当前位置:网站首页>Application of four ergodic square of binary tree
Application of four ergodic square of binary tree
2020-11-08 15:22:00 【osc_03803522】
Preface
In the last chapter we started with 0 To 1 The implementation of a binary search tree , And understand the characteristics and basic operation of binary search tree , This chapter introduces more about binary trees , That's tree traversal , Access to each node of the tree . It mainly includes preorder traversal 、 In the sequence traversal 、 After the sequence traversal 、 Sequence traversal , The first three are also called depth first traversal (DFS), The last sequence traversal is also called breadth first traversal (BFS), Understand the differences between these four traversal methods , When we encounter the tree related algorithm problem again , And you can be more comfortable . It's not just a binary search tree , The idea of traversal also applies to multitree .
Depth-first traversal (DFS)
Depth first, as the name suggests , Start with the depth of the tree , That is, visit one of the subtrees first , And then visit another subtree . The depth priority of the tree is divided into the front / in / After the sequence traversal , The only difference between them is when accessing a specific node , They are different in order . Depth first is usually implemented recursively , Because it's easy to understand , Of course, you can also use traversal to implement , But that will increase the complexity of the code and the semantics of the code .(LeetCode The non recursive implementation of up and down traversal is difficult )
The former sequence traversal
In other words, access the node of the tree from the front , First post the code , Add the method of preorder traversal to the binary search tree implemented in the previous chapter :
Use one prev Variables cache the last visited node , Each time, let the current access node value minus the previous node value , Because it's a middle order traversal , So the value of the current node must be greater than that of the previous node , Go through the whole tree , Return the minimum value of subtraction .
After the sequence traversal
Just change the location of the access node , Visit the left subtree first , Visit the right subtree , Finally, visit its own root node , Post code :
class BST {
constructor() {
this.root = null // The root node
}
...
postorder(fn) { // After the sequence traversal
const _helper = node => {
if (!node) {
return
}
_helper(node.left) // First visit the left child
_helper(node.right) // And then interview the right child
fn(node.val) // Finally, the root node is accessed
}
_helper(root)
}
}
First visit the left subtree , And then the right subtree , Finally, there is the node itself , The order of access is as follows : 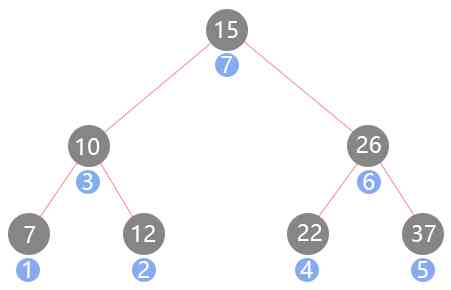
Postorder traversal applications - 563- The slope of the binary tree
Given a binary tree , Calculate the slope of the whole tree .
The slope of a tree node is defined as , The absolute value of the difference between the sum of the nodes of the left subtree and the sum of the nodes of the right subtree . The slope of the empty node is 0.
The slope of the whole tree is the sum of the slopes of all its nodes .
In short, the slope of each node is equal to the absolute difference between the sum of its left and right subtrees , So the slope of the leaf node is 0, Because the left and right children are empty nodes , Back to you 0-0 Value . If we disassemble the subproblem , It can be understood that the slope of the whole tree is the sum of the slopes of its left and right sub trees , Therefore, it is necessary to calculate the slope of the left and right children before calculating the slope of the current node , Post order traversal is very suitable for . 
The solution code is as follows :
var findTilt = function (root) {
let tilt = 0
const _helper = (node) => {
if (!node) {
return 0 // The slope of leaf node is 0
}
const l = _helper(node.left) // First find the sum of the left subtree
const r = _helper(node.right) // Then find the sum of the right subtree
tilt += Math.abs(l - r) // The slope of the current node is equal to the absolute difference between the sum of the left and right subtrees
return l + r + node.val // Return to the subtree and
}
_helper(root)
return tilt
};
Depth-first traversal (DFS) Advanced application
The above three algorithms , The front of the tree is shown separately / in / The practical application of postorder traversal , That's not enough . Some algorithmic problems can not be solved by the conventional traversal method , At this time, we need to deeply understand the tree's (DFS) After traversing the properties , Make extra flexible processing to solve .
Anti normal ordinal traversal - 538- Convert binary search tree to accumulation tree
Given a binary search tree , Turn it into an accumulation tree , So that the value of each node is the sum of the original node value plus all nodes greater than it .
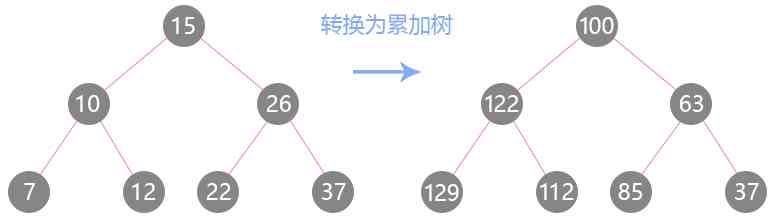
The topic is not easy to understand , But as you can see from the example of the transformation , Start with the rightmost leaf node of the right subtree , Add the node values in pairs , Finally, the whole tree is accumulated from right to left . If you think of this binary search tree as an array [7,10,12,15,22,26,37], Then its operation is to add the array from back to front and cover the previous value . For trees , We need to do an unconventional middle order traversal , First, traverse the right subtree , Then traverse the root node , Finally, traverse the left subtree , That is, a descending traversal .
var convertBST = function (root) {
let sum = 0
const _helper = (node) => {
if (!node) {
return null
}
_helper(node.right) // First traverse the right subtree
node.val += sum // After the right subtree to the bottom, the values are accumulated and covered one by one
sum = node.val // It records the value of the last node that was covered
_helper(node.left) // Finally, traverse the left subtree
}
_helper(root)
return root // Returns a new cumulative tree
};
Preorder and postorder traversal - 257- All paths of binary tree
Given a binary tree , Return all paths from the root node to the leaf node .

The requirement of the title is from the root node to the leaf node , So record the current node of each step , The order of preorder traversal can record the entire path from root to leaf node . The interesting thing about this problem is that when the preorder traversal returns , The last leaf node needs to be removed from the path , Re add another node path value , So it can be in the order of post traversal , Like a greedy snake, you eat the paths you have visited . Some people take this solution to a very powerful, called backtracking . The code is as follows :
版权声明
本文为[osc_03803522]所创,转载请带上原文链接,感谢
边栏推荐
- Don't release resources in finally, unlock a new pose!
- Elasticsearch learning one (basic introduction)
- On the concurrency of update operation
- 区块链周报:数字货币发展写入十四五规划;拜登邀请MIT数字货币计划高级顾问加入总统过渡团队;委内瑞拉推出国营加密交易所
- Rabbitmq (1) - basic introduction
- I used Python to find out all the people who deleted my wechat and deleted them automatically
- 喝汽水,1瓶汽水1元,2个空瓶可以换一瓶汽水,给20元,可以多少汽水
- On DSA of OpenGL
- 三、函数的参数
- The progress bar written in Python is so wonderful~
猜你喜欢

Android Basics - check box

Flink从入门到真香(7、Sink数据输出-文件)

Is there no way out for older programmers?

laravel8更新之速率限制改进

Flink从入门到真香(6、Flink实现UDF函数-实现更细粒度的控制流)

喜获蚂蚁offer,定级p7,面经分享,万字长文带你走完面试全过程

一文读懂机器学习“数据中毒”

金融领域首个开源中文BERT预训练模型,熵简科技推出FinBERT 1.0

Leancloud changes in October

Improvement of rate limit for laravel8 update
随机推荐
Talking about, check the history of which famous computer viruses, 80% of the people do not know!
阿里云加速增长,进一步巩固领先优势
京东落地DevOps平台时爆发的冲突如何解决?
Improvement of maintenance mode of laravel8 update
新型存算一体芯片诞生,利好人工智能应用~
Millet and oppo continue to soar in the European market, and Xiaomi is even closer to apple
python基础教程python opencv pytesseract 验证码识别的实现
构建者模式(Builder pattern)
Is there no way out for older programmers?
模板引擎的整理归纳
这次,快手终于比抖音'快'了!
Golang 系统ping程序探测存活主机(任意权限)
浅谈,盘点历史上有哪些著名的电脑病毒,80%的人都不知道!
大龄程序员没有出路吗?
小青台正式踏上不归路的第3天
应届生年薪35w+ !倒挂老员工,互联网大厂薪资为何越来越高?
The network adapter could not establish the connection
The birth of a new integrated memory and computing chip is conducive to the application of artificial intelligence~
Flink从入门到真香(6、Flink实现UDF函数-实现更细粒度的控制流)
我用 Python 找出了删除我微信的所有人并将他们自动化删除了