当前位置:网站首页>Batch normalization (Standardization) processing
Batch normalization (Standardization) processing
2022-07-07 05:01:00 【Yinque Guangqian】
In fact, the normalization of sample data , We're in the front Kaggle Practice of house price prediction (K Crossover verification ) Have done good specific experiments , Also got good results , Here we mainly focus on how to normalize , And why we should do such a treatment , What are the benefits .
When we get the data samples , There are usually some exceptions ( Relatively speaking, it is larger or smaller ) The sample of , Or the dispersion of samples is very high , So when we are training , We need to do some extra work , For example, normalization is done , You will get the following two obvious benefits .
1、 The output of each layer in the depth model will be more stable , Because after normalization , The characteristics of the sample are concentrated in a section ( such as , The mean for 0, The standard deviation is 1), So it's eliminated “ Abnormal samples ” Adverse effects , Because the distribution is relatively uniform , So it will be easier to train an effective model .
2、 In training , Convergence will be faster , This is very helpful for deepening the model .
How to do normalization , There are many ways , such as : Maximum and minimum standardization 、log Logarithmic function normalization 、 Normalization of arctangent function 、 L2 Norm normalization, etc , This paper mainly introduces a method commonly used in Neural Networks , The picture is more intuitive , Let's look at the picture first ( Pretty simple , Find the mean and variance , Then do a division operation ):

Normalized layer
First find the mean and variance , Then the eigenvalue is subtracted from the mean and divided by the variance , The normalized processing data is obtained
import d2lzh as d2l
from mxnet import gluon,init,nd,autograd
from mxnet.gluon import nn
# Batch normalization
'''
There is one more γ and β Parameters , They are learnable stretch and offset parameters
If batch normalization is not beneficial , These two parameters can determine the input X Do not normalize
moving_mean,moving_var These two parameters are moving average and variance , It is estimated in the whole training data set
Therefore, the calculation results of training mode and prediction mode are different
'''
def batch_norm(X,gamma,beta,moving_mean,moving_var,eps,momentum):
if not autograd.is_training():
# The prediction model directly uses the estimated moving average and variance
X_hat=(X-moving_mean)/nd.sqrt(moving_var+eps)
else:
# Training mode , It is divided into 2 dimension ( Fully connected layer ) And 4 dimension ( Convolution layer )
assert(X.ndim in (2,4))
if X.ndim==2:
meanV=X.mean(axis=0)
var=((X-meanV)**2).mean(axis=0)
else:
meanV=X.mean(axis=(0,2,3),keepdims=True)
var=((X-meanV)**2).mean(axis=(0,2,3),keepdims=True)
X_hat=(X-meanV)/nd.sqrt(var+eps)
# Update the mean and variance of the moving average
moving_mean = momentum * moving_mean + (1.0 - momentum) * meanV
moving_var = momentum * moving_var + (1.0 - momentum) * var
Y=gamma*X_hat+beta
return Y,moving_mean,moving_varCustomize BatchNorm layer
# Parameters num_features In the full connection layer, the number of outputs , Convolution layer is the number of output channels
class BatchNorm(nn.Block):
def __init__(self,num_features,num_dims,**kwargs):
super(BatchNorm,self).__init__(**kwargs)
if num_dims==2:
shape=(1,num_features)
else:
shape=(1,num_features,1,1)
# Stretch and offset parameters involved in gradient and iteration , They are initialized to 1 and 0
self.gamma=self.params.get('gamma',shape=shape,init=init.One())
self.beta=self.params.get('beta',shape=shape,init=init.Zero())
# Variables that do not participate in the gradient sum iteration , All initialized in memory as 0
self.moving_mean=nd.zeros(shape)
self.moving_var=nd.zeros(shape)
def forward(self,X):
# If X Not in memory , take moving_mean,moving_var Copied to the X On the video memory
if self.moving_mean.context!=X.context:
self.moving_mean=self.moving_mean.copyto(X.context)
self.moving_var=self.moving_var.copyto(X.context)
# Save the updated moving_mean and moving_var
Y,self.moving_mean,self.moving_var=batch_norm(X,self.gamma.data(),self.beta.data(),self.moving_mean,self.moving_var,eps=1e-5,momentum=0.9)
return Yadded BN Layer of LeNet Model
#LeNet
net=nn.Sequential()
net.add(nn.Conv2D(6,kernel_size=5),
BatchNorm(6,num_dims=4),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
nn.Conv2D(16,kernel_size=5),
BatchNorm(16,num_dims=4),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
nn.Dense(120),
BatchNorm(120,num_dims=2),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),
nn.Dense(10)
)
lr,num_epochs,batch_size,ctx=1.0,5,256,d2l.try_gpu()
net.initialize(ctx=ctx,init=init.Xavier())
trainer=gluon.Trainer(net.collect_params(),'sgd',{'learning_rate':lr})
train_iter,test_iter=d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size)
d2l.train_ch5(net,train_iter,test_iter,batch_size,trainer,ctx,num_epochs)
'''
epoch 1, loss 0.7461, train acc 0.748, test acc 0.827, time 8.1 sec
epoch 2, loss 0.4090, train acc 0.853, test acc 0.858, time 7.9 sec
epoch 3, loss 0.3635, train acc 0.867, test acc 0.822, time 7.8 sec
epoch 4, loss 0.3268, train acc 0.881, test acc 0.775, time 7.7 sec
epoch 5, loss 0.3099, train acc 0.888, test acc 0.857, time 7.6 sec
'''
# Print gamma and beta data
print(net[1].gamma.data())
'''
[[[[1.5982468]]
[[1.6550801]]
[[1.4356986]]
[[1.1882782]]
[[1.2812225]]
[[1.8739824]]]]
<NDArray 1x6x1x1 @gpu(0)>
'''
print(net[1].beta.data())
'''
[[[[ 1.1335251 ]]
[[-0.18426114]]
[[-0.02497273]]
[[ 0.99639875]]
[[-1.2256573 ]]
[[-2.2048857 ]]]]
'''LeNet Simple implementation of the model
As can be seen from the above ,BN Layers are placed in front of the activation function . In addition, for batch normalization layer , It is already defined in the framework , And there is no need to specify num_features and num_dims, These parameters will be automatically obtained after delayed initialization , Let's look at the effect .
net=nn.Sequential()
net.add(nn.Conv2D(6,kernel_size=5),
nn.BatchNorm(),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
nn.Conv2D(16,kernel_size=5),
nn.BatchNorm(),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),nn.MaxPool2D(pool_size=2,strides=2),
nn.Dense(120),
nn.BatchNorm(),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),
nn.Dense(84),
nn.BatchNorm(),nn.Activation('sigmoid'),
nn.Dense(10)
)
'''
training on gpu(0)
epoch 1, loss 0.6276, train acc 0.779, test acc 0.799, time 5.9 sec
epoch 2, loss 0.3885, train acc 0.859, test acc 0.856, time 5.8 sec
epoch 3, loss 0.3456, train acc 0.875, test acc 0.815, time 5.9 sec
epoch 4, loss 0.3201, train acc 0.885, test acc 0.873, time 5.9 sec
epoch 5, loss 0.3053, train acc 0.888, test acc 0.855, time 6.0 sec
'''Examples of averaging different dimensions
For finding the mean or variance of a dimension , Here is an example , Let everyone know more intuitively , How to operate in different dimensions
import numpy as np
a1=np.arange(10).reshape(2,5)
print(a1)
print(a1[:,0])# View the first set of data in the first dimension [0 5]
print(a1.mean(axis=0))#[2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5]
'''
[[0 1 2 3 4]
[5 6 7 8 9]]
[0 5]
[2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 6.5]
'''
a2=np.arange(30).reshape(2,3,1,5)
print(a2)
print(a2[:,0,:,:])# View channel dimension (NCHW, The second dimension ) The first set of data
print(a2.mean(axis=(0,2,3)))#[ 9.5 14.5 19.5]
'''
[[[[ 0 1 2 3 4]]
[[ 5 6 7 8 9]]
[[10 11 12 13 14]]]
[[[15 16 17 18 19]]
[[20 21 22 23 24]]
[[25 26 27 28 29]]]]
[[[ 0 1 2 3 4]]
[[15 16 17 18 19]]]
[ 9.5 14.5 19.5]
'''
# Keep dimensions the same
print(a2.mean(axis=(0,2,3),keepdims=True))
'''
[[[[ 9.5]]
[[14.5]]
[[19.5]]]]
shape :(1, 3, 1, 1)
'''边栏推荐
- The most complete learning rate adjustment strategy in history LR_ scheduler
- 计数排序基础思路
- JDBC link Oracle reference code
- 3.基金的类型
- 深入解析Kubebuilder
- Using thread class and runnable interface to realize the difference between multithreading
- [line segment tree practice] recent requests + area and retrieval - array modifiable + my schedule I / III
- 组织实战攻防演练的5个阶段
- 架构实战训练营|课后作业|模块 6
- Leetcode longest public prefix
猜你喜欢
【736. Lisp 语法解析】
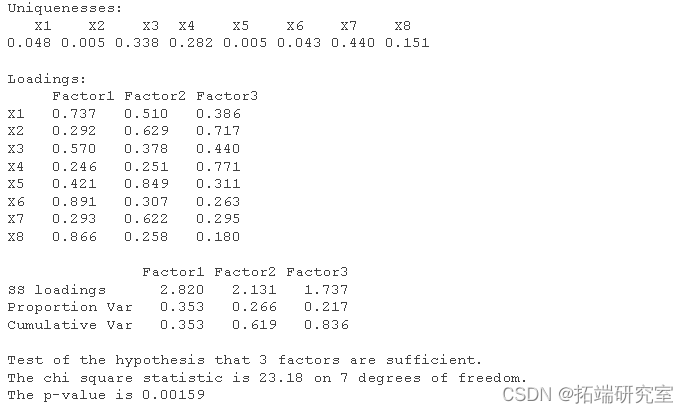
R language principal component PCA, factor analysis, clustering analysis of regional economy analysis of Chongqing Economic Indicators

R语言主成分pca、因子分析、聚类对地区经济研究分析重庆市经济指标

Windows are not cheap things
九章云极DataCanvas公司蝉联中国机器学习平台市场TOP 3
Read of shell internal value command

为什么很多人对技术债务产生误解
Vscode 如何使用内置浏览器?
Oracle - views and sequences
U++ 游戏类 学习笔记
随机推荐
Leetcode notes
Pointer and array are input in function to realize reverse order output
offer如何选择该考虑哪些因素
架构实战训练营|课后作业|模块 6
【736. Lisp 语法解析】
动态生成表格
Basic idea of counting and sorting
National meteorological data / rainfall distribution data / solar radiation data /npp net primary productivity data / vegetation coverage data
组织实战攻防演练的5个阶段
What work items do programmers hate most in their daily work?
Introduction to namespace Basics
Chapter 9 Yunji datacanvas was rated as 36 krypton "the hard core technology enterprise most concerned by investors"
acwing 843. N-queen problem
【Android Kotlin协程】利用CoroutineContext实现网络请求失败后重试逻辑
What is Web3
Decorator basic learning 02
Programmers go to work fishing, so play high-end!
How does vscade use the built-in browser?
Vscode automatically adds a semicolon and jumps to the next line
一文搞懂常见的网络I/O模型