当前位置:网站首页>[MySQL] detailed explanation of trigger content of database advanced
[MySQL] detailed explanation of trigger content of database advanced
2022-07-07 08:47:00 【Xiaohuang Xiaohuang is no longer confused】
Personal home page : Huang Xiaohuang's blog home page
️ Stand by me : give the thumbs-up Collection Focus on
Maxim : Only one step at a time can we accept the so-called luckThis article is from the column :MySQL8.0 Learning notes
This article refers to the video :MySQL Database complete tutorial
Welcome to the support subscription column ️
List of articles
1 Trigger Overview
Trigger introduction :
- trigger , Is a special stored procedure . A trigger, like a stored procedure, is a function that can perform a specific function , Stored on the database server SQL fragment . But the trigger does not need to call , When executing DML This will be triggered automatically during operation SQL Execution of fragments , No manual call required .
- stay MySQL in , Only execute insert、delete、update The execution of the trigger can only be triggered when the operation ;
- This feature of trigger can help to ensure the integrity of data in database , logging , Data verification and other operations ;
- Use the alias OLD And NEW To reference the record content where the trigger changes , This is similar to other databases . Now the trigger is still Only row level triggering is supported , Statement level triggering is not supported .
Schematic diagram of trigger :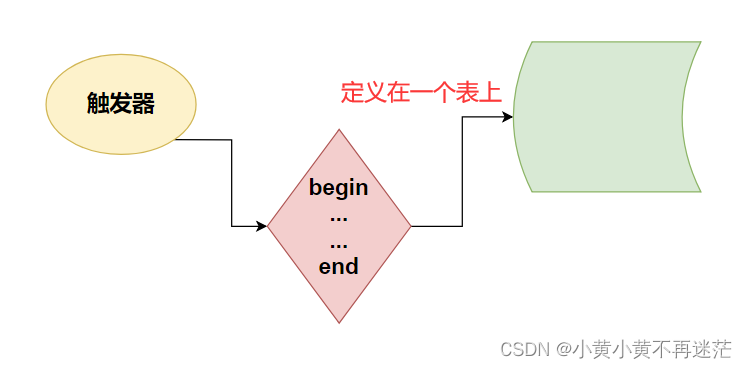
Triggers are defined on the table , Attach to table .
Triggers are defined , You need to specify the :
- What conditions trigger ? Insert 、 Delete 、 to update ?
- When to trigger ? Before or after addition, deletion and modification ?
- Trigger frequency , For each line .
2 The basic operation of trigger
2.1 Create trigger
1. Create a trigger with only one execution statement :
create trigger Trigger Name before|after Triggering event
on Table name for each row
Execute statement ;
2. Create a trigger with multiple execution statements :
create trigger Trigger Name before|after Triggering event
on Table name for each row
begin
Execute statement list
end;
2.2 Trigger operation instance
First, prepare the data , Define two tables user And user_logs, Record the user registration information and user operation log respectively . Hope to be user When something changes ,user_logs Change automatically ( It is realized by trigger ). The relevant codes for data preparation are as follows :
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS mydatabase_tigger;
USE mydatabase_tigger;
-- User table creation
CREATE TABLE user(
uid INT PRIMARY KEY ,
username VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL ,
password VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL
);
-- User information operation log table
CREATE TABLE user_logs(
id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
time TIMESTAMP,
log_text VARCHAR(255)
);
- If you want to give user When adding information to the table ,user_logs The table automatically adds a row of data , A trigger is defined in the following code trigger_test01 To meet the needs , The relevant codes and results are as follows :
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_test01
AFTER INSERT
ON user
FOR EACH ROW
INSERT INTO user_logs
VALUES (NULL, NOW(), ' New users add ');
INSERT INTO user VALUES (1, 'nezuko', '123456');
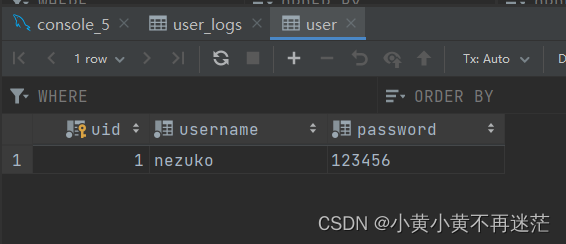
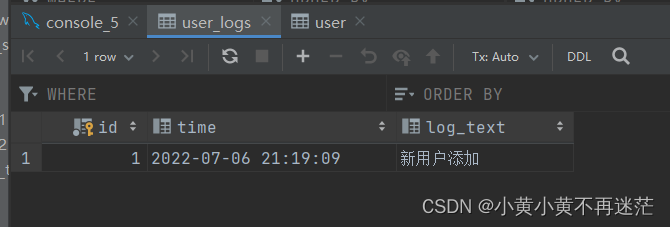
- When user When the table data is modified , Automatically in user_logs Add logging ., A trigger is defined in the following code trigger_test02 To meet the needs , The relevant codes and results are as follows :
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_test02
BEFORE UPDATE
ON user
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
INSERT INTO user_logs VALUES (NULL, NOW(), ' User information is modified ');
END $$
DELIMITER ;
UPDATE user SET password = '111111' WHERE uid = 1;
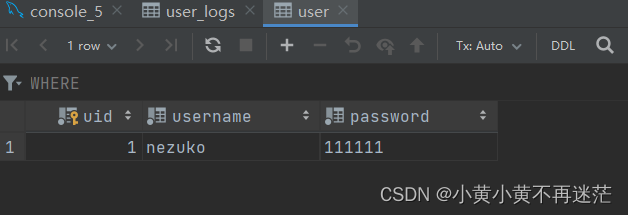
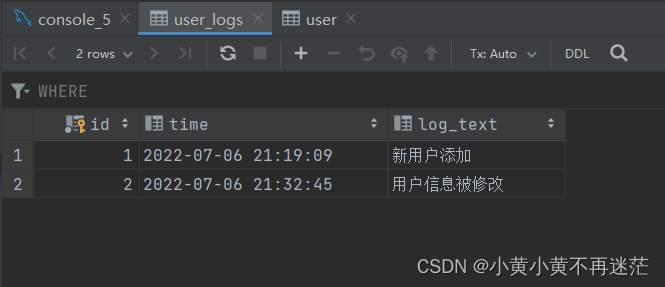
You can see user The password in the table has been changed , The record of modification information is successfully added to the log table .
3 NEW And OLD
3.1 Why NEW And OLD?
MySQL It defines NEW and OLD, Used to indicate that the trigger is in the table , Which row of data triggered the trigger , To refer to the changed record content in the trigger , See the following table for details :
| Trigger Type | Trigger Type NEW And OLD Use |
|---|---|
| INSERT Type trigger | NEW Indicates the data to be added or added |
| UPDATE Type trigger | OLD Represents the data before modification ,NEW Indicates the data to be or have been modified |
| DELETE Type trigger | OLD Data that will be or has been deleted |
Usage method :
NEW.columnName(columnName A column name representing the corresponding data )
What kind of requirements will be used NEW and OLD Well ?
In the case illustrated above , We modify user The password in the table , to user_logs Modification information is added to the table . But it only prompts the modified information , There is no indication that . If , It is necessary to indicate the password before modification or the password after modification in the information , You need to use the OLD and NEW Used for triggers to reference data !
3.2 NEW And OLD example
Defining triggers trigger_test03, You can give user_logs Insert modification information , Show the user's password before and after modification . The relevant codes and results are as follows :
DELIMITER $$
CREATE TRIGGER trigger_test03
BEFORE UPDATE
ON user
FOR EACH ROW
BEGIN
INSERT INTO user_logs VALUES (NULL, NOW(), CONCAT(' User information is modified , The password before modification is ', OLD.password, ', Modified for ', NEW.password));
END $$
DELIMITER ;
UPDATE user SET password = '99999999' WHERE uid = 1;
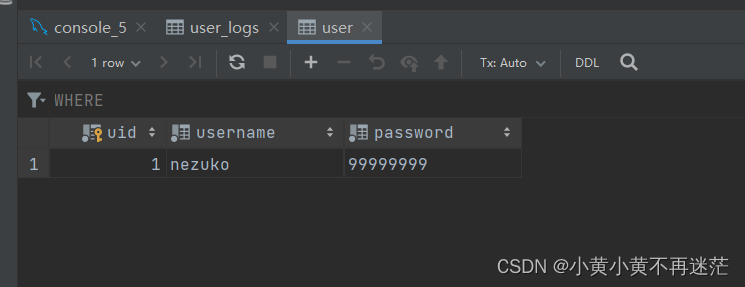
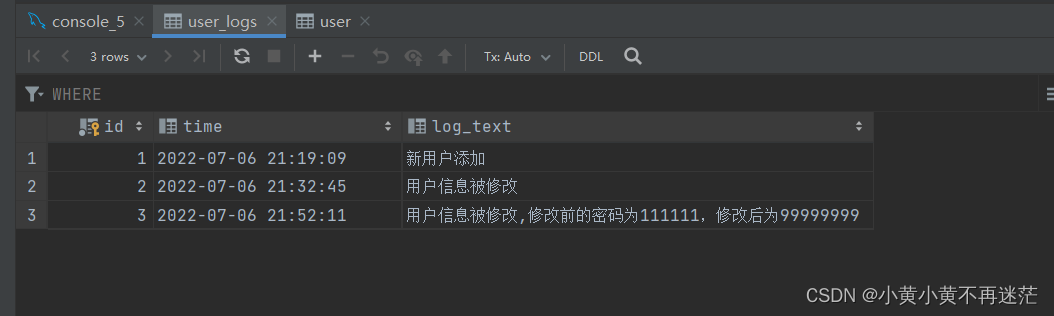
If you want to delete the trigger , You can use the following statement : Delete the three triggers created so far .
DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS trigger_test01;
DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS trigger_test02;
DROP TRIGGER IF EXISTS trigger_test03;
4 Other operations of trigger
- Check triggers :
show triggers;
- Delete trigger :
drop trigger if exists trigger_name;
5 Precautions for trigger
- MySQL This table cannot be insert、update、delete operation , To prevent recursive loops from triggering ;
- Use as few triggers as possible , Suppose the trigger triggers each execution 1s, Then modify the table every time 、 The update operation will take some extra time , Thus, the efficiency of table operation is low ;
- Triggers are for each row , Try not to use triggers for tables that are frequently added, deleted, or modified , Avoid additional consumption of resources ;
- Frequent use of triggers will lead to more trouble in maintaining data in the future , Because there are many behaviors in one change .
At the end
The above is the whole content of this article , The follow-up will continue Free update , If the article helps you , Please use your hands Point a praise + Focus on , Thank you very much ️ ️ ️ !
If there are questions , Welcome to the private letter or comment area !
Mutual encouragement :“ You make intermittent efforts and muddle through , It's all about clearing the previous efforts .”
边栏推荐
- 国标GB28181协议视频平台EasyGBS新增拉流超时配置
- 下载和安装orcale database11.2.0.4
- 指针进阶,字符串函数
- [wechat applet: cache operation]
- Greenplum 6.x build_ install
- 21 general principles of wiring in circuit board design_ Provided by Chengdu circuit board design
- [step on the pit] Nacos registration has been connected to localhost:8848, no available server
- [kuangbin]专题十五 数位DP
- How to add a mask of a target in a picture
- Componentspace2022, assertions, protocols, bindings, and configuration files
猜你喜欢
ncs成都新電面試經驗

Three series of BOM elements
Merge sort and non comparison sort
Arm GIC (IV) GIC V3 register class analysis notes.
Splunk query CSV lookup table data dynamic query
![[Yu Yue education] basic reference materials of electrical and electronic technology of Nanjing Institute of information technology](/img/2a/01db1b84c26502c851786aaca56abe.jpg)
[Yu Yue education] basic reference materials of electrical and electronic technology of Nanjing Institute of information technology
Virtual address space
![[step on the pit] Nacos registration has been connected to localhost:8848, no available server](/img/ee/ab4d62745929acec2f5ba57155b3fa.png)
[step on the pit] Nacos registration has been connected to localhost:8848, no available server
为什么要选择云原生数据库
23 Chengdu instrument customization undertaking_ Discussion on automatic wiring method of PCB in Protel DXP
随机推荐
Componentspace2022, assertions, protocols, bindings, and configuration files
POJ - 3784 Running Median(对顶堆)
Opencv learning note 4 - expansion / corrosion / open operation / close operation
Qt Charts使用(重写QChartView,实现一些自定义功能)
字符串操作
[Yugong series] February 2022 U3D full stack class 008 - build a galaxy scene
Sign and authenticate API interface or H5 interface
Input and output of floating point data (C language)
Exercise arrangement 2.10, 11
String operation
[Yugong series] February 2022 U3D full stack class 007 - production and setting skybox resources
Train your dataset with swinunet
調用華為遊戲多媒體服務的創建引擎接口返回錯誤碼1002,錯誤信息:the params is error
National SMS center number inquiry
Three series of BOM elements
Splunk query CSV lookup table data dynamic query
[Yugong series] February 2022 U3D full stack class 006 unity toolbar
Mock.js用法详解
GOLand idea intellij 无法输入汉字
国标GB28181协议视频平台EasyGBS新增拉流超时配置

