当前位置:网站首页>Quick sorting (detailed illustration of single way, double way, three way)
Quick sorting (detailed illustration of single way, double way, three way)
2022-07-07 08:37:00 【S dream chasing boy】
One 、 Quick sort
Select any data of the array to be sorted as the benchmark , Traversing elements in an array . Place elements smaller than the reference value to the left of the reference value , Those greater than the reference value are placed to the right of the reference value , Put the reference value in the middle , At this time, the reference value reaches the final position . Then, the subarray on the left and the subarray on the right of the benchmark are processed in the same way , Until the interval is reduced to 1, It means that the array is ordered .
Two 、 One way sorting
Example : Given a length of 10 Array of {6,1,2,7,9,3,4,5,10,8}
The problem solving steps ;
(1) The idea of quick sorting is to put the first element of the array 6 Move to a position in the sequence M, Give Way M The elements on the left are <=6,M The right elements of are >=6; So we need to define two pointers i and j At the beginning and end of the sequence ;
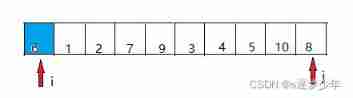
(2)i Move backward in turn (i++) Move to greater than 6 The element of stops ,j Move forward (j--) Move to less than 6 The elements of , And will i,j Corresponding element exchange .

(3) according to (2) Step by step until i,j coincidence ; And because the element referred to in coincidence is 3,3<6 In exchange ; here 6 The left side of is smaller than 6,6 The right side of is larger than 6.
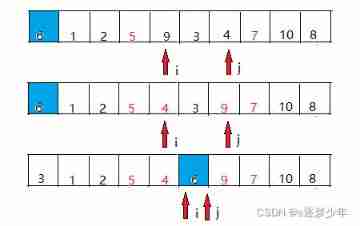
(4) The sequence element at this time 6 The left side of is smaller than 6, The right side is larger than 6; take 6 Repeat the left part of (1)(2)(3) Until the first element of the sequence is 1;
(5)6 The right part of is the same as the left part ;
(7) Code implementation ; from (1)~(6) It can be seen that the implementation steps have been repeated , So use recursive method .
void Quick_Sort(int *arr, int begin, int end){
if(begin > end)
return;
int tmp = arr[begin];
int i = begin;
int j = end;
while(i != j){
while(arr[j] >= tmp && j > i)
j--;
while(arr[i] <= tmp && j > i)
i++;
if(j > i){
int t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
}
arr[begin] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
Quick_Sort(arr, begin, i-1);
Quick_Sort(arr, i+1, end);
}3、 ... and 、 Two way sorting
The quick sort algorithm mentioned before is to >v and <v Both partial elements are placed in the index value i The left part of the position pointed to , Our two-way quick sort algorithm is different , He uses two index values (i、j) Used to traverse our sequence , take <v Put the elements in the index i To the left of the position pointed to , And will be >v Put the elements in the index j To the right of the position pointed .

(1) Code implementation ;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class QuickSort {
private static Random random;
private QuickSort() {
}
public static <E extends Comparable<E>> void sort2ways(E[] arr) {
random = new Random();
sort2ways(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
}
private static <E extends Comparable<E>> void sort2ways(E[] arr, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) {
return;
}
int p = partition2(arr, l, r);
sort2ways(arr, l, p - 1);
sort2ways(arr, p + 1, r);
}
private static <E extends Comparable<E>> int partition2(E[] arr, int l, int r) {
// Generate [l,r] Random index between
int p = l+random.nextInt(r-l+1);
swap(arr,l,p);
// arr[l+1...i-1]<= v;arr[j+1...r]>=v
int i = l+1,j = r;
while (true){
while (i<=j && arr[i].compareTo(arr[l])<0)
i++;
while (j>=i && arr[j].compareTo(arr[l])>0)
j--;
if (i>=j)
break;
swap(arr,i,j);
i++;
j--;
}
swap(arr,l,j);
return j;
}
}Four 、 Three way sorting
Divide the whole array into values v, Divided into less than v The area of is called smaller than area , be equal to v The area of is equal to the area and greater than v The area of is larger than the three parts of the area , In the next recursion, there is no need to deal with equal v Equal area of , Because the element equal to the area has reached the final position , For the existence of a large number equals v The three-way fast array greatly improves the efficiency .

(1) Code implementation
import java.util.*;
public class QuickSort3Ways {
// Use quick sort recursively , Yes arr[l...r] The scope of the order
private static void sort(Comparable[] arr, int l, int r){
// For small arrays , Use insert sort
if( r - l <= 15 ){
InsertionSort.sort(arr, l, r);
return;
}
// Random in arr[l...r] In the range of , Select a value as the calibration point pivot
swap( arr, l, (int)(Math.random()*(r-l+1)) + l );
Comparable v = arr[l];
int lt = l; // arr[l+1...lt] < v
int gt = r + 1; // arr[gt...r] > v
int i = l+1; // arr[lt+1...i) == v
while( i < gt ){
if( arr[i].compareTo(v) < 0 ){
swap( arr, i, lt+1);
i ++;
lt ++;
} else if( arr[i].compareTo(v) > 0 ){
swap( arr, i, gt-1);
gt --;
} else{ // arr[i] == v
i ++;
}
}
swap( arr, l, lt );
sort(arr, l, lt-1);
sort(arr, gt, r);
}
public static void sort(Comparable[] arr){
int n = arr.length;
sort(arr, 0, n-1);
}
private static void swap(Object[] arr, int i, int j) {
Object t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[j];
arr[j] = t;
}
}
边栏推荐
- Iptables' state module (FTP service exercise)
- String operation
- Basic data types and string types are converted to each other
- Practice of combining rook CEPH and rainbow, a cloud native storage solution
- MES系统,是企业生产的必要选择
- 打通法律服务群众“最后一公里”,方正璞华劳动人事法律自助咨询服务平台频获“点赞”
- 如何理解分布式架构和微服务架构呢
- Opencv learning notes II - basic image operations
- About using CDN based on Kangle and EP panel
- [Yu Yue education] higher vocational English reference materials of Nanjing Polytechnic University
猜你喜欢
2-3查找树
SSM 整合
数据分片介绍
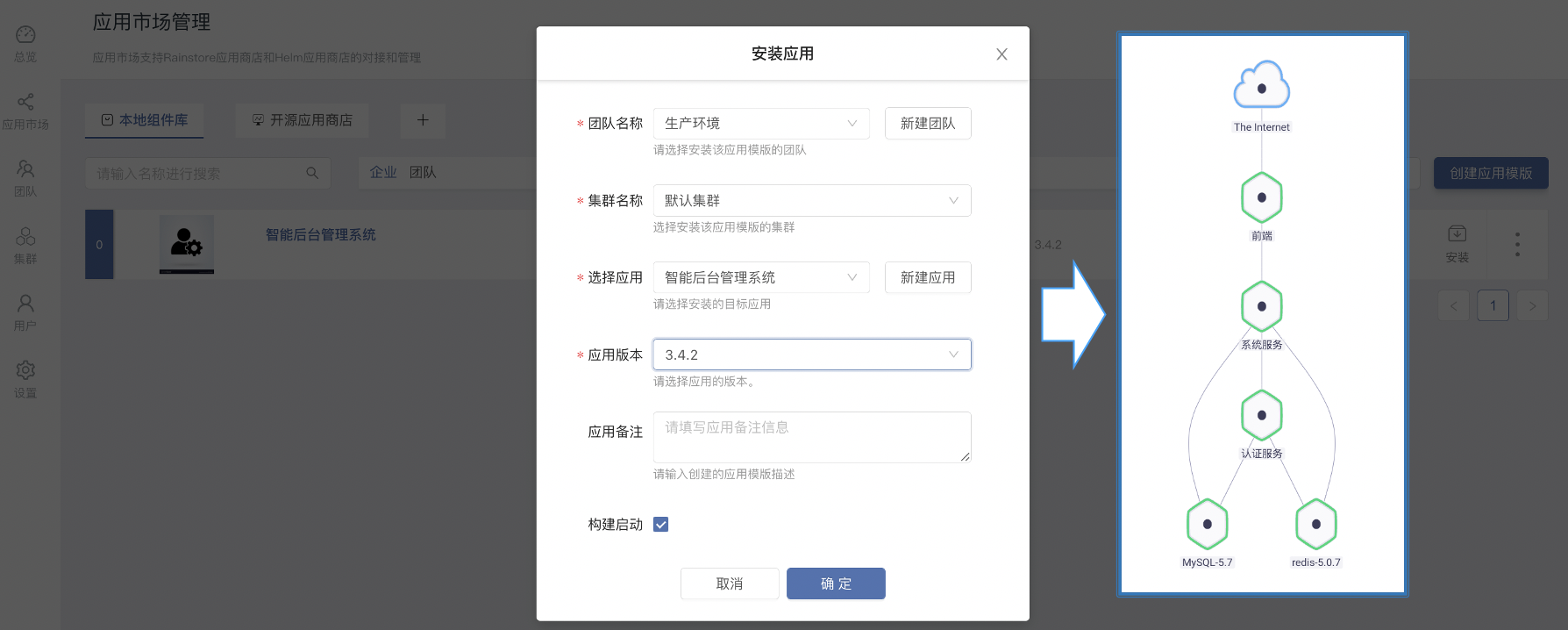
Improve the delivery efficiency of enterprise products (1) -- one click installation and upgrade of enterprise applications
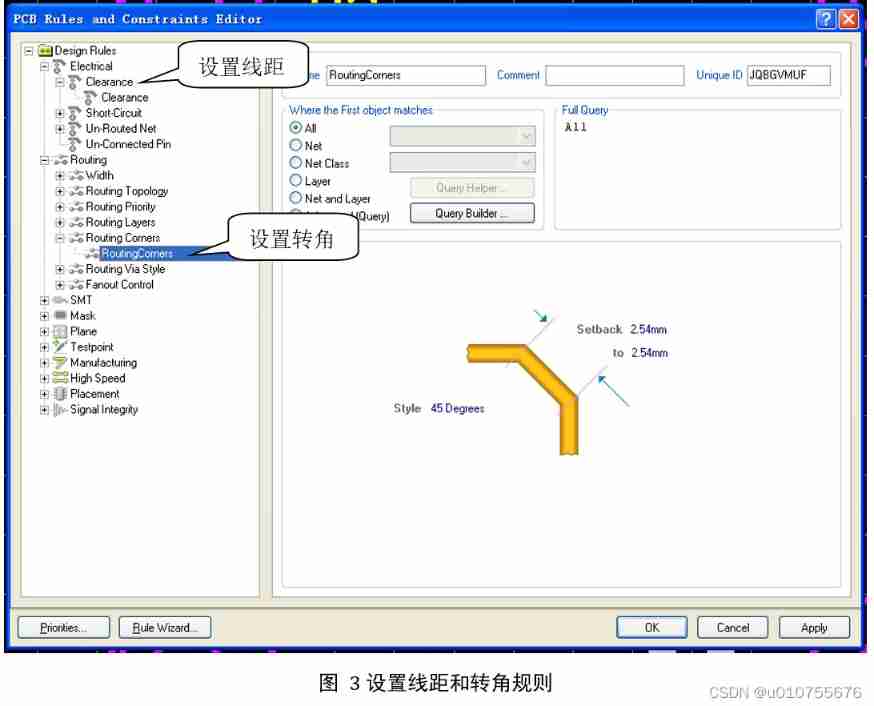
What is the method of manual wiring in PCB design in 22protel DXP_ Chengdu electromechanical Development Undertaking
How to integrate app linking services in harmonyos applications
Exercise arrangement 2.10, 11
All about PDF crack, a complete solution to meet all your PDF needs

Novice entry SCM must understand those things

idea里使用module项目的一个bug
随机推荐
[hard core science popularization] working principle of dynamic loop monitoring system
[paper reading] icml2020: can autonomous vehicles identify, recover from, and adapt to distribution shifts?
All about PDF crack, a complete solution to meet all your PDF needs
[Yu Yue education] basic reference materials of electrical and electronic technology of Nanjing Institute of information technology
Upload an e-office V9 arbitrary file [vulnerability recurrence practice]
調用華為遊戲多媒體服務的創建引擎接口返回錯誤碼1002,錯誤信息:the params is error
String operation
Snyk dependency security vulnerability scanning tool
How to realize the high temperature alarm of the machine room in the moving ring monitoring system
One click deployment of highly available emqx clusters in rainbow
[Chongqing Guangdong education] organic electronics (Bilingual) reference materials of Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications
Open3D ISS关键点
A single game with goods increased by 100000, and the rural anchor sold men's clothes on top of the list?
Required String parameter ‘XXX‘ is not present
Mock.js用法详解
idea里使用module项目的一个bug
PVTV2--Pyramid Vision TransformerV2学习笔记
Tuowei information uses the cloud native landing practice of rainbow
数据分析方法论与前人经验总结2【笔记干货】
IP-guard助力能源企业完善终端防泄密措施,保护机密资料安全