当前位置:网站首页>Pytorch entry record
Pytorch entry record
2022-07-05 08:36:00 【Muyu orange wind 24】
This is my study b standing up Main small mound Pytorch Record after the introduction video , link https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1hE411t7RN?p=1
One 、Pytorch Load data
Reading data mainly involves two classes :Dataset And DataLoader
1.Dataset
First, you can inherit torch.utils.data Medium Dataset Class loads its own dataset
from pytorch The official source code can be seen , It mainly includes three methods __init__、__getitem__ and __len__
__init__ The purpose of is to get a containing data and labels list, Each element can find the picture position and its corresponding label .
__getitem__ Method to obtain the image pixel matrix and label of each element , return img and label.
__len__ The method is to get the length of the data .
class MyData(Dataset):
def __init__(self, root_dir, image_dir, label_dir, transform):
self.root_dir = root_dir
self.image_dir = image_dir
self.label_dir = label_dir
self.label_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir)
self.image_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.image_dir)
self.image_list = os.listdir(self.image_path)
self.label_list = os.listdir(self.label_path)
self.transform = transform
# because label and Image Same file name , Do the same sort , It can guarantee the extracted data and label It's one-to-one
self.image_list.sort()
self.label_list.sort()
def __getitem__(self, idx):
img_name = self.image_list[idx]
label_name = self.label_list[idx]
img_item_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.image_dir, img_name)
label_item_path = os.path.join(self.root_dir, self.label_dir, label_name)
img = Image.open(img_item_path)
with open(label_item_path, 'r') as f:
label = f.readline()
# img = np.array(img)
img = self.transform(img)
sample = {'img': img, 'label': label}
return sample
def __len__(self):
assert len(self.image_list) == len(self.label_list)
return len(self.image_list)secondly , It can be used torchvision.dataset Load existing datasets
torchvision.dataset Contains many data sets , for example COCO、CIFAR、MNIST etc.
With CIFAR10 For example , Using this dataset requires 5 Parameters
root: Is where the data set is stored .
train: yes bool type ,True Indicates that the data set is a training set ,False Expressed as a test set .
transform: Transform the picture , For example, cutting 、 rotate 、 Change size or become tensor data type (.ToTensor) etc.
download:bool type ,True Indicates that the data set needs to be downloaded , General choice True
dataset_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
])
train_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="./dataset", train=True, transform=dataset_transform, download=True)
test_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="./dataset", train=False, transform=dataset_transform, download=True)
torch.utils.tensorboard Data visualization
import torchvision
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
dataset_transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()
])
test_set = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root="./dataset", train=False, transform=dataset_transform, download=True)
writer = SummaryWriter("CIFAR_Test")
for i in range(10):
img, target = test_set[i]
writer.add_image("test_set", img, i)
writer.close()stay tensorboard You can see CIFAR10 Before the test set 10 A picture , Here's the picture :
2.Dataloader
When the dataset is ready , In general use torch.utils.data.DataLoader Load data
It can be seen from official documents ,Dataloader The use of classes requires many parameters , The most common one is :
dataset: Ready data sets
batch—size: The number of samples captured in a single training
shuffle: At every epoch Whether to disturb the order of capturing pictures , The default is False
num_workers: Use multiprocess loading ,0 Indicates that the main process is used to load
drop_last: There is not enough data to grab for the last time batch_size Discard or not
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
test_loader = DataLoader(dataset=test_data, batch_size=64, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, drop_last=True)
Two 、 Neural network model construction nn.Module
1. Convolution layer
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = Conv2d(in_channels=3, out_channels=6, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
return xin_channels: Enter the number of channels
out_channels: Number of output channels
kernel_size: Convolution kernel size
stride: The convolution kernel moves the step size
padding: Add a boundary to the input matrix padding_mode:‘zeros’ Boundary complement 0
bias: Whether to add offset
2. Pooling layer
Take the largest pool

ceil_mode:True Similar to rounding up , The remaining elements of the boundary are also maximized ;False The remaining elements of the boundary will be discarded , Take code as an example :
import torch
input = torch.tensor([[1,2,3,4,5],
[4,5,6,7,8],
[7,8,9,11,2],
[2,4,6,3,2],
[7,3,5,2,1]],dtype=torch.float32)
input = torch.reshape(input,(1,1,5,5))
output = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2,ceil_mode=True)
output = output(input)
print(output)When set to True When the output is :
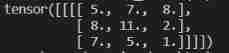
When set to False When the output is :
![]()
ps: The step size is generally equal to the convolution kernel size by default
3. Nonlinear activation function
Commonly used functions are Sigmoid function 、Relu Functions, etc
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.relu1 = ReLU()
self.sigmoid1 = Sigmoid()
def forward(self, input):
output = self.sigmoid1(input)
#output = self.relu1(input)
return output4. Linear layer and other layers
Other layers such as Normalization layer 、Dropout Layers, etc. are not introduced in detail , The specific use method can still be queried through official documents .
The linear layer is generally expressed as ![]()
, Each neuron is connected to all neurons of the previous layer , Realize the linear combination or linear transformation of the previous layer .


in_features: Enter the size of the image
out_features: The size of the output image
bias: Whether to add offset
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model, self).__init__()
self.linear1 = Linear(128, 10)
def forward(self, input):
output = self.linear1(input)
return output5. Loss function and back propagation
L1Loss: Find the absolute value of the difference between the input and the target
MSELoss: Find the square of the difference between the input and the target
CrossEntropyLoss: Cross entropy loss function , Generally used in classification models
import torch
from torch import nn
inputs = torch.tensor([1, 4, 6], dtype=torch.float32)
targets = torch.tensor([1, 5, 9], dtype=torch.float32)
inputs = torch.reshape(inputs, (1, 1, 1, 3))
targets = torch.reshape(targets, (1, 1, 1, 3))
loss = nn.L1Loss(reduction='sum')
result = loss(inputs, targets)
loss_mse = nn.MSELoss()
result_mse = loss_mse(inputs, targets)
print(result)
print(result_mse)
x = torch.tensor([0.1, 0.2, 0.3])
y = torch.tensor([1])
x = torch.reshape(x, (1, 3))
loss_cross = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
result_cross = loss_cross(x, y)
print(result_cross)In particular, we need to focus on the input and output required by different loss functions .
Back propagation is to update the parameters of the network continuously by minimizing the loss function .
loss.backward()6. Optimizer
With SGD For example

params: Parameters of the model
lr: Learning rate
optim = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
optim.zero_grad() # Gradient clear
loss_fn(model(input), target).backward()
optim.step()7. Use and modification of existing network model
With VGG16 For example
import torchvision
from torch import nn
vgg16_false = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=False)
vgg16_true = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
print(vgg16_true)
#print(vgg16_false)pretrained:True Indicates that the model is already in ImageNet Data sets are preprocessed
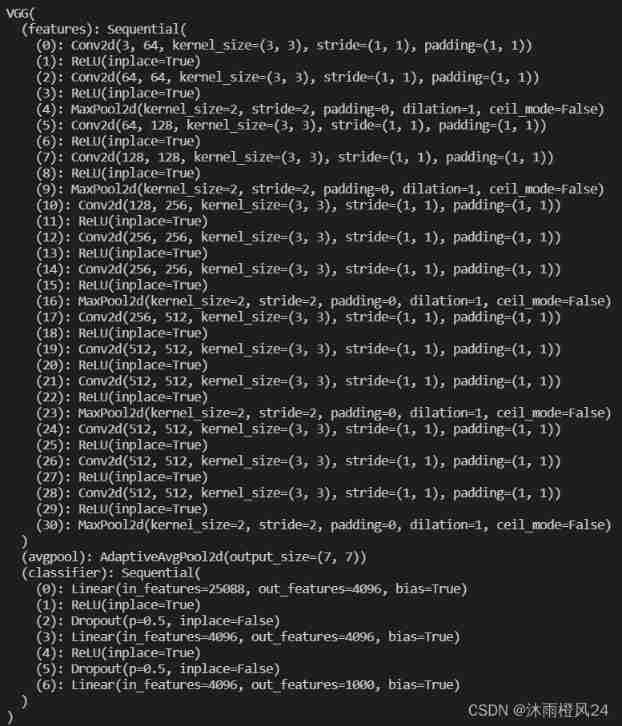
Model modification : If you want to VGG16 A linear layer is added at the end of the network
vgg16_true.classifier.add_module('add_linear', nn.Linear(1000, 10))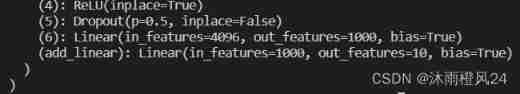
If you want to modify the network structure
vgg16_false.classifier[6] = nn.Linear(4096, 10)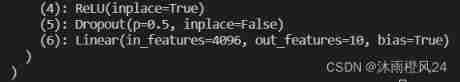
8. Save and read the model
Model preservation
There are generally two ways to save models
The first one is : Save the model structure + Model parameters
torch.save(vgg16, "vgg16_method1.pth")The second kind : Save model parameters ( The official recommendation )
torch.save(vgg16.state_dict(), "vgg16_method2.pth")Model reading
There are two ways to save the corresponding model , There are also two ways to read models
The first one is :
model = torch.load("vgg16_method1.pth")Be careful : The first method is to read your own model , You need to import the class of the model from the model file in advance , Otherwise, an error will be reported
from model_save import *The second kind :
vgg16 = torchvision.models.vgg16(pretrained=False)
vgg16.load_state_dict(torch.load("vgg16_method2.pth"))You need to load the model first , Then update the saved model parameters to the network
3、 ... and 、 Complete model training and verification
model.py
# coding=gbk
import torch
from torch import nn
# structure LeNet-5 The Internet
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Model,self).__init__()
self.model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels=3,out_channels=6,kernel_size=(5,5),stride=1,padding=0,bias=True),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2),
nn.Conv2d(6,16,5),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(2),
nn.Flatten(),
nn.Linear(16*5*5,120),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(120,84),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(84,10)
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.model(x)
return x
# Used to test the correctness of the network structure
if __name__ == '__main__':
model = Model()
input = torch.ones((64,3,32,32))
output = model(input)
print(output.shape)structure LeNet-5 Network structure , Use CIFAR10 Data sets are trained
train.py
# -*-coding:gbk-*-
import torch
from torch import nn, no_grad
import torchvision
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from model import *
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
import time
# Define the training equipment
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
# Prepare the dataset
train_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('./data',train=True,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
test_data = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10('./data',train=False,transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
train_data_size = len(train_data)
test_data_size = len(test_data)
# Use DataLoader Load data set
train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_data,batch_size=64,shuffle=True)
test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_data,batch_size=64)
# Build a network structure
LeNet = Model()
LeNet.to(device)
# Loss function
loss_fn = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
loss_fn.to(device)
# Optimizer
lr = 1e-3
optim = torch.optim.SGD(LeNet.parameters(),lr,momentum=0.9)
# Training times
train_step = 0
test_step = 0
# Number of training rounds
epoch = 50
#Tensorboard visualization
writer = SummaryWriter('./log_train')
# Start timing
start_time = time.time()
for i in range(epoch):
print(f'-------------- The first {i+1} Round of training begins --------------')
# Start training
LeNet.train()
for data in train_dataloader:
imgs , targets = data
imgs = imgs.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
outputs = LeNet(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
optim.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optim.step()
train_step += 1
if (train_step % 100 == 0):
end_time = time.time()
print(end_time - start_time)
print(f" Training times {train_step},Loss:{loss.item()}")
writer.add_scalar("train_loss",loss.item(),train_step)
# Use the test set to evaluate the training
LeNet.eval()
test_loss = 0
accuracy = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for data in test_dataloader:
imgs , targets = data
imgs = imgs.to(device)
targets = targets.to(device)
outputs = LeNet(imgs)
loss = loss_fn(outputs,targets)
test_loss += loss.item()
accuracy += (outputs.argmax(1) == targets).sum()
print(f" On test set Loss:{test_loss}")
print(f" Test set accuracy Accuracy:{accuracy / test_data_size}")
writer.add_scalar("test_loss",test_loss,test_step)
writer.add_scalar("test_accuracy",accuracy,test_step)
test_step += 1
# Model preservation
torch.save(LeNet,"LeNet.pth")
print(" Model saved ")
writer.close()

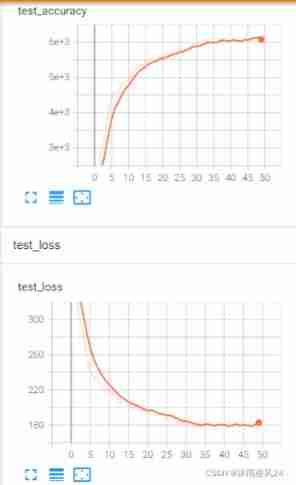
after 50 Round training , The network reached 60.88% The accuracy of
test.py
# -*- coding: gbk -*-
import imp
from PIL import Image
import torch
import torchvision
from model import *
classes = ('plane', 'car', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck')
#image_path = "dog.jpg"
image_path = "airplane.jpg"
img = Image.open(image_path)
#print(image)
transform = torchvision.transforms.Compose([torchvision.transforms.Resize((32,32)),
torchvision.transforms.ToTensor()])
image = transform(img)
#print(image.shape)
LeNet = torch.load("LeNet.pth",map_location=torch.device("cpu"))
image = torch.reshape(image,(1,3,32,32))
LeNet.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output = LeNet(image)
#print(output.argmax(1).item())
label = output.argmax(1).item()
print(classes[label])
img.show()Test with pictures of dogs and planes respectively , Finally, the network correctly predicts the category .


![]()
![]()
边栏推荐
- Agile project management of project management
- STM32 single chip microcomputer - bit band operation
- 剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
- 实例005:三数排序 输入三个整数x,y,z,请把这三个数由小到大输出。
- 实例009:暂停一秒输出
- 287. 寻找重复数-快慢指针
- Explore the authentication mechanism of StarUML
- Google sitemap files for rails Projects - Google sitemap files for rails projects
- PIP installation
- Lori remote control LEGO motor
猜你喜欢

Guess riddles (6)
Take you to understand the working principle of lithium battery protection board

Example 008: 99 multiplication table
![[three tier architecture]](/img/73/c4c75a453f03830e83cabb0762eb9b.png)
[three tier architecture]
Typical low code apaas manufacturer cases

MySQL之MHA高可用集群

STM32---ADC
An enterprise information integration system
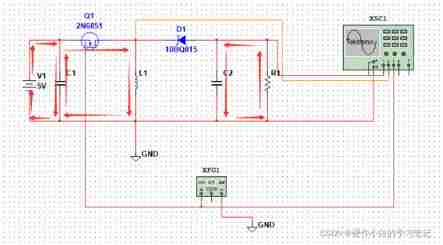
Negative pressure generation of buck-boost circuit
Run menu analysis
随机推荐
Guess riddles (2)
On boost circuit
STM32 virtualization environment of QEMU
猜谜语啦(5)
[cloud native | learn kubernetes from scratch] III. kubernetes cluster management tool kubectl
Arduino+a4988 control stepper motor
暑假第一周
Shell script
第十八章 使用工作队列管理器(一)
STM32 single chip microcomputer - bit band operation
每日一题——替换空格
Various types of questions judged by prime numbers within 100 (C language)
【NOI模拟赛】汁树(树形DP)
Sword finger offer 05 Replace spaces
STM32 --- NVIC interrupt
Summary of SIM card circuit knowledge
STM32 single chip microcomputer -- debug in keil5 cannot enter the main function
Meizu Bluetooth remote control temperature and humidity access homeassistant
实例006:斐波那契数列
Guess riddles (11)