当前位置:网站首页>R language [import and export of dataset]
R language [import and export of dataset]
2022-07-05 05:39:00 【桜キャンドル yuan】
Catalog
One 、 Enter data from keyboard
Four 、 Read the table data file
5、 ... and 、 Read tables from the network or CSV Data files
One 、 Enter data from keyboard
mydata <- data.frame(age=numeric(0), gender=character(0),
weight=numeric(0))
mydata <- edit(mydata)After entering our above code , We enter a text editing mode , We can use vim The syntax command of editing text to edit our data
Two 、 Function method read
1. Read data file
x<-scan(text = "1 2 3")
x
# Enter the file path to read , And store the read data as a vector
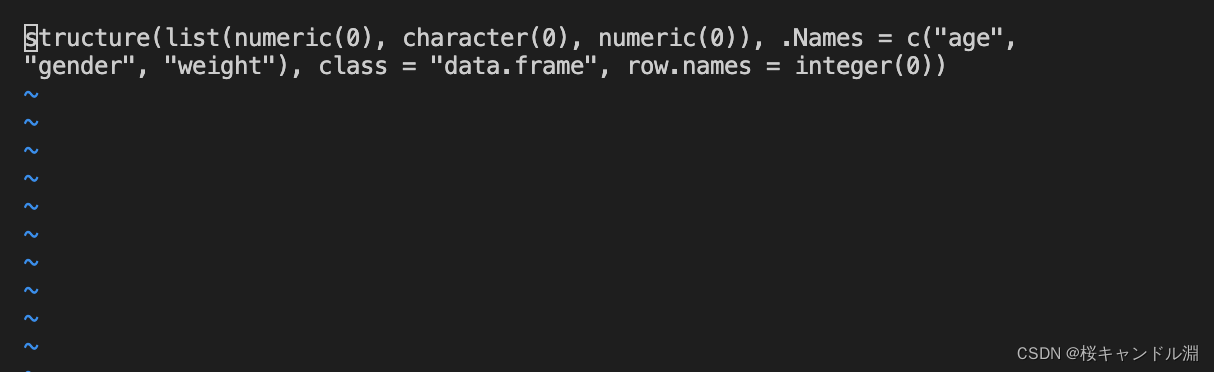
w <- scan("/Users/Documents/R/city.txt")
w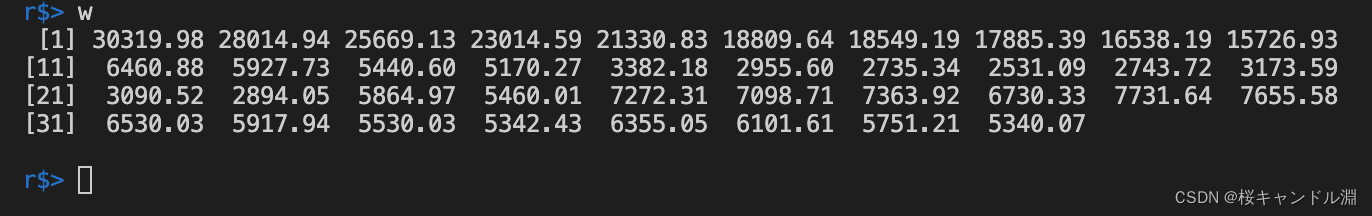
w<-scan("/Users/Documents/R/data/weight.data")
w 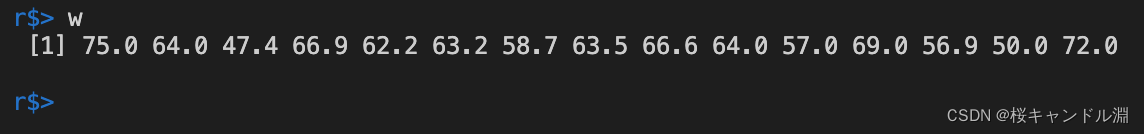
2. Read data from the screen
1.scan
Read numerical data from the screen , After we input our data , We return twice in a row , You can end the input , Generate a numerical vector .
x<-scan()
x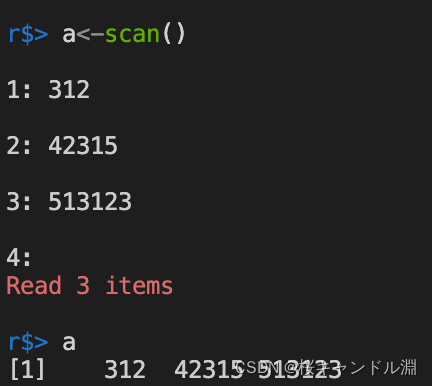
Read string data from the screen
y <- scan(what="")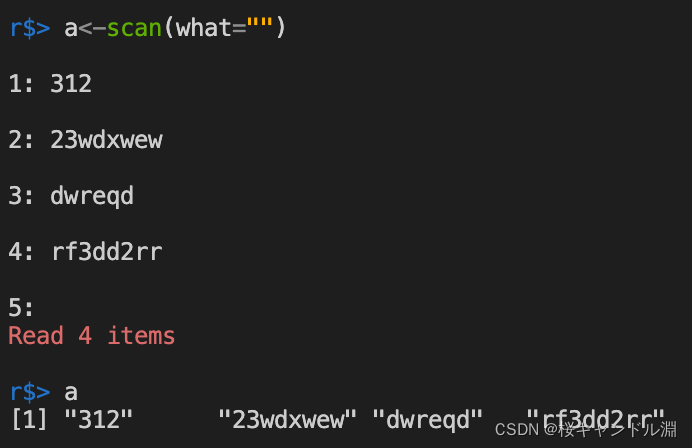
Or use the following method
2.readline
readline It can support reading a line of data input from the keyboard , Press enter to transfer the whole row of data into the variable
x=readline() 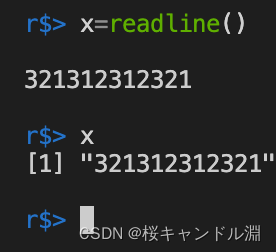
3. Read fixed width data file
The first parameter is the full pathname of our file , The width is a vector ,w1 Represents the width of the first variable ,w2 Indicates the width of the second variable , And so on .
mydata <- read.fwf("filename",widths=c(W1,W2,...,Wn))
mydata1 <- read.fwf("/Users/Documents/R/city.txt",widths=c(4))
mydata1 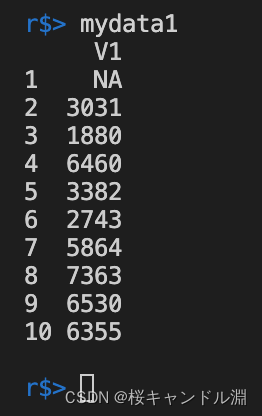
mydata<-read.fwf("/Users/Documents/R/data/FixWideData.txt",widths=c(10,10,4,-1,4)) 
We can also specify col.names Method to specify the name of our index , among -1 Parameter means to ignore the space between two years .( As we R Language entry blog ,-1 Indicates that a column of data is ignored )
mydata2<-read.fwf("/Users/Documents/R/data/FixWideData.txt",widths=c(10,10,4,-1,4),col.names=c("Last","First","Born","Died"))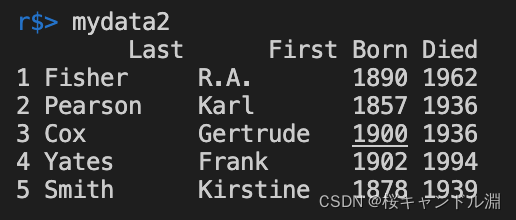
The following image is our data file , We found that although our data is long and short , But it is aligned by spaces , So we can specify the width of the file to read our specific data

However, we found that such data files will have the following errors , This is because we didn't enter at the end of the last line of the data file , Our compiler can't find the sign of our end , Just add a carriage return at the end of the file , It won't be wrong
3、 ... and 、 Read csv file
# Here we will transfer our file path
mydata0<-read.csv("/Users/Documents/R/city.csv")
mydata0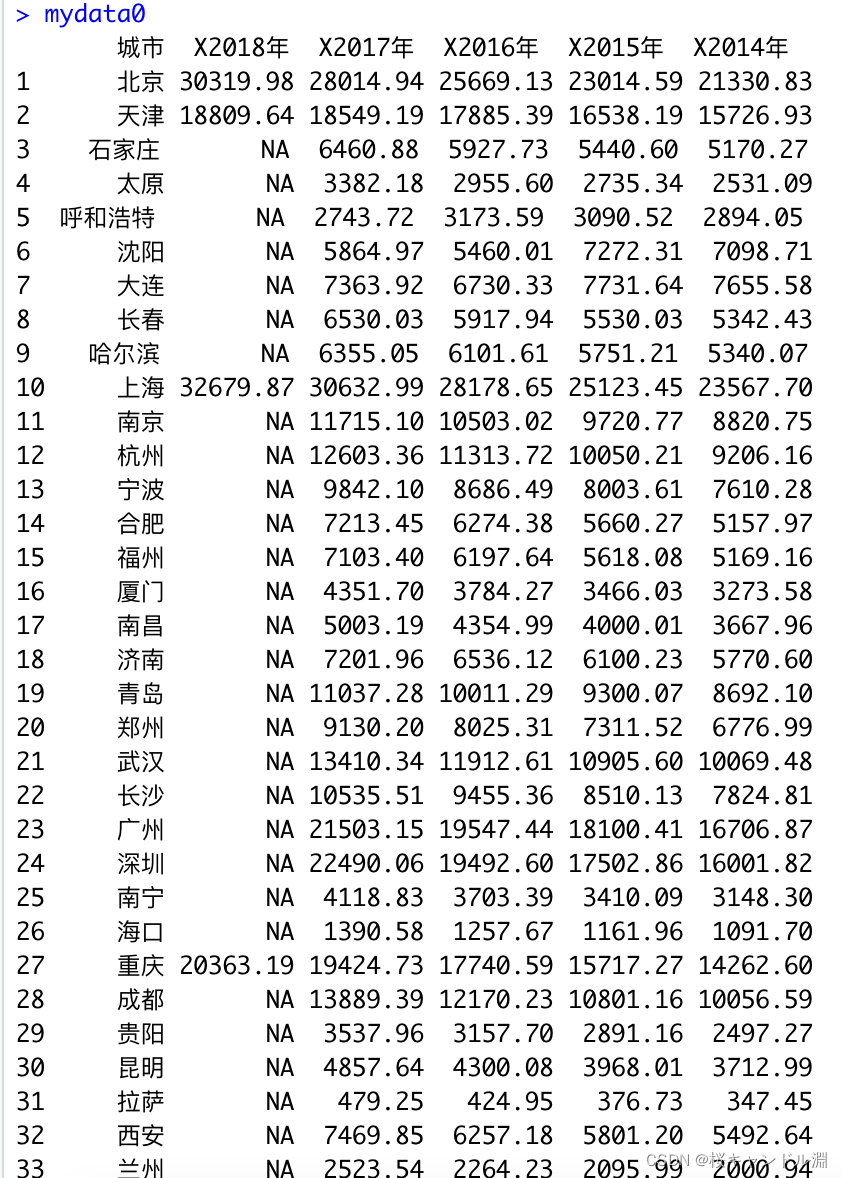
# When we specify our header by F after , The column names in our original dataset are included in the data , Then a new set of indexes will be automatically generated , As shown in the figure below
mydata1<-read.csv("/Users/Documents/R/city.csv",header = F)
mydata1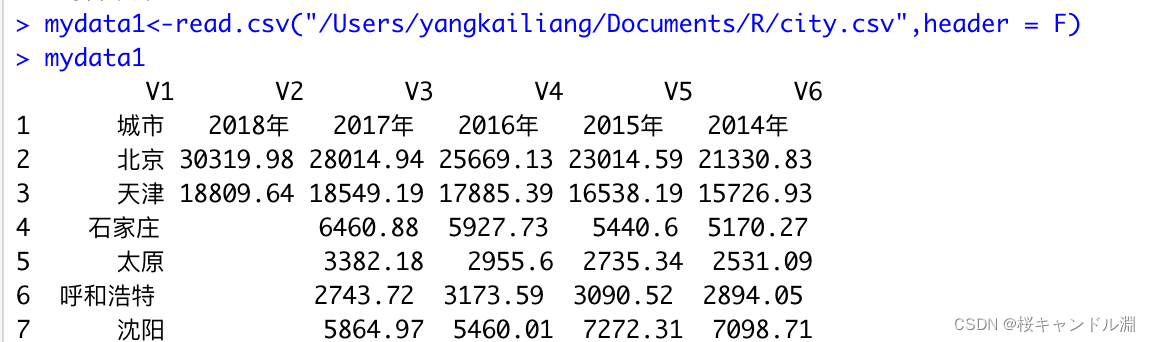
as.is It is to set whether to convert character type into factor type variable
mydata2 <- read.csv("/Users/Documents/R/data/TableData.txt", as.is=F)
mydata2
mydata2 <- read.csv("/Users/Documents/R/data/TableData.txt", as.is=T)
mydata2
Four 、 Read the table data file
Each row of data is an observation
In each observation , Different variables are separated by a separator , Such as the blank space ,tab, The colon , comma
Each observation contains the same number of variables .
read.table( ).
mydata <- read.table(file, header= logical_value,sep="delimiter", rowname="name"
mydata0 <- read.table("/Users/Documents/R/data/TableData.txt") 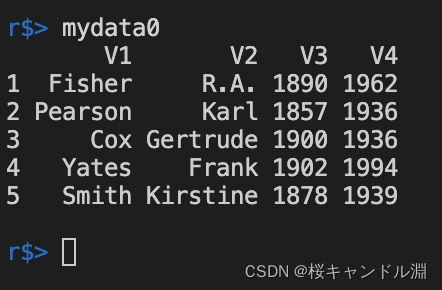
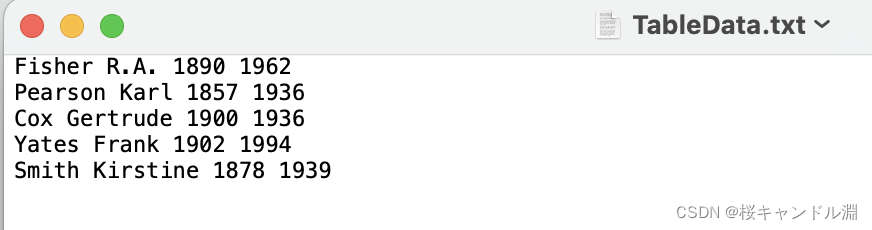
Of course, we can also specify our separator
mydata1 <- read.table("/Users/Documents/R/data/CommaData.txt", sep=",")
mydata1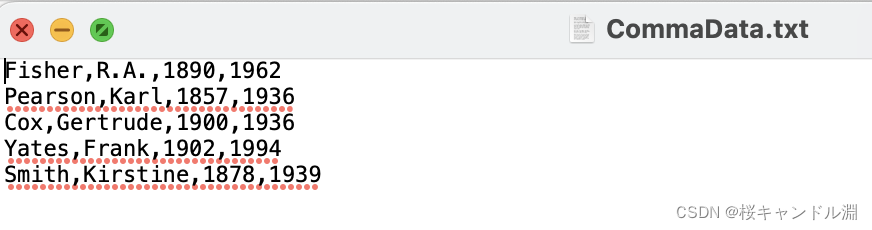
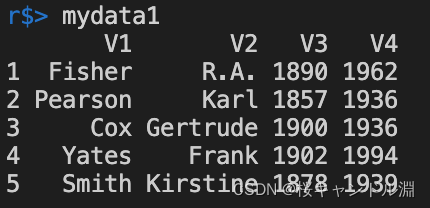
Added stringAsFactor=False after , Data frames do not convert character types to factors
mydata2 <- read.table("/Users/Documents/R/data/TableData.txt",stringsAsFactor=FALSE)
mydata2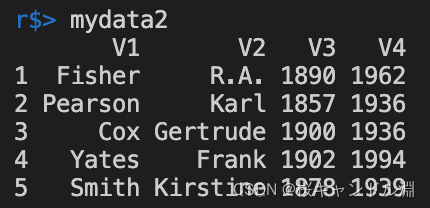
When we add parameters header=T in the future , The data in the first row of our original data set will become our index
mydata3 <- read.table("/Users/Documents/R/data/TableData.txt",header=T,stringsAsFactor=F)
mydata3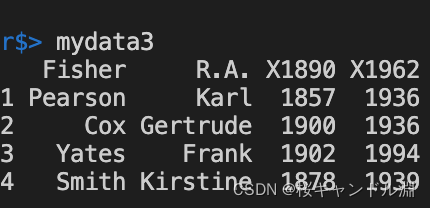
5、 ... and 、 Read tables from the network or CSV Data files
read.csv()
read.table()
scan()
Can get the data of the remote server
mydata0 <- read.csv("http://www.example.com/download/data.csv")
mydata1 <- read.table("ftp://ftp.example.com/download/data.csv")
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

剑指 Offer 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
YOLOv5-Shufflenetv2

F - Two Exam(AtCoder Beginner Contest 238)
网络工程师考核的一些常见的问题:WLAN、BGP、交换机
Sword finger offer 53 - I. find the number I in the sorted array

Corridor and bridge distribution (csp-s-2021-t1) popular problem solution
Light a light with stm32
![[jailhouse article] performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors](/img/c0/4843f887f77b80e3b2329e12d28987.png)
[jailhouse article] performance measurements for hypervisors on embedded ARM processors
Time of process
Codeforces round 712 (Div. 2) d. 3-coloring (construction)
随机推荐
F - Two Exam(AtCoder Beginner Contest 238)
R语言【数据集的导入导出】
Hang wait lock vs spin lock (where both are used)
Codeforces Round #715 (Div. 2) D. Binary Literature
全排列的代码 (递归写法)
26、 File system API (device sharing between applications; directory and file API)
挂起等待锁 vs 自旋锁(两者的使用场合)
记录QT内存泄漏的一种问题和解决方案
Bit mask of bit operation
Gbase database helps the development of digital finance in the Bay Area
How can the Solon framework easily obtain the response time of each request?
ssh免密登录设置及使用脚本进行ssh登录并执行指令
MySQL数据库(一)
Pointnet++ learning
Alu logic operation unit
Haut OJ 1245: large factorial of CDs --- high precision factorial
YOLOv5-Shufflenetv2
剑指 Offer 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
【Jailhouse 文章】Jailhouse Hypervisor
Talking about JVM (frequent interview)