当前位置:网站首页>pytorch笔记:TD3
pytorch笔记:TD3
2022-07-27 05:43:00 【UQI-LIUWJ】
参考代码来源:easy-rl/codes/TD3 at master · datawhalechina/easy-rl (github.com)
理论部分:强化学习笔记:双延时确定策略梯度 (TD3)_UQI-LIUWJ的博客-CSDN博客
1 task1_train.py
1.1 导入库
import sys,os
curr_path = os.path.dirname(__file__)
parent_path=os.path.dirname(curr_path)
sys.path.append(parent_path) # add current terminal path to sys.path
import torch
import gym
import numpy as np
import datetime
from agent import TD3
from utils import save_results,make_dir,plot_rewards
curr_time = datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y%m%d-%H%M%S")
# 获取当前时间1.2 TD3Config
TD3的一些基本配置
class TD3Config:
def __init__(self) -> None:
self.algo = 'TD3'
# 算法名称
self.env_name = 'Pendulum-v1'
# 环境名称
self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# 是否使用GPU
self.train_eps = 600
# 训练的回合数
self.epsilon_start = 50
#在这一步之前的episode,随机选择动作;
#在这一步之后的episode,根据actor选择动作
self.eval_freq = 10
# 多少轮episode输出一次中间结果
self.max_timestep = 100000
# 一个episode最大迭代多少轮
self.expl_noise = 0.1
#exploration的时候,高斯噪声的标准差
self.batch_size = 256
# actor和critic的batch size
self.gamma = 0.9
# 折扣因子
self.lr=3e-4
# 学习率
self.soft = 0.0005
# 软更新大小
self.policy_noise = 0.2
# 在更新actor的时候,往动作上加截断正态分布,这个policy_noise是乘在N(0,1)上的系数
self.noise_clip = 0.3
# 在更新actor的时候,往动作上加截断正态分布,这个noise_clip就是截断值
self.policy_freq = 2
#不是每一步都更新actor和目标网络,隔几步再更新它们1.3 PlotConfig
绘图路径的一些配置
class PlotConfig(TD3Config):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.result_path = "./outputs/" + self.env_name + '/'+curr_time+'/results/'
print(self.result_path)
# 保存结果的路径
self.model_path = "./outputs/" + self.env_name + '/'+curr_time+'/models/'
# 保存模型的路径
self.save = True
# 是否保存图片1.4 train
def train(cfg,env,agent):
print('开始训练!')
print(f'环境:{cfg.env_name}, 算法:{cfg.algo}, 设备:{cfg.device}')
rewards = []
# 记录所有回合的奖励
ma_rewards = []
# 记录所有回合的滑动平均奖励
for i_ep in range(int(cfg.train_eps)):
ep_reward = 0
ep_timesteps = 0
state, done = env.reset(), False
while not done:
ep_timesteps += 1
if i_ep < cfg.epsilon_start:
action = env.action_space.sample()
#随机选择动作
else:
action = (
agent.choose_action(np.array(state))
+ np.random.normal(0, max_action * cfg.expl_noise, size=n_actions)
).clip(-max_action, max_action)
#根据actor选择动作,然后添加高斯噪声,最后进行截断(保证动作是一个可行的动作)
'''
一开始critic都不准的时候,如果贸然使用critic来辅佐actor选择动作,可能效果不太好,所以一开始随机选择action,来train critic
到一定程度之后,critic已经训出一点感觉了,就可以使用actor来选择动作了
'''
next_state, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
#用这个action和环境进行交互
done_bool = float(done) if ep_timesteps < env._max_episode_steps else 0
#是否是终止状态(有无后续的state)
#两种情况没有后续state:到达最大的episode数量/环境返回终止状态
agent.memory.push(state, action, next_state, reward, done_bool)
#将transition存入经验回放中
state = next_state
ep_reward += reward
# Train agent after collecting sufficient data
if i_ep+1 >= cfg.epsilon_start:
agent.update()
#在此之间,由于动作都是随机选的,和actor的决策无关,所以不用更新actor
if (i_ep+1)%cfg.eval_freq == 0:
print('回合:{}/{}, 奖励:{:.2f}'.format(i_ep+1, cfg.train_eps, ep_reward))
rewards.append(ep_reward)
if ma_rewards:
ma_rewards.append(0.9*ma_rewards[-1]+0.1*ep_reward)
else:
ma_rewards.append(ep_reward)
#滑动平均奖励
print('完成训练!')
return rewards, ma_rewards
1.5 eval
def eval(env_name,agent, eval_episodes=10):
eval_env = gym.make(env_name)
rewards,ma_rewards =[],[]
for i_episode in range(eval_episodes):
ep_reward = 0
state, done = eval_env.reset(), False
while not done:
# eval_env.render()
action = agent.choose_action(np.array(state))
#根据学到的agent的actor选择action
state, reward, done, _ = eval_env.step(action)
ep_reward += reward
print(f"Episode:{i_episode+1}, Reward:{ep_reward:.3f}")
rewards.append(ep_reward)
# 计算滑动窗口的reward
if ma_rewards:
ma_rewards.append(0.9*ma_rewards[-1]+0.1*ep_reward)
else:
ma_rewards.append(ep_reward)
return rewards,ma_rewards1.6 主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
cfg = TD3Config()
#配置TD3相关的参数
plot_cfg = PlotConfig()
#配置画图的路径
env = gym.make(cfg.env_name)
#导入环境
env.seed(1)
torch.manual_seed(1)
np.random.seed(1)
# 设置随机种子
n_states = env.observation_space.shape[0]
n_actions = env.action_space.shape[0]
#根据环境确定状态数和动作数
max_action = float(env.action_space.high[0])
#动作空间最大的数值(2.0)
agent = TD3(n_states,n_actions,max_action,cfg)
#初始化模型
#输入维度为3,输出维度为1
rewards,ma_rewards = train(cfg,env,agent)
#训练TD3
make_dir(plot_cfg.result_path,plot_cfg.model_path)
#逐个创建文件夹
agent.save(path=plot_cfg.model_path)
#保存actor和critic的路径
save_results(rewards,ma_rewards,tag='train',path=plot_cfg.result_path)
#保存 奖励和滑动奖励
plot_rewards(rewards,ma_rewards,plot_cfg,tag="train")
#绘图
###############################测试部分##########################################
eval_agent=TD3(n_states,n_actions,max_action,cfg)
eval_agent.load(path=plot_cfg.model_path)
rewards,ma_rewards = eval(cfg.env_name,eval_agent)
make_dir(plot_cfg.result_path_eval)
save_results(rewards,ma_rewards,tag='eval',path=plot_cfg.result_path_eval)
plot_rewards(rewards,ma_rewards,plot_cfg,tag="eval")
################################################################################
2 agent.py

2.1 导入库
import copy
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from TD3.memory import ReplayBuffer2.2 Actor
class Actor(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim, max_action):
'''[summary]
Args:
input_dim (int): 输入维度,这里等于n_states
output_dim (int): 输出维度,这里等于n_actions
max_action (int): action的最大值
'''
super(Actor, self).__init__()
self.l1 = nn.Linear(input_dim, 256)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.l3 = nn.Linear(256, output_dim)
self.max_action = max_action
def forward(self, state):
a = F.relu(self.l1(state))
a = F.relu(self.l2(a))
return self.max_action * torch.tanh(self.l3(a))
#经过tanh之后,返回[-1,1]区间的内容,再乘上max_action,就是环境需要的action范围2.3 Critic
class Critic(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, output_dim):
super(Critic, self).__init__()
# Q1 architecture
self.l1 = nn.Linear(input_dim + output_dim, 256)
self.l2 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.l3 = nn.Linear(256, 1)
# Q2 architecture
self.l4 = nn.Linear(input_dim + output_dim, 256)
self.l5 = nn.Linear(256, 256)
self.l6 = nn.Linear(256, 1)
'''
相当于把TD3图中的目测策略网络1和目标策略网络2在一个class中实现了
'''
def forward(self, state, action):
sa = torch.cat([state, action], 1)
q1 = F.relu(self.l1(sa))
q1 = F.relu(self.l2(q1))
q1 = self.l3(q1)
q2 = F.relu(self.l4(sa))
q2 = F.relu(self.l5(q2))
q2 = self.l6(q2)
return q1, q2
def Q1(self, state, action):
sa = torch.cat([state, action], 1)
q1 = F.relu(self.l1(sa))
q1 = F.relu(self.l2(q1))
q1 = self.l3(q1)
return q12.4 TD3
class TD3(object):
def __init__(
self,
input_dim,
output_dim,
max_action,
cfg,
):
self.max_action = max_action
#动作空间最大的数值(2.0)
self.gamma = cfg.gamma
# 折扣因子
self.lr = cfg.lr
# 学习率
self.soft=cfg.soft
# 软更新大小
self.policy_noise = cfg.policy_noise
# 在更新actor的时候,往动作上加截断正态分布,这个policy_noise是乘在N(0,1)上的系数
self.noise_clip = cfg.noise_clip
# 在更新actor的时候,往动作上加截断正态分布,这个noise_clip就是截断值
self.policy_freq = cfg.policy_freq
#不是每一步都更新actor,隔几步再更新actor(但是每一步都更新critic)
self.batch_size = cfg.batch_size
#actor和critic的batch size
self.device = cfg.device
#进行训练的设备
self.total_it = 0
#迭代次数的计数器(由于区分哪些步骤需要更新actor和目标函数)
self.actor = Actor(input_dim, output_dim, max_action).to(self.device)
self.actor_target = copy.deepcopy(self.actor)
#目标策略网络
self.actor_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.actor.parameters(), lr=self.lr)
self.critic = Critic(input_dim, output_dim).to(self.device)
self.critic_target = copy.deepcopy(self.critic)
#目标价值网络(这里将TD3的两个目标价值网络二合一了)
self.critic_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.critic.parameters(), lr=self.lr)
self.memory = ReplayBuffer(input_dim, output_dim)
#经验回放
def choose_action(self, state):
state = torch.FloatTensor(state.reshape(1, -1)).to(self.device)
#state[3]——>[1,3]
return self.actor(state).cpu().data.numpy().flatten()
#[1,3]——>[1]
def update(self):
self.total_it += 1
# Sample replay buffer
state, action, next_state, reward, not_done = self.memory.sample(self.batch_size)
with torch.no_grad():
# Select action according to policy and add clipped noise
noise = (
torch.randn_like(action) * self.policy_noise
).clamp(-self.noise_clip, self.noise_clip)
#截断正态分布
next_action = (
self.actor_target(next_state) + noise
).clamp(-self.max_action, self.max_action)
#加上截断高斯分布的next_action
#目标策略网络的输出
# Compute the target Q value
target_Q1, target_Q2 = self.critic_target(next_state, next_action)
#两个目标策略网络的输出
target_Q = torch.min(target_Q1, target_Q2)
#用两个目标策略网络输出较小的一个作为下一个时刻TD target
target_Q = reward + not_done * self.gamma * target_Q
#根据是否终止 计算当前时刻的TD target
current_Q1, current_Q2 = self.critic(state, action)
#两个价值网络的输出
critic_loss = F.mse_loss(current_Q1, target_Q) + F.mse_loss(current_Q2, target_Q)
self.critic_optimizer.zero_grad()
critic_loss.backward()
self.critic_optimizer.step()
#同步更新两个价值网络的参数
if self.total_it % self.policy_freq == 0:
#不是每一步都更新actor和目标网络,隔几步再更新它们(但是每一步都更新critic)
actor_loss = -self.critic.Q1(state, self.actor(state)).mean()
#计算actor的loss
#根据TD3,只是价值网络1的输出,所以这里只是Q1的value
self.actor_optimizer.zero_grad()
actor_loss.backward()
self.actor_optimizer.step()
#更新actor
for param, target_param in zip(self.critic.parameters(), self.critic_target.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(self.soft * param.data + (1 - self.soft) * target_param.data)
for param, target_param in zip(self.actor.parameters(), self.actor_target.parameters()):
target_param.data.copy_(self.soft * param.data + (1 - self.soft) * target_param.data)
#软更新目标网络
def save(self, path):
torch.save(self.critic.state_dict(), path + "td3_critic")
torch.save(self.critic_optimizer.state_dict(), path + "td3_critic_optimizer")
torch.save(self.actor.state_dict(), path + "td3_actor")
torch.save(self.actor_optimizer.state_dict(), path + "td3_actor_optimizer")
def load(self, path):
self.critic.load_state_dict(torch.load(path + "td3_critic"))
self.critic_optimizer.load_state_dict(torch.load(path + "td3_critic_optimizer"))
self.critic_target = copy.deepcopy(self.critic)
self.actor.load_state_dict(torch.load(path + "td3_actor"))
self.actor_optimizer.load_state_dict(torch.load(path + "td3_actor_optimizer"))
self.actor_target = copy.deepcopy(self.actor)
3 memory.py
import numpy as np
import torch
class ReplayBuffer(object):
def __init__(self, n_states, n_actions, max_size=int(1e6)):
self.max_size = max_size
#经验回放的最大大小
self.ptr = 0
#当前指针位置(下一个push进来的值的坐标)
self.size = 0
#当前经验回放的大小
self.state = np.zeros((max_size, n_states))
self.action = np.zeros((max_size, n_actions))
self.next_state = np.zeros((max_size, n_states))
self.reward = np.zeros((max_size, 1))
self.not_done = np.zeros((max_size, 1))
self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def push(self, state, action, next_state, reward, done):
#将transition放入经验回放中
self.state[self.ptr] = state
self.action[self.ptr] = action
self.next_state[self.ptr] = next_state
self.reward[self.ptr] = reward
self.not_done[self.ptr] = 1. - done
self.ptr = (self.ptr + 1) % self.max_size
self.size = min(self.size + 1, self.max_size)
def sample(self, batch_size):
#随机采样batch_size个transition
ind = np.random.randint(0, self.size, size=batch_size)
return (
torch.FloatTensor(self.state[ind]).to(self.device),
torch.FloatTensor(self.action[ind]).to(self.device),
torch.FloatTensor(self.next_state[ind]).to(self.device),
torch.FloatTensor(self.reward[ind]).to(self.device),
torch.FloatTensor(self.not_done[ind]).to(self.device)
)
4 utils.py
import os
import numpy as np
from pathlib import Path
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
4.1 plot_rewards
def plot_rewards(rewards, ma_rewards, plot_cfg, tag='train'):
sns.set()
plt.figure()
plt.title("learning curve on {} of {}".format(plot_cfg.device, 'TD3'))
plt.xlabel('epsiodes')
plt.plot(rewards, label='rewards')
plt.plot(ma_rewards, label='ma rewards')
#分别画出奖励和滑动奖励的图
plt.legend()
if plot_cfg.save:
plt.savefig(plot_cfg.result_path+"{}_rewards_curve".format(tag))
plt.show()
4.2 save_results
def save_results(rewards, ma_rewards, tag='train', path='./results'):
''' 保存奖励
'''
np.save(path+'{}_rewards.npy'.format(tag), rewards)
np.save(path+'{}_ma_rewards.npy'.format(tag), ma_rewards)
print('结果保存完毕!')4.3 make_dir
def make_dir(*paths):
''' 创建文件夹
'''
for path in paths:
Path(path).mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)5 输出结果

边栏推荐
- Web configuration software for industrial control is more efficient than configuration software
- deepsort源码解读(七)
- Problems related to pytorch to onnx
- Basic statement of MySQL (1) - add, delete, modify and query
- Pytorch uses data_ Prefetcher improves data reading speed
- AI:业余时间打比赛—挣它个小小目标—【阿里安全×ICDM 2022】大规模电商图上的风险商品检测比赛
- Working principle analysis of deepsort
- String类的用法
- MangoDB
- CASS11.0.0.4 for AutoCAD2010-2023免狗使用方法
猜你喜欢
![AI: play games in your spare time - earn it a small goal - [Alibaba security × ICDM 2022] large scale e-commerce map of risk commodity inspection competition](/img/d8/a367c26b51d9dbaf53bf4fe2a13917.png)
AI: play games in your spare time - earn it a small goal - [Alibaba security × ICDM 2022] large scale e-commerce map of risk commodity inspection competition

Watermelon book learning Chapter 5 --- neural network

Significance of NVIDIA SMI parameters

(转帖)eureka、consul、nacos的对比2

regular expression
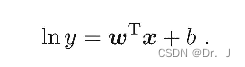
Watermelon book chapter 3 - linear model learning notes
脱氧核糖核酸DNA修饰氧化锌|DNA修饰纳米金颗粒|DNA偶联修饰碳纳米材料

DNA coupled PbSe quantum dots | near infrared lead selenide PbSe quantum dots modified DNA | PbSe DNA QDs

Qi Yue: thiol modified oligodna | DNA modified cdte/cds core-shell quantum dots | DNA coupled indium arsenide InAs quantum dots InAs DNA QDs

CentOS上使用Docker安装和部署Redis
随机推荐
Student achievement management system based on SSM
Book borrowing management system based on SSM
Music website management system based on SSM
Campus news release management system based on SSM
Dsgan degenerate network
硫化镉CdS量子点修饰脱氧核糖核酸DNA|CdS-DNA QDs|近红外CdS量子点偶联DNA规格信息
Jest single test style problem [identity obj proxy] NPM package
Shell programming specifications and variables
How to delete or replace the loading style of easyplayer streaming media player?
Watermelon book chapter 3 - linear model learning notes
Code random notes_ Hash_ 242 effective letter heterotopic words
齐岳:巯基修饰寡聚DNA|DNA修饰CdTe/CdS核壳量子点|DNA偶联砷化铟InAs量子点InAs-DNA QDs
TS learning (VIII): classes in TS
Day012 一维数组的应用
基于SSM医院预约管理系统
Interpretation of deepsort source code (VII)
Dajiang livox customized format custommsg format conversion pointcloud2
regular expression
【11】 Binary code: "holding two roller handcuffs, crying out for hot hot hot"?
Express receive request parameters