当前位置:网站首页>【NOI模拟赛】汁树(树形DP)
【NOI模拟赛】汁树(树形DP)
2022-07-05 08:23:00 【DD(XYX)】
题面
原题:「牛客 31454H」Permutation on Tree


题解
我们把绝对值符号拆开
∑ i = 1 n − 1 ∣ P i + 1 − P i ∣ = ∑ i = 1 n − 1 ( P i + 1 − P i ) [ P i + 1 > P i ] + ( P i − P i + 1 ) [ P i + 1 < P i ] \sum_{i=1}^{n-1}|P_{i+1}-P_i|=\sum_{i=1}^{n-1}(P_{i+1}-P_i)[P_{i+1}>P_i]+(P_{i}-P_{i+1})[P_{i+1}<P_i] i=1∑n−1∣Pi+1−Pi∣=i=1∑n−1(Pi+1−Pi)[Pi+1>Pi]+(Pi−Pi+1)[Pi+1<Pi]
然后对于每个数 x x x,计算它系数为 1 的方案数和系数为 -1 的方案数。
以系数为 1 的方案数为例。
原本全局方案数是通过一个简单的 DP( d p [ x ] = ( s i z [ x ] − 1 ) ! ∏ x → y d p [ y ] s i z [ y ] ! dp[x]=(siz[x]-1)!\prod_{x\rightarrow y}\frac{dp[y]}{siz[y]!} dp[x]=(siz[x]−1)!∏x→ysiz[y]!dp[y])来计算的,我们要专门考虑 x x x ,就把整个排列砍成两半,在树上表现为砍掉 x x x 的子树(单独计算子树内部方案数),然后在剩余的树中挑选一些放到排列中 x x x 的后面。同时,我们还得给 x x x找个学伴找个邻居来配对。于是设计状态:
- d p 0 [ i ] [ j ] dp0[i][j] dp0[i][j] :仅考虑 i i i 的子树内部,放了 j j j 个到 x x x 的后面,没有给 x x x 配对的方案数。
- d p 1 [ i ] [ j ] dp1[i][j] dp1[i][j] :仅考虑 i i i 的子树内部,放了 j j j 个到 x x x 的后面,子树内已经给 x x x 配对的方案数。
当我们合并两个子树 A , B A,B A,B 时,
d p 0 ′ [ r o o t ] [ j + k ] ← d p 0 [ A ] [ j ] ⋅ d p 0 [ B ] [ k ] ⋅ ( s i z [ A ] + s i z [ B ] s i z [ A ] ) ⋅ ( i + k i ) d p 1 ′ [ r o o t ] [ j + k ] ← d p 0 [ A ] [ j ] ⋅ d p 1 [ B ] [ k ] ⋅ ( s i z [ A ] + s i z [ B ] − 1 s i z [ B ] − 1 ) ⋅ ( i + k i ) ← d p 1 [ A ] [ j ] ⋅ d p 0 [ B ] [ k ] ⋅ ( s i z [ A ] + s i z [ B ] − 1 s i z [ A ] − 1 ) ⋅ ( i + k i ) dp0'[root][j+k]\leftarrow dp0[A][j]\cdot dp0[B][k]\cdot {siz[A]+siz[B]\choose siz[A]}\cdot {i+k\choose i}\\ dp1'[root][j+k]\leftarrow dp0[A][j]\cdot dp1[B][k]\cdot {siz[A]+siz[B]-1\choose siz[B]-1}\cdot {i+k\choose i}\\ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ ~ \,\leftarrow dp1[A][j]\cdot dp0[B][k]\cdot {siz[A]+siz[B]-1\choose siz[A]-1}\cdot {i+k\choose i} dp0′[root][j+k]←dp0[A][j]⋅dp0[B][k]⋅(siz[A]siz[A]+siz[B])⋅(ii+k)dp1′[root][j+k]←dp0[A][j]⋅dp1[B][k]⋅(siz[B]−1siz[A]+siz[B]−1)⋅(ii+k) ←dp1[A][j]⋅dp0[B][k]⋅(siz[A]−1siz[A]+siz[B]−1)⋅(ii+k)
然后,若 i i i 不是 x x x 的祖先,可以有
d p 0 [ i ] [ s i z [ i ] ] ← d p 0 [ i ] [ 0 ] dp0[i][siz[i]]\leftarrow dp0[i][0] dp0[i][siz[i]]←dp0[i][0]
若 i i i 比 x x x 小(与 x x x 配对可使之系数为 1),有
d p 1 [ i ] [ s i z [ i ] − 1 ] ← d p 0 [ i ] [ 0 ] ⋅ ( [ i = f a [ x ] ∨ l c a ( i , x ) ≠ i ] + [ l c a ( i , x ) ≠ i ] ) dp1[i][siz[i]-1]\leftarrow dp0[i][0]\cdot([i=fa[x]\lor lca(i,x)\not=i]+[lca(i,x)\not=i]) dp1[i][siz[i]−1]←dp0[i][0]⋅([i=fa[x]∨lca(i,x)=i]+[lca(i,x)=i])
最后再考虑一下 x x x 的儿子与之配对的情况。
总状态数 O ( ∑ s i z [ i ] ) O(\sum siz[i]) O(∑siz[i]) ,转移是经典树上背包,所以总时间复杂度 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3) 。
CODE
没怎么卡常,甚至有大量废用代码
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<cmath>
#include<ctime>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<random>
#include<bitset>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<unordered_map>
#pragma GCC optimize(2)
using namespace std;
#define MAXN 205
#define LL long long
#define ULL unsigned long long
#define ENDL putchar('\n')
#define DB double
#define lowbit(x) (-(x) & (x))
#define FI first
#define SE second
#define PR pair<int,int>
#define UIN unsigned int
int xchar() {
static const int maxn = 1000000;
static char b[maxn];
static int pos = 0,len = 0;
if(pos == len) pos = 0,len = fread(b,1,maxn,stdin);
if(pos == len) return -1;
return b[pos ++];
}
// #define getchar() xchar()
inline LL read() {
LL f = 1,x = 0;int s = getchar();
while(s < '0' || s > '9') {
if(s<0)return -1;if(s=='-')f=-f;s = getchar();}
while(s >= '0' && s <= '9') {
x = (x<<1) + (x<<3) + (s^48);s = getchar();}
return f*x;
}
void putpos(LL x) {
if(!x)return ;putpos(x/10);putchar((x%10)^48);}
inline void putnum(LL x) {
if(!x) {
putchar('0');return ;}
if(x<0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
return putpos(x);
}
inline void AIput(LL x,int c) {
putnum(x);putchar(c);}
const int MOD = 1000000007;
int n,m,s,o,k;
int rt,C[MAXN<<1][MAXN<<1];
int hd[MAXN],nx[MAXN<<1],v[MAXN<<1],cne;
void ins(int x,int y) {
nx[++ cne] = hd[x]; v[cne] = y; hd[x] = cne;
}
int d[MAXN],fa[MAXN];
void dfs0(int x,int ff) {
d[x] = d[fa[x] = ff] + 1;
for(int i = hd[x];i;i = nx[i]) {
if(v[i] != ff) {
dfs0(v[i],x);
}
}return ;
}
int lca(int a,int b) {
if(d[a] < d[b]) swap(a,b);
while(d[a] > d[b]) a = fa[a];
if(a == b) return a;
while(a != b) a = fa[a],b = fa[b];
return a;
}
int Ft;
int dp[MAXN][MAXN],dp1[MAXN][MAXN],siz[MAXN];
bool ifa[MAXN],mg[MAXN];
void dfsi(int x,int ff) {
dp[x][0] = 1; siz[x] = 0;
for(int i = hd[x];i;i = nx[i]) {
int y = v[i]; if(y == ff) continue;
dfsi(y,x); siz[x] += siz[y];
dp[x][0] = dp[x][0] *1ll* dp[y][0] % MOD * C[siz[x]][siz[y]] % MOD;
} siz[x] ++; return ;
}
void dfs(int x,int ff) {
for(int i = 0;i <= n;i ++) dp[x][i] = dp1[x][i] = 0;
dp[x][0] = 1; siz[x] = 0;
for(int i = hd[x];i;i = nx[i]) {
int y = v[i]; if(y==ff || y==Ft) continue;
dfs(y,x); siz[x] += siz[y];
for(int i = siz[x];i >= 0;i --) {
int dpp = 0,dpp1 = 0;
for(int j = max(0,siz[y]-(siz[x]-i));j <= siz[y] && j <= i;j ++) {
(dpp += dp[x][i-j]*1ll*dp[y][j]%MOD * C[siz[x]-i][siz[y]-j] % MOD * C[i][j] % MOD) %= MOD;
if(i<siz[x]) (dpp1 += dp1[x][i-j]*1ll*dp[y][j]%MOD * C[siz[x]-i-1][siz[y]-j] % MOD * C[i][j] % MOD) %= MOD;
if(i<siz[x] && j<siz[y]) (dpp1 += dp[x][i-j]*1ll*dp1[y][j]%MOD * C[siz[x]-i-1][siz[y]-j-1] % MOD * C[i][j] % MOD) %= MOD;
}
dp[x][i] = dpp; dp1[x][i] = dpp1;
}
}
siz[x] ++;
if(!ifa[x]) dp[x][siz[x]] = dp[x][0];
if(mg[x] && (!ifa[x] || x == fa[Ft])) (dp1[x][siz[x]-1] += dp[x][0]) %= MOD;
if(mg[x] && !ifa[x]) (dp1[x][siz[x]-1] += dp[x][0]) %= MOD;
return ;
}
int solve(int s,int op) {
Ft = s;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {
ifa[i] = mg[i] = 0;
if(op > 0) mg[i] = (i > s);
else mg[i] = (i < s);
}
int as = 0;
int p = s; while(p) ifa[p] = 1,p = fa[p];
dfsi(s,fa[s]);
int le = siz[s];
int as0 = 1,as1 = 0,sz = 0;
for(int i = hd[s];i;i = nx[i]) {
int y = v[i]; if(y == fa[s]) continue;
sz += siz[y];
as1 = as1 *1ll* dp[y][0] % MOD * C[sz-1][siz[y]] % MOD;
if(mg[y]) (as1 += as0 *1ll* dp[y][0] % MOD * C[sz-1][siz[y]-1] % MOD) %= MOD;
as0 = as0 *1ll* dp[y][0] % MOD * C[sz][siz[y]] % MOD;
}
if(rt != s) {
dfs(rt,0);
for(int i = 0;i <= siz[rt];i ++) {
(as += dp1[rt][i] *1ll* dp[s][0] % MOD * C[le-1+i][i] % MOD) %= MOD;
if(le>1) (as += dp[rt][i] *1ll* as1 % MOD * C[le-2+i][i] % MOD) %= MOD;
}
}
else as = as1;
return as;
}
int main() {
freopen("tree.in","r",stdin);
freopen("tree.out","w",stdout);
n = read(); rt = read();
for(int i = 1;i < n;i ++) {
s = read();o = read();
ins(s,o); ins(o,s);
}
dfs0(rt,0);
C[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {
C[i][0] = C[i][i] = 1;
for(int j = 1;j < i;j ++) {
C[i][j] = (C[i-1][j-1] + C[i-1][j]) % MOD;
}
}
int ans = 0;
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i ++) {
int A = solve(i,-1),B = solve(i,1);
ans = (ans + (A +MOD- B) *1ll* i) % MOD;
}
AIput(ans,'\n');
return 0;
}
边栏推荐
- 【三层架构及JDBC总结】
- Several important parameters of LDO circuit design and type selection
- Sword finger offer 05 Replace spaces
- STM32 single chip microcomputer -- volatile keyword
- [three tier architecture]
- leetcode - 445. 两数相加 II
- Infected Tree(树形dp)
- Classic application of MOS transistor circuit design (2) - switch circuit design
- Measurement fitting based on Halcon learning [i] fuse Hdev routine
- STM32 single chip microcomputer -- debug in keil5 cannot enter the main function
猜你喜欢
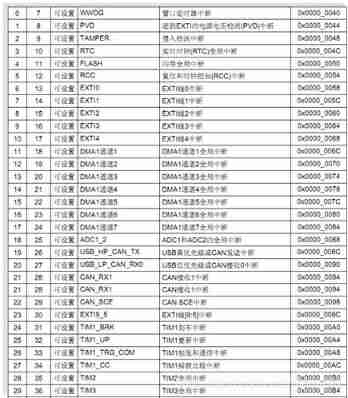
STM32 --- NVIC interrupt
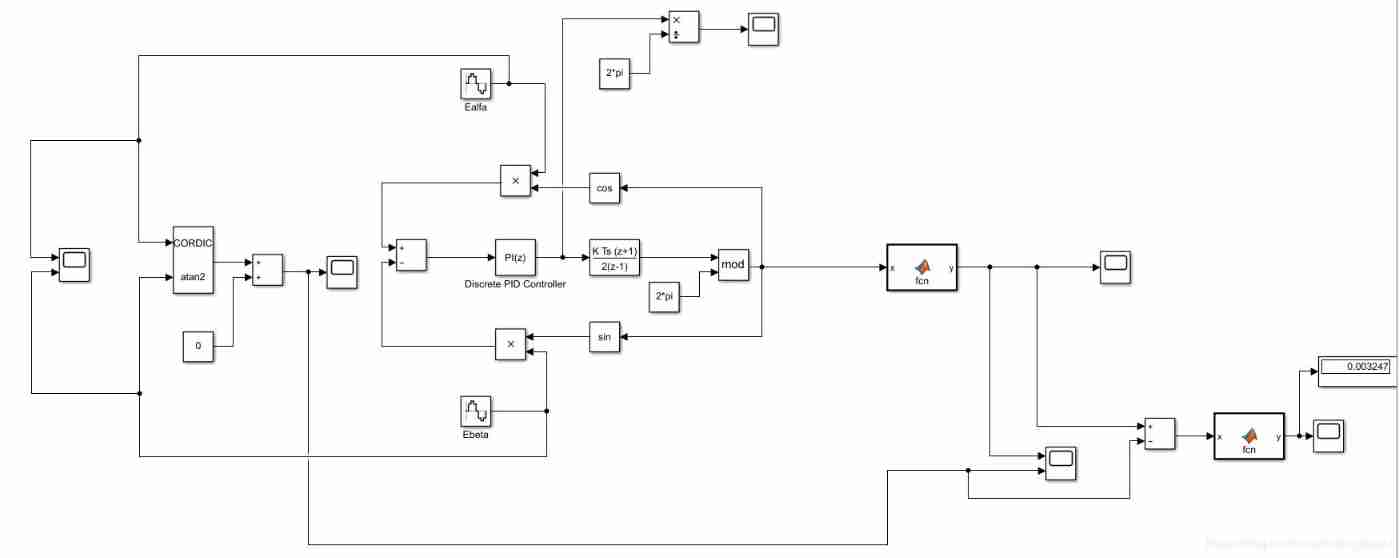
Some thoughts on extracting perspectives from ealfa and Ebeta
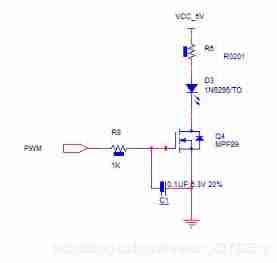
Classic application of MOS transistor circuit design (2) - switch circuit design
![[tutorial 19 of trio basic from introduction to proficiency] detailed introduction of trio as a slave station connecting to the third-party bus (anybus PROFIBUS DP...)](/img/54/2fe86f54af01f10de93818103f2154.jpg)
[tutorial 19 of trio basic from introduction to proficiency] detailed introduction of trio as a slave station connecting to the third-party bus (anybus PROFIBUS DP...)
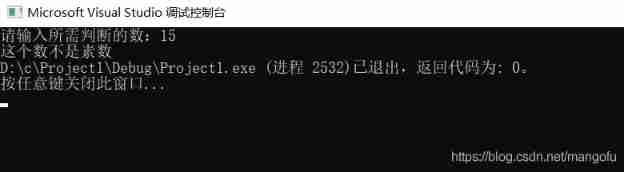
Various types of questions judged by prime numbers within 100 (C language)

Sword finger offer 09 Implementing queues with two stacks
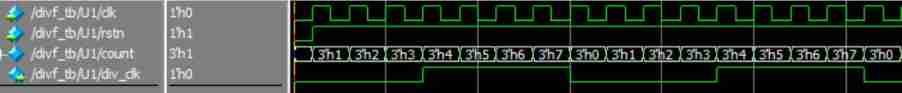
Design a clock frequency division circuit that can be switched arbitrarily
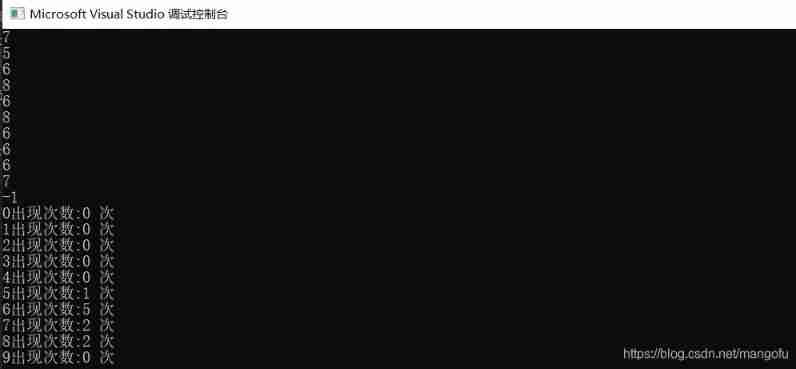
Count the number of inputs (C language)

实例005:三数排序 输入三个整数x,y,z,请把这三个数由小到大输出。
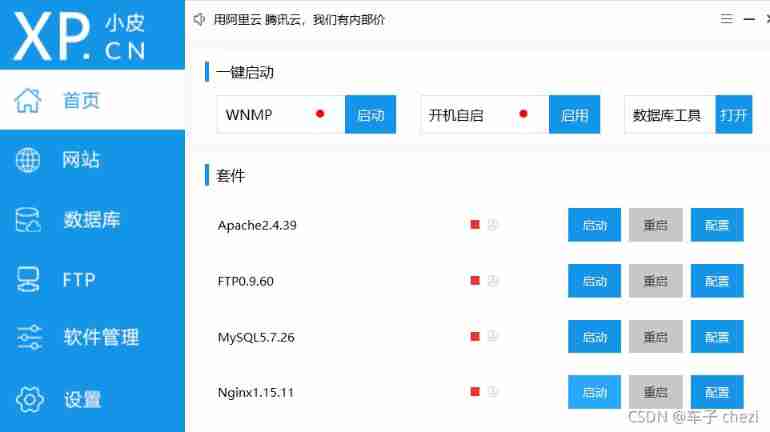
DokuWiki deployment notes
随机推荐
[trio basic tutorial 16 from introduction to proficiency] UDP communication test supplement
OLED 0.96 inch test
[cloud native | learn kubernetes from scratch] III. kubernetes cluster management tool kubectl
List of linked lists
[trio basic from introduction to mastery tutorial 20] trio calculates the arc center and radius through three points of spatial arc
Classic application of MOS transistor circuit design (1) -iic bidirectional level shift
Stablq of linked list
DokuWiki deployment notes
Five design details of linear regulator
STM32 summary (HAL Library) - DHT11 temperature sensor (intelligent safety assisted driving system)
Example 005: three numbers sorting input three integers x, y, Z, please output these three numbers from small to large.
STM32 virtualization environment of QEMU
Hardware and software solution of FPGA key chattering elimination
Stm32--- systick timer
General makefile (I) single C language compilation template
NTC thermistor application - temperature measurement
剑指 Offer 09. 用两个栈实现队列
Installation and use of libjpeg and ligpng
STM32 --- configuration of external interrupt
OC and OD gate circuit