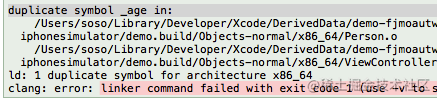
当前位置:网站首页>Confusing basic concepts member variables local variables global variables
Confusing basic concepts member variables local variables global variables
2022-07-05 08:48:00 【InfoQ】
Member variables
@interface Person:NSObject
{
int age;
}
@end
- Variables written in braces of class declarations , We call it a member variable ( attribute 、 Instance variables )
- Member variables can only be accessed through objects
- Member variables cannot leave the class , After leaving the class, it is not a member variable
- Member variables cannot be initialized while being defined
- Storage : Pile up ( The storage space of the heap corresponding to the current object ). Data stored in the heap , Will not be released by the system , Only programmers can release
local variable
-(void)info{
int age = 0;
}
- Variables written in functions or code blocks , We call it a local variable
- Scope : Start with the line of definition , Until braces or
return
- Local variables can be defined first and then initialized , It can also be defined and initialized at the same time
- Storage : Stack . Data stored in the stack , The system will automatically release
Global variables
@implementation Person
int age = 0;
-(void)info{
}
@end
- Variables written outside functions and braces , It's called all variables
- Scope : Start with the line of definition , All the way to the end of the file
- Global variables can be defined first and then initialized , It can also be defined and initialized at the same time
- Storage : Static zone , As soon as the program starts, it allocates storage space , Not released until the end of the program
- There are two types of global variables :
staticModify global variable , Available only in this source file
static int age =3;
@implementation Person
@end
- stay OC Declared in the syntax of `static` Static variables cannot be accessed directly through class names in other classes , Its scope can only be in the declared .m In file . However, you can call the method of this class to indirectly modify the value of this static variable
- `static` The variables declared by the keyword must be placed in `implementation` outside , Or in the method , If you don't assign a value to it , The default is 0, It initializes only once the program starts up ( It is not initialized after the class is instantiated )
- take static Static variables are written in methods , Its initialization is also when the program starts up , Once the program starts `static` Cannot be created in
externModify global variable , Can be referenced by other classes .h The header file states
//.h In file
extern int age;
.m Implement the assignment in the file
//.m In file
#import "Person.h"
int age = 10;
@implementation Person
@end
externCan be placed before variables or functions , To represent the definition of a variable or function in another file , Prompt the compiler when it encounters this variable or function , Look for its definition in other modules . in addition ,externIt can also be used to specify Links
- Be careful : Naming must be unique , To distinguish from global variables in other source files , If a global variable with the same name as another source file appears , It will report an error
- difference :
externDecorated global variables have external links by default , Scope is the whole project , Global variables defined in a file , In another file , adopt external Declaration of global variables , You can use global variables .
staticDecorated global static variables , The scope is the file where the variable is declared .
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢

Guess riddles (8)
TypeScript手把手教程,简单易懂
Typical low code apaas manufacturer cases

Lori remote control LEGO motor
EA introduction notes
Ros- learn basic knowledge of 0 ROS - nodes, running ROS nodes, topics, services, etc

Halcon snap, get the area and position of coins

猜谜语啦(4)

Programming implementation of subscriber node of ROS learning 3 subscriber

猜谜语啦(10)
随机推荐
C# LINQ源码分析之Count
Basic number theory - factors
OpenFeign
696. Count binary substring
kubeadm系列-02-kubelet的配置和启动
The first week of summer vacation
Mathematical modeling: factor analysis
Several problems to be considered and solved in the design of multi tenant architecture
[daiy4] jz32 print binary tree from top to bottom
Task failed task_ 1641530057069_ 0002_ m_ 000000
猜谜语啦(2)
Basic number theory -- Euler function
[noi simulation] juice tree (tree DP)
Halcon: check of blob analysis_ Blister capsule detection
我从技术到产品经理的几点体会
Business modeling of software model | stakeholders
暑假第一周
猜谜语啦(7)
How can fresh students write resumes to attract HR and interviewers
[Niuke brush questions day4] jz55 depth of binary tree