当前位置:网站首页>Deep learning: numpy
Deep learning: numpy
2022-06-26 18:17:00 【Little fox dreams of going to fairy tale town】
【 Knowledge framework 】
Deep learning Numpy piece
One 、ndarray Array
1、 establish ndarray Array
array function
This function converts the list to an array
import numpy as np
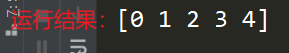
a = [0,1,2,3,4]
b = np.array(a)
print(b)
arange function
Create an array , The array is a set range 、 Determine the interval 、 Incremental array
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)# from 0 Start to 10 end ( barring 10), The increment interval is 2
print(a)
【 Running results 】
zeros function
Creates the full length of a shape of a specified length 0 Array
import numpy as np
a = np.zeros([3,3])# Create a 3*3 Of all the 0 Array
print(a)
【 Running results 】

ones function
Creates a full... Of the specified length and shape 1 Array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])# Create a 3*3 Of all the 1 Array
print(a)
【 Running results 】
2、ndarray Properties of array
shape
The shape of the array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])# Create a 3*3 Of all the 1 Array
print(a.shape)
【 Running results 】
dtype
Data type of array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(a.dtype)
【 Running results 】
size
The number of elements in the array , Its size is equal to the product of each dimension
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(a.size)
【 Running results 】
ndim
The dimension size of the array , Its size is equal to shape The number of elements contained
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(a.ndim)
【 Running results 】
Change the shape and data type of the array
Change shape with reshape( Slice of array )
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(' Original array shape ',a.shape)
a = a.reshape([1,9])
print(' Current array shape ',a.shape)
【 Running results 】
Change the data type with astype
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
print(' Original array type ',a.dtype)
a = a.astype(np.int64)
print(' Current array type ',a.dtype)
【 Running results 】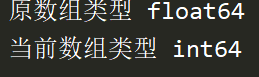
3、 Scalar sum ndarray Operations between arrays
Scalar and array 4 Operations ( Add, subtract, multiply and divide )
Scalars operate on every element in an array
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
b = 2.0+a
c = 2.0-a
d = 2.0*a
e = 2.0/a
print(' The original array is :\n',a)
print('2+ Array :\n',b)
print('2- Array :\n',c)
print('2* Array :\n',d)
print('2/ Array :\n',e)
【 Running results 】
Array and array operation
Operation between corresponding elements
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
b = np.zeros([3,3])
c = a+b
d = a*b
print(' Array a:\n',a,'\n Array b:\n',b)
print('a+b:\n',c)
print('a*b:\n',d)
【 Running results 】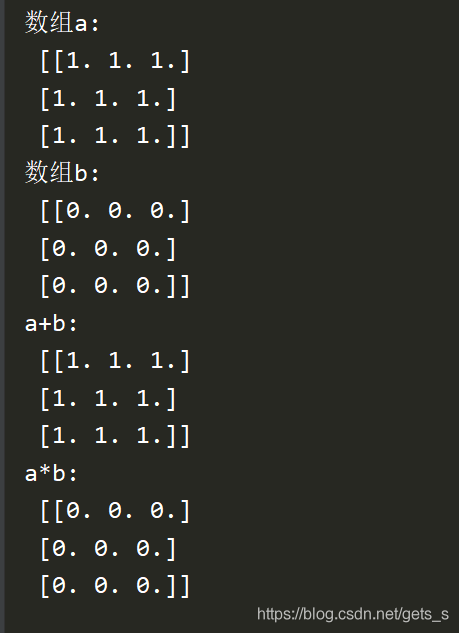
4、ndarray Statistical method of array
mean
Calculate the arithmetic mean
import numpy as np
a = np.ones([3,3])
# Two expressions
print(np.mean(a))
print(a.mean())
【 Running results 】
std var
std: Standard deviation var: variance
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' The standard deviation is :',a.std())
print(' The variance of :',a.var())
【 Running results 】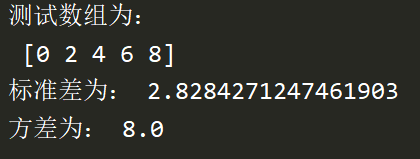
sum
Sum up
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' Sum for :',a.sum())
【 Running results 】
max min
max: Maximum min: minimum value
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' The maximum value is :',a.max())
print(' The minimum value is :',a.min())
【 Running results 】

argmin argmax
minimum value 、 Maximum index
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' The maximum index is :',a.argmax())
print(' The minimum index is :',a.argmin())
【 Running results 】
cumsum cumprod
Accumulation and accumulation ( Look at the results )
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10,2)
print(' The test array is :\n',a)
print(' Add up to :',a.cumsum())
print(' Accumulated as :',a.cumprod())
【 Running results 】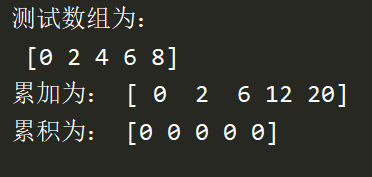
Two 、np.random random number
1、 Random array
Uniform distribution
import numpy as np
a = np.random.rand(10)
print(a)
【 Running results 】
Specify the value range and shape
import numpy as np
a = np.random.uniform(low=-1.0,high=1.0,size=(3,3))#low Lower limit ,high ceiling ,size shape
print(a)
【 Running results 】
Normal distribution
import numpy as np
a = np.random.randn(9)
print(a)
【 Running results 】
Specified mean loc And variance scale
import numpy as np
a = np.random.normal(loc=2.0,scale=2.0,size=(3,3))
print(a)
【 Running results 】
2、 Random disorder order
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10)
print(' Original array a by :\n',a)
np.random.shuffle(a)
print(' After randomly disrupting the order :\n',a)
【 Running results 】
3、 Random selection of elements
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,10)
print(' Original array a by :\n',a)
b = np.random.choice(a)
print(' The randomly selected elements are :',b)
【 Running results 】
3、 ... and 、 linear algebra
diag Find diagonal elements
Returns the diagonal elements of a square array in the form of a one-dimensional array
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
a = a.reshape([3,3])
b = np.diag(a)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',a)
print(' The diagonal element is :',b)
【 Running results 】
dot Matrix multiplication
Matrix multiplication
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(0,12)
b = a.reshape([3,4])
c = a.reshape([4,3])
d = b.dot(c)
print(' matrix b:\n',b)
print(' matrix c:\n',c)
print(' matrix b* matrix c:\n',d)
【 Running results 】
trace Sum of diagonal elements
Calculate the sum of diagonal elements
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
b = a.reshape([3,3])
c = np.trace(b)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',b)
print(' matrix b The sum of the diagonal elements of is :',c)
【 Running results 】
det Matrix determinants
Calculate the determinant of a matrix
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
b = a.reshape([3,3])
c = np.linalg.det(b)
print(' matrix b The determinant of is :',c)
【 Running results 】
eig Eigenvalues and eigenvectors
Calculate the eigenvalues and eigenvectors of a square matrix
import numpy as np
a = np.arange(1,10)
b = a.reshape([3,3])
c = np.linalg.eig(b)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',b)
print(' matrix b Eigenvalues and eigenvectors :\n',c)
【 Running results 】
inv The inverse of the square
Calculate the inverse of the square
import numpy as np
a = np.random.rand(3,3)
b = np.linalg.inv(a)
print(' The test matrix is :\n',a)
print(' matrix b The inverse matrix of is :\n',b)
【 Running results 】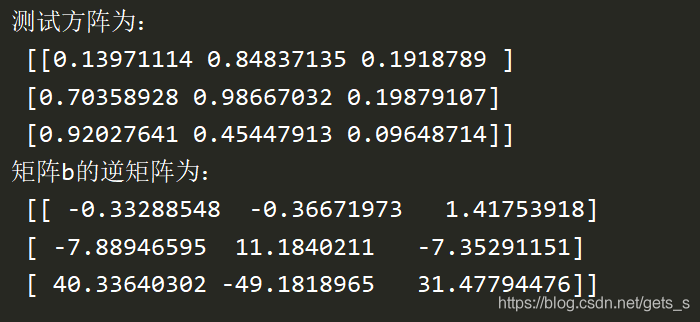
Remember the praise. 、 Focus on 、 Comment on 、 Collection 、 forward
边栏推荐
猜你喜欢
Class inheritance of 25class

Deep understanding of MySQL lock and transaction isolation level
Idea collection code, quickly open favorites collection window

VCD-影音光碟

Lm06 the mystery of constructing the bottom and top trading strategy only by trading volume
你了解如何比较两个对象吗

wechat_ Solve the problem of page Jump and parameter transfer by navigator in wechat applet

Numpy之matplotlib
Introduction to Ethereum Technology Architecture

深度学习之Numpy篇
随机推荐
RSA encryption and decryption details
VCD video disc
Summary of alter operation in SQL
vutils. make_ A little experience of grid () in relation to black and white images
[QNX] Command
Binary search-1
PC端录制扫515地机器人/scan数据
Soft test preparation multimedia system
Regular match same character
贝叶斯网络详解
Insert string B into string A. how many insertion methods can make the new string a palindrome string
Which securities company is better for a novice to open a stock trading account? How is it safer to speculate in stocks??
新手炒股开户选哪个证券公司比较好?怎样炒股比较安全??
in和exsits、count(*)查询优化
Digital signature standard (DSS)
CD-CompactDisk
Case study of row lock and isolation level
Clion breakpoint single step debugging
Leetcode 128 longest continuous sequence
Discussion and generation of digital signature and analysis of its advantages