当前位置:网站首页>【To .NET】C#集合类源码解析
【To .NET】C#集合类源码解析
2022-07-01 18:43:00 【未来村村长】
大家好!我是未来村村长,就是那个“请你跟我这样做,我就跟你这样做!”的村长!
“人生苦短,你用Python”,“Java内卷,我用C#”。
从Java到C#,不仅仅是语言使用的改变,更是我从理想到现实,从象牙塔到大熔炉的第一步。.NET是微软的一盘棋,而C#是我的棋子,只希望微软能下好这盘棋,而我能好好利用这个棋子。
上一篇文章:【C#数据模型,从Entity Framework Core到LINQ】,我们介绍了C#如何通过EF Core与SQL Server如何建立映射关系并进行交互。这节我们通过C#集合的源码来探究集合的使用。
一、接口与实现类🧭
所有集合类或与集合相关的接口命名空间都是 System.Collections,在该命名空间中提供的常用接口如下:
- IEnumerable:使用LINQ查询数据常以该类型作为返回对象接收类型,使用foreach进行遍历时需要该对象实现IEnumerable。
- IEnumerator:迭代器模式被IEnumerator和IEnumerable及其对应的泛型接口所封装。如果一个类实现了IEnumerable接口,那么就能够被迭代;调用GetEnumerator方法将返回IEnumerator接口的实现,它就是迭代器本身。
- ICollection:定义所有非泛型集合的大小、枚举数和同步方法。
- IList:IList 泛型接口是 ICollection 泛型接口的子代,并且是所有泛型列表的基接口,并继承了 IEnumerable。
针对上述的接口有一些常用的接口实现类,如下表所示。
| 类名称 | 实现接口 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | ICollection、IList、IEnumerable、ICloneable | 集合中元素的个数是可变的,提供添加、删除等方法 |
| Queue | ICollection、IEnumerable、ICloneable | 集合实现了先进先出的机制,即元素将在集合的尾部添加、在集合的头部移除 |
| Stack | ICollection、IEnumerable、ICloneable | 集合实现了先进后出的机制,即元素将在集合的尾部添加、在集合的尾部移除 |
| Hashtable | IDictionary、ICollection、IEnumerable、 ICloneable 等接口 | 集合中的元素是以键值对的形式存放的,是 DictionaryEntry 类型的 |
| SortedList | IDictionary、ICollection、IEnumerable、 ICloneable 等接口 | 与 Hashtable 集合类似,集合中的元素以键值对的形式存放,不同的是该集合会按照 key 值自动对集合中的元素排序 |
二、ArrayList️
ArrayList源码:https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#mscorlib/system/collections/arraylist.cs,3e3f6715773d6643
在源码讲解中,我会将详细讲解放到源码注释中,并且会删去错误验证(throw)或不影响原理的代码来达到便于阅读的效果。
1、声明
ArrayList是一个非泛型集合,它只实现了 IList, ICloneable接口而没有实现其泛型接口,因此无法使用标准查询运算。
public class ArrayList : IList, ICloneable
2、属性与变量
(1)公有属性
ArrayList定义了以下公有属性,其作用见注释。
//获取或设置 ArrayList 可以包含的元素个数。
public virtual int Capacity { get; set; }
//获取一个值,表示 ArrayList 是否具有固定大小。
public virtual bool IsFixedSize { get; }
//获取 ArrayList 中实际包含的元素个数。
public virtual int Count { get; }
//定义了索引器
public virtual object? this[int index] { get; set; }
//获取一个值,表示访问 ArrayList 是否同步(线程安全)。
public virtual bool IsSynchronized { get; }
//获取一个值,表示 ArrayList 是否只读。
public virtual bool IsReadOnly { get; }
//获取一个对象用于同步访问 ArrayList。
public virtual object SyncRoot { get; }
(2)私有变量
除此ArrayList还定义了一系列私有变量,用于内部实现。
//声明了_items数组,用于存放数据,类型为Object
private Object[] _items;
//大小
private int _size;
//定义了version,作为Array的变动版本记录
private int _version;
//定义了const常量,默认容量为4
private const int _defaultCapacity = 4;
//只读的空数组
private static readonly Object[] emptyArray = EmptyArray<Object>.Value;
3、关键方法
(1)构造方法
ArrayList构造器有三类,为了便于阅读我们删去了含有throw关键字的语句,相关解释见注释。
//空参数构造构造器
public ArrayList() {
//项目数组,初始构造时为只读的空数组
_items = emptyArray;
}
//指定容量构造器
public ArrayList(int capacity) {
//如果指定大小为0,则初始为只读空数组
if (capacity == 0)
_items = emptyArray;
//若不为0则初始化并定义数组大小
else
_items = new Object[capacity];
}
//传入集合参数的构造器
public ArrayList(ICollection c) {
//获取集合的大小
int count = c.Count;
//大小为0,则初始化为只读空数组
if (count == 0)
{
_items = emptyArray;
}
//大小不为0,则初始化相应大小,并通过AddRange将集合C加入到该ArrayList中
else {
_items = new Object[count];
AddRange(c);
}
}
(2)Add
public virtual int Add(Object value) {
//判断容量是否足够
if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
//存放数据
_items[_size] = value;
//版本更新
_version++;
//返回集合大小
return _size++;
}
//确保容量足够,如果不够则执行_items.Length * 2,进行二倍扩容
private void EnsureCapacity(int min) {
if (_items.Length < min){
int newCapacity = _items.Length == 0? _defaultCapacity: _items.Length * 2;
if ((uint)newCapacity > Array.MaxArrayLength) newCapacity = Array.MaxArrayLength;
if (newCapacity < min) newCapacity = min;
Capacity = newCapacity;
}
}
(3)AddRange
public virtual void AddRange(ICollection c) {
//调用InsertRange方法,传入数组大小和集合c
InsertRange(_size, c);
}
public virtual void InsertRange(int index, ICollection c) {
//获取集合c的大小
int count = c.Count;
if (count > 0) {
//确保容量足够,否则扩容
EnsureCapacity(_size + count);
//创建一个新的数组itemsToInsert
Object[] itemsToInsert = new Object[count];
//将集合c中的元素,复制到数组itemsToInsert中
c.CopyTo(itemsToInsert, 0);
//将itemsToInsert数组复制到ArrayList集合中的_items数组中
itemsToInsert.CopyTo(_items, index);
//增加容量
_size += count;
//更新版本
_version++;
}
}
(4)Containers
for循环遍历_items数组,通过Equals方法进行比较。
public virtual bool Contains(Object item) {
if (item==null) {
for(int i=0; i<_size; i++)
if (_items[i]==null)
return true;
return false;
}
else {
for(int i=0; i<_size; i++)
if ( (_items[i] != null) && (_items[i].Equals(item)) )
return true;
return false;
}
}
(5)Insert
通过Copy将index后的元素向后移动位,最后空出index进行赋值。
public virtual void Insert(int index, Object value) {
if (_size == _items.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(_items, index, _items, index + 1, _size - index);
}
_items[index] = value;
_size++;
_version++;
}
(6)Remove
先通过IndexOf找到被删除元素的索引,然后通过RemoveAt,进行删除,此处是将index后的元素集体向前移动一位,最后将末尾元素置为null。
public virtual void Remove(Object obj) {
int index = IndexOf(obj);
if (index >=0)
RemoveAt(index);
}
public virtual void RemoveAt(int index) {
_size--;
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(_items, index + 1, _items, index, _size - index);
}
_items[_size] = null;
_version++;
}
4、其它方法
在其它方法中,不解读,只保留关键代码。
(1)Reverse
public virtual void Reverse(int index, int count) {
Array.Reverse(_items, index, count);
_version++;
}
(2)Sort
public virtual void Sort(int index, int count, IComparer comparer) {
Array.Sort(_items, index, count, comparer);
_version++;
}
(3)ToArray
public virtual Array ToArray(Type type) {
Array array = Array.UnsafeCreateInstance(type, _size);
Array.Copy(_items, 0, array, 0, _size);
return array;
}
(4)Clear
public virtual void Clear() {
Array.Clear(_items, 0, _size);
_size = 0;
_version++;
}
5、说说索引器和?
我们发现C#中的集合中很少看到GET方法,因为C#集合统一使用索引器来进行集合元素的访问。像Get(int index)或Get(String key)都可以使用collection[index]或collection[key],来进行访问和修改。
当您为类定义一个索引器时,该类的行为就会像一个 虚拟数组(virtual array) 一样。您可以使用数组访问运算符 [ ] 来访问该类的的成员。
索引器格式为:
Type this[int index]{get{};set{};}
ArrayList的索引器:
public virtual object? this[int index] { get; set; }
这里使用了?,我们来回顾以下C#中的?相关语法糖。来源:[https://www.cnblogs.com/youmingkuang/p/11459615.html]
(1)可空类型修饰符(?)
引用类型可以使用空引用表示一个不存在的值,而值类型通常不能表示为空。
例如:string str=null; 是正确的,int i=null; 编译器就会报错。
为了使值类型也可为空,就可以使用可空类型,即用可空类型修饰符"?“来表示,表现形式为"T?”
(2) 三元(运算符)表达式(?: )
例如:x?y:z 表示如果表达式x为true,则返回y;
如果x为false,则返回z,是省略if{}else{}的简单形式。
(3)空合并运算符(??)
用于定义可空类型和引用类型的默认值。
如果此运算符的左操作数不为null,则此运算符将返回左操作数,否则返回右操作数。
例如:a??b 当a为null时则返回b,a不为null时则返回a本身。
(4)NULL检查运算符(?.)
如果对象为NULL,则不进行后面的获取成员的运算,直接返回NULL。
三、SortedList
它可以使用键和索引来访问列表中的项。
排序列表是数组和哈希表的组合。它包含一个可使用键或索引访问各项的列表。如果您使用索引访问各项,则它是一个动态数组(ArrayList),如果您使用键访问各项,则它是一个哈希表(Hashtable)。集合中的各项总是按键值排序。
1、声明
public class SortedList : IDictionary, ICloneable
2、属性和变量
(1)私有变量
//两个数组
private Object[] keys;
private Object[] values;
private int _size;
private int version;
private IComparer comparer;
private KeyList keyList;
private ValueList valueList;
[NonSerialized]
private Object _syncRoot;
private const int _defaultCapacity = 16;
private static Object[] emptyArray = EmptyArray<Object>.Value;
(2)属性
public virtual int Capacity;
public virtual int Count;
public virtual ICollection Keys;
public virtual ICollection Values;
public virtual bool IsSynchronized;
public virtual Object SyncRoot;
public virtual bool IsReadOnly;
3、关键方法
(1)构造器
public SortedList(int initialCapacity) {
keys = new Object[initialCapacity];
values = new Object[initialCapacity];
comparer = new Comparer(CultureInfo.CurrentCulture);
}
public SortedList(IComparer comparer):this() {
if (comparer != null) this.comparer = comparer;
}
public SortedList(IComparer comparer, int capacity):this(comparer) {
Capacity = capacity;
}
IComparer:继承IComparer接口,可以自定义比较器,IComparable提供了方法int CompareTo(object obj)用于两个对象的比较。
(2)Add
public virtual void Add(Object key, Object value) {
int i = Array.BinarySearch(keys, 0, _size, key, comparer);
Insert(~i, key, value);
}
private void Insert(int index, Object key, Object value) {
//扩容
if (_size == keys.Length) EnsureCapacity(_size + 1);
//如果插入到中间,则将index之后的元素后移一位
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(keys, index, keys, index + 1, _size - index);
Array.Copy(values, index, values, index + 1, _size - index);
}
//插入元素到index
keys[index] = key;
values[index] = value;
_size++;
version++;
}
~ 运算符通过反转每个位产生其操作数的按位求补
(3)GetKey
public virtual Object GetKey(int index) {
return keys[index];
}
(4)GetKeyList和GetValueList
public virtual IList GetKeyList() {
if (keyList == null) keyList = new KeyList(this);
return keyList;
}
public virtual IList GetValueList() {
if (valueList == null) valueList = new ValueList(this);
return valueList;
}
(5)Remove
public virtual void Remove(Object key) {
int i = IndexOfKey(key);
if (i >= 0) RemoveAt(i);
}
public virtual void RemoveAt(int index) {
_size--;
//如果删除到中间,则将index之前的元素后移一位
if (index < _size) {
Array.Copy(keys, index + 1, keys, index, _size - index);
Array.Copy(values, index + 1, values, index, _size - index);
}
keys[_size] = null;
values[_size] = null;
version++;
}
4、说说Array
C#中的Array是一个很强大的类。Array 类是 C# 中所有数组的基类,它是在 System 命名空间中定义。Array 类提供了各种用于数组的属性和方法。
public abstract class Array : ICloneable, IList, IStructuralComparable, IStructuralEquatable
其常用方法如下:
//Copy
public static void Copy(Array sourceArray, Array destinationArray, int length);
public static void Copy(Array sourceArray, int sourceIndex, Array destinationArray, int destinationIndex, int length);
//CopyTo
public void CopyTo(Array array, int index);
//IndexOf
public static int IndexOf(Array array, Object value);
public static int LastIndexOf(Array array, Object value);
//Sort
public static void Sort(Array array);
//Reverse
public static void Reverse(Array array);
public static void Reverse(Array array, int index, int length);
四、LinkedList
LinkedList源码:https://referencesource.microsoft.com/#System/compmod/system/collections/generic/linkedlist.cs
在源码讲解中,我会将详细讲解放到源码注释中,并且会删去错误验证(throw)或不影响原理的代码来达到便于阅读的效果。
1、声明
与ArrayList不同的是LinkedList的命名空间为namespace System.Collections.Generic,除此还实现了ICollection<T>,是泛型类集合[本文只有该集合来自Generic]。
public class LinkedList<T>: ICollection<T>, System.Collections.ICollection, IReadOnlyCollection<T>,ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback
2、属性与变量
(1)变量
//内部变量
//头节点
internal LinkedListNode<T> head;
//大小
internal int count;
internal int version;
//私有变量
private Object _syncRoot;
private SerializationInfo siInfo; //A temporary variable which we need during deserialization. //常量
const String VersionName = "Version";
const String CountName = "Count";
const String ValuesName = "Data";
(2)节点密封类
sealed的中文意思是密封,由它修饰的类或方法将不能被继承或是重写,sealed修饰符不能和 abstract 同时使用,因为抽象类必须由提供抽象方法或属性的实现的类来继承,密封类不能同时又是抽象类,因为抽象总是希望被继承的。abstract是抽象,那sealed就是硬性标准。
public sealed class LinkedListNode<T> {
//变量
//链表
internal LinkedList<T> list;
//后置节点
internal LinkedListNode<T> next;
//前驱节点
internal LinkedListNode<T> prev;
//存放数据
internal T item;
//属性
//对应item
public T Value {
get { return item;}
set { item = value;}
}
//对应链表
public LinkedList<T> List {
get { return list;}
}
//对应后置节点
public LinkedListNode<T> Next {
get { return next == null || next == list.head? null: next;}
}
//对应前驱节点
public LinkedListNode<T> Previous {
get { return prev == null || this == list.head? null: prev;}
}
//方法
public LinkedListNode(T value) {
this.item = value;
}
internal LinkedListNode(LinkedList<T> list, T value) {
this.list = list;
this.item = value;
}
//使无效:当前节点以及节点引用置为空
internal void Invalidate() {
list = null;
next = null;
prev = null;
}
}
}
3、关键方法
(1)构造函数
//空参构造
public LinkedList() {}
//传入泛型集合类型参数构造
public LinkedList(IEnumerable<T> collection) {
//遍历泛型集合类对象,将该对象节点逐个加入到LinkedList尾部
foreach( T item in collection) {
AddLast(item);
}
}
(2)AddFirst
public LinkedListNode<T> AddFirst(T value) {
//传入当前list对象和value,生成节点
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
//如果头节点为空
if (head == null) {
//插入为头节点
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
}
else {
//头节点不为空,新节点作为头节点
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
head = result;
}
return result;
}
private void InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(LinkedListNode<T> newNode) {
//将该节点的前后节点都指向新节点
newNode.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = newNode;
//将该节点赋值成为头节点
head = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}
private void InternalInsertNodeBefore(LinkedListNode<T> node, LinkedListNode<T> newNode) {
//将该节点的下一个节点指向传入节点[传入的是头节点的话,指向头节点]
newNode.next = node;
//新节点的前驱指向传入节点的前驱
newNode.prev = node.prev;
//将传入节点的前驱节点的后置指向新节点
node.prev.next = newNode;
//将传入节点的前驱指向新节点
node.prev = newNode;
version++;
count++;
}
(3)AddLast
public LinkedListNode<T> AddLast(T value) {
LinkedListNode<T> result = new LinkedListNode<T>(this, value);
if (head==null) {
InternalInsertNodeToEmptyList(result);
}
else {
InternalInsertNodeBefore(head, result);
}
return result;
}
我们发现这个方法和AddFirst方法十分相似,唯一缺少的一步是[head = result;],那如此新节点就会插入到头节点的前一个节点。那每次节点的插入都是插到head头节点的前面,前插则新节点成为新头节点,尾插则头节点的前一个节点就是尾节点。(此处不同于Java中的LinkedList属性中含有头尾节点)。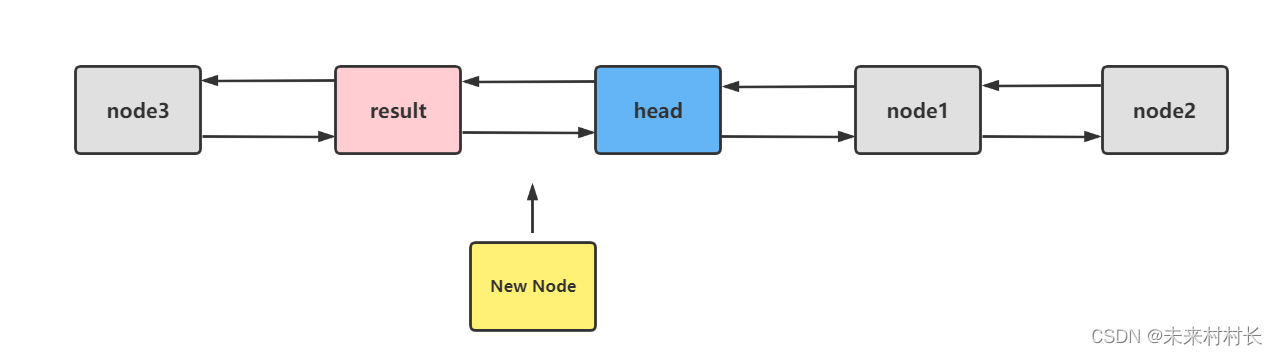
(4)Remove
public bool Remove(T value) {
LinkedListNode<T> node = Find(value);
if (node != null) {
InternalRemoveNode(node);
return true;
}
return false;
}
internal void InternalRemoveNode(LinkedListNode<T> node) {
//该节点后置的前驱指向该节点的前驱
node.next.prev = node.prev;
//该节点的前驱的后置指向该节点的后置
node.prev.next = node.next;
//如果是头节点,则该节点的后置节点成为头节点
if ( head == node) {
head = node.next;
}
node.Invalidate();
count--;
version++;
}
(5)Find
public LinkedListNode<T> Find(T value) {
//获取头节点
LinkedListNode<T> node = head;
EqualityComparer<T> c = EqualityComparer<T>.Default;
//如果头节点不为null
if (node != null) {
if (value != null) {
do {
//直到当前节点等于查询节点
if (c.Equals(node.item, value)) {
return node;
}
//迭代到下一个节点
node = node.next;
//循环遍历
} while (node != head);
}
else {
do {
if (node.item == null) {
return node;
}
node = node.next;
} while (node != head);
}
}
return null;
}
4、其它方法
(1)Contains
public bool Contains(T value) {
return Find(value) != null;
}
(2)Clear
public void Clear() {
LinkedListNode<T> current = head;
//循环遍历
while (current != null ) {
LinkedListNode<T> temp = current;
current = current.Next;
//使每个节点置为空[使无效]
temp.Invalidate();
}
//头节点置为null
head = null;
count = 0;
version++;
}
(3)GetEnumerator
获取迭代器。
public Enumerator GetEnumerator() {
return new Enumerator(this);
}
5、说说泛型
泛型(Generic)允许您延迟编写类或方法中的编程元素的数据类型的规范,直到实际在程序中使用它的时候。换句话说,泛型允许您编写一个可以与任何数据类型一起工作的类或方法。
泛型类:
public class MyGenericArray<T>
{
private T[] array;
public MyGenericArray(int size)
{
array = new T[size + 1];
}
public T getItem(int index)
{
return array[index];
}
public void setItem(int index, T value)
{
array[index] = value;
}
}
泛型方法:
static void Swap<T>(ref T lhs, ref T rhs)
{
T temp;
temp = lhs;
lhs = rhs;
rhs = temp;
}
五、Queue️
1、声明
Queue同样也是非泛型集合。
public class Queue : ICollection, ICloneable
实现ICloneable接口使一个类型成为可克隆的(cloneable),这需要提供Clone方法来提供该类型的对象的副本。Clone方法不接受任何参数,返回object类型的对象(不管是何种类型实现该接口)。所以我们获得副本后仍需要进行显式地转换。
深拷贝与浅拷贝:如果自定义类型包含引用类型的数据成员,必须考虑Clone方法是实现浅拷贝(shallow copy)还是深拷贝(deep copy)。浅拷贝是指副本对象中的引用类型的数据成员与源对象的数据成员指向相同的对象。而如果是深拷贝,则必须创建整个对象的结构,副本对象中的引用类型的数据成员与源对象的数据成员指向不同的对象。
2、属性与变量
(1)私有变量与常量
private Object[] _array;//数组
private int _head;//头部
private int _tail;//尾部
private int _size;//大小
private int _growFactor;
private int _version;//版本
[NonSerialized]
private Object _syncRoot;//同步源
//私有常量
private const int _MinimumGrow = 4;
private const int _ShrinkThreshold = 32;
(2)属性
public virtual int Count {
get { return _size; }
}
public virtual bool IsSynchronized {
get { return false; }
}
public virtual Object SyncRoot {
get {
if( _syncRoot == null) {
System.Threading.Interlocked.CompareExchange(ref _syncRoot, new Object(), null);
}
return _syncRoot;
}
}
3、关键方法
(1)构造方法
public Queue(int capacity, float growFactor) {
//传入容量
_array = new Object[capacity];
_head = 0;
_tail = 0;
_size = 0;
_growFactor = (int)(growFactor * 100);
}
//空参构造
public Queue():this(32, (float)2.0){}
//指定容量构造
public Queue(int capacity) : this(capacity, (float)2.0) {}
(2)Enqueue:入队
public virtual void Enqueue(Object obj){
//如果_size等于数组大小,则进行扩容
if (_size == _array.Length) {
int newcapacity = (int)((long)_array.Length * (long)_growFactor / 100);
if (newcapacity < _array.Length + _MinimumGrow) {
newcapacity = _array.Length + _MinimumGrow;
}
//扩容方法
SetCapacity(newcapacity);
}
//加入到索引tail处
_array[_tail] = obj;
//更新索引_tail
_tail = (_tail + 1) % _array.Length;
_size++;
_version++;
}
//设置容量大小
private void SetCapacity(int capacity) {
//新建数组
Object[] newarray = new Object[capacity];
//将原数组元素复制到新数组
if (_size > 0) {
if (_head < _tail) {
Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _size);
} else {
Array.Copy(_array, _head, newarray, 0, _array.Length - _head);
Array.Copy(_array, 0, newarray, _array.Length - _head, _tail);
}
}
//数组更新为新容量数组
_array = newarray;
//更新头尾索引
_head = 0;
_tail = (_size == capacity) ? 0 : _size;
_version++;
}
(3)Dequque:出队
public virtual Object Dequeue() {
//获取头索引元素
Object removed = _array[_head];
//移除头索引元素
_array[_head] = null;
//更新头索引
_head = (_head + 1) % _array.Length;
_size--;
_version++;
return removed;
}
看了出队入队以后,我们发现C#的队列实现是一个循环数组,通过%数组长度来达到循环效果。
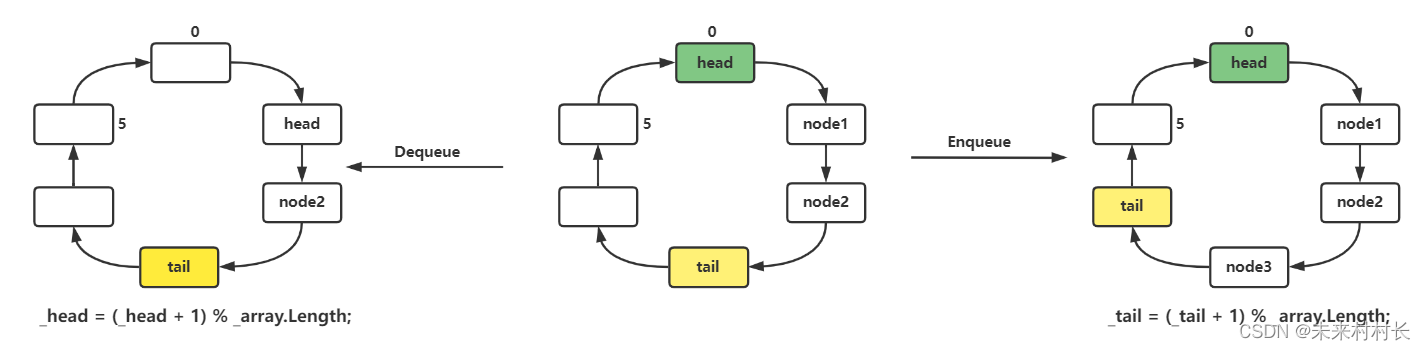
4、其它方法
(1)Peek
public virtual Object Peek() {
return _array[_head];
}
(2)Contains
public virtual bool Contains(Object obj) {
int index = _head;
int count = _size;
//循环遍历,从头节点开始
while (count-- > 0) {
if (obj == null) {
if (_array[index] == null)
return true;
} else if (_array[index] != null && _array[index].Equals(obj)) {
return true;
}
//需要注意的是index不是从0开始,每次取索引都需要%
index = (index + 1) % _array.Length;
}
return false;
}
六、Stack️
1、声明
public class Stack : ICollection, ICloneable
2、属性与变量
(1)私有变量
private Object[] _array; // Storage for stack elements
[ContractPublicPropertyName("Count")]
private int _size; // Number of items in the stack.
private int _version; // Used to keep enumerator in sync w/ collection.
[NonSerialized]
private Object _syncRoot;
private const int _defaultCapacity = 10;
(2)属性
public virtual int Count
public virtual bool IsSynchronized
public virtual Object SyncRoot
3、关键方法
(1)Push:入栈
public virtual void Push(Object obj) {
//扩容
if (_size == _array.Length) {
Object[] newArray = new Object[2*_array.Length];
Array.Copy(_array, 0, newArray, 0, _size);
_array = newArray;
}
//按照顺序存放
_array[_size++] = obj;
_version++;
}
(2)Pop:出栈
public virtual Object Pop() {
_version++;
//后进先出
Object obj = _array[--_size];
_array[_size] = null;
return obj;
}
(3)Peek
取到size-1,这里说明size处没有具体存放元素。
public virtual Object Peek() {
return _array[_size-1];
}
4、说说lock
我们在这里说说之前一直没提到的同步方法。
[HostProtection(Synchronization=true)]
public static Stack Synchronized(Stack stack) {
return new SyncStack(stack);
}
internal SyncStack(Stack stack) {
_s = stack;
_root = stack.SyncRoot;
}
这里使用Synchronized使栈同步,实际上是调用其私有同步栈的构造器。
[Serializable]
private class SyncStack : Stack
{
private Stack _s;
private Object _root;
internal SyncStack(Stack stack) {
_s = stack;
_root = stack.SyncRoot;
}
public override bool IsSynchronized {get { return true; }}
public override Object SyncRoot {get {return _root;}}
public override int Count {
get {
lock (_root) {
return _s.Count;
}
}
}
}
我们看来几个较为关键的方法。
public override void Push(Object value) {
lock (_root) {
_s.Push(value);
}
}
public override Object Pop() {
lock (_root) {
return _s.Pop();
}
}
public override Object Peek() {
lock (_root) {
return _s.Peek();
}
}
我们发现每一个方法都使用如下结构。
lock (_root) {
方法名();
}
这里的_root是一个Object对象,用为。
lock 关键字可以用来确保代码块完成运行,而不会被其他线程中断。它可以定义一段代码为临界区代码段(线程访问互斥),一个时刻只允许一个线程进入临界区代码段,其它线程必须等待。这是通过在代码块运行期间为给定对象获取互斥锁来实现的。
lock关键字定义: lock(expression) statement_block,其中expression代表你希望跟踪的对象,通常是对象引用。
通常,应避免锁定 public 类型,否则实例将超出代码的控制范围。 lock (this)、lock (typeof (MyType)) 同步控制的范围较大,我们尽量通过集合类中lock(private object _root)这样的方式,缩小临界范围。因为lock锁定的对象是一个程序块的内存边界,我们应当缩小该边界范围。
最后:
- lock不能锁定空值
- lock不能锁定string类型:相同内容的字符串都代表着同一个实例
- lock不能锁定值类型:值类型不是引用类型的,虽然可以装箱,但是会报错
- lock(this)的缺点:该实例被一个线程访问后,便不允许其它线程进行访问,哪怕访问的内容非临界区代码
- lock最好不要锁定public修饰的类型引用或不受程序控制的对象,否则将超出代码的控制范围
七、HashTable🦽
C#中实现了哈希表数据结构的集合类有System.Collections.Hashtable和System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary<TKey,TValue>,前者为一般类型的哈希表,后者是泛型版本的哈希表。Dictionary和Hashtable之间并非只是简单的泛型和非泛型的区别,两者使用了完全不同的哈希冲突解决办法。
1、声明
public class Hashtable : IDictionary, ISerializable, IDeserializationCallback, ICloneable
2、属性和变量
//这里定义了结构体—桶
private struct bucket {
public Object key;//键
public Object val;//值
public int hash_coll;//Hash码
}
//桶数组,用于存放key-value对
private bucket[] buckets;
private int count;
private int occupancy;
private int loadsize;
//装填因子
private float loadFactor;
private volatile int version;
private volatile bool isWriterInProgress;
private ICollection keys;
private ICollection values;
private IEqualityComparer _keycomparer;
private Object _syncRoot;
3、说说预处理器指令️
【以下来自官方文档】
使用四个预处理器指令来控制条件编译:
#if:打开条件编译,其中仅在定义了指定的符号时才会编译代码。#elif:关闭前面的条件编译,并基于是否定义了指定的符号打开一个新的条件编译。#else:关闭前面的条件编译,如果没有定义前面指定的符号,打开一个新的条件编译。#endif:关闭前面的条件编译。
如果 C# 编译器遇到 #if 指令,最后跟着一个 #endif 指令,则仅当定义指定的符号时,它才编译这些指令之间的代码。 与 C 和 C++ 不同,不能将数字值分配给符号。 C# 中的 #if 语句是布尔值,且仅测试是否已定义该符号。 例如:
#if DEBUG
Console.WriteLine("Debug version");
#endif
可以使用运算符 ==(相等)和 !=(不相等)来测试 bool 值是 true 还是 false。 true 表示定义该符号。 语句 #if DEBUG 具有与 #if (DEBUG == true) 相同的含义。 可以使用 && (and)、|| (or) 和 !(not) 运算符来计算是否已定义多个符号。 还可以用括号对符号和运算符进行分组。
#if 以及 #else、#elif、#endif、#define 和 #undef 指令,允许基于是否存在一个或多个符号包括或排除代码。 条件编译在编译调试版本的代码或编译特定配置的代码时会很有用。
以 #if 指令开头的条件指令必须以 #endif 指令显式终止。 #define 允许你定义一个符号。 通过将该符号用作传递给 #if 指令的表达式,该表达式的计算结果为 true。 还可以通过 DefineConstants 编译器选项来定义符号。 可以通过 #undef 取消定义符号。 使用 #define 创建的符号的作用域是在其中定义它的文件。 使用 DefineConstants 或 #define 定义的符号与具有相同名称的变量不冲突。 也就是说,变量名称不应传递给预处理器指令,且符号仅能由预处理器指令评估。
#elif 可以创建复合条件指令。 如果之前的 #if 和任何之前的可选 #elif 指令表达式的值都不为 true,则计算 #elif 表达式。 如果 #elif 表达式计算结果为 true,编译器将计算 #elif 和下一条件指令间的所有代码。 例如:
#define VC7
//...
#if debug
Console.WriteLine("Debug build");
#elif VC7
Console.WriteLine("Visual Studio 7");
#endif
#else 允许创建复合条件指令,因此,如果先前 #if 或(可选)#elif 指令中的任何表达式的计算结果都不是 true,则编译器将对介于 #else 和下一个 #endif 之间的所有代码进行求值。 #endif(#endif) 必须是 #else 之后的下一个预处理器指令。
#endif 指定条件指令的末尾,以 #if 指令开头。
4、关键方法
HashTable的源码较为复杂,此处未能详细解读,待以后补充。
(1)构造方法
public Hashtable() : this(0, 1.0f) {}
public Hashtable(int capacity, float loadFactor) {
//0.72是基于性能测试的较优选
this.loadFactor = 0.72f * loadFactor;
//确定Hashtable容量大小
double rawsize = capacity / this.loadFactor;
int hashsize = (rawsize > InitialSize) ? HashHelpers.GetPrime((int)rawsize) : InitialSize;
//初始化桶
buckets = new bucket[hashsize];
loadsize = (int)(this.loadFactor * hashsize);
isWriterInProgress = false;
// Based on the current algorithm, loadsize must be less than hashsize.
Contract.Assert( loadsize < hashsize, "Invalid hashtable loadsize!");
}
(2)Add
public virtual void Add(Object key, Object value) {
Insert(key, value, true);
}
(3)InitHash
private uint InitHash(Object key, int hashsize, out uint seed, out uint incr) {
uint hashcode = (uint) GetHash(key) & 0x7FFFFFFF;
seed = (uint) hashcode;
incr = (uint)(1 + ((seed * HashPrime) % ((uint)hashsize - 1)));
return hashcode;
}
(4)this索引器
这里的索引器不通过index来进行索引,而是通过Object key进行索引。
public virtual Object this[Object key] {
get {
uint seed;
uint incr;
bucket[] lbuckets = buckets;
uint hashcode = InitHash(key, lbuckets.Length, out seed, out incr);
int ntry = 0;
bucket b;
int bucketNumber = (int) (seed % (uint)lbuckets.Length);
do{
int currentversion;
int spinCount = 0;
do {
currentversion = version;
b = lbuckets[bucketNumber];
if( (++spinCount) % 8 == 0 ) {
Thread.Sleep(1);
}
} while ( isWriterInProgress || (currentversion != version) );
if (b.key == null) {
return null;
}
if (((b.hash_coll & 0x7FFFFFFF) == hashcode) && KeyEquals (b.key, key))
return b.val;
bucketNumber = (int) (((long)bucketNumber + incr)% (uint)lbuckets.Length); } while (b.hash_coll < 0 && ++ntry < lbuckets.Length);
return null;
}
set {
Insert(key, value, false);
}
}
(5)Remove
public virtual void Remove(Object key) {
uint seed;
uint incr;
//获取hash码
uint hashcode = InitHash(key, buckets.Length, out seed, out incr);
int ntry = 0;
bucket b;
//桶的号码定位
int bn = (int) (seed % (uint)buckets.Length);
do {
b = buckets[bn];
if (((b.hash_coll & 0x7FFFFFFF) == hashcode) && KeyEquals (b.key, key)) {
isWriterInProgress = true;
buckets[bn].hash_coll &= unchecked((int)0x80000000);
if (buckets[bn].hash_coll != 0) {
buckets[bn].key = buckets;
}
else {
buckets[bn].key = null;
}
buckets[bn].val = null;
count--;
UpdateVersion();
isWriterInProgress = false;
return;
}
bn = (int) (((long)bn + incr)% (uint)buckets.Length);
} while (b.hash_coll < 0 && ++ntry < buckets.Length);
}
边栏推荐
- Excel之VBA简单宏编程
- Summary of cases of players' disconnection and reconnection in Huawei online battle service
- Lake Shore continuous flow cryostat transmission line
- Go language self-study series | go language data type
- Bao, que se passe - t - il si le serveur 100 + O & M a mal à la tête? Utilisez le majordome xingyun!
- Example explanation: move graph explorer to jupyterlab
- 案例分享:QinQ基本组网配置
- Clean up system cache and free memory under Linux
- Dom4J解析XML、Xpath检索XML
- Lake Shore 连续流动低温恒温器传输线
猜你喜欢

Lake Shore continuous flow cryostat transmission line
Dlib+opencv library for fatigue detection
前4A高管搞代运营,拿下一个IPO
数商云:从规划到落地,五矿集团如何快速构建数字化发展新格局?

Lake Shore 连续流动低温恒温器传输线

Getting started with kubernetes command (namespaces, pods)
Lumiprobe 活性染料丨吲哚菁绿说明书

Lake Shore—CRX-EM-HF 型低温探针台

【直播预约】数据库OBCP认证全面升级公开课

Is PMP cancelled??
随机推荐
Lumiprobe 活性染料丨吲哚菁绿说明书
MATLAB中subplot函数的使用
Helium transmission line of lake shore cryostat
Digital business cloud: from planning to implementation, how does Minmetals Group quickly build a new pattern of digital development?
Dom4J解析XML、Xpath检索XML
Team up to learn! 14 days of Hongmeng equipment development "learning, practicing and testing" practical camp, free of charge!
[pytorch record] automatic hybrid accuracy training torch cuda. amp
华为联机对战服务玩家掉线重连案例总结
[live broadcast appointment] database obcp certification comprehensive upgrade open class
【pytorch记录】模型的分布式训练DataParallel、DistributedDataParallel
Altair HyperWorks 2022软件安装包和安装教程
Altair HyperWorks 2022 software installation package and installation tutorial
Graduation season | Huawei experts teach the interview secret: how to get a high paying offer from a large factory?
Appgallery connect scenario development practice - image storage and sharing
Manufacturing SRM management system supplier all-round closed-loop management, to achieve procurement sourcing and process efficient collaboration
Lake Shore—OptiMag 超导磁体系统 — OM 系列
Clean up system cache and free memory under Linux
摄像头的MIPI接口、DVP接口和CSI接口[通俗易懂]
一次SQL优化,数据库查询速度提升 60 倍
Huawei game failed to initialize init with error code 907135000