当前位置:网站首页>Autoregressive model of Lantern Festival
Autoregressive model of Lantern Festival
2022-06-26 08:54:00 【Py little brother】
Autoregressive model (AutoRegression Model) It can be used to predict the future value of time series , The model assumes that the relationship between the front and back values is linear . When using this model , It is usually assumed that the value of a random variable depends on its previous value . What we have to do is fit the data , Find the appropriate parameters for the data . The mathematical formula of the autoregressive model is as follows :
x t x_t xt=c+ ∑ i = 1 p a i ∗ x k \sum_{i=1}^{p}a_i*x_k ∑i=1pai∗xk+ g t g_t gt (k=t-i)
In the above formula ,c For constant , The last term is the random component , Also known as white noise .
In regression analysis , If new data points are introduced when the sample fitting degree is very good , The fitting performance may deteriorate immediately . We can cross verify , Or use the algorithm without fitting problem to solve this problem .
Pass below scipy.optimize.least() Function to build a model , We use sunspot data to train the model . The code is as follows :
'''Xu Yong Kang'''
from scipy.optimize import leastsq
import statsmodels.api as sm
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Use scipy.optimize.leastp Function to build the model
def model(p,x1,x10):
p1,p10=p
return p1*x1+p10*x10
def error(p,data,x1,x10):
return data-model(p,x1,x10)
# Fitting model
def fit(data):
p0=[0.5,0.5]
params=leastsq(error,p0,args=(data[10:],data[9:-1],data[:-10]))
return params
# Training models on sunspot data sets
data_loader=sm.datasets.sunspots.load_pandas()
sunspots=data_loader.data['SUNACTIVITY'].values
cutoff=0.9*len(sunspots)
params=fit(sunspots[:int(cutoff)])
print('Params',params) # Get parameters
print(params[0].shape)
print(params[1])
# Predict the value and calculate each index
pred=params[0][0]*sunspots[int(cutoff-1):-1]+params[0][1]*sunspots[int(cutoff-10):-10]
actual=sunspots[int(cutoff):]
print('Root mean square error',np.sqrt(np.mean((actual-pred)**2)))
print('Mean absolute error',np.mean(np.abs(actual-pred)))
print('Mean absolute percentage error',100*np.mean(np.abs(actual-pred)/actual))
print('Cofficient of determination',1-((actual-pred)**2).sum()/((actual-actual.mean())**2).sum())
year_range=data_loader.data['YEAR'].values[int(cutoff):]
plt.plot(year_range,actual,'x',label='Actual Sunspots',color='red')
plt.plot(year_range,pred,'o',label='Prediction',color='blue')
plt.grid(True)
plt.xlabel('Year')
plt.ylabel('Activity')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
We can get the parameters from the training results
Params (array([0.67172672, 0.33626295]), 2)
From these, we can get the predicted value 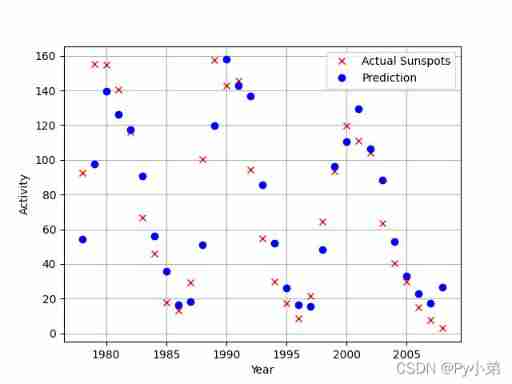
From the picture we can see , Many predictions are almost successful , But there are also some poor results .
notes :
stay pred There is a problem about numpy The problem of broadcasting
边栏推荐
- Addition of attention function in yolov5
- Regular Expression 正则表达式
- Matlab function foundation (directly abandon version)
- Leetcode22 summary of types of questions brushing in 2002 (XII) and collection search
- Koa_ mySQL_ Integration of TS
- Yolov5进阶之三训练环境
- Using transformers of hugging face to realize multi label text classification
- Two ways to realize time format printing
- Summary of mobile terminal lightweight model data
- Segmentation of structured light images using segmentation network
猜你喜欢

Exploration of webots and ROS joint simulation (II): model import
SQL learning experience (II): question brushing record

What are the conditions for Mitsubishi PLC to realize Ethernet wireless communication?

Isinstance() function usage

Reverse crawling verification code identification login (OCR character recognition)

Exploration of webots and ROS joint simulation (I): software installation
XSS cross site scripting attack

Whale conference one-stop intelligent conference system helps organizers realize digital conference management

Partial summary of 45 lectures on geek time MySQL

opencv学习笔记二
随机推荐
torch. fft
在 KubeSphere 部署 Wiki 系统 wiki.js 并启用中文全文检索
Pandas vs. SQL 1_ nanyangjx
opencv学习笔记二
Ultrasonic image segmentation
How to use leetcode
Yolov5进阶之三训练环境
利用无线技术实现分散传感器信号远程集中控制
Detailed process of generating URDF file from SW model
Bezier curve learning
Partial summary of 45 lectures on geek time MySQL
[已解决]setOnNavigationItemSelectedListener()被弃用
What are the conditions for Mitsubishi PLC to realize Ethernet wireless communication?
Fourier transform of image
uniapp用uParse实现解析后台的富文本编辑器的内容及修改uParse样式
Using MySQL and Qt5 to develop takeout management system (I): environment configuration
How to realize wireless Ethernet high-speed communication for multiple Mitsubishi PLCs?
Installation of jupyter
ROS learning notes (6) -- function package encapsulated into Library and called
Implementation of ffmpeg audio and video player