当前位置:网站首页>Basic principle of servlet and application of common API methods
Basic principle of servlet and application of common API methods
2022-07-04 10:10:00 【No smell of flowers】
️ In front of the word ️
This article will introduce Servlet The basic principle of has been Servlet API Some of the methods commonly used in , We will use these methods to achieve some Servlet A little case of .
Blog home page : The blog home page without flowers
Welcome to focus on the likes collection ️ Leaving a message.
This paper is written by No smell of flowers original ,CSDN First episode !
Starting time :2022 year 7 month 2 Japan
️ Persistence and hard work will surely bring poetry and distance !
Reference books :《 no 》
Refer to the online programming website : Cattle from Power button
Blogger's code cloud gitee, Usually the program code written by bloggers is inside .
Blogger's github, Usually the program code written by bloggers is inside .
The author's level is very limited , If an error is found , Be sure to inform the author in time ! Thank you thank you !
Navigation assistant

1.Tomcat How to call Servlet
1.1Servlet principle
Servlet It belongs to superstructure , It is in the application layer , Its lower layer has a transport layer , The network layer , Data link layer , Hardware , Belong to “ economic base ”, After all, the lower economic base determines the superstructure . As I said before ,Servlet It's a set of operations HTTP Of API,Tomcat Can be used as HTTP Server to process requests , The key to processing the request is to call Servlet To operate HTTP Respond to the client .
What we wrote Servlet The code doesn't have main Method , How does it work ? It's actually Tomcat Calling Servlet,Tomcat It's actually an application , It is a common Java process .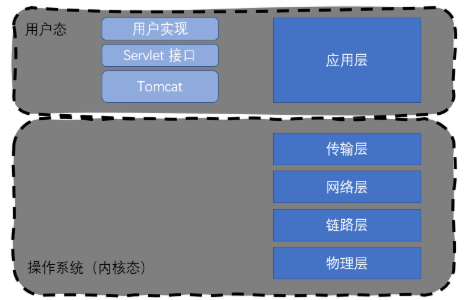
When the browser sends a request to the server ,Tomcat As HTTP Server Would call Serlvet API, Then execute what we wrote Servlet Program to process requests .
Processing requests involves more than HTTP, There are other layer protocols , But we are not aware of the details of other layer protocols , Only focus on the application layer HTTP Details of the agreement , This is the benefit of protocol layering , When programmers implement processing requests , Don't care about the details under the application layer .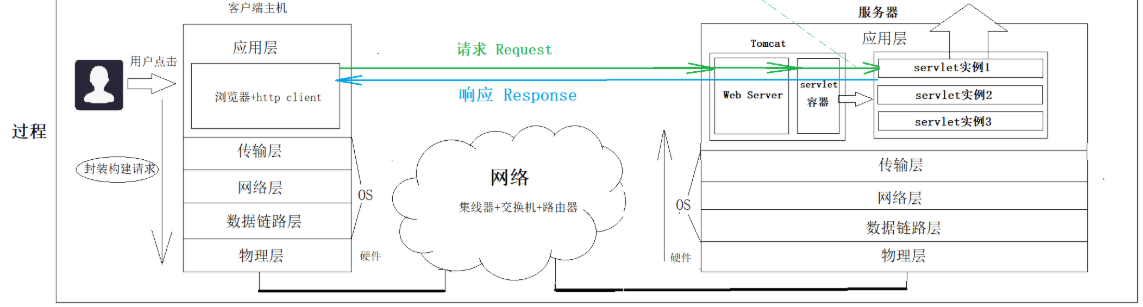
1.2Tomcat Execution logic
For ease of description Tomcat Execution logic , We use pseudocode to analyze :
Initialization and closeout , It is subdivided into the following parts :
1) Find... From the specified directory Servlet class , And load .
2 According to the loading results , Create instances of these classes .
3) After creating the instance , call Servlet Object init Method .
4) establish TCP socket object , monitor 8080 port , Wait for the client to connect .
5) If the request is processed , That is, the cycle of processing requests exits , that Tomcat It's over , call destroy Method to end the process , But this link is not necessarily reliable , In the case of normal exit , It needs to be on the management port (8005) To call destroy, take Tomcat close , But most of the time, the process is directly killed to achieve the purpose of shutdown , There is no time to call dsetroy Method .
class Tomcat {
// Used to store all Servlet object
private List<Servlet> instanceList = new ArrayList<>();
public void start() {
// According to the contract , Read WEB-INF/web.xml The configuration file ;
// And parsed by @WebServlet Annotated class
// Let's assume that this array contains all the parsed @WebServlet Annotated class .
Class<Servlet>[] allServletClasses = ...;
// What we need to do here is to instantiate all Servlet The object comes out ;
for (Class<Servlet> cls : allServletClasses) {
// Here is the use of java The reflection characteristics in
// In fact, it also involves a class loading problem , Because our class bytecode file , As agreed
// The way ( All in WEB-INF/classes Under the folder ) Deposited , therefore tomcat The internal is
// Implemented a custom class loader (ClassLoader) Used to take charge of this part of the work .
Servlet ins = cls.newInstance();
instanceList.add(ins);
}
// Call each Servlet Object's init() Method , This method will only be called once in the life of the object ;
for (Servlet ins : instanceList) {
ins.init();
}
// Use what we've learned before , Start a HTTP The server
// And use the way of thread pool to deal with each Request
ServerSocket serverSocket = new ServerSocket(8080);
// actually tomcat Not a fixed thread pool , This is just to illustrate the situation
ExecuteService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
while (true) {
Socket socket = ServerSocket.accept();
// Each request is independently supported by a thread , This reflects our Servlet It runs in a multithreaded environment
pool.execute(new Runnable() {
doHttpRequest(socket);// Processing requests
});
}
// Call each Servlet Object's destroy() Method , This method will only be called once in the life of the object ;
for (Servlet ins : instanceList) {
ins.destroy();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Tomcat().start();
}
}
Tomcat Process request work :
1) Read socket Data in , And in accordance with the HTTP The format of the Protocol , Get request .
2) Determine whether the request requires static content or dynamic content , If it's static content , You can find the destination file on the root path , Return request
3) If it's a dynamic file , You have to go through URL The first level path and the second level path on the are used to determine which one to pass Servlet Class to process , If not, it will return 404
4) To find the corresponding Servlet object , Call... In the object service Method , Call the corresponding... According to the requested method do... Method
class Tomcat {
void doHttpRequest(Socket socket) {
// Refer to what we learned before HTTP The principle of server is similar , Conduct HTTP Request resolution of protocol , And response building
HttpServletRequest req = HttpServletRequest.parse(socket);
HttpServletRequest resp = HttpServletRequest.build(socket);
// Judge URL Whether the corresponding file can be found directly in our root path , If you find , It's static
// Directly use what we have learned IO Output content
if (file.exists()) {
// Return static content
return;
}
// The logic here is dynamic
// According to what we said in the configuration , according to URL -> servlet-name -> Servlet The chain of objects
// Finally find the... To process this request Servlet object
Servlet ins = findInstance(req.getURL());
// call Servlet Object's service Method
// This will eventually call to our own HttpServlet Methods in subclasses of
try {
ins.service(req, resp);
} catch (Exception e) {
// return 500 page , Indicates an internal server error
}
}
}
service Method execution logic :
class Servlet {
public void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) {
String method = req.getMethod();
if (method.equals("GET")) {
doGet(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("POST")) {
doPost(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("PUT")) {
doPut(req, resp);
} else if (method.equals("DELETE")) {
doDelete(req, resp);
}
......
}
}
In the whole process , There are three key methods :
- init Method , In the initialization phase , Used to initialize each Servlet object , After the object is created , Will execute , Users can override this method , To execute some initialization program logic , No rewriting ,
initMethods are generally empty , That is, do nothing . - destroy Method , After exiting the main loop of request processing ,tomcat The method will be executed before the end , To release resources .
- service Method , Called during the processing phase of the request , Every request for dynamic resources needs to call .
2.Servlet Key points in API
2.1 Common methods are listed
HttpServlet Key methods :
| Method name | Timing of invocation |
|---|---|
| init | stay HttpServlet After being instantiated once |
| destory | stay HttpServlet Called once when the instance is no longer in use |
| service | received HTTP Call when requested |
| doGet | received GET Call when requested ( from service Method call ) |
| doPost | received POST Call when requested ( from service Method call ) |
| doPut/doDelete/doOptions/… | Called when other requests are received ( from service Method call ) |
When these methods are called , That makes up. “Servlet” Life cycle of .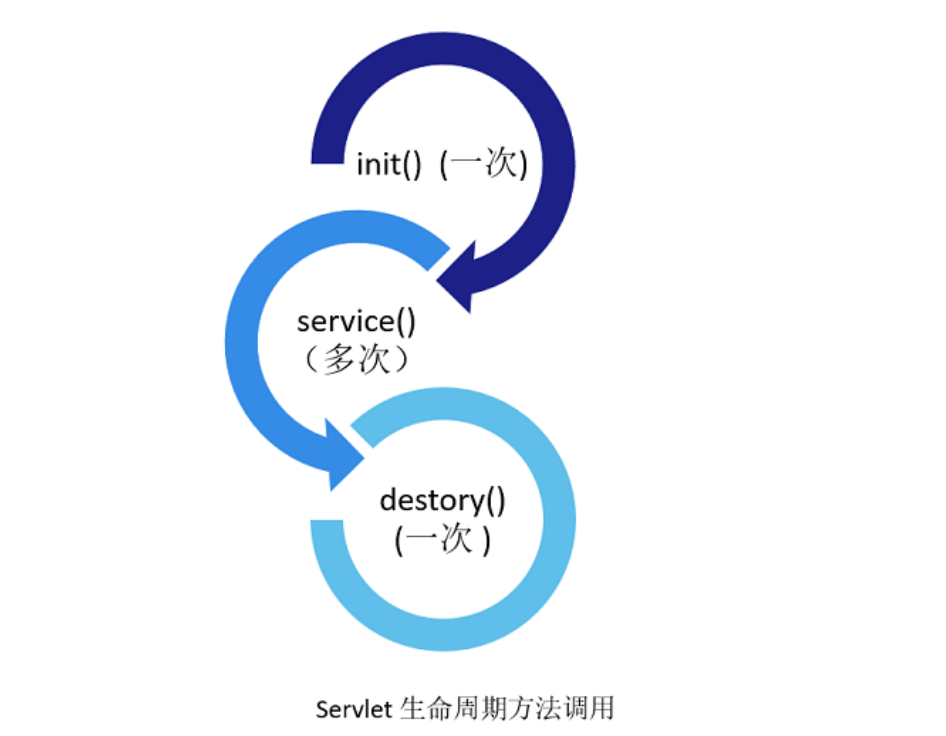
HttpServletRequest Key methods :
| Method | describe |
|---|---|
| String getProtocol() | Returns the name and version of the request protocol . |
| String getMethod() | Return requested HTTP Method name , for example ,GET、POST or PUT. |
| String getRequestURI() | From the name of the agreement to HTTP In the query string of the first line of the request , Return the requested URL The hierarchical path part of . |
| String getContextPath() | Returns a request indicating the context of the request URI part ( First level path ). |
| String getQueryString() | Return the request contained after the path URL The query string in . |
| Enumeration getParameterNames() | Return to one String Enumeration of objects , The name of the parameter contained in the request . |
| String getParameter(String name) | Returns the value of the request parameter as a string , Or if the parameter does not exist, return null. |
| String[] getParameterValues(String name) | Returns an array of string objects , Contains the values of all given request parameters , If the parameter does not exist, return null. |
| Enumeration getHeaderNames() | Returns an enumeration , Include all headers included in the request . |
| String getHeader(String name) | Returns the value of the specified request header as a string . |
| String getCharacterEncoding() | Returns the name of the character encoding used in the request body . |
| String getContentType() | Return the MIME type , If you don't know the type, return null. |
| int getContentLength() | Returns the length of the request body in bytes , And provide input stream , Or if the length is unknown, return -1. |
| InputStream getInputStream() | Used to read the requested body Content . Return to one InputStream object . |
HttpServletResponse Key methods :
| Method | describe |
|---|---|
| void setStatus(int sc) | Set the status code... For this response . |
| void setHeader(String name, String value) | Set a with a given name and value header. If name Already exist , Then overwrite the old value , You can refresh the page |
| void addHeader(String name, String value) | Add a with the given name and value header. If name Already exist , Do not overwrite old values , Add new key value pairs side by side |
| void setContentType(String type) | Set the content type of the response sent to the client . |
| void setCharacterEncoding(String charset) | Set the character encoding of the response sent to the client (MIME Character set ) for example ,UTF-8. |
| void sendRedirect(String location) | Use the specified redirection location URL Send temporary redirect response to client . |
| PrintWriter getWriter() | Used to go to body Write data in text format . |
| OutputStream getOutputStream() | Used to go to body Write data in binary format . |
2.2Post The structure of the request
In the same webapp Inside , The association path cannot be the same , Otherwise Tomcat Can't run , about GET request , have access to URL The query string of , however POST No, please , Need to use form perhaps ajax.
structure Post request ( Use ajax structure ):
stay webapp Create one in the directory HTML file , Used for construction POST request , First, let's introduce jquery rely on ( Bloggers use local import , You can if the network address :https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min.js Import dependence ), And then call ajax Construct request .
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/jquery/3.6.0/jquery.min.js"></script>
<script> $.ajax({
type: "post", url: "method", success: function (body){
console.log(body); } }) </script>
Notice the top URL Attribute cannot be added /, Plus, it means the absolute path , You can also use it ./ To represent the relative path , But in Servlet Annotation Association path must be added /.
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/method")
public class MethodServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("POST request ");
}
}
We visit http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello_servlet/test.html Take a look at the return result of the console output .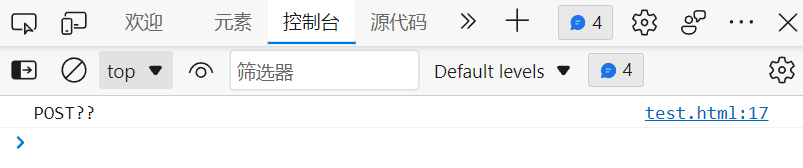
We found it inconsistent with our expectations , We returned when processing the request POST request , And here it shows POST??, The reason is that there is a garbled code ,idea The default encoding format is utf-8,Windows The default encoding format is gbk, The browser parses body The time is also with gbk Format to parse , To unify the format , You have to first tell the browser what the encoding format of the response data is , We need to be in Servlet Set character format in the program , Set the method to call HttpServletResponse Object's setContentType Method , Pass in the parameter text/html; charset=utf8.
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/method")
public class MethodServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
resp.getWriter().write("POST request ");
}
}
Repackage deployment , Refresh the page :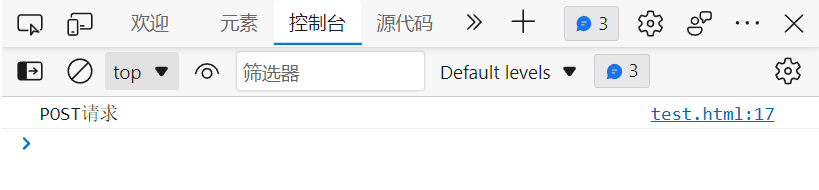
2.3 Get request information
For requested information , We use HttpServletRequest Class to obtain the requested information :
For example, we visited url by http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello_servlet/showreq?key=10&a=100&b=200, Obviously, this is a..., constructed using query strings GET request , adopt HttpServletRequest Class a series of corresponding methods , We can get the method type of this request , Protocol version ,URL, Query string , Some information of the head . Among them, the query string and header information must be obtained first getParameterNames Methods or getHeaderNames Method to get all the query strings or header information key value , This is an enumeration object , And then according to getParameter perhaps getHeader Methods by key Value traverses the enumeration object to get value.
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
@WebServlet("/showreq")
public class ShowRequestServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Access link :http://127.0.0.1:8080/hello_servlet/showreq?key=10&a=100&b=200
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf-8");
//1 Agreement name and version
stringBuilder.append(" Protocol version :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getProtocol());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//2 Method type
stringBuilder.append(" Method :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getMethod());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//3 Access check URL route
stringBuilder.append("URL route :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getRequestURI());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//4URL( Excluding the part after the query string )
stringBuilder.append("URL( Excluding the part after the query string ):");
stringBuilder.append(req.getRequestURL());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//5 First level path
stringBuilder.append(" First level path :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getContextPath());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//6 Query string
stringBuilder.append(" Query string :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getQueryString());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//7 Text encoding format
stringBuilder.append(" Text encoding format :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getCharacterEncoding());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//8mine
stringBuilder.append("mine:");
stringBuilder.append(req.getContentType());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//9 Length of text
stringBuilder.append(" Length of text :");
stringBuilder.append(req.getContentLength());
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
//10 Get the key value of each query string :
stringBuilder.append("<h3> Get the key value of each query string :</h3>");
Enumeration query = req.getParameterNames();
while(query.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String)query.nextElement();
stringBuilder.append(key);
stringBuilder.append(":");
stringBuilder.append(req.getParameter(key));
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
}
//11 Get the key value of the header
stringBuilder.append("<h3> Get the key value of the header :</h3>");
Enumeration header = req.getHeaderNames();
while(header.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String)header.nextElement();
stringBuilder.append(key);
stringBuilder.append(":");
stringBuilder.append(req.getHeader(key));
stringBuilder.append("<br>");
}
resp.getWriter().write(stringBuilder.toString());
}
}
result :
2.4Post Request for information
We know post The requested request information is in http In the format body Part , and body There are many formats of request content in , For example, the most common ones are :
- x-www-form-urlencode Format , adopt form The form or postman structure .
- json Format
- form-data Format
x-www-form-urlencode Format :
k e y = v a l u e & k e y = v a l u e & . . . key=value\&key=value\&... key=value&key=value&...
form Form creation x-www-form-urlencode Format request :
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ch">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>post</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="./postParameter" method="post" accept-charset="utf-8">
<span>userId</span>
<input type="text" name="userId">
<span>classId</span>
<input type="text" name="classId">
<input type="submit" value=" Submit ">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Servlet The program receives and processes requests :
about x-www-form-urlencode Format The request can be used directly HttpServletRequest Medium getParameter The method is based on key To get value, Then return the obtained data ,form The request of form construction will automatically jump to the page .
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/postParameter")
public class GetPostParameterServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// obtain post request body Parameters in the request
// Set request and response encoding format
req.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
// such as useId = classId=
String userId = req.getParameter("userId");
String classId = req.getParameter("classId");
// Write data
resp.getWriter().write("userId=" + userId + ", " + "classId=" + classId);
}
}
Running results :

json Format :
{ \{ {
k e y : v a l u e , key:value, key:value,
k e y : v a l u e , key:value, key:value,
k e y : v a l u e , key:value, key:value,
. . . ... ...
} \} }
about json Format , Manual parsing is not easy , because json The fields inside can be nested , But we can use the third-party library to parse and process json, such as Jackson,Jackson The dependency import process is as follows :
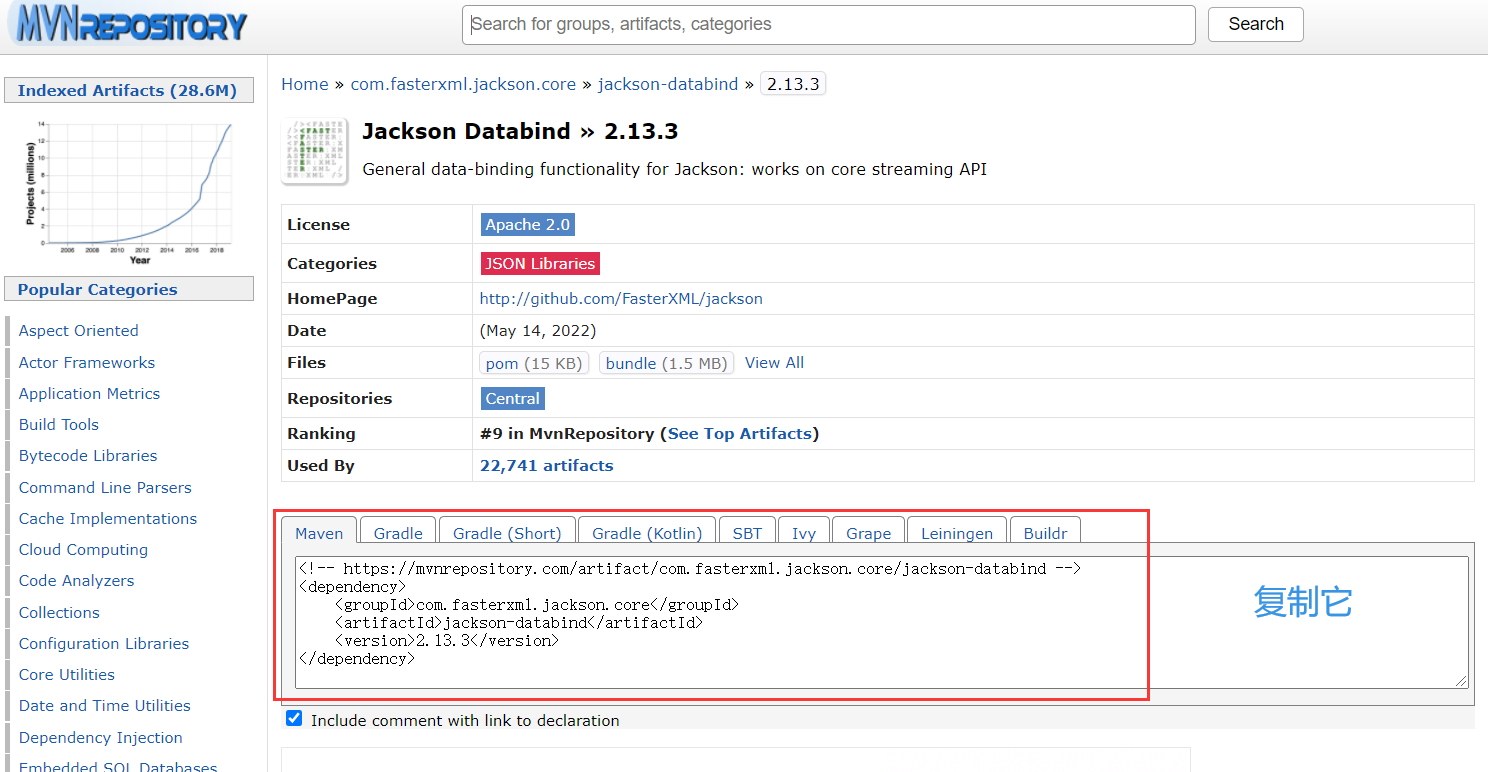
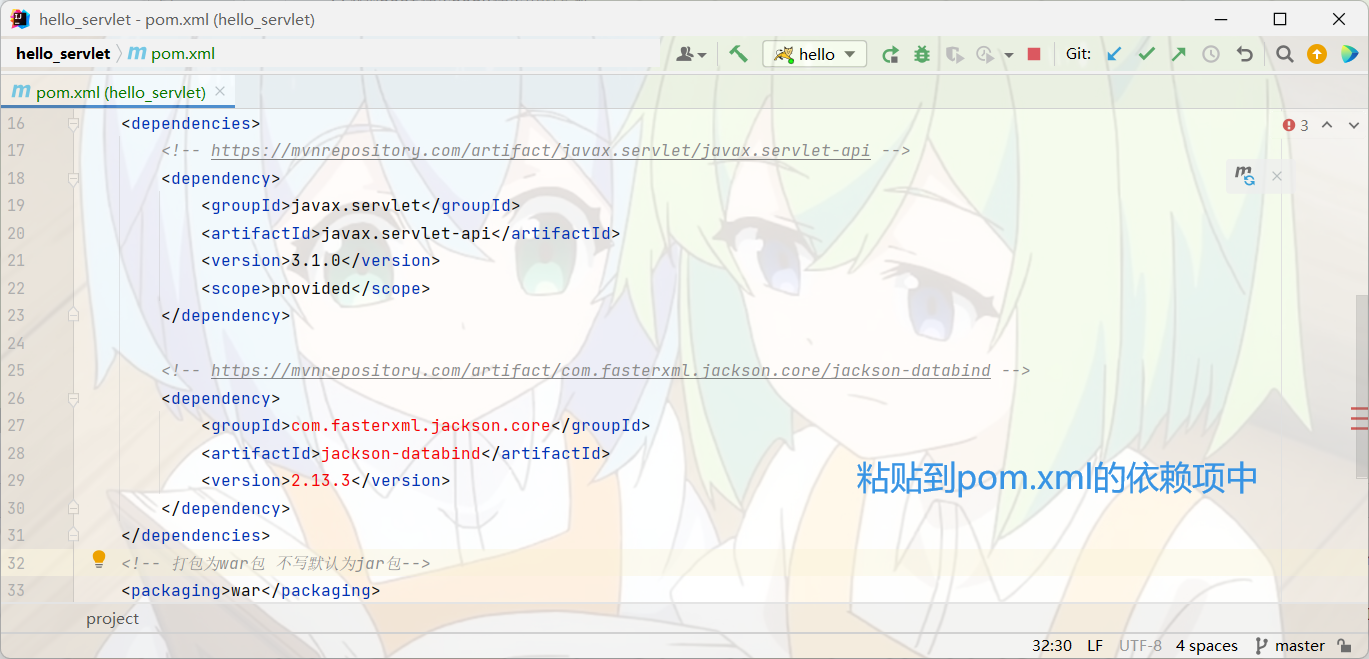
Handle json Request step :
First step , On the front end js The format constructed in the code is json Format request .
among ajax structure post request , Use contentType To specify the type of request ,data Property to set body The content of .
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="cn">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>json</title>
</head>
<body>
<!-- front end HTML part -->
<input type="text" id="userId">
<input type="text" id="classId">
<input type="button" id="submit" value=" Submit ">
<!-- If you have prepared local jQuery Just import local , Otherwise, you can find online jQuery cdn Network path -->
<script src="./jquery3.6.0.js"></script>
<script> let userIdInput = document.querySelector("#userId"); let classIdInput = document.querySelector("#classId"); let button = document.querySelector("#submit"); button.onclick = function() {
$.ajax({
type : "post", url: "getJsonPost", contentType: "appliaction/json", data:JSON.stringify({
userId: userIdInput.value, classId:classIdInput.value }), success: function(body){
console.log(body); } }) } </script>
</body>
</html>
The second step , stay java Used in back-end code Jackson Handle .
- 1) establish Jackson The core object ObjectMapper object .
- 2) Read... In the request body Information , The process passes ObjectMapper Object's
readValueMethod realization . - 3) Create to accept
jsonThe class of data . - 4)
readValueMethod has two parameters , The first parameter is used to indicate the source of the request , It can be a path string , And can beInputSreamobject , It can also beFileobject , The second parameter indicates reception json Class object of data . - 5) Process and respond to requests .
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
class User {
public String userId;
public String classId;
}
@WebServlet("/getJsonPost")
public class GetJsonPostServlet extends HttpServlet {
//1. Create a Jackson Core objects of
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Format
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
// Handle
//2. Read body Requested content , Use ObjectMapper Object's readValue Method to parse
// Is to convert a string into java The object of ,readValue The first parameter of the method can be the path string, or the input stream object , The introduction can be File object
// The second parameter , Indicates that the requested json Which format data to convert java object
User user = objectMapper.readValue(req.getInputStream(), User.class);
System.out.println(user.userId);
System.out.println(user.classId);
resp.getWriter().write("userId=" + user.userId + " ,classId=" + user.classId);
}
}
Running results :
readValue Method fundamentals :
- Read json Formatted data , And parsed into key value pairs .
- Facilitate these key value pairs , get
key, And with the attributes in the object you want to pass in ( Reflection ) comparison , IfkeySame name as attribute , Then putkeyCorrespondingvalueAssign to this property , Otherwise, skip , After all the key value pairs are convenient , This object is almost constructed .
2.5 Construction of response
Case study 1: Set response status code
It's easy to set up , Just call httpServletResponse Object setStatus The method is ok
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/status")
public class StatusServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Format
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset=utf8");
// Set status code
int status = 200;
resp.setStatus(status);
resp.getWriter().write("hello, This is a " + status + " The response content of the status code !");
}
}
Start the program , The web page shows :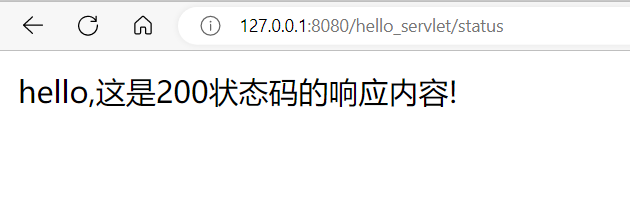
I changed the status code to 404, The web page shows :
Then why not the kind we met before 404 What about the page ? This is because the page response content we set is hello, This is a 404 The response content of the status code !, It can be understood as customized 404 Status response page , Just like other websites , If you can't access the page , The reminder page displayed is also different , such as b The page of the station is like this :
Case study 2: Page auto refresh
Automatic page refresh only needs to set one in the response header: Refresh You can refresh the page regularly , For response header Set up , We can go through HttpServletResponse Object setHeader Method to set Refresh Properties and refresh rate .
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/autorefresh")
public class AutoRefreshServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Format
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset = utf8");
// Set up Refresh, The second parameter represents the refresh rate , The unit is seconds
resp.setHeader("Refresh", "1");
// Respond to
resp.getWriter().write(" Time stamp :" + System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}
effect :
Case study 3: Redirect case
First step , Set the status code to 302.
The second step , Set up header:Location, call setHeader When the method is used , The first parameter is filled in Location, Presentation settings header Field is Location, The second parameter is the destination address of redirection , The string of which address you want to redirect to .
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/redirect")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Format
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset = utf8");
// Set status code
resp.setStatus(302);
// Set redirection fields and addresses , Such as jumping to the official website of Li Kou
resp.setHeader("Location", "https://leetcode.cn/");
}
}
effect :

Of course ,servlet Provides a simpler redirection method , Is the use of HttpServletResponse Class sendRedirect Method .
@WebServlet("/redirect")
public class RedirectServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// Format
resp.setContentType("text/html; charset = utf8");
// Set status code
// resp.setStatus(302);
// // Set redirection fields and addresses , Such as jumping to the official website of Li Kou
// resp.setHeader("Location", "https://leetcode.cn/");
resp.sendRedirect("https://leetcode.cn/");
}
}
The effect is the same as the first method above .
Next up : A small case of confession wall

边栏推荐
- 7-17 crawling worms (15 points)
- Dynamic memory management
- Some summaries of the third anniversary of joining Ping An in China
- Whether a person is reliable or not, closed loop is very important
- How to display √ 2 on the command line terminal ̅? This is actually a blog's Unicode test article
- [FAQ] summary of common causes and solutions of Huawei account service error 907135701
- Hands on deep learning (43) -- machine translation and its data construction
- On Multus CNI
- SSM online examination system source code, database using mysql, online examination system, fully functional, randomly generated question bank, supporting a variety of question types, students, teache
- Lavel document reading notes -how to use @auth and @guest directives in lavel
猜你喜欢

Hands on deep learning (40) -- short and long term memory network (LSTM)

Baidu R & D suffered Waterloo on three sides: I was stunned by the interviewer's set of combination punches on the spot
Work order management system OTRs
el-table单选并隐藏全选框
Hands on deep learning (39) -- gating cycle unit Gru
技术管理进阶——如何设计并跟进不同层级同学的绩效
【Day2】 convolutional-neural-networks
Machine learning -- neural network (IV): BP neural network
Custom type: structure, enumeration, union

uniapp 处理过去时间对比现在时间的时间差 如刚刚、几分钟前,几小时前,几个月前
随机推荐
Write a jison parser from scratch (6/10): parse, not define syntax
2021-08-10 character pointer
Mmclassification annotation file generation
mmclassification 标注文件生成
2. Data type
C # use smtpclient The sendasync method fails to send mail, and always returns canceled
Nuxt reports an error: render function or template not defined in component: anonymous
Pueue data migration from '0.4.0' to '0.5.0' versions
5g/4g wireless networking scheme for brand chain stores
In the case of easyUI DataGrid paging, click the small triangle icon in the header to reorder all the data in the database
C语言指针面试题——第二弹
按键精灵跑商学习-商品数量、价格提醒、判断背包
How web pages interact with applets
Hands on deep learning (45) -- bundle search
Golang Modules
Kotlin: collection use
C language pointer classic interview question - the first bullet
A little feeling
How can Huawei online match improve the success rate of player matching
What is devsecops? Definitions, processes, frameworks and best practices for 2022