当前位置:网站首页>Merge sort and non comparison sort
Merge sort and non comparison sort
2022-07-07 08:27:00 【Old fish 37】
Merging and sorting is still difficult to understand , We should master the recursive and non recursive methods of merge sorting .
Now let's first understand what merge sorting is :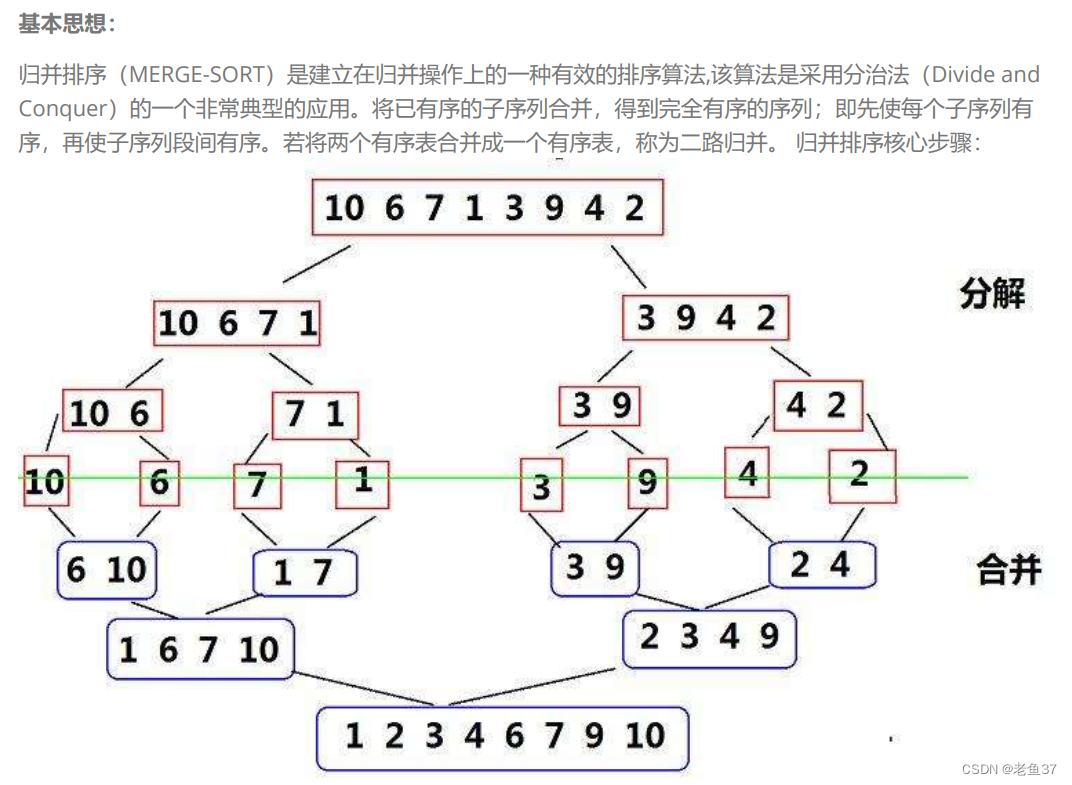
Four words ---- Divide and rule
First merge from the whole small , Then to the overall consolidation
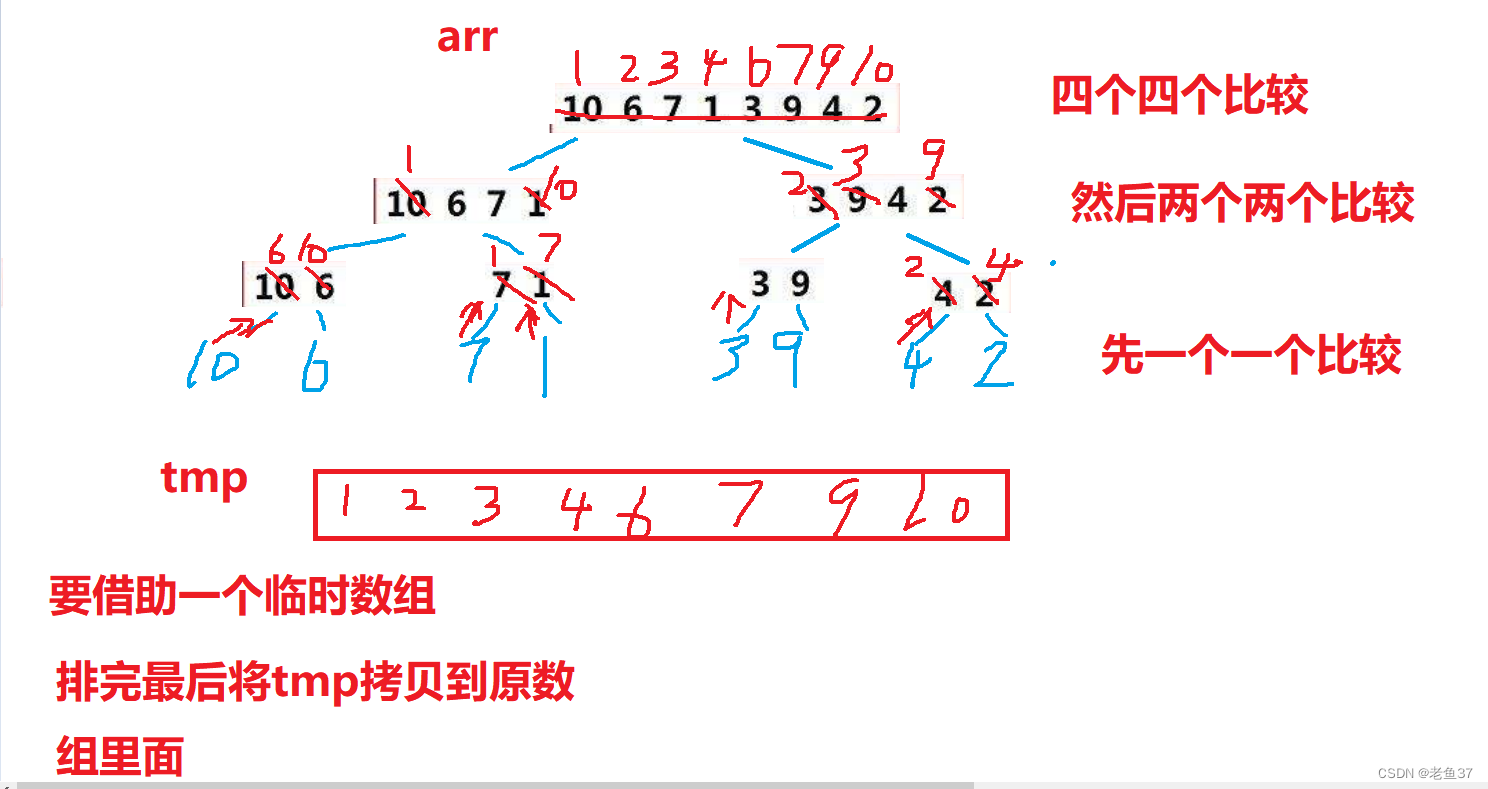
Complete code :
void _MerGetSort(int* arr, int begin, int end, int* tmp)
{
if (begin >= end)
{
return;
}// Divide the area
int mid = (begin + end) / 2;
// recursive
_MerGetSort(arr, begin, mid, tmp);
_MerGetSort(arr, mid + 1, end, tmp);
// Merge and compare
int begin1 = begin;
int end1 = mid;
int begin2 = mid + 1;
int end2 = end;
int i = begin1;
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (arr[begin1] < arr[begin2])
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin2++];
}
}
// One of them must have finished Merge the rest into tmp in
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin2++];
}// It's over , take tmp Copy back arr Array
memcpy(arr + begin, tmp + begin, sizeof(int) * (end - begin + 1));
}void MerGetSort(int* arr, int len)
{
// Open up an array
int* tmp = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * len);
_MerGetSort(arr, 0, len - 1, tmp);
free(tmp);
}
void PrintSort(int* arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3,1,2,4,9,5,6};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
MerGetSort(arr, len);
PrintSort(arr, len);
}
The following describes non recursive writing :
void MerGetSort(int* arr, int len)
{
// Create a new array
int* tmp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * len);
if (tmp == NULL)// Judge
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
int gap = 1;// determine gap
while (gap < len)
{
printf("%d->", gap);
for (int i = 0; i < len; i += 2 * gap)
{
//[i, i + gap - 1] [gap + i, i + 2 * gap - 1] Divide the area
int begin1 = i, end1 = i + gap - 1;
int begin2 = gap + i, end2 = i + 2 * gap - 1;
printf("[%d][%d] [%d][%d]", begin1, end1, begin2, end2);
// Judge the cross-border area , And then modify
// because gap How much is the begin1 Will be the last , So from end1 Start to modify
if (end1 >= len)
{
end1 = len - 1;
begin2 = len; // here [begin2,end2]----[len,len-1] unreasonable , They don't execute
end2 = len - 1;
}
else if (begin2 >= len)// Invalid area modify
{
begin2 = len;
end2 = len - 1;
}
else if (end2 >= len)
{
end2 = len - 1;
}
int i = begin1;
// Then merge and compare
while (begin1 <= end1 && begin2 <= end2)
{
if (arr[begin1] < arr[begin2])
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin1++];
}
else
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin2++];
}
}
// After a walk , Put the remaining data into tmp
while (begin1 <= end1)
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin1++];
}
while (begin2 <= end2)
{
tmp[i++] = arr[begin2++];
}
}
printf("\n");
memcpy(arr, tmp, sizeof(int) * len);// Copy
gap = gap * 2;
}
}
void PrintSort(int* arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 3,1,2,4,9,5,6};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
MerGetSort(arr, len);
PrintSort(arr, len);
}
As for the invalid area, it refers to :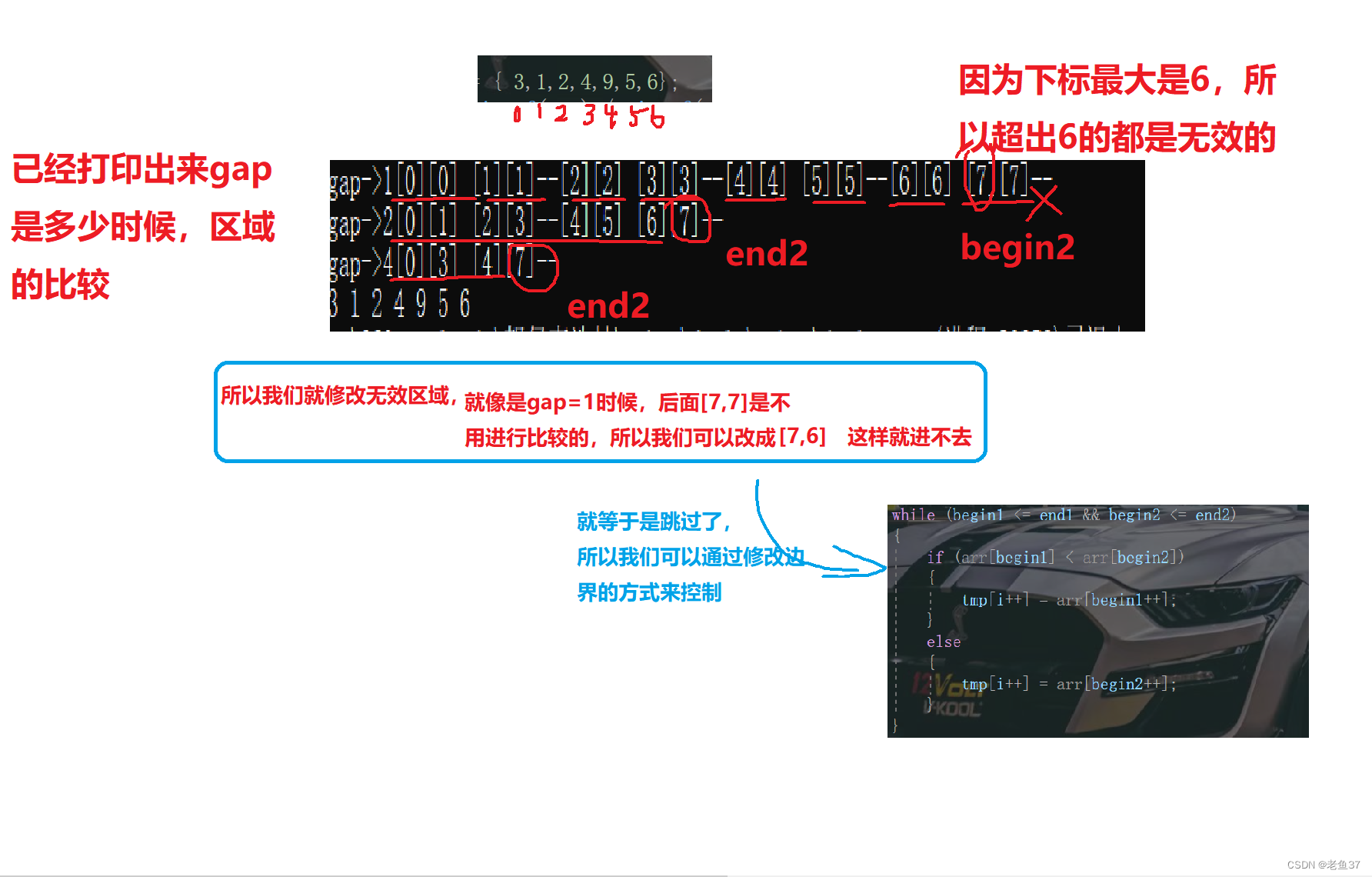
If you don't want to change the boundary , It can also be skipped directly , Revised as follows :
Method 2 :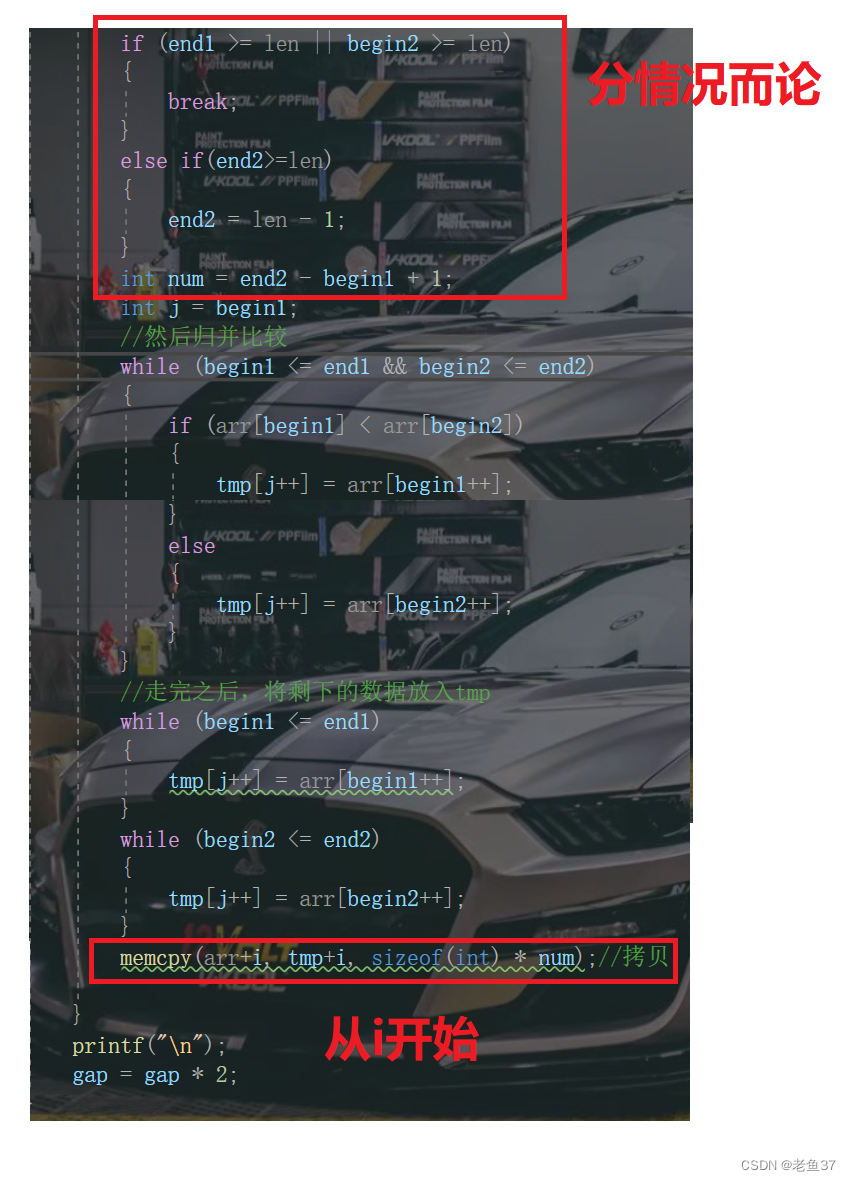
such memcpy It's copied piece by piece , The first way is to copy all together , There are two ways to look at personal preferences .
Next, we will introduce non comparison sorting

What we will learn next is counting and sorting
Learn about counting sorting
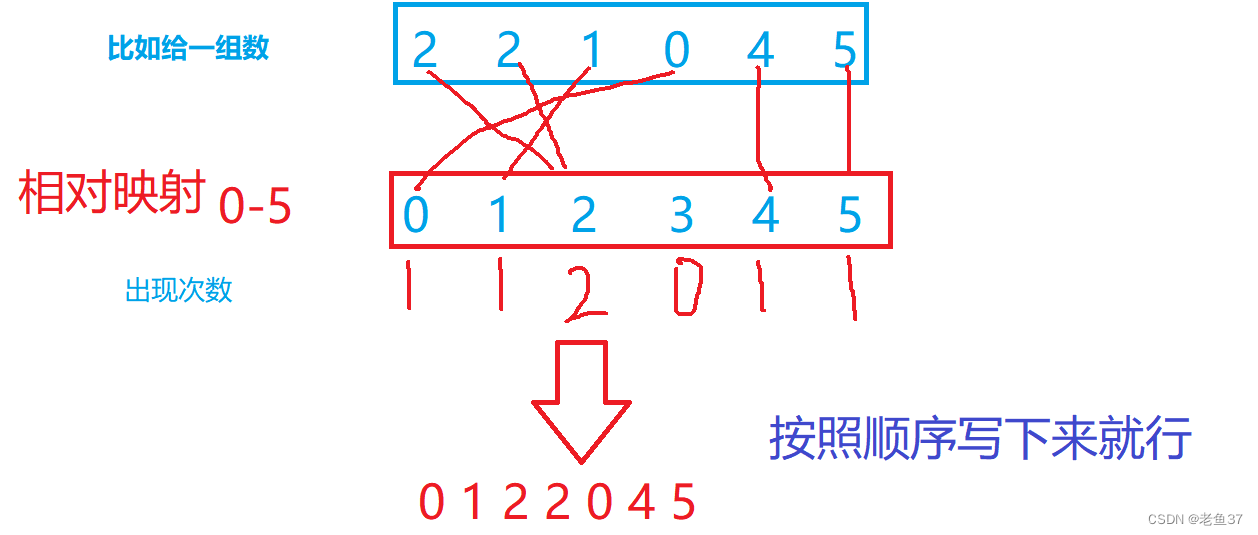
This sort of counting has limitations :
1、 If it's a floating point number , String cannot be played
2、 If the data range is large , The space complexity will be very high , You can't play
3、 Generally, the difference between these data is relatively small
When you meet 100、1000 These data , If it's not much different , Using relative mapping is very practical .
// Count sorting
void CountSort(int* arr, int len)
{
int min = arr[0], max = arr[0];// The smallest and largest are the first Go to the back
for (int i = 1; i < len; i++)
{
if (arr[i] < min)
{
min = arr[i];
}
if (arr[i] > max)
{
max = arr[i];
}
}
// The largest and smallest have been found Open up space
int range = max - min + 1;
int* count = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * range);
if (count == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
memset(count, 0, sizeof(int) * range);// All initialized to 0// Count the number of times
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
count[arr[i] - min]++;
}// Write back sort
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < range; i++)
{
while (count[i]--)
{
arr[j++] = i + min;
}
}
}
void PrintSort(int* arr, int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1003,1001,1002,1004,1009,1005,1006};
int len = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
CountSort(arr, len);
PrintSort(arr, len);
}

Here we classify the previous sorts , And flawed assessment
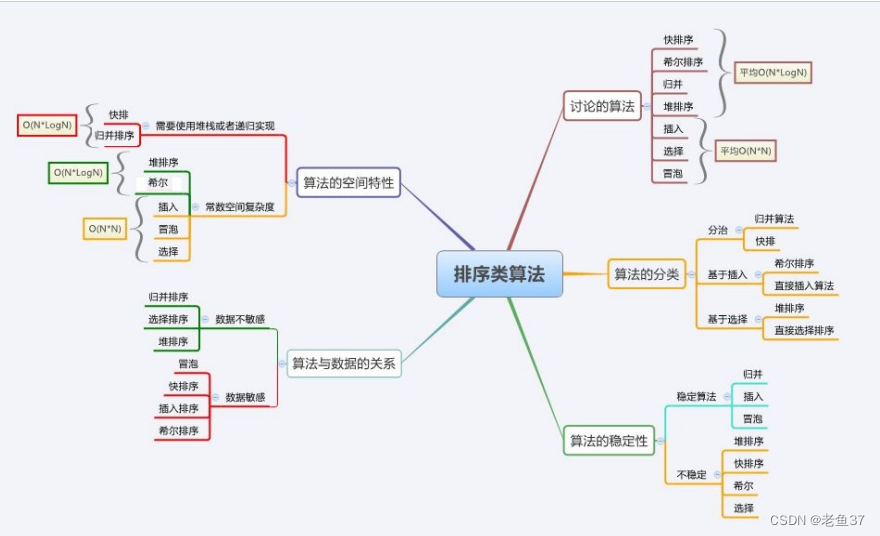
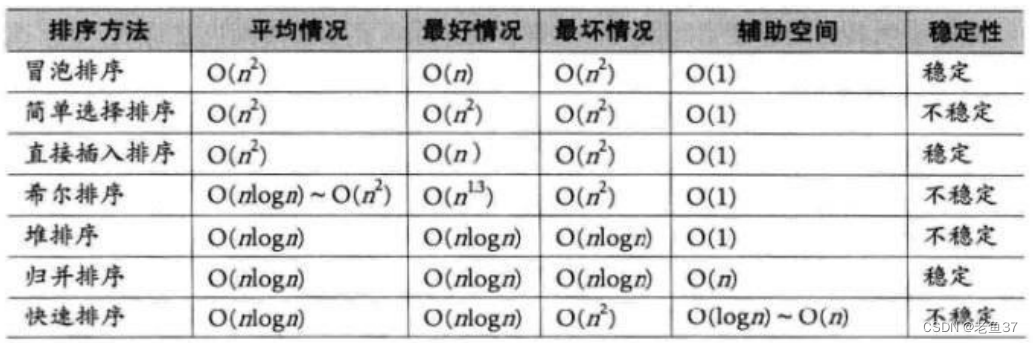
I hope all my friends can learn these sorting , Your support is my driving force !
If there is a mistake , Your smile !
边栏推荐
- Analyzing the influence of robot science and technology development concept on Social Research
- Coquette data completes the cloud native transformation through rainbow to realize offline continuous delivery to customers
- Make LIVELINK's initial pose consistent with that of the mobile capture actor
- Leetcode simple question: find the K beauty value of a number
- BiSeNet的特点
- Battery and motor technology have received great attention, but electric control technology is rarely mentioned?
- Full text query classification
- Qinglong panel - today's headlines
- Using nocalhost to develop microservice application on rainbow
- JS copy picture to clipboard read clipboard
猜你喜欢

Opencv learning note 4 - expansion / corrosion / open operation / close operation

打通法律服务群众“最后一公里”,方正璞华劳动人事法律自助咨询服务平台频获“点赞”
Obsidan之数学公式的输入
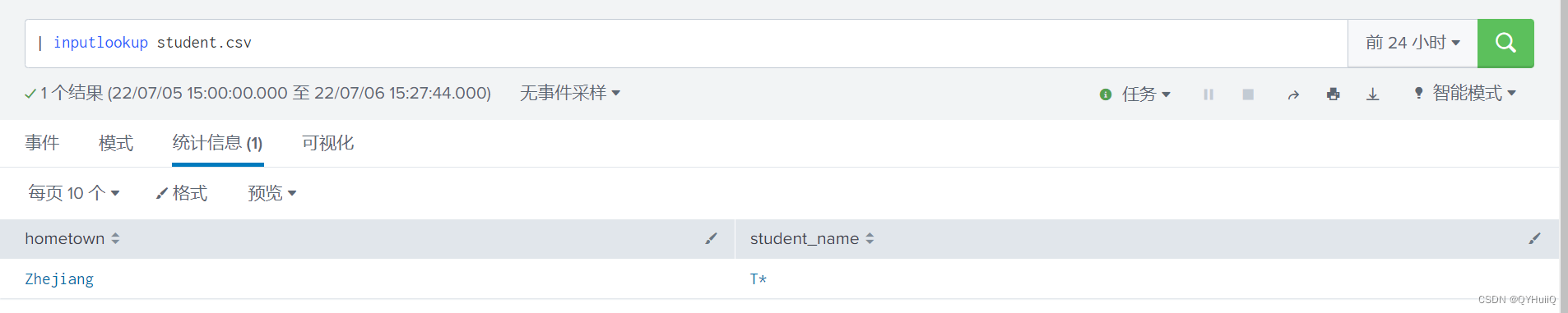
The field value in Splunk subquery fuzzy matching CSV is*

一种适用于应用频繁测试下快速查看Pod的日志的方法(grep awk xargs kuberctl)
Rainbond 5.7.1 支持对接多家公有云和集群异常报警
Open3d ISS key points

Interpreting the practical application of maker thinking and mathematics curriculum
OpenVSCode云端IDE加入Rainbond一体化开发体系
Practice of combining rook CEPH and rainbow, a cloud native storage solution
随机推荐
Qinglong panel -- Huahua reading
JS copy picture to clipboard read clipboard
IELTS review progress and method use [daily revision]
Low success rate of unit test report
Go语言中,函数是一种类型
接口作为参数(接口回调)
MySQL introduction - crud Foundation (establishment of the prototype of the idea of adding, deleting, changing and searching)
Using helm to install rainbow in various kubernetes
Basic use of CTF web shrink template injection nmap
Learn how to compile basic components of rainbow from the source code
Caractéristiques de bisenet
Réplication de vulnérabilité - désrialisation fastjson
PVTV2--Pyramid Vision TransformerV2学习笔记
发挥创客教育空间的广泛实用性
Full text query classification
Rainbond结合NeuVector实践容器安全管理
Splunk子查询模糊匹配csv中字段值为*
国标GB28181协议视频平台EasyGBS新增拉流超时配置
MES系統,是企業生產的必要選擇
The use of generics and vararg variable parameters in kotlin