当前位置:网站首页>Based on pytorch, we use CNN to classify our own data sets
Based on pytorch, we use CNN to classify our own data sets
2022-07-07 17:41:00 【AI cannon fodder】
main.py file
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
import torchvision
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from pathlib import Path
from model import CNN_MODEL
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
import os
from PIL import Image
epoch = 200
train_transformser = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToPILImage(),
transforms.Resize([224,224]),
transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1),
#transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5),std=(0.5))
])
'''
test_transformser = transforms.Compose([
#transforms.ToPILImage(),
transforms.Resize([224,224]),
transforms.Grayscale(num_output_channels=1),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=(0.5),std=(0.5))
])
'''
def prepareData(dir_path):
dir_path = Path(dir_path)
classes = []
for category in dir_path.iterdir():
if category.is_dir():
classes.append(category.name)
images_list = []
labels_list = []
for index,name in enumerate(classes):
class_path = dir_path / name
if not class_path.is_dir():
continue
for img_path in class_path.glob('*.jpg'):
images_list.append(str(img_path))
labels_list.append(int(index))
return images_list,labels_list
class MyDataSet(Dataset):
def __init__(self,dir_path):
self.dir_path = dir_path
self.images, self.labels = prepareData(self.dir_path)
def __len__(self):
return len(self.images)
def __getitem__(self,index):
img_path = self.images[index]
label = self.labels[index]
#img = Image.open(img_path)
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img = train_transformser(img)
sample = {'image': img, 'label': label}
return sample
def train(model, criterion, optimizer, trainloader, traindataSetLen, testloader, testdataSetLen, epochs=epoch, log_interval=50,learning_rate=0.001):
print('--------- Train Start ---------')
train_loss_history = []
test_loss_history = []
train_acc_history = []
test_acc_history = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
print('epoch:[%d]'%epoch)
model.train()
tarin_running_loss = 0.0
train_accuracy = 0.0
for data in trainloader:
img = data['image']
label = data['label']
output = model(img)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss = criterion(output, label)
loss.backward()
_,pred = torch.max(output,1)
num_correct = (pred==label).sum()
train_accuracy += num_correct.data.item()
optimizer.step()
tarin_running_loss += loss.item()
#train_loss_history.append(loss.item())
print('[%d] train loss: %.4f , train Accuracy: %.4f' %(epoch + 1, tarin_running_loss / traindataSetLen, train_accuracy / traindataSetLen))
train_loss_history.append(tarin_running_loss / traindataSetLen)
train_acc_history.append(train_accuracy / traindataSetLen)
tarin_running_loss = 0.0
print('--------- Test Start ---------')
model.eval()
test_running_loss = 0.0
test_accuracy = 0.0
for data in testloader:
img = data['image']
label = data['label']
output = model(img)
loss = criterion(output,label)
test_running_loss += loss.item()
_,pred = torch.max(output,1)
num_correct = (pred==label).sum()
test_accuracy += num_correct.data.item()
print('[%d] Test loss: %.4f , Accuracy: %.4f' %(epoch + 1, test_running_loss / testdataSetLen, test_accuracy / testdataSetLen))
test_loss_history.append(test_running_loss / testdataSetLen)
test_acc_history.append(test_accuracy / testdataSetLen)
test_running_loss = 0.0
print('----- Train Finished -----')
return {
'train_loss_history':train_loss_history,
'test_loss_history':test_loss_history,
'train_acc_history':train_acc_history,
'test_acc_history':test_acc_history
}
font = FontProperties(fname="SimHei.ttf", size=14)
plt.rcParams['font.family']=['SimHei']
DIR_PATH = 'F:\\radarData\\test'
#gpu or cpu
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
print(device)
print('--------- Prepare Data Start---------')
#load data
dataset = MyDataSet(DIR_PATH)
#split data
train_dataset_size = int(len(dataset)*0.8)
test_dataset_size = len(dataset) - train_dataset_size
train_dataset, test_dataset = torch.utils.data.random_split(dataset,[train_dataset_size, test_dataset_size])
train_dataset_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size = 2, shuffle=True)
test_dataset_loader = DataLoader(test_dataset, batch_size = 2, shuffle=True)
print('--------- Prepare Data End---------')
model = CNN_MODEL()
#learning rate
learning_rate = 0.0001
#loss function
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
#random grad down
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=learning_rate)
result = train(model, criterion, optimizer, train_dataset_loader, train_dataset_size, test_dataset_loader, test_dataset_size, epochs=epoch, log_interval=50, learning_rate = 0.01)
plt.figure()
plt.plot(result['train_loss_history'], label=' Training loss value ')
plt.plot(result['test_loss_history'], label=' Test loss value ')
plt.xlabel(' Training batch ',fontsize=13, fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel(' Loss value ',fontsize=13, fontproperties=font)
plt.ylim(0,1.2)
plt.title(' Training and testing loss value ',fontsize=13, fontproperties=font)
plt.legend(loc='upper right')
plt.savefig("./epoch_loss.png")
plt.show()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(result['train_acc_history'], label=' Training accuracy ')
plt.plot(result['test_acc_history'], label=' Test accuracy ')
plt.xlabel(' Training batch ',fontsize=13, fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel(' Accuracy rate ',fontsize=13, fontproperties=font)
plt.ylim(0,1.2)
plt.title(' Training and testing accuracy ',fontsize=13, fontproperties=font)
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.savefig("./epoch_acc.png")
plt.show()model.py
import torch.nn as nn
from torch import nn, optim
from torch.autograd import Variable
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torchvision import datasets, transforms
from torchsummary import summary
class CNN_MODEL(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN_MODEL, self).__init__()
# Commonly used Layer It is divided into convolution 、 Pooling layer 、 Activate the function layer 、 Loop network, etc 、 Regularization layer 、 Loss function layer
self.layer1 = nn.Sequential(
#stride Convolution step
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=1, out_channels=32, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
#BatchNorm2d Normalize the data , This makes the data ReLU Before, the network performance would not be unstable because the data was too large
nn.BatchNorm2d(32),
#ReLU Activation function ,inplace If bit True, Will overwrite the output directly into the input
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.layer2 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=32, out_channels=64, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.layer3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=128, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1),
nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2)
)
self.layer4 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=128*3*3, out_features=2048),
nn.Dropout2d(0.2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.layer5 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=2048),
nn.Dropout2d(0.2),
nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
)
self.layer6 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(in_features=2048, out_features=10),
nn.Softmax()
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
# print(x.size())
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.layer5(x)
x = self.layer6(x)
return x边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

麒麟信安云平台全新升级!
TabHOST 选项卡的功能和用法

深度学习机器学习各种数据集汇总地址
赋能智慧电力建设 | 麒麟信安高可用集群管理系统,保障用户关键业务连续性
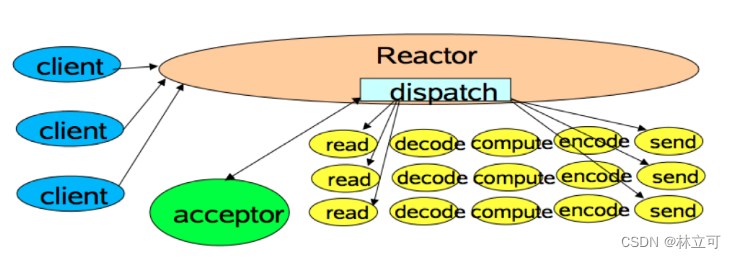
【重新理解通信模型】Reactor 模式在 Redis 和 Kafka 中的应用
![[re understand the communication model] the application of reactor mode in redis and Kafka](/img/d6/8a6124bb7f96be92bf8c6d3aeef12d.png)
[re understand the communication model] the application of reactor mode in redis and Kafka
ViewSwitcher的功能和用法
基于百度飞浆平台(EasyDL)设计的人脸识别考勤系统
做软件测试 掌握哪些技术才能算作 “ 测试高手 ”?
【TPM2.0原理及应用指南】 9、10、11章
随机推荐
With the latest Alibaba P7 technology system, mom doesn't have to worry about me looking for a job anymore
Matplotlib绘图界面设置
第3章业务功能开发(用户登录)
【网络攻防原理与技术】第4章:网络扫描技术
深入浅出【机器学习之线性回归】
actionBar 导航栏学习
L1-027 出租(Lua)
[re understand the communication model] the application of reactor mode in redis and Kafka
做软件测试 掌握哪些技术才能算作 “ 测试高手 ”?
【4500字归纳总结】一名软件测试工程师需要掌握的技能大全
到底有多二(Lua)
【可信计算】第十二次课:TPM授权与会话
使用 xml资源文件定义菜单
原生js验证码
Define menus using XML resource files
深入浅出图解CNN-卷积神经网络
本周小贴士#140:常量:安全习语
Simple loading animation
calendarview日历视图组件的功能和用法
【网络攻防原理与技术】第5章:拒绝服务攻击