当前位置:网站首页>Analysis of ROS calculation diagram level
Analysis of ROS calculation diagram level
2022-06-26 09:12:00 【Mediocre self admiration】
Calculation drawing level yes ROS A distributed network that processes data , Used to describe program operation and data communication , When the program is running , All processes and the data they process can be represented through a point-to-point network , The network can be accessed through rqt_graph Visual tools to view 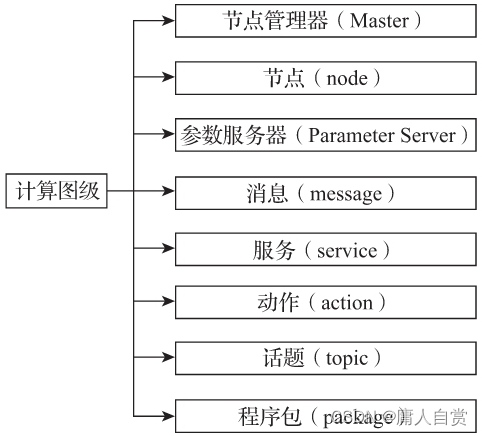
node node
ROS The running instance of the executable in the package is called a node , A node is essentially a process that performs arithmetic tasks . One ROS The system can have multiple nodes when running , Nodes usually have a clear division of labor , For example, a node controls the laser sensor , Another node controls the motor, etc , Nodes can also be distributed on different physical devices .
$rosrun [ Package name ] [ The node name ]
$roslaunch [ Options ] [ Package name ] <launch file name > [ Variable parameters ]
topic of conversation topic
The communication between nodes can be passed through messages , The message is encapsulated in the topic , The topic is essentially an encapsulation of sockets . News to publish / The mode of subscription , A node can publish messages to a given topic , Another node can subscribe to messages of a specific message type in a given topic . Publishers and subscribers can decouple through topics . It should be noted that , stay ROS in , The topic must be unique , Otherwise, message routing will generate errors .
Topics can be visualized using tools rqt_graph To view the
rostopic Common usage of :
# Display the receiving speed of topic data, i.e. bandwidth
$rostopic bw [ Topic name ]
# Show the delay of the topic
$rostopic delay [ Options ] [ Topic name ]
# Show the message content of the topic
$rostopic echo [ Options ] [ Topic name ]
# View specific types of topics
$rostopic find [ Topic type ]
# Display the publishing speed of topic data
$rostopic hz [ Options ] [ Topic name ]
# Display information about the active topic
$rostopic info [ Topic name ]
# List activity topics
$rostopic list
# Publish data to the topic
$rostopic pub [ Topic name ] [ Message type ] [ Parameters ]
# Print topics / Domain type
$rostopic type [ Topic name / Domain type ]
# Show a list of all topics
$rostopic list -v
The output is as follows :
Published topics:
* /turtle1/color_sensor [turtlesim/Color] 1 publisher
* /turtle1/cmd_vel [geometry_msgs/Twist] 1 publisher
* /rosout [rosgraph_msgs/Log] 3 publishers
* /rosout_agg [rosgraph_msgs/Log] 1 publisher
* /turtle1/pose [turtlesim/Pose] 1 publisher
Subscribed topics:
* /turtle1/cmd_vel [geometry_msgs/Twist] 1 subscriber
* /rosout [rosgraph_msgs/Log] 1 subscriber
From the output results, you can see the current topic type and the message type delivered by the topic , Such as /turtle1/color_sensor The message type of topic delivery is turtlesim/Color. If you want to view information about a topic , The method is as follows :
$rostopic info [ Topic name ]
such as , If you want to know the topic of little turtle /turtle1/cmd_vel Information about , The method is as follows :
$rostopic info /turtle1/cmd_vel
The corresponding output results are as follows :
Type: geometry_msgs/Twist
Publishers:
* /teleop_turtle (http://miaozl-ThinkPad-T470p:42883/)
Subscribers:
* /turtlesim (http://miaozl-ThinkPad-T470p:43015/)
This topic has a publishing node turtlesim And a subscription node teleop_turtle, If you want to know the topic /turtle1/cmd_vel The message type of , The method is as follows :
$rostopic type /turtle1/cmd_vel
If you want to view the topic /turtle1/cmd_vel Specific content published on , The method is as follows :
$rostopic echo /turtle1/cmd_vel
news message
ROS The most important mechanism for communication between nodes is message passing , For message communication between modules implemented in different development languages ,ROS Using the simple 、 The development language independent interface definition language is used to describe the messages passed between modules .
stay ROS in , A message is essentially a data type that passes information between nodes , When a node wants to share information , Nodes can publish messages to corresponding topics , When a node needs to receive information , Nodes can subscribe to corresponding topics .
The node manager will ensure the interoperability of messaging , But the message does not need to be forwarded through the node manager .ROS There are many predefined message types , But developers can use the suffix msg Custom message types for message files ,msg The file should be placed in the... Of the package msg Under the table of contents .
1. Message type
Message types describe the information carried by each message and how it is organized . Each message type belongs to a specific package , The message type is named :
Package name / Message name
Message type “rosgraph_msgs/Log” Represents a package rosgraph_msgs Of Log Log message , The package name and the message name are separated by “/” separation . This naming method can avoid message type name conflicts .
The declaration of each line of the message type must contain two parts : Fields and variables ; The field defines the data type of the message , The variable defines the name of the domain . A domain can be an independent domain or a composite domain .
The so-called composite domain refers to a domain composed of one or more simple subdomains , Each of these sub domains can be another composite domain or an independent domain , Independent fields consist of basic data types .ROS The basic data types supported are integer (int8、int16、int32、int64)、 floating-point (float32、float64)、 String type (string)、 Time type (time、duration)、 Other message types 、 Variable array or fixed array, etc .
geometry_msgs/Twist Is a typical message type composed of composite domains , It defines the robot in 3D Linear and angular velocity information in space , The details are as follows :
geometry_msgs/Vector3 linear
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
geometry_msgs/Vector3 angular
float64 x
float64 y
float64 z
among , Linear velocity linear、 angular velocity angular The domain of is a composite domain geometry_msgs/Vector3, Indent format indicates x、y、z The domain of is a member of the parent domain . For a robot moving on a plane ,linear Of z and angular Of z Are all 0, For UAVs, etc 3D Robots moving in space ,linear Of z and angular Of z Are not as 0.
Mutable array in ROS It is also widely used in , Variable arrays are made by adding... After the field [] To express , Indicates the message type of the point cloud sensor_msgs/PointCloud A variable array is used , It reads as follows
Header header
geometry_msgs/Point32[] points
ChannelFloat32[] channels
2. view message
utilize rosmsg You can check the message , Common usage is as follows :
# Displays the message type description
$rosmsg show [ Message type ]
# The functions and rosmsg show identical
$rosmsg info [ Message type ]
# List all message types
$rosmsg list
# Displays the of the message MD5 Signature
$rosmsg md5
# Lists the message types in the display package
$rosmsg package [ Message type ]
# List packages that contain specific message types
$rosmsg packages
If you want to view the topic /turtle1/cmd_vel The message type of geometry_msgs/Twist Details of , The method is as follows :
$rosmsg show geometry_msgs/Twist
If you want to view the package turtlesim Message types in , The method is as follows :
$rosmsg package turtlesim
The corresponding output results are as follows :
turtlesim/Color
turtlesim/Pose
3. Release the news
Most of the time , Publishing messages is mainly carried out in the package , But sometimes you need to post messages manually , The release method of rate mode is as follows :
$rostopic pub –r rate-in-hz [ Topic name ] [ Message type ] [ news ]
This command repeats the message to the topic at the specified frequency . The example code of a little turtle movement is as follows :
$rostopic pub -r /turtle1/cmd_vel geometry_msgs/Twist 1--'[2.0, 0.0, 0.0]' '[0.0, 0.0, -1.8]'
Driven by this message , The little turtle will always do a circular motion , Unless you stop executing the command .
service service
action action
边栏推荐
- Yolov5进阶之一摄像头实时采集识别
- 基于SSM的电脑商城
- Self taught neural network series - 4 learning of neural network
- yolov5进阶之零环境快速创建及测试
- Tensor
- Yolov5 advanced III training environment
- 【300+精选大厂面试题持续分享】大数据运维尖刀面试题专栏(一)
- Lagrange multiplier method
- Autoregressive model of Lantern Festival
- Self taught machine learning series - 1 basic framework of machine learning
猜你喜欢

MySQL cannot be found in the service (not uninstalled)
如何编译构建

MySQL在服务里找不到(未卸载)
![[program compilation and pretreatment]](/img/c9/45353cf6578628ad44f149350873f5.png)
[program compilation and pretreatment]

【C】青蛙跳台阶和汉诺塔问题(递归)

Vipshop work practice: Jason's deserialization application
![Li Kou 399 [division evaluation] [joint query]](/img/25/ea7d526c0628f11277141f51d4ccae.png)
Li Kou 399 [division evaluation] [joint query]

phpcms v9后台文章列表增加一键推送到百度功能

JSON file to XML file

20220623 getting started with Adobe Illustrator
随机推荐
Self taught programming series - 4 numpy arrays
Phpcms mobile station module implements custom pseudo static settings
Differences between commonjs and ES6 modularity
【微积分】拉格朗日乘子法
Lagrange multiplier method
[qnx hypervisor 2.2 user manual]12.2 terminology (II)
Phpcms V9 remove the phpsso module
基于SSM的毕业论文管理系统
Self taught programming series - 2 file path and text reading and writing
How to convert wechat applet into Baidu applet
Yolov5进阶之二安装labelImg
Efficiency thesis Reading 1
Mongodb分片环境搭建和验证(redis期末大作业)
Chargement à chaud du fichier XML de l'arbre de comportement
【C】青蛙跳台阶和汉诺塔问题(递归)
行为树 文件说明
编辑类型信息
[qnx hypervisor 2.2 user manual]12.1 terminology (I)
yolov5进阶之零环境快速创建及测试
【300+精选大厂面试题持续分享】大数据运维尖刀面试题专栏(一)