当前位置:网站首页>自定义View基础之Layout
自定义View基础之Layout
2022-06-11 05:08:00 【jxq1994】
当上一节执行完measure操作后,接下来的layout过程其实是比较简单的,其目的就是父视图按照
子视图的大小及布局参数,将子视图放置到合适的位置上。布局参数最核心的是处理gravity参数。
layout过程的设计思路
最初调用 layout()函数是从 ViewRoot 类的 performTraversals(),host 是一个 View 对象,View 类中 layout()函数的类型是final,其子类不能重载该函数,以保证View系统中layout过程不变。
在layout()函数中,首先调用setFrame()函数给当前视图设置参数中指定的位置,然后回调onLayou()函数。ViewGroup类中重载了onLayout()函数,并且将其函数类型设置成了一个abstract类型,因此, 所有的ViewGroup实例必须实现onLayout()。View系统希望程序员能够在onLayout()函数中对该视图所包含的子视图进行layout操作,当该视图是ViewGroup时,程序员一般会在onLayout()函数中调用子视 图 child的 layout()方法,从而完成对子视图的位置分配。当然,如果子视图也是一个ViewGroup实例, 就又会调用相应的onLayout()函数。
View类 中 layout()函数的原型为:
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b)
参数指定了该子视图在父视图中的左、上、右、下的位置。该函数的
内部流程如下。
- 调用
setFrame(l, t, r, b)将位置参数保存起来。
这些参数将保存到View内部变量(mLeft、mTop、 mRight、mBottom),保存完变量前,会先对比这些参数是否和原来的相同,如果相同,则什么都不做, 如果不同才进行重新赋值,并且在赋值前,会给
mPrivateFlags中添加DRAWN标识,同时调用invalidate告诉View系统原来占用的位置需要重绘。注意是先调用invalidate(),而后赋值的,因为需要重绘的是老的区域。
- 回调onLayout()。
View中定义的
onLayout()函数默认什么都不做,View系统提供onLayout()函数的目的是为了使系统包含有子视图的父视图能够在onLayout()函数对子视图进行位置分配,正因为如此,如果是父视图,就必须重载onLayout(),也正因为如此,ViewGroup类才把onLayout()重载修改为了一个abstract 类型。
- 清除
mPrivateFlags中的LAYOUT_REQUIRED标识,因为layout的操作已经完成了。
LinearLayout 中 onLayout()内部过程
LinearLayout中的子视图有两种排列方式,一种是水平的,另一种是垂直的,本节仅说明垂直方式
下的工作流程。onLayout()函 数 中 首 先 根 据 mOrientation变 量 判 断 是 水 平 还 是 垂 直 ,如 果 是 垂 直 ,则调用layoutVertical()开始进行 layout 操作。
1. 获得子视图可用的宽度。
这里是进行垂直方向上的布局,为什么却要可用的宽度,而不是可用的髙度呢?
因为,就算是垂直方向,子视图本身也货以水平居中,而要居中就得知道可用的宽度是多少,从而计算出子视图左边沿的位置,如 图 所示,至于高度信息将在后面步骤中获得。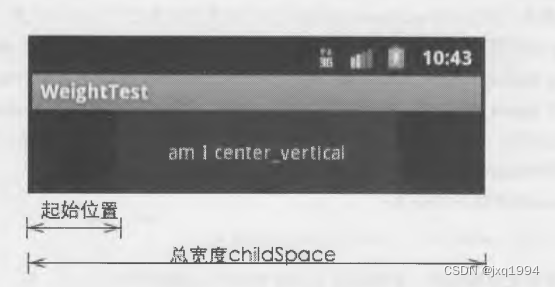
2. 根据父视图中的gravity属性,决定子视图的起始位置。
在默认情况下,gravity是 TOP,应用 程序可以设置为BOTTOM或 者CENTER_VERTICAL,这三者对应的起始位置如图所示。
3. 此时已经确定了子视图的垂直方向上的位置,于是就开始for()循环为每一个子视图分配位置。
(1) 取出子视图的
LayoutParams,并得到gravity的值。注意这个gravity值并不是子视图中android:gravity的值,而是android:layou_gravity的值,关于这一点的解释见下一小节。
( 2 ) 根 据 gravity的值确定水平方向上的起始位置,分为三种,分 别 是 LEFT、 CENTER HORIZONTAL及 RIGHT,三者对应的起始位置如图所示。
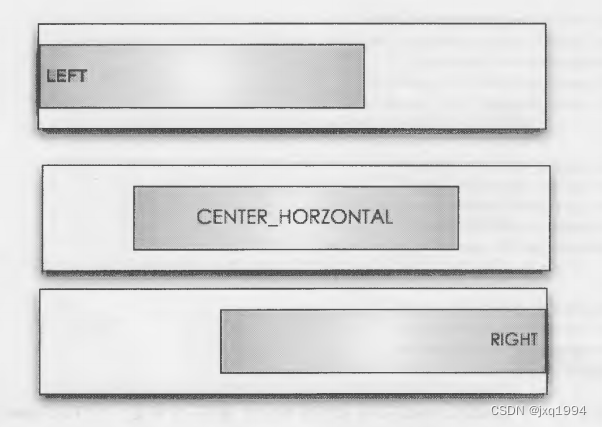
( 3 ) 调 用
setChildFrame(),该函数内部实际上就是调用child.layout()为子视图设置布局位置。
至此,LinearLayout就完成了为所包含的子视图分配布局位置的过程。
TextView 中 gravity 与 layout 的关系
上一节说到,子视图中gravity的值并不是android:gravity的值,而 是 android:layout__gravity,这是
怎么回事呢?
这个问题其实包含了一个重要概念,那就是 LayoutParams是如何被赋值的。应用程序可以在layout.xml文件中使用诸如< LinearLayout >、< TextView > 标签定义一个界面。无论是ViewGroup还是View,这些标签定义的仅仅是一个视图,而不能定义LayoutParams,因为LayoutParams正如其名称所讲,它是一个布局属性,而一个视图在没有被布局时又哪里来的布局属性呢?
而 在 过 去 的 开 发 经 验 中 ,大 家 几 乎 都 使 用 过 android:layout_height、android:layout_width、 android:gravity等 XM L语法为一个LinearLayout或 者 TextView添加相应的布局属性,并且这些值似乎都工作正常,表面上看,它就是该视图对应的LayoutParams值,这又作何解释?
另外,在LayoutInflater类中有一个inflate(int resId,View root)函数,在大多数情况下,大家调用该
函数时,第二个参数root都为空。那么这个参数的意义又是什么?为什么大多数情况下都要为空呢?
要回答以上问题,就需要弄清楚系统内部是如何从一个XM L文件创建一个对应的View树对象的,
以下面这段XML代码为例说明该过程:
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:background="@color/white"
android:text="am i center_vertical"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"/>
<ListView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:background="@color/black"/>
</LinearLayout>
该段代码包含了一个LinearLayout,其中又包含两个子视图,分别是一个TextView及一个ListView。
从 XML文件中构造对应的View树是在
Layoutlnflater中 的inflate()函数中完成的,如果该段代码是作为setContentView()的参数,则会被当作Activity的界面,那么LinearLayout中定义的layout_width及height都是有意义的。但如果这段代码仅仅是应用程序调用inflate()函数创建一个View对象,那 么layout_width及 height就没有任何意义。
inflate()函数会首先判断参数root是否为空,如果为空,就以XML文件中的根视图构造一个临时
的 View对象,此处是LinearLayout对象,此时该LinearLayout中声明的layout_width及 height都没有任何用处。接下来继续读取XML文件中TextView,读取TextView后,就需要把该TextView添加到LinearLayout中。因为要添加,所以必须有一个LayoutParams对象,于是,inflate()函数中就以TextView中定义的layout_width及 height为参数,回 调 TextView父视图generateLayoutParams()函数。
TextView 的父视图正是 LinearLayout,而在 LinearLayout 的generateLayoutParams(attrs)函数中,参数 attrs正是来源于TextView中所声明的全部属性值,除了 layout_width和 height夕卜,还包含background、text等所有声明的属性值,但generateLayoutParams(atts)中却只对其中四个属性感兴趣:
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a =
c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout);
weight = a.getFloat(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_weight, 0);
gravity = a.getInt(com.android.internal.R.styleable.LinearLayout_Layout_layout_gravity, -1);
a.recycle();
}
在以上代码中,super(c,attrs)中将读取layout_height和 layout_width的属性,如以下代码所示。然后继续读取weight属性和gravity属性,而这两个属性的名称却分别是layout_weight和 layout_ gravity。generateLayoutParams(atts)最终将根据 TextView中的以上四个属性构造一个 LinearLayout.ayoutParams 对象,并以该对象把 TextView 添加到 LinearLayout 中。
回过头来再看上面提出的问题,< TextView >标签中包含的
android:layout_width、height等并没有定义LayoutParams对象,它只是提供了构造LayoutParams参数所需要的值,而真正构造LayoutParams对象的是它的父视图,这些参数最终会产生什么样的LayoutParams取决于该TextView的父视图中generateLayoutParams(attrs)的具体实现。
这也就是上一节中所说的为什么要使用
layout_gravity而不是gravity的原因,因为在LinearLayout
的generateLayoutParams()函数中,是把android:layout_gravity属性值赋值给了LayoutParams.gravity,而不是android:gravity。事实上,android:gravity属性将作为TextView内部的参数,TextView在内部的 onDraw()函数中将根据android:gravity的值决定把文字显示在什么地方。
而当调用
setContentView(int resld)时,系统内部也同样调用了inflate()方法从指定的XML文件中产生 View树,并且调用时参数root设置的是内部的一个FrameLayout对象。root参数的意义在于它将提 供generateLayoutParams()函数,该函数产生的LayoutParams对象将作为XML文件中包含的视图被添加到 root时的布局属性。
如果你在一个XM L文件中仅仅定义了一个TextView标签,然后调用inflate(xml, null)从这个XML
文件中infalte出一个TextView对象,那么该TextView标签中所包含的android:layout_width、height将没有任何意义。当 你 想 把 infalte出 来 的 TextView对象添加到某个ViewGroup时,还必须构造一个 LayoutParams 对象。
边栏推荐
- lower_ Personal understanding of bound function
- Paper recommendation: relicv2, can the new self supervised learning surpass supervised learning on RESNET?
- [aaai 2021 timing action nomination generation] detailed interpretation of bsn++ long article
- 免费数据 | 新库上线 | CnOpenData全国文物商店及拍卖企业数据
- 华为设备配置BGP/MPLS IP 虚拟专用网命令
- Yolact paper reading and analysis
- [Transformer]MViTv2:Improved Multiscale Vision Transformers for Classification and Detection
- Paper reproduction: pare
- Yolov5 training personal data set summary
- KD-Tree and LSH
猜你喜欢

How to apply for free idea with official documents

Comparison of gigabit network card chips: who is better, a rising star or a Jianghu elder?

Huawei equipment is configured with bgp/mpls IP virtual private network

免费数据 | 新库上线 | CnOpenData全国文物商店及拍卖企业数据

Tightly coupled laser vision inertial navigation slam system: paper notes_ S2D. 66_ ICRA_ 2021_ LVI-SAM

AAAI2022-ShiftVIT: When Shift Operation Meets Vision Transformer
![[Transformer]On the Integration of Self-Attention and Convolution](/img/64/59f611533ebb0cc130d08c596a8ab2.jpg)
[Transformer]On the Integration of Self-Attention and Convolution

华为设备配置通过GRE接入虚拟专用网

2021 iccv paper sharing - occlusion boundary detection
Conversion relationship between coordinate systems (ECEF, LLA, ENU)
随机推荐
Sealem finance builds Web3 decentralized financial platform infrastructure
2021 iccv paper sharing - occlusion boundary detection
选择数字资产托管人时,要问的 6 个问题
Cascade EF gan: local focus progressive facial expression editing
C language test question 3 (grammar multiple choice question - including detailed explanation of knowledge points)
[Transformer]AutoFormerV2:Searching the Search Space of Vision Transformer
Pytoch machine learning GPU usage (conversion from CPU to GPU)
How to purchase 25g optical network card
Top 100 video information of station B
Take stock of the AI black technologies in the Beijing Winter Olympic Games, and Shenzhen Yancheng Technology
Concurrent search set
Electrolytic solution for ThinkPad X1 carbon battery
Opencv learning path (2-2) -- Deep parsing namedwindow function
Intercept file extension
Deep extension technology: intelligent OCR recognition technology based on deep learning has great potential
使用acme.sh自动申请免费SSL证书
Share | defend against physically realizable image classification attacks
Inventory | ICLR 2022 migration learning, visual transformer article summary
Course design summary
【Markdown语法高级】 让你的博客更精彩(三:常用图标模板)