and index data
Including query optimizer MySQL Server layer , Do not store statistics about data and indexes . This is the job of the storage engine , Because each storage engine may retain different kinds of Statistics ( Or save it in different ways ).
because MySQL The server does not store statistics , therefore MySQL The query optimizer must obtain the statistics of the tables in the query from the storage engine . The storage engine provides statistics for the optimizer , For example, the number of pages per table or index , Cardinality of tables and indexes , Length of rows and index keys , And index key distribution information . The optimizer can use the above information to help determine the best execution plan .
3.3.2.2. Implementation plan
Many other database products generate bytecode to execute queries ,MySQL Unlike them ,MySQL No bytecode will be generated to execute the query . contrary , The query execution plan is actually an instruction tree , The query execution engine will generate query results according to the query execution plan instruction tree . The final plan contains enough information to rebuild the original query .
3.4. Query execution engine
The parsing and optimization phase outputs the query execution plan ,MySQL The query execution engine of will use the query execution plan to process the query . Query execution plan is a data structure , Not executable bytecode .
Compared with the optimization stage , The execution phase is usually not that complicated :MySQL Only follow the instructions given in the query execution plan . Many operations in the query execution plan call the methods implemented by the storage engine interface , Also known as handler API.
On query execution ,MySQL The server only needs to repeat the instructions , Until there are no more lines to check .
Reference resources MySQL About in the document MySQL Schematic diagram of the server accessing the storage engine , It can be seen that the middle will pass handler API, The picture address is https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/images/innodb_memcached2.jpg , As shown below :

3.5. Returns the result to the client
The last step in executing the query is to reply to the client . Even if the query does not return a result set , Information about queries will still be used ( For example, the number of rows affected ), Reply to the client connection .
If the query is cacheable ,MySQL At this stage, the results will also be put into the query cache .
MySQL The server gradually generates and sends results . When MySQL When the last table is processed and a row is successfully generated , It can and should send this line to the client .
The above has two advantages : Make the server avoid keeping rows in memory ; This means that the client will start getting results as soon as possible .
Each row of the result set is marked with MySQL client / The server protocol sends separate packets , Agreement package in TCP The protocol layer can buffer and merge sending .
4. WHERE Clause execution
Usually ,MySQL There are three ways to deal with WHERE Clause , The following are the best to worst treatment methods :
Apply conditions to index lookup operations , With ( From the query results ) Eliminate mismatched rows . The above occurs in the storage engine layer ;
Use overlay index (covering index) Avoid accessing rows , And filter out mismatched rows after getting each result from the index . The above occurs in the server layer , But you don't need to read rows from the table ;
Retrieve rows from the table , Then filter the mismatched rows . This happens at the server layer , The server needs to read rows from the table to filter them .
5. MySQL Statement execution process analysis method
5.1. obtain MySQL Recently executed statement
5.1.1. Use SHOW PROFILES Get the executed statement
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/show-profiles.html 、 https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/show-profile.html .
SHOW PROFILES、SHOW PROFILE Statement display analysis (profiling) Information , Indicates the resource usage of executing statements during the current session .
SHOW PROFILES Displays a list of statements recently sent to the server . The size of the list is determined by the session variable profiling_history_size control , The default value is 15. The maximum value is 100. Set its value to 0 Will disable analysis .
All statements will be analyzed , except SHOW PROFILE And SHOW PROFILES, Therefore, the above statement will not appear in the analysis result list . Malformed statements will appear in the analysis results
Session variables profiling It can be used to control the analysis , The default value is 0(OFF), take profiling The variable value is set to 1 or ON Analysis can be started :
SET profiling = 1;
Analysis is enabled for each session . When the session ends , Its analysis information will be lost .
SHOW PROFILES The output example is as follows :
Query_ID | Duration | Query
---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------
1 | 0.00026232 | select now()
2 | 0.00249026 | select * from test_table
4 | 3.32405767 | select * from test_table_log where other2=2 limit 1
5.2. obtain MySQL Resource usage of recently executed statements
5.2.1. Use SHOW PROFILE Get statement resource usage
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/show-profile.html .
5.2.1.1. SHOW PROFILE Function and enable
SHOW PROFILE Show details about a single statement .
Enable SHOW PROFILE when , You need to set the session variable profiling Set to 1 or ON.
5.2.1.2. SHOW PROFILE grammar
SHOW PROFILE The grammar is as follows :
SHOW PROFILE [type [, type] ... ]
[FOR QUERY n]
[LIMIT row_count [OFFSET offset]]
type Value is optional , Can be used to specify additional types of information that need to be displayed , Optional values include ALL、BLOCK IO、CONTEXT SWITCHES、CPU、IPC、MEMORY、PAGE FAULTS、SOURCE、SWAPS.
without FOR QUERY n Clause , Then output the most recently executed statement . If it includes FOR QUERY n Clause , The second n Information of statements .n The value of corresponds to SHOW PROFILES According to the Query_ID value .
By default ,SHOW PROFILE Show Status And Duration Column .Status The value of the column is the same as SHOW PROCESSLIST Displayed State The value is similar to .
5.2.1.3. SHOW PROFILE Output format
SHOW PROFILE In the output Status field value , May refer to https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/general-thread-states.html .
For query statement execution SHOW PROFILE, In the output result Status The common values of the column are as follows :
starting
checking permissions
Opening tables
After opening tables
System lock
Table lock
After opening tables
init
optimizing
statistics
preparing
executing
Sending data
end
query end
closing tables
freeing items
updating status
logging slow query
cleaning up
Sending data Indicates that the thread is reading and processing rows for the query statement , And send the data to the client . Because operations in this state usually require a lot of disk access ( Read ), Therefore, this state is usually the longest running state in a given query lifecycle .
The meaning of other states is close to the displayed name , And MySQL The execution steps when executing the statement correspond to .
SHOW PROFILE In the output Duration Column , Represents the execution time of the statement in the specified state , The unit is in seconds .
SHOW PROFILE The meaning of the remaining columns in the output can be referred to INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROFILING Table description .
5.2.2. Get the statement resource usage from the database table
Reference resources https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.6/en/profiling-table.html .
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROFILING Table provides analysis information of statements , Its content is similar to SHOW PROFILE and SHOW PROFILES The information generated by the statement corresponds to .
Session variables profiling I need to set to 1, Otherwise, the above table is empty .
INFORMATION_SCHEMA.PROFILING The table contains the following columns of interest :
- QUERY_ID
The numeric form identifier of the statement ;
- SEQ
Serial number , Indicates the same QUERY_ID The order in which the rows of values are displayed ;
- STATE
Same as SHOW PROFILE In the output result Status Column ;
- DURATION
Same as SHOW PROFILE In the output result Duration Column ;
- SOURCE_FUNCTION, SOURCE_FILE, SOURCE_LINE
Information indicating the source code location of the analyzed state execution .
边栏推荐
- 李沐动手学深度学习V2-transformer和代码实现
- Error in running code: libboost_ filesystem.so.1.58.0: cannot open shared object file: No such file or directory
- jest单测样式问题【identity-obj-proxy】npm包
- CentOS上使用Docker安装和部署Redis
- What is OKR and what is the difference between OKR and KPI
- 2021 interview questions for php+go of Zhongda factory (2)
- deepsort源码解读(七)
- TS learning (VIII): classes in TS
- 网易云信亮相 GIAC 全球互联网架构大会,解密新一代音视频架构在元宇宙场景的实践...
- DNA科研实验应用|环糊精修饰核酸CD-RNA/DNA|环糊精核酸探针/量子点核酸探针
猜你喜欢

newest! SASAC releases new measures for digital transformation of state-owned enterprises

基于SSM图书借阅管理系统

内部类--看这篇就懂啦~

pytorch笔记:TD3

Netease Yunxin appeared at the giac global Internet architecture conference to decrypt the practice of the new generation of audio and video architecture in the meta universe scene

PNA modified polypeptide arms PNA PNA DNA suc aapf PNA suc - (ALA) 3 PNA

脱氧核糖核酸DNA改性近红外二区砷化镓GaAs量子点|GaAs-DNA QDs|DNA修饰GaAs量子点

Image super-resolution evaluation index

把Excel转换成CSV/CSV UTF-8

Variance and covariance
随机推荐
DNA modified zinc oxide | DNA modified gold nanoparticles | DNA coupled modified carbon nanomaterials
2021 interview question of php+go for Zhongda factory (1)
Matlab drawing (ultra detailed)
Gbase 8C - SQL reference 6 SQL syntax (11)
vscode运行命令报错:标记“&&”不是此版本中的有效语句分隔符。
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) supply | carbon nanotube nucleic acid loaded dna/rna material | dna/rna nucleic acid modified magnetic nanoparticles
How to delete or replace the loading style of easyplayer streaming media player?
PNA肽核酸修饰多肽Suc-Tyr-Leu-Val-pNA|Suc-Ala-Pro-Phe-pNA 11
MangoDB
指令集董事长潘爱民出席2022 ECUG Con,为中国技术力量发声
Visual horizontal topic bug1:filenotfounderror: could not find module 'mvcameracontrol dll‘ (or one of it
PNA修饰多肽ARMS-PNA|PNA-DNA|suc-AAPF-pNA|Suc-(Ala)3-pNA
Dajiang livox customized format custommsg format conversion pointcloud2
泛型 -- 学会它,好处多多
Cyclegan parsing
Brief introduction of simulation model
DNA modified noble metal nanoparticles | DNA modified gold nanoparticles (scientific research level)
Two ways of multi GPU training of pytorch
【Latex格式】双栏双图左右并排有小标题、上下并列有小标题
基于SSM图书借阅管理系统