当前位置:网站首页>Count of C # LINQ source code analysis
Count of C # LINQ source code analysis
2022-07-05 08:43:00 【Lazy Ethan】
Summary
LINQ In the code base Count Method as the key method of data statistics , Often used . In Statistics ,Count Method whether to traverse the whole sequence every time to get the number of sequence elements ,Count Whether there is an optimization mechanism for the content of the method . In order to better understand the working principle of this method , We analyze it from the perspective of source code .
The content of this article is based on C# LINQ Source code analysis Select and
C# LINQ Source code analysis Where Based on , Yes Count Method source code analysis .
Count Methods to introduce
Count The basic function of the method is to obtain the number of elements in the sequence .LINQ The code base provides 2 individual Count The method of overloading is as follows :
| Method name | Basic introduction |
|---|---|
| Count(IEnumerable) | Get the number of elements in the sequence |
| Count(IEnumerable, Func<TSource,Boolean>) | Returns the number of elements in the sequence that meet the condition |
Count Key source code analysis
Count The method is IEnumerable An extended method of , To support a TSource The generic parameter .
public static int Count<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
if (source == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.source);
}
if (source is ICollection<TSource> collectionoft)
{
return collectionoft.Count;
}
if (source is IIListProvider<TSource> listProv)
{
return listProv.GetCount(onlyIfCheap: false);
}
if (source is ICollection collection)
{
return collection.Count;
}
int count = 0;
using (IEnumerator<TSource> e = source.GetEnumerator())
{
checked
{
while (e.MoveNext())
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
- If the sequence is empty , Throw an exception ;
- If the sequence is implemented ICollection An instance of an interface , for example List Example , Directly return the Count attribute ;
- If the sequence is I Realization IListProvider An instance of an interface , Calling the GetCount Method , Parameters are passed in by default false,IListProvider The interface is described below ;
- If the sequence is implemented ICollection An instance of an interface , for example List Example , Directly return the Count attribute ;
- If source It's an iterator , And the iterator is not implemented IListProvider, Call the iterator , Then complete the iteration , And count the number of elements .
Count Another overloaded method code of is similar , I won't repeat .
Count How methods work
For inspection Count How the method works , This paper deals with Count Method and its associated content for code extraction , Defined Count2 Method , To increase various log, Specific code appendix .
Realization ICollection Object call of interface Count Method
Student See Appendix .
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
The results are as follows :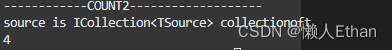
We can see from the result that , obtain List Number of elements in the object , You don't have to traverse the entire List, Just go back to ICollection Interface Count Property value .
Realization IListProvider Object call of interface Count Method
For one List Generic sequence xx, If there is xx.Where().Count() Call to , We want to filter and calculate the number of elements in one iteration , I don't want to realize through two iterations .
The key to achieving the above goals is IListProvider Interface , It mainly defines ToList,ToArray and GetCount Specification of three methods , This article mainly discusses GetCount Method .
We discussed in the previous article ,LINQ The main implementation basis of is inside the extension method , Use various iterators to implement specific operations , for example Where Methodical WhereListIterator iterator , Can achieve List Element filtering .
IListProvider It is to let various iterators implement GetCount Method , So that GetCount Operations are attached to various iterative operations .
The key codes are as follows , among ToList and ToArray Beyond the scope of this article , Has been omitted .
private sealed partial class WhereListIterator<TSource> : Iterator<TSource>, IIListProvider<TSource>
{
public int GetCount(bool onlyIfCheap)
{
if (onlyIfCheap)
{
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _source.Count; i++)
{
TSource item = _source[i];
if (_predicate(item))
{
checked
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
We can see , Sealing class WhereListIterator Realized IIListProvider Medium GetCount, In this method, filtering and counting are combined into one .
List Generic sequence xx.Where().Count() Implementation principle of
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList
.Where2(s=>s.MathResult >= 90)
.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
- Get into Where2 Extension method , return WhereListIterator Iterator object .
- Get into Count2 Extension method ,WhereListIterator It's done IIListProvider Method .
- call WhereListIterator Object's GetCount Method ,onlyIfCheap Parameter is false.
- Complete filtering and statistics .
The results are as follows , In line with expectations :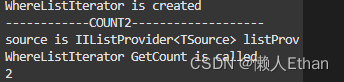
List Generic sequence xx.Select().Count() Implementation principle of
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList
.Select2(s => new {
Name= s.Name, Math = s.MathResult})
.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
- Get into Select2 Extension method , return SelectListIterator object
- Get into Count2 Extension method ,SelectListIterator It's done IIListProvider Method .
- call SelectListIterator Object's GetCount Method ,onlyIfCheap Parameter is false.
- Complete projection and statistical operations ,SelectListIterator Class related source code is as follows :
private sealed partial class SelectListIterator<TSource, TResult> : IPartition<TResult>
{
public int GetCount(bool onlyIfCheap)
{
// In case someone uses Count() to force evaluation of
// the selector, run it provided `onlyIfCheap` is false.
int count = _source.Count;
if (!onlyIfCheap)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
_selector(_source[i]);
}
}
return count;
}
}
List Generic sequence xx.Where().Select().Count() Implementation principle of
In the discussion of the previous article , We have learned ,xx.Where().Select() The filtering and projection operations in will be merged into , adopt WhereSelectListIterator iterator , In a traverse List Generic sequence , Will satisfy Where Conditional elements are projected , One time traversal .
Again WhereSelectListIterator It has also been realized. IIListProvider Generic interface , The code is as follows , among ToList and ToArray Beyond the scope of this article , Has been omitted .
private sealed partial class WhereSelectListIterator<TSource, TResult> : IIListProvider<TResult>
{
public int GetCount(bool onlyIfCheap)
{
// In case someone uses Count() to force evaluation of
// the selector, run it provided `onlyIfCheap` is false.
if (onlyIfCheap)
{
return -1;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _source.Count; i++)
{
TSource item = _source[i];
if (_predicate(item))
{
_selector(item);
checked
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
It's not hard to see from the code that ,GetCount Method will filter , Projection and statistical elements , In one traversal .
therefore , The implementation logic of the following code is very clear , As follows :
List<Student> studentList = new List<Student>()
{
new Student("x001", "Tom", "CN-1" , 90),
new Student("x002", "Jack", "CN-1", 88),
new Student("x003", "Mary", "CN-2", 87),
new Student("x004", "Frank", "CN-2", 97),
};
var count = studentList
.Where2(s=>s.MathResult >= 90)
.Select2(s => new {
Name= s.Name, Math = s.MathResult})
.Count2();
System.Console.WriteLine(count);
- Enter the extension method Where2, return WhereListIterator Iterator instance .
- Enter the extension method Select2,WhereListIterator Is an iterator instance , Call the instance's own Select Method , return WhereSelectListIterator example .
- Enter the extension method Count2,WhereSelectListIterator Realized IIListProvider Interface , So call the instance's own GetCount Method , Will filter , Projection and statistical elements , In one traversal .
The results of the implementation are in line with expectations :
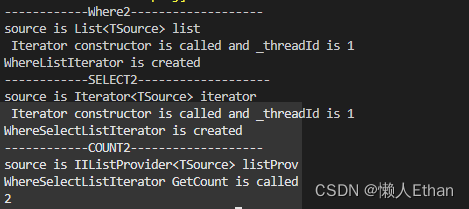
Conclusion
Count The way to deal with List,Array When collecting data types , Will directly return to their implementation ICollection Interface Count Property value ; In and other extension methods Where, Select When used together , The statistical operation and other extended method operations , A merger , Avoid traversing the same sequence multiple times .
appendix
Count2 Method :
public static int Count2<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source)
{
Console.WriteLine("------------COUNT2-------------------");
if (source == null)
{
ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.source);
}
if (source is ICollection<TSource> collectionoft)
{
Console.WriteLine("source is ICollection<TSource> collectionoft");
return collectionoft.Count;
}
if (source is IIListProvider<TSource> listProv)
{
Console.WriteLine("source is IIListProvider<TSource> listProv");
return listProv.GetCount(onlyIfCheap: false);
}
if (source is ICollection collection)
{
Console.WriteLine("source is ICollection collection");
return collection.Count;
}
Console.WriteLine("source is Iterator");
int count = 0;
using (IEnumerator<TSource> e = source.GetEnumerator())
{
checked
{
while (e.MoveNext())
{
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
Student class
public class Student {
public string Id {
get; set; }
public string Name {
get; set; }
public string Classroom {
get; set; }
public int MathResult {
get; set; }
}
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
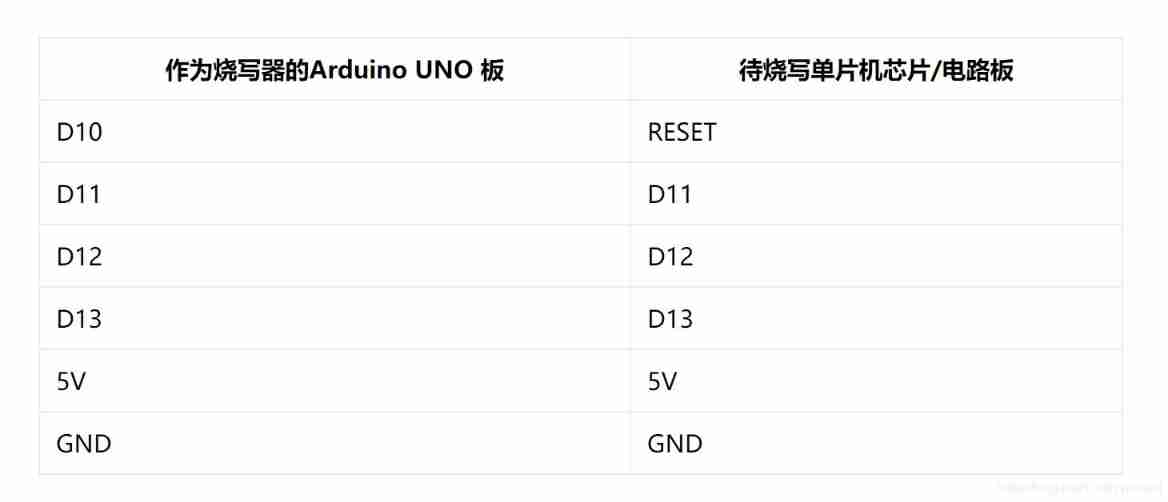
Arduino burning program and Arduino burning bootloader

猜谜语啦(4)

我从技术到产品经理的几点体会
Business modeling of software model | object modeling

猜谜语啦(142)

Guess riddles (2)

Example 005: three numbers sorting input three integers x, y, Z, please output these three numbers from small to large.

My university
![[牛客网刷题 Day4] JZ35 复杂链表的复制](/img/bc/ce90bb3cb6f52605255f1d6d6894b0.png)
[牛客网刷题 Day4] JZ35 复杂链表的复制
![[matlab] matlab reads and writes Excel](/img/80/78e4c7fcd27473526e480d4b930e2c.jpg)
[matlab] matlab reads and writes Excel
随机推荐
Halcon snap, get the area and position of coins
Halcon clolor_ pieces. Hedv: classifier_ Color recognition
Example 009: pause output for one second
Halcon shape_ trans
[three tier architecture and JDBC summary]
C# LINQ源码分析之Count
Guess riddles (9)
【日常训练--腾讯精选50】557. 反转字符串中的单词 III
C语言标准函数scanf不安全的原因
287. Looking for repeats - fast and slow pointer
猜谜语啦(8)
Bluebridge cup internet of things competition basic graphic tutorial - clock selection
Lori remote control commissioning record
Example 003: a complete square is an integer. It is a complete square after adding 100, and it is a complete square after adding 168. What is the number?
Matlab tips (28) fuzzy comprehensive evaluation
Halcon affine transformations to regions
Business modeling | process of software model
Is the security account given by Yixue school safe? Where can I open an account
Guess riddles (11)
Example 006: Fibonacci series