当前位置:网站首页>Optaplanner learning notes (I) case cloud balance
Optaplanner learning notes (I) case cloud balance
2022-07-01 19:36:00 【Deep sea wandering goose】
Problem description :
Suppose your company has some cloud computers , You need to run some programs on these computers , Each process needs to be assigned to run on a computer . The following constraints must be met :
Each computer must be able to handle the minimum hardware requirements for the sum of its processes .
CPU power : A computer's CPU Power must be at least what the process assigned to the computer needs CPU Sum of power .
Memory capacity : A computer's RAM The memory must be at least what the process allocated to the computer needs RAM The sum of memory .
Network capacity : The network bandwidth of a computer must be at least the sum of the network bandwidth required by the processes assigned to that computer .
The following soft constraints should be optimized :
- Each computer assigned one or more processes will incur maintenance costs ( The cost of each computer is fixed ).
- cost : Minimize total maintenance costs .
This problem is a form of packing problem . Here is a simple example , We use a simple algorithm , Allocate four processes to two constrained (CPU and RAM) The computer .
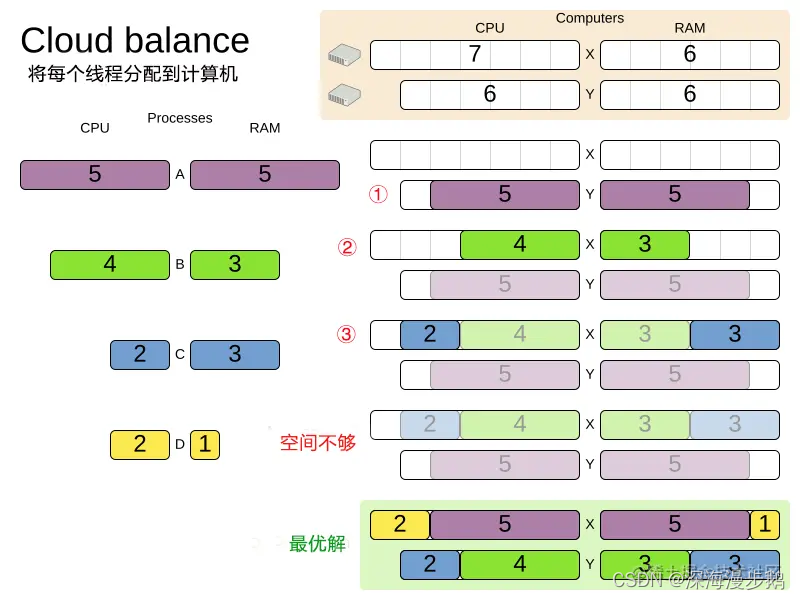
The simple algorithm used here is the greedy algorithm ( Also known as greedy algorithm , When solving a problem , Always make what seems to be the best choice at the moment . in other words , Don't take into account the overall optimum , The algorithm obtains the local optimal solution in a sense ).
It allocates larger processes first , Then allocate the smaller processes to the remaining space . As we can see , It's not optimal , Because it doesn't leave enough space to allocate the Yellow process D.
OptaPlanner By using additional 、 Smarter algorithms find better solutions . It can also be expanded : In the data ( More progress , More computers ) And constraints ( More hardware requirements , Other constraints ) aspect .
Business modeling
When we're modeling , We need to distinguish which ones are Planning entities Planning entity , Which of their attributes are Planning variables Planning attributes .
The input data object representing the problem is defined in the model of this example , In this simple example , These objects are Computer、Progress. A single object in this model must represent the complete data set of the problem , It contains input data and solutions . In this case , This object holds a Computer And a list of Progress A list of . Every Progress Assigned to a computer Computer;Computer Between Progress Distribution is the solution .
step
1、 draw UML chart .
2、 Planning model data , Don't have duplicate data .
3、 Write each instance in the model :
- Computer: Represents a computer with hardware and maintenance costs . In this case ,Computer The property of is :cpuPower, memory, networkBandwidth, cost.
- Progress: Represents a process in need . Need by OptaPlanner Assigned to a computer .Progress The attributes of are :requiredCpuPower, requiredMemory, and requiredNetworkBandwidth.
- CloudBalance: Representing one Problem. Each computer and process that contains a data set .
4、 Find out which fields will change during the solution .
- Planning entity:OptaPlanner Classes that can be changed in the process of solving . In this case , It is Progress class , because OptaPlanner Can be Progress Assigned to Computer.
- Planning variable: What changes in the process of solving PlanningEntity Attributes of a class . In this case , It is Progress Properties on classes computer.
- Problem fact: Solving data supported classes .Computer It's about providing data , No information is changed during the solution .
- Planning solution: The class representing the solution to the problem . This class must represent the complete dataset and contain all planning entities . In this case , Namely CloudBalance This class .

Object specific implementation
Computer
public class CloudComputer ... {
private int cpuPower;
private int memory;
private int networkBandwidth;
private int cost;
... // getters
}
Progress
Progress Class is very important , It is the class that is modified in the process of solving .
We need to tell OptaPlanner, It can modify properties computer. Use @PlanningEntity To annotate this class , And use @PlanningVariable annotation getter getComputer() Method .
OptaPlanner It's through setter Method is modified , So there needs to be setter Method .
@PlanningEntity
public class CloudProcess ... {
private int requiredCpuPower;
private int requiredMemory;
private int requiredNetworkBandwidth;
private CloudComputer computer;
... // getters
@PlanningVariable(valueRangeProviderRefs = {
"computerRange"})
public CloudComputer getComputer() {
return computer;
}
public void setComputer(CloudComputer computer) {
computer = computer;
}
...
}
OptaPlanner You need to know which values it can choose to assign to the property computer. These values are derived from CloudBalance.getComputerList() Get from method , This method returns a list of all computers in the current dataset .
CloudProcess.getComputer() Upper @PlanningVariable Of valueRangeProviderRefs Parameters need to be related to CloudBalance.getComputerList() Upper @ValueRangeProvider Of id One-to-one correspondence .
CloudBalance
CloudBalance Class has one. @PlanningSolution annotation , This class is the entry of data in the process of solving and the exit of the final result . It has a Computer List and Progress List data , among Progress Class computer It's the output of the whole final result , Because the result of our solution is every Progress Which one was assigned to Computer.
@PlanningSolution
public class CloudBalance ... {
private List<CloudComputer> computerList;
private List<CloudProcess> processList;
private HardSoftScore score;
@ValueRangeProvider(id = "computerRange")
@ProblemFactCollectionProperty
public List<CloudComputer> getComputerList() {
return computerList;
}
@PlanningEntityCollectionProperty
public List<CloudProcess> getProcessList() {
return processList;
}
@PlanningScore
public HardSoftScore getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(HardSoftScore score) {
this.score = score;
}
...
}
processList Property holds a list of processes .OptaPlanner It can change the process , Assign them to different computers . therefore , The process is a ProblemEntity Planning entity ,processList It's a collection of planning entities . Need to be in getProcessList() Method @PlanningEntityCollectionProperty annotation .
computerList Property holds a list of computers .OptaPlanner You can't change these computers . therefore , The computer is a ProblemFact The problem is the fact that . Especially for the use of Drools The score calculation of , attribute computerList Need to use @ProblemFactCollectionProperty To annotate , such OptaPlanner You can retrieve the list of computers (ProblemFact), And make it right Drools The engine is available .
CloudBalance Class also has a @PlanningScore Properties of annotations score, It is the score of the solution in the current state .OptaPlanner When calculating a solution instance Score It will be updated automatically when it's finished . therefore , This property requires a setter.
Constraint score definition
So far, we've built the model , because OptaPlanner It's judging each solution by its score , So next we need to write the corresponding score calculation , And will “ Problem description ” Hard inside / Soft constraints are written into corresponding code .
Let's start with a picture :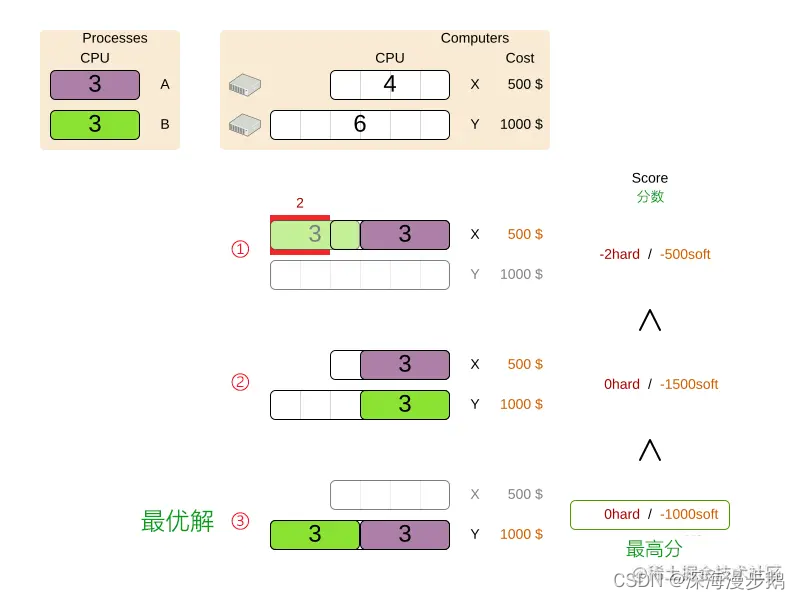
AB Thread assigned to XY On the machine , Three different results, the final score results show .
From the description of the problem , We can conclude that there are hard constraints and soft constraints in this problem , Hard constraints usually represent constraints that cannot be broken , Soft constraints are conditions where expectations are not worth breaking .
Constraint configuration class
We have to come out from the problem ,3 A hard constraint and 1 A rule of soft constraints .
CloudBalancingConstraintProvider.java
public class CloudBalancingConstraintProvider implements ConstraintProvider {
@Override
public Constraint[] defineConstraints(ConstraintFactory constraintFactory) {
return new Constraint[] {
requiredCpuPowerTotal(constraintFactory),
requiredMemoryTotal(constraintFactory),
requiredNetworkBandwidthTotal(constraintFactory),
computerCost(constraintFactory)
};
}
// ************************************************************************
// Hard constraints - Hard constraints
// ************************************************************************
Constraint requiredCpuPowerTotal(ConstraintFactory constraintFactory) {
return constraintFactory.from(CloudProcess.class)
.groupBy(CloudProcess::getComputer, sum(CloudProcess::getRequiredCpuPower))
.filter((computer, requiredCpuPower) -> requiredCpuPower > computer.getCpuPower())
.penalize("requiredCpuPowerTotal",
HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD,
(computer, requiredCpuPower) -> requiredCpuPower - computer.getCpuPower());
}
Constraint requiredMemoryTotal(ConstraintFactory constraintFactory) {
return constraintFactory.from(CloudProcess.class)
.groupBy(CloudProcess::getComputer, sum(CloudProcess::getRequiredMemory))
.filter((computer, requiredMemory) -> requiredMemory > computer.getMemory())
.penalize("requiredMemoryTotal",
HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD,
(computer, requiredMemory) -> requiredMemory - computer.getMemory());
}
Constraint requiredNetworkBandwidthTotal(ConstraintFactory constraintFactory) {
return constraintFactory.from(CloudProcess.class)
.groupBy(CloudProcess::getComputer, sum(CloudProcess::getRequiredNetworkBandwidth))
.filter((computer, requiredNetworkBandwidth) -> requiredNetworkBandwidth > computer.getNetworkBandwidth())
.penalize("requiredNetworkBandwidthTotal",
HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD,
(computer, requiredNetworkBandwidth) -> requiredNetworkBandwidth - computer.getNetworkBandwidth());
}
// ************************************************************************
// Soft constraints - Soft constraint
// ************************************************************************
Constraint computerCost(ConstraintFactory constraintFactory) {
return constraintFactory.from(CloudComputer.class)
.ifExists(CloudProcess.class, equal(Function.identity(), CloudProcess::getComputer))
.penalize("computerCost",
HardSoftScore.ONE_SOFT,
CloudComputer::getCost);
}
}
requiredCpuPowerTotal The current rule represents , If at present progress The goal of process allocation Computer Computer , its cpuPower Less than the present Computer On all the progress Required by the process cpuPower The sum of the , Then punishment will be carried out , Levels are hard constraints HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD, What's the score cpuPower The part beyond .
requiredMemoryTotal The current rule represents , If at present progress The goal of process allocation Computer Computer , its memory Less than the present Computer On all the progress Required by the process memory The sum of the , Then punishment will be carried out , Levels are hard constraints HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD, What's the score memory The part beyond .
requiredNetworkBandwidthTotal The current rule represents , If at present progress The goal of process allocation Computer Computer , its networkBandwidth Less than the present Computer On all the progress Required by the process networkBandwidth The sum of the , Then punishment will be carried out , Levels are hard constraints HardSoftScore.ONE_HARD, What's the score networkBandwidth The part beyond .
computerCost The rule represents the current cost , In terms of punitive points , The score is each Computer Of cost.
function CloudBalance Program
Now let's write a HelloWorld class CloudBalancingHelloWorld.java.
public class CloudBalancingHelloWorld {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create a solver
SolverFactory<CloudBalance> solverFactory = SolverFactory.create(new SolverConfig()
.withSolutionClass(CloudBalance.class)
.withEntityClasses(CloudProcess.class)
.withConstraintProviderClass(CloudBalancingConstraintProvider.class)
.withTerminationSpentLimit(Duration.ofMinutes(2)));
Solver<CloudBalance> solver = solverFactory.buildSolver();
// Load a file with 400 Two computers and 1200 Data for each process
CloudBalance unsolvedCloudBalance = new CloudBalancingGenerator().createCloudBalance(400, 1200);
// Submit the solution
CloudBalance solvedCloudBalance = solver.solve(unsolvedCloudBalance);
// Output results
System.out.println("\nSolved cloudBalance with 400 computers and 1200 processes:\n"
+ toDisplayString(solvedCloudBalance));
}
public static String toDisplayString(CloudBalance cloudBalance) {
StringBuilder displayString = new StringBuilder();
for (CloudProcess process : cloudBalance.getProcessList()) {
CloudComputer computer = process.getComputer();
displayString.append(" ").append(process.getLabel()).append(" -> ")
.append(computer == null ? null : computer.getLabel()).append("\n");
}
return displayString.toString();
}
}
withTerminationSpentLimit(Duration.ofMinutes(2))) What's written here is 2 minute , You can change the size and end time of the problem according to your needs .
summary
So far, we have completed a cloud resource optimization program , Let's start with examples , Be familiar with it. OptaPlanner The way to solve it , In the following chapters, we will focus on some important concepts .
I'm learning optaplanner In the process , Main reference PeterOne Teacher's blog ,https://juejin.cn/user/3835556294573207
边栏推荐
- AAAI2020: Real-time Scene Text Detection with Differentiable Binarization
- sql查询去重统计的方法总结
- Solidity - truncated and checked modes of arithmetic operations - new features of 0.8.0
- Parallelism, concurrency and life cycle of threads
- English grammar_ Adjective / adverb Level 3 - precautions
- 求各种极限的方法
- Write it down once Net travel management background CPU Explosion Analysis
- Opencv video quality diagnosis - VIDEO occlusion diagnosis
- 241. Different Ways to Add Parentheses
- 使用环信提供的uni-app Demo,快速实现一对一单聊
猜你喜欢
![[pytorch record] automatic hybrid accuracy training torch cuda. amp](/img/a5/cf1eb2801380cf2887dfd532d3eb1e.jpg)
[pytorch record] automatic hybrid accuracy training torch cuda. amp
Case sharing: basic networking configuration of QinQ

Intensive cultivation of channels for joint development Fuxin and Weishi Jiajie held a new product training conference

wireshark报文分析tcp,ftp

DTD modeling
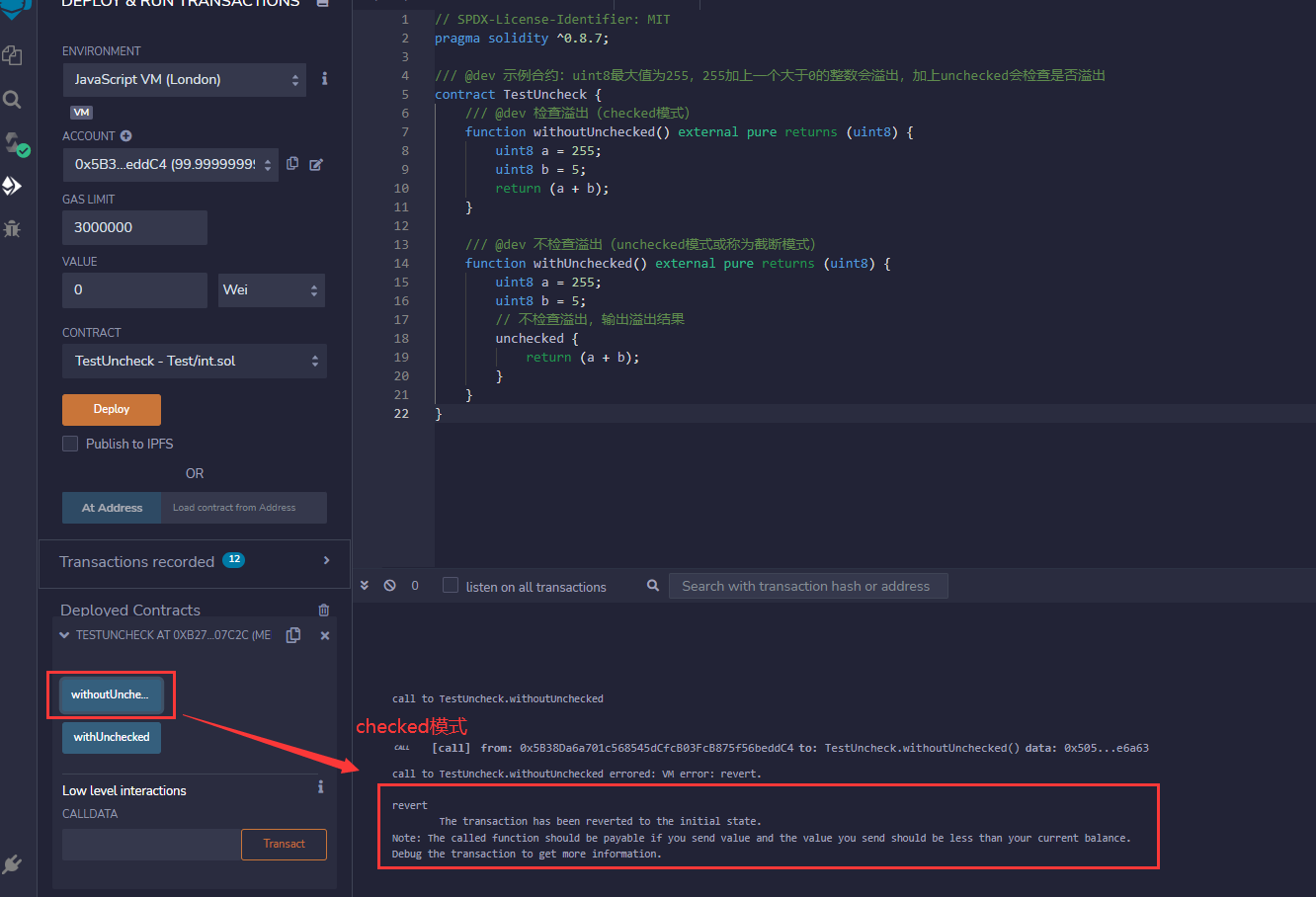
Solidity - truncated and checked modes of arithmetic operations - new features of 0.8.0

Interview questions for audio and video positions in Dachang -- today's headline

ECS summer money saving secret, this time @ old users come and take it away
Introduction to relevant processes and functions of wechat official account development
奔赴山海之前,毕业季一定要做的那些事情
随机推荐
torch.nn.functional.interpolate函数
奔赴山海之前,毕业季一定要做的那些事情
The difference between indexof and includes
论文阅读【Discriminative Latent Semantic Graph for Video Captioning】
Contos 7 搭建sftp之创建用户、用户组以及删除用户
白盒加密技术浅理解
原生js打造日程表-支持鼠标滚轮滚动选择月份-可以移植到任何框架中
ubuntu14安装MySQL并配置root账户本地与远程访问
Compile ffmpeg source code with msys+vs2019 under win10
Helium transmission line of lake shore cryostat
Implement a Prometheus exporter
Extensive reading of the paper [film: visual reasoning with a general condition layer]
A brief understanding of white box encryption technology
pickle. Load error [attributeerror: can't get attribute 'volatile' on < module '\u main']
Detailed explanation of JUnit unit test framework
大厂音视频职位面试题目--今日头条
Basic knowledge of audio coding and decoding
EasyGBS网络不稳定情况下重复请求视频拉流问题的优化
【To .NET】C#集合类源码解析
241. Different Ways to Add Parentheses