当前位置:网站首页>JS operation
JS operation
2022-07-07 08:43:00 【Desire and Yu Yu】
1 js
1.1Js Output statement
js You can output the content in the following ways , It's just that different statements are output to different locations
Use window.alert() Write warning box
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> window.alert("hello js");// Write warning box </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
Use document.write() write in HTML Output
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> document.write("hello js 2~");// write in html page </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>
Use console.log() Write to browser console
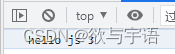
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <script> console.log("hello js 3");// Write to the browser's console </script> </head> <body> </body> </html>The above code opens through the browser , Can pass F12 see console.log( Content ) Output content , It is output on the console
1.2 Variable
JavaScript of use var keyword (variable Abbreviation ) To declare variables . Format var Variable name = Data values ; . And in the JavaScript It's a weak type language , Variables can hold different types of values ; The following values are assigned as numeric data when defining variables , You can also change the value of the variable to a number of string types
var test = 20;
test = " Zhang San ";
js There are also the following rules for naming variable names in , and java The language is basically the same
- The constituent character can be any letter 、 Numbers 、 Underline (_) Or the dollar sign ($)
- The number can't start
- It is suggested to name humps
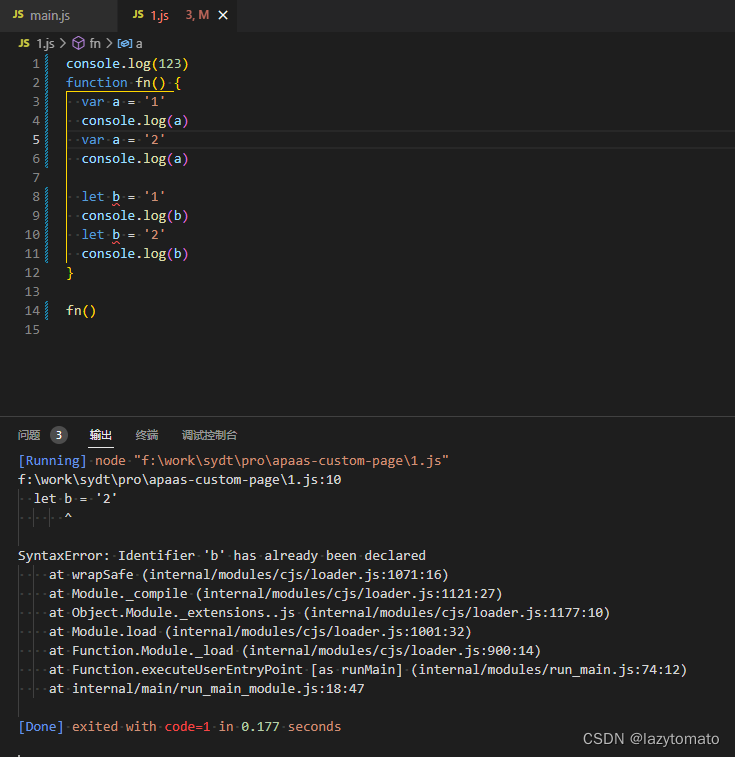
JavaScript in var Keywords are a little special , The following are different from other languages
Scope : Global variables
{ var age = 20; } alert(age); // Defined in a code block age Variable , You can also use... Outside the code blockVariables can be defined repeatedly
{
var age = 20;
var age = 30;//JavaScript Will use 30 Before age Variable 20 Replace
}
alert(age); // The result of printing is 30
Because of these, we need to use Let To define variables , Its usage is similar to var , But the declared variable , Only in let Turn off
The code block where the key word is located is valid , And it is not allowed to repeat the declaration .
1.3 data type
| data type | explain |
|---|---|
| number | Numbers ( Integers , decimal ,NaN(Not a number)) |
| string | character , character string , Single and double citation |
| boolean | Boolean type :True False |
| null | The object is empty |
| underfinded | When the declared variable is uninitialized , The default value of this variable is not Undefined |
Use type Operator can get the data type
var age = 20;
var price = 99.8;
alert(typeof age); // The result is : number
alert(typeof price);// The result is : number
1.4. Operator
Unary operator :++,–
Arithmetic operator :+,-,*,/,%
Assignment operator :=,+=,-=…
Relational operator :>,<,>=,<=,!=,==, === …
Logical operators :&&,||,!
Ternary operator : Conditional expression ? true_value : false_value
1.4.1 == and === difference
summary :
- ==:
- Judge whether the type is the same , If it's not the same , Type conversion
- Then compare its value
- ===:js All in is equal to
- Judge whether the type is the same , If it's not the same , Go straight back to false
- Then compare its value
var age1 = 20;
var age2 = "20";
alert(age1 == age2);// true
alert(age1 === age2);// false
1.4.2 Type conversion
- Other types turn to number
- string Convert to number type : According to the literal value of the string , Turn to numbers . If the face value is not a number , Turn to NaN
take string Convert to number There are two ways :Use + Plus operator :
var str = +"20"; alert(str + 1) //21Use parseInt() function ( Method ):
var str = "20"; alert(parseInt(str) + 1);
- boolean Convert to number type :true To 1,false To 0
var flag = +false; alert(flag); // 0
- string Convert to number type : According to the literal value of the string , Turn to numbers . If the face value is not a number , Turn to NaN
- Other types turn to boolean
- number Type conversion to boolean type :0 and NaN To false, The other figures turn to true
- string Type conversion to boolean type : Empty string to false, Other strings are converted to true
- null Type conversion to boolean The type is false
- undefined Convert to boolean The type is false
1.5 Process control
JavaScript And Java The same process control statement , as follows
- if
- switch
- for
- while
- dowhile
1.5.1 if
if sentence : Be satisfied and execute , If you are not satisfied, you will not execute
var count = 3;
if (count == 3) {
alert(count);
}
1.5.2 switch
Evaluate the value of an expression . And compare them one by one with the value of the constant expression after them , When the value of an expression is equal to the value of a constant expression , That is, execute the following statements , And then stop judging , Go ahead with all the rest case The following sentence . For example, the value of an expression is related to all case After the constant expression are not the same , execute default The following sentence .
var num = 3;
switch (num) {
case 1:
alert(" Monday ");
break;
case 2:
alert(" Tuesday ");
break;
case 3:
alert(" Wednesday ");
break;
case 4:
alert(" Thursday ");
break;
case 5:
alert(" Friday ");
break;
case 6:
alert(" Saturday ");
break;
case 7:
alert(" Sunday ");
break;
default:
alert(" Wrong week entered ");
break;
}
1.5.3 for Loop statement
Loop traversal
var sum = 0;
for (let i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
// Suggest for The variables defined in the loop parentheses use let
sum += i;
}
alert(sum);
1.5.4 while Loop statement
If the conditions are met, execute Do not perform if the conditions are not met
var sum = 0;
var i = 1;
while (i <= 100) {
sum += i;
i++;
}
alert(sum);
1.5.5 do-while Loop statement
Whether the conditions are met or not, it will be executed once , Then judge whether the conditions are met , If the conditions are met, execute , If you are not satisfied, do not implement
var sum = 0;
var i = 1;
do {
sum += i;
i++;
}
while (i <= 100);
alert(sum);
1.6 function
function ( Namely Java The method in ) Are blocks of code designed to perform specific tasks ;JavaScript Function by function Key words to define .
1.6.1 Define format
There are two forms of function definition :
- The way 1
function Function name ( Parameters 1, Parameters 2..){ Code to execute } - Mode two
var Function name = function ( parameter list ){ Code to execute }
Be careful : because js It is a weakly typed language, so you don't need to define data types The return value also does not need to define the type direct reture Just go back
1.6.2 Function call
Function call function :
The name of the function ( List of actual parameters );
Practical examples :
function add(a, b){
return a + b;
}
let result = add(10,20);
Be careful :
- JS in , Function calls can pass any number of parameters
- for example let result = add(1,2,3);
It is to put data 1 Passed to variable a, Put the data 2 Passed to variable b, And data 3 No variables are received .
2 JavaScript Common objects
JavaScript Many objects are provided for users to use . These objects fall into three categories
- The basic object
- Array
- Boolean
- Date
- Math
- Number
- String
- RegExp
- Global
- Bom object
- Window
- Nayigator
- Screen
- History
- Location
- Dom object
- Document
- Anchor
- Area
2.1 Array object
JavaScript Array Used to define an array of objects
2.1.1 Define format
There are two formats for defining arrays :
- The way 1
var Variable name = new Array( List of elements ); var arr = new Array(1,2,3); //1,2,3 Is the data stored in the array ( Elements ) - Mode two
var Variable name = [ List of elements ]; var arr = [1,2,3]; //1,2,3 Is the data stored in the array ( Elements )
Be careful :Java The static initialization of the array in uses {} Definition , and JavaScript Is used in [] Definition
2.1.2 Element access
Access the elements and... In the array Java The language is the same , The format is as follows :
//arr[ Indexes ] = value ;
// Mode one
var arr = new Array(1,2,3);
// alert(arr);
// Mode two
var arr2 = [1,2,3];
//alert(arr2);
// visit
arr2[0] = 10;
alert(arr2)
2.1.3 characteristic
JavaScript The array in is equivalent to Java Middle set . The length of an array can vary , and JavaScript Weak type , So you can store numbers of any type
According to the
// Lengthening
var arr3 = [1,2,3];
arr3[10] = 10;
alert(arr3[10]); // 10
alert(arr3[9]); //undefined
// If arr3 Add string data to the array , It can also be added successfully
arr3[5] = "hello";
alert(arr3[5]); // hello
2.1.4 attribute
Array Object provides many properties
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| constructor | Returns the array function reference of the create object |
| length | Returns the number of elements in the array |
| prototype | Enables you to add properties and methods to objects |
such as :
var arr = [1,2,3];
for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
alert(arr[i]);
}
2.1.5 Method
| Method | describe |
|---|---|
| concat() | Join two or more arrays , And return the result . |
| copyWithin() | Copy elements from the specified location of the array to another specified location of the array . |
| entries() | Returns the iteratable object of the array . |
| every() | Checks whether each element of a numeric element is eligible . |
| fill() | Fill the array with a fixed value . |
| filter() | Detect value elements , And returns an array of all elements that meet the criteria . |
| find() | Return compliance with incoming test ( function ) Conditional array elements . |
| findIndex() | Return compliance with incoming test ( function ) Conditional array element index . |
| forEach() | Each element of the array performs a callback function . |
| from() | Create an array from the given object . |
| includes() | Determine whether an array contains a specified value . |
| indexOf() | Search for elements in the array , And return to where it is . |
| isArray() | Determine whether the object is an array . |
| join() | Put all the elements of the array into a string . |
| keys() | Returns the iteratable object of the array , Contains the key of the original array (key). |
| lastIndexOf() | Search for elements in the array , And return to where it last appeared . |
| map() | Handle each element of the array by specifying a function , And return the processed array . |
| pop() | Delete the last element of the array and return the deleted element . |
| push() | Add one or more elements... To the end of the array , And returns the new length . |
| reduce() | Evaluate an array element to a value ( From left to right ). |
| reduceRight() | Evaluate an array element to a value ( From right to left ). |
| reverse() | Reverse the order of elements in an array . |
| shift() | Delete and return the first element of the array . |
| slice() | Pick a part of the array , And return a new array . |
| some() | Check whether any element in the array element meets the specified conditions . |
| sort() | Sort elements of an array . |
| splice() | Add or remove elements from an array . |
| toString() | Convert an array to a string , And return the result . |
| unshift() | Add one or more elements to the beginning of an array , And returns the new length . |
| valueOf() | Returns the original value of the array object . |
Example :
push function : Add elements to the array , That is, adding elements to the end of the array , The parameter represents the element to be added
// push: Add method var arr5 = [1,2,3]; arr5.push(10); alert(arr5); // The elements of an array are {1,2,3,10}splice function : Remove elements
Parameters 1: Indexes . Indicates the index location from which to delete
Parameters 2: Number . Means to delete several elements// splice: Remove elements var arr5 = [1,2,3]; arr5.splice(0,1); // from 0 The index position starts to be deleted , Delete an element alert(arr5); // {2,3}
2.2 String object
String There are two ways to create objects
- Mode one :
var Variable name = new String(s);
- Mode two :
var Variable name = " Array ";
attribute :
The main thing is length , This property is used to dynamically obtain the length of the string
function :
The main three
charAt(): Returns the character in the specified position
indexOf(): Retrieve string
trim(): Remove the spaces on both sides
2.3 Custom object
stay JavaScript Custom objects in are particularly simple , The following is the format of custom objects :
var Object name = {
The attribute name 1: Property value 1,
The attribute name 2: Property value 2,
...,
The name of the function :function ( Parameter list ){
},
...
};
The format of the calling property :
Object name . Property name
The format of the calling function :
Object name . Function name ()
demonstration :
var person = {
name : "zhangsan",
age : 23,
eat: function (){
alert(" Dry rice ~");
}
};
alert(person.name); //zhangsan
alert(person.age); //23
person.eat(); // Dry rice ~
边栏推荐
- [paper reading] icml2020: can autonomous vehicles identify, recover from, and adapt to distribution shifts?
- [kuangbin] topic 15 digit DP
- Required String parameter ‘XXX‘ is not present
- Greenplum6.x-版本变化记录-常用手册
- 联想混合云Lenovo xCloud:4大产品线+IT服务门户
- Gson转换实体类为json时报declares multiple JSON fields named
- Practice of implementing cloud native Devops based on rainbow library app
- [Chongqing Guangdong education] audio visual language reference materials of Xinyang Normal University
- idea里使用module项目的一个bug
- Rsync remote synchronization
猜你喜欢

Compilation and linking of programs
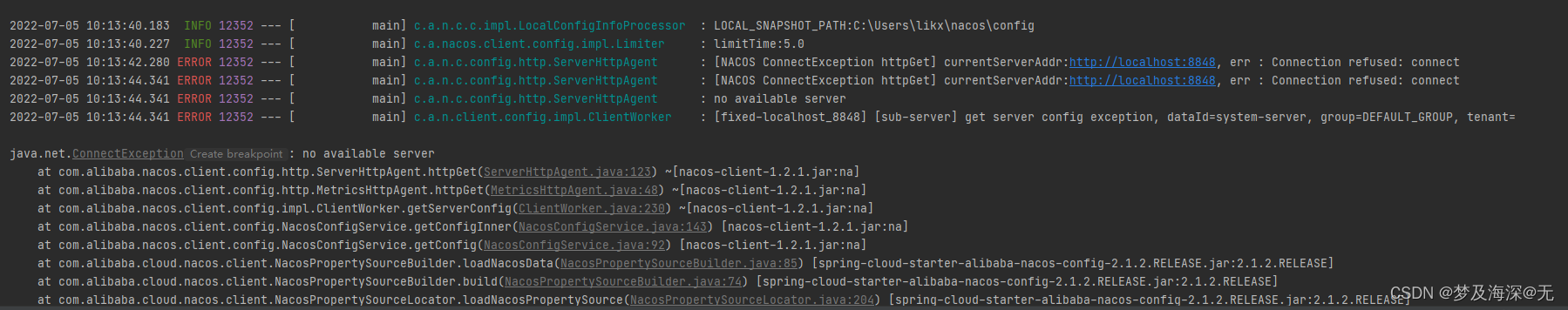
【踩坑】nacos注册一直连接localhost:8848,no available server
![[paper reading] icml2020: can autonomous vehicles identify, recover from, and adapt to distribution shifts?](/img/ff/81a7b2ec08a6a422a5cf578c1fed13.jpg)
[paper reading] icml2020: can autonomous vehicles identify, recover from, and adapt to distribution shifts?
快速集成认证服务-HarmonyOS平台

Implementation of navigation bar at the bottom of applet

关于基于kangle和EP面板使用CDN
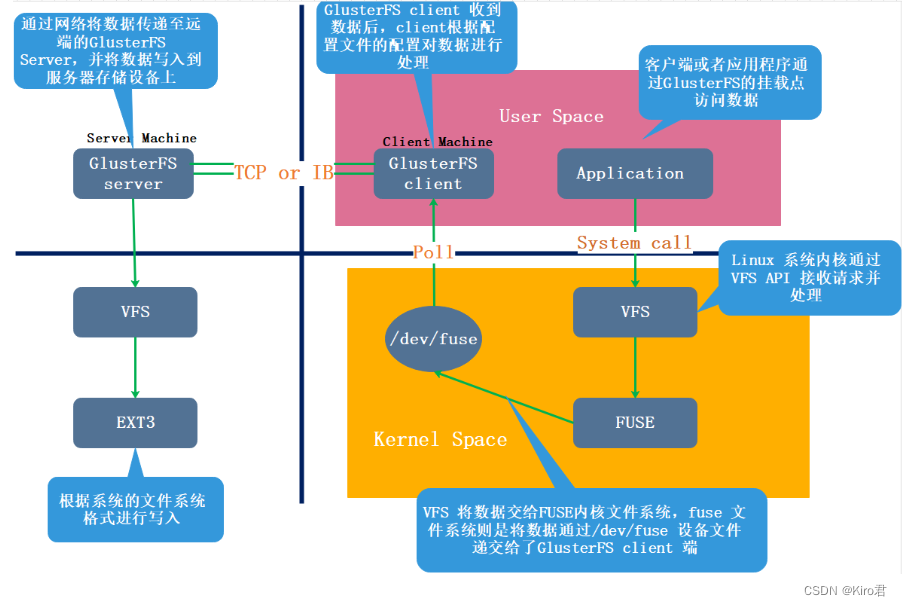
GFS distributed file system
let const
2-3查找树
如何在HarmonyOS应用中集成App Linking服务
随机推荐
指针进阶,字符串函数
Other 7 features of TCP [sliding window mechanism ▲]
Several ways of lambda used in functions in kotlin (higher-order functions)
In go language, function is a type
Snyk dependency security vulnerability scanning tool
如何在HarmonyOS应用中集成App Linking服务
Teach you how to select PCB board by hand (II)
Low success rate of unit test report
The single value view in Splunk uses to replace numeric values with text
数据分析方法论与前人经验总结2【笔记干货】
Golang 编译约束/条件编译 ( // +build <tags> )
leetcode134. gas station
Greenplum6.x搭建_环境配置
Installation and configuration of PLSQL
Novice entry SCM must understand those things
Greenplum6.x重新初始化
oracle一次性说清楚,多种分隔符的一个字段拆分多行,再多行多列多种分隔符拆多行,最终处理超亿亿。。亿级别数据量
[step on the pit] Nacos registration has been connected to localhost:8848, no available server
Opencv learning notes 1 -- several methods of reading images
Le système mes est un choix nécessaire pour la production de l'entreprise