当前位置:网站首页>Binary tree (program)
Binary tree (program)
2022-06-12 12:39:00 【Joey Liao】
At the beginning, I would like to summarize , The thinking mode of binary tree problem-solving is divided into two categories :
- Whether you can get the answer by traversing the binary tree ? If possible , Use one
traverseWith external variables , This is called 「 Traverse 」 The mode of thinking . - Whether a recursive function can be defined , Pass the subproblem ( subtree ) The answer to the original question ? If possible , Write the definition of this recursive function , And make full use of the return value of this function , This is called 「
Break down the problem」 The mode of thinking .
No matter which mode of thinking you use , You need to think :
If you extract a binary tree node separately , What does it need to do ? When do I need to ( front / in / Post sequence position ) do ? You don't have to worry about other nodes , Recursive functions will help you perform the same operation on all nodes .
List of articles
The importance of binary trees
for instance , For example, two classical sorting algorithms Quick sort and Merge sort , For both of them , What do you understand ?
If you tell me , Quicksort is a preorder traversal of a binary tree , Merge sort is the post order traversal of a binary tree , So I know you're a great algorithmic .
Why can quick sort and merge sort have something to do with binary trees ? Let's briefly analyze their algorithm ideas and code framework :
The logic of quick sort is , If you want to be right nums[lo..hi] Sort , Let's find a cut-off point p, Make by exchanging elements nums[lo..p-1] Are less than or equal to nums[p], And nums[p+1..hi] Is greater than nums[p], And then recursively nums[lo..p-1] and nums[p+1..hi] Looking for a new dividing point , Finally, the entire array is sorted .
The code framework for quick sort is as follows :
void sort(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
/****** Preorder traversal position ******/
// Building a demarcation point by exchanging elements p
int p = partition(nums, lo, hi);
/************************/
sort(nums, lo, p - 1);
sort(nums, p + 1, hi);
}
First construct the boundary point , Then go to the left and right subarrays to construct the dividing point , Don't you think this is the preorder traversal of a binary tree ?
Let's talk about the logic of merging and sorting , If you want to be right nums[lo..hi] Sort , Let's start with nums[lo..mid] Sort , Right again nums[mid+1..hi] Sort , Finally, merge the two ordered subarrays , The whole array is in order .
The code framework for merge sort is as follows :
// Definition : Sort nums[lo..hi]
void sort(int[] nums, int lo, int hi) {
int mid = (lo + hi) / 2;
// Sort nums[lo..mid]
sort(nums, lo, mid);
// Sort nums[mid+1..hi]
sort(nums, mid + 1, hi);
/****** Post sequence position ******/
// Merge nums[lo..mid] and nums[mid+1..hi]
merge(nums, lo, mid, hi);
/*********************/
}
Sort the left and right subarrays first , Then merge ( Similar to the logic of merging ordered linked lists ), Do you think this is a post order traversal framework for binary trees ? in addition , This is the legendary divide and conquer algorithm , But so .
If you can see through these sorting algorithms at a glance , Do you still need to recite these classical algorithms ? Unwanted . You can catch it with your hand , The algorithm can be extended from the binary tree traversal framework .
Have a deep understanding of the preface
A few questions :
What do you understand about the traversal of binary tree before, during and after the sequence , Just three different orders List Do you ?
Please analyze , What's special about postorder traversal ?
Please analyze , Why is there no middle order traversal in a multi fork tree ?
Binary tree traversal framework :
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// Preamble position
traverse(root.left);
// Middle order position
traverse(root.right);
// Post sequence position
}
Ignore the so-called first, middle and second order , Just look traverse function , You said it was doing something ?
In fact, it is a function that can traverse all nodes of a binary tree , It is essentially no different from traversing arrays or linked lists :
/* Iterate through arrays */
void traverse(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
}
}
/* Recursively traverses the array */
void traverse(int[] arr, int i) {
if (i == arr.length) {
return;
}
// Preamble position
traverse(arr, i + 1);
// Post sequence position
}
/* Iterate through the single linked list */
void traverse(ListNode head) {
for (ListNode p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {
}
}
/* Recursive traversal of single linked list */
void traverse(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
// Preamble position
traverse(head.next);
// Post sequence position
}
The traversal of single linked list and array can be iterative , It can also be recursive , The structure of binary tree is nothing more than binary linked list , There's no way to rewrite it into a simple form , So generally speaking, the traversal framework of binary tree refers to the form of recursion .
You've noticed , As long as it is a recursive traversal , Can have pre sequence position and post sequence position , Before and after recursion, respectively .
The so-called preamble position , Just entered a node ( Elements ) When , The subsequent position is the node that is about to leave ( Elements ) When , So further , You write the code in different places , The timing of code execution is also different :

for instance , If I let you Print in reverse order The values of all nodes in a single linked list , What are you doing ?
Of course, there are many ways to implement , But if you have a thorough understanding of recursion , You can use In the following order Position to operate :
/* Recursive traversal of single linked list , Print linked list elements in reverse order */
void traverse(ListNode head) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
traverse(head.next);
// Post sequence position
print(head.val);
}
So back to the binary tree is the same , It's just one more middle order position .
The code of the preamble position is executed when it just enters a binary tree node ;
The code of the post order position is executed when it is about to leave a binary tree node ;
The code of the middle order position traverses the left subtree of a binary tree node , When you are about to start traversing the right subtree, execute .
You can find that every node has 「 only 」 It belongs to its own front, middle and back order position , So I say that the first, middle and last order traversal is the process of traversing a binary tree Handle three special points in time for each node .
Here you can also understand why there is no middle order position in a multi fork tree , Because each node of the binary tree will only switch the left subtree to the right subtree once , A multi tree node may have many child nodes , Will switch the subtree several times to traverse , So there is no node in the multi tree 「 only 」 The middle order traversal position of .
Said so many basic , Is to help you establish a correct understanding of binary tree , And then you'll see :
All the problems of binary tree , Is to let you inject ingenious code logic in the front, middle and rear positions , To achieve one's purpose , You just need to think about what each node should do , Don't worry about the others , Throw it to the binary tree traversal framework , Recursion will do the same operation on all nodes .
Two ways to solve problems
The recursive solution of binary tree problem can be divided into two kinds of ideas , The first is to traverse the binary tree to get the answer , The second type is to calculate the answer by decomposing the problem , These two kinds of ideas correspond to The core framework of backtracking algorithm and Dynamic programming core framework .
Force to buckle 104 topic 「 The maximum depth of a binary tree 」

Obviously, go through the binary tree , Use an external variable to record the depth of each node , Take the maximum value to get the maximum depth , This is the idea of traversing the binary tree to calculate the answer .
// Record the maximum depth
int res = 0;
// Record the depth of the node traversed
int depth = 0;
// The main function
int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
traverse(root);
return res;
}
// Binary tree traversal framework
void traverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// Preamble position
depth++;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// To the leaf node , Update maximum depth
res = Math.max(res, depth);
}
traverse(root.left);
traverse(root.right);
// Post sequence position
depth--;
}
Of course , You can also easily find that the maximum depth of a binary tree can pass through The maximum height of the subtree is derived , This is the idea of decomposing the question and calculating the answer .
The solution code is as follows :
// Definition : Enter the root node , Returns the maximum depth of the binary tree
int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
// Using definitions , Calculate the maximum depth of the left and right subtrees
int leftMax = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightMax = maxDepth(root.right);
// The maximum depth of the whole tree is equal to the maximum depth of the left and right subtrees, and the maximum value is taken ,
// Then add the root node itself
int res = Math.max(leftMax, rightMax) + 1;
return res;
}
Sum up , The general thinking process when encountering the problem of a binary tree is :
1、 Is it ok to pass Traverse Go through the binary tree and get the answer ? If possible , Use one traverse With external variables .
2、 Can I define a recursive function , Pass the subproblem ( subtree ) The answer to the original question ? If possible , Write the definition of this recursive function , and Make full use of the return value of this function .
3、 No matter which mode of thinking you use , You have to understand what each node of the binary tree needs to do , When do I need to ( First, middle and last ) do .
The particularity of the post order position
Before saying the post order position , First, let's briefly talk about the middle order and the front order .
The middle order position is mainly used in BST Scene , You can do that BST The middle order traversal of is considered to be traversing an ordered array .
The preamble position itself has no special properties , The reason why you find that it seems that many questions are written in the preamble , In fact, it's because we are used to writing code that is not sensitive to the first, middle and last order position in the first order position .
You can see that , Before the order The code execution of the location is The top-down Of , and In the following order The code execution of the location is Bottom up Of :
There are many mysteries in it , This means that the code in the preamble position can only get the data passed by the parent node from the function parameters , The code at the back order position can not only obtain the parameter data , You can also get the data passed back from the subtree through the return value of the function .
So in other words , Once you find that the problem is related to subtree , The big probability is to set a reasonable definition and return value for the function , Write the code in the subsequent position .
Next, let's look at how the post order position plays a role in the actual topic , Let's talk about force deduction 543 topic 「 The diameter of a binary tree 」
// Record the length of the maximum diameter
int maxDiameter = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
maxDepth(root);
return maxDiameter;
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftMax = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightMax = maxDepth(root.right);
// Post sequence position , By the way, calculate the maximum diameter
int myDiameter = leftMax + rightMax;
maxDiameter = Math.max(maxDiameter, myDiameter);
return 1 + Math.max(leftMax, rightMax);
}
Now the time complexity is only maxDepth Functional O(N) 了 .
Here we are. , Take care of the foregoing : Encountered subtree problem , The first thought is to set the return value of the function , Then make an article in the post order position .
In turn, , If you write something like the one you started with Recursive nested recursion Solution method , The probability also needs to reflect whether it can be passed Post order traversal optimization 了 .
Sequence traversal
Binary tree questions are mainly used to cultivate recursive thinking , Sequence traversal belongs to iterative traversal , It's easier , Here's the code framework :
// Enter the root node of a binary tree , You can traverse this binary tree
void levelTraverse(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
// Traverse every layer of the binary tree from top to bottom
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
int sz = q.size();
// Traverse each node of each layer from left to right
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
TreeNode cur = q.poll();
// Put the next level node in the queue
if (cur.left != null) {
q.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
q.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
}
Inside this while Circulation and for The loop runs from top to bottom and from left to right :
above BFS Algorithm framework It is extended from the sequence traversal of binary tree , It is often used to find graphs without authority Shortest path problem .
Of course, this framework can also be modified flexibly , The title does not need to record the number of layers ( They count ) You can remove... From the above frame for loop
边栏推荐
- 配准后图像对比函数itk::CheckerBoardImageFilter
- Simple picture preview
- Examples of Cartesian product and natural connection of relational algebra
- JS built in object
- OpenMAX (OMX)框架
- VGg small convolution instead of large convolution vs deep separable convolution
- C语言进阶篇——万字详解指针和qsort函数
- [C language] keyword static & Multi file & guessing game
- 二叉树(序列化篇)
- Object value taking method in JS And []
猜你喜欢

JS convert string to array object

this.$ How to solve the problem when refs is undefined?
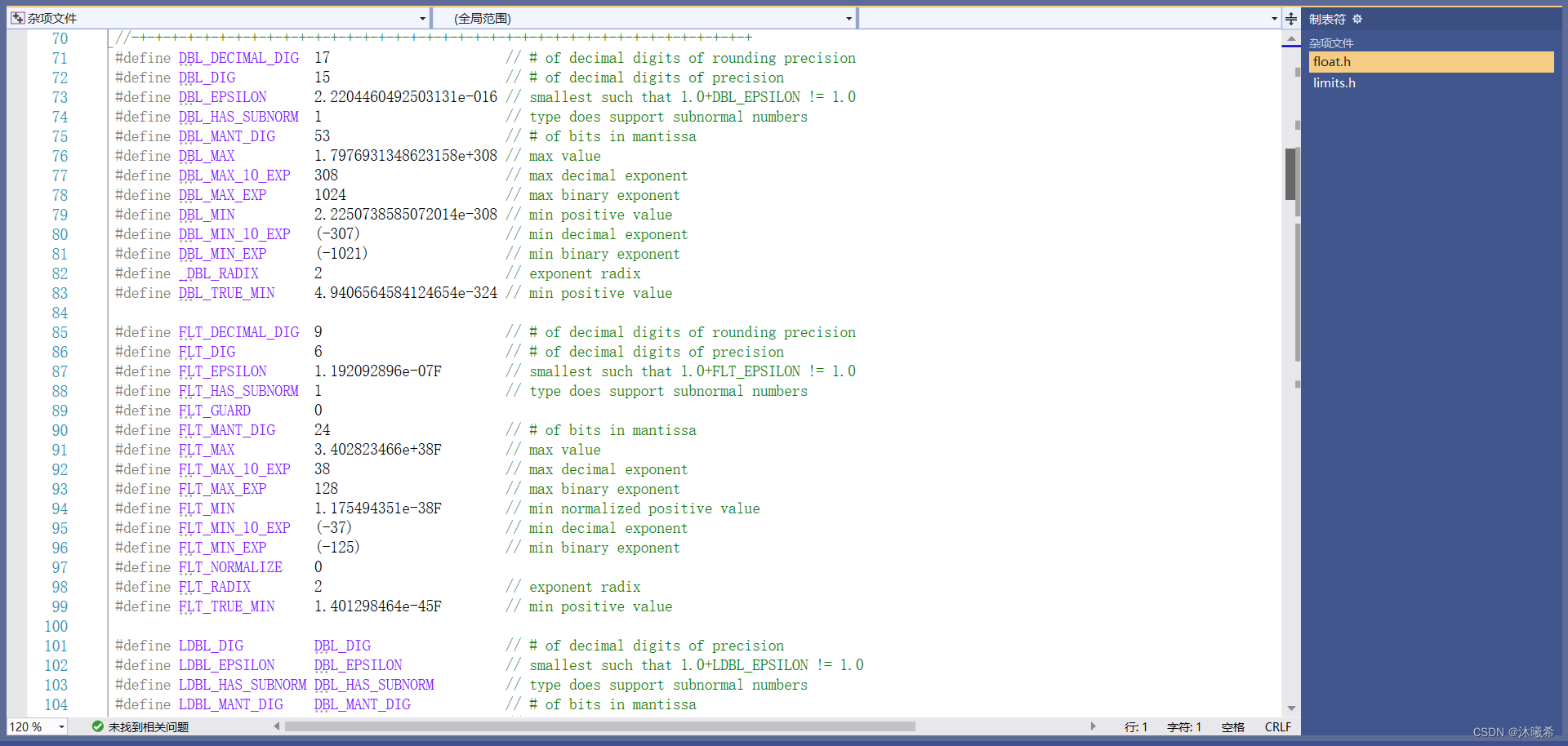
C语言进阶篇——浮点型在内存中的存储
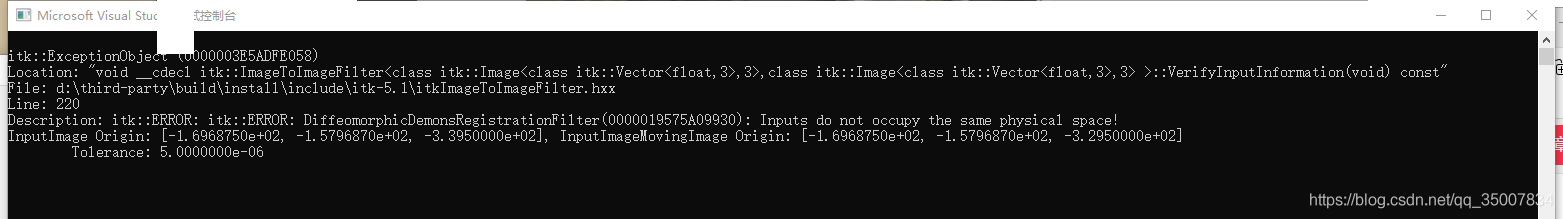
itk::SymmetricForcesDemonsRegistrationFilter

Promise knowledge

二叉树(思路篇)
Introduction, installation and use of core JS

In depth anatomy of C language - key words & supplementary contents

【C语言】关键字static&&多文件&&猜字游戏

从基础到源码统统帮你搞定,技术详细介绍
随机推荐
Problems encountered in installing canvas and errors encountered in running the project
NewOJ Week 10题解
Native JS implements the copy text function
Numpy数值计算基础
Geek challenge 2021 Web
安全KNN
this.$ How to solve the problem when refs is undefined?
itk neighbhood
Point cloud registration -- GICP principle and its application in PCL
【您编码,我修复】WhiteSource正式更名为Mend
【数据库】navicat --oracle数据库创建
JS pre parsing, object, new keyword
A short guide to SSH port forwarding
Difference between Definition and Declaration
2021-11-16
From simple to deep - websocket
Suggestions and skills for advanced version of go language test
itk itk::BSplineDeformableTransform
二叉树(序列化篇)
This direction of ordinary function and arrow function