1.创建集合
创建集合分为两步,-是对对集合设定规则,二是创建集合,创建mongoose.Schema构造函数的实例即可创建集合。
// mongoose.Schema() 是一个构造函数,要new一个实例对象
//2、设定集合规则
const courseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
author: String ,
isPub1ished: Boolean
});
//3、使用规则创建集合 这里创建的集合也是一个构造函数
const Course = mongoose.model ('Course', courseSchema); //第一个参数是集合名称,第二个是集合规则。实际在数据库中产生的集合名为courses
1.创建文档
创建文档实际上就是向集合中插入数据。
方法1
分为两步: ①创建集合实例。
②调用实例对象下的save方法将数据保存到数据库中。
//4、创建文档 插入数据
// 创建集合实例对象
const course = new Course({
name: 'node.js',
author: 'xc-dh',
isPublished: true
});
// 调用实例对象下的save方法将数据保存到数据库中。
course.save();
方法2
和数据库相关的所有操作都是异步操作
创建文档 插入数据
Course.create({
name: 'JavaScript',
author: '星辰大海',
isPublished: false
}, (err, result) => {
console.log(err);
console.log(result);
});
// 可以使用promise的方法
Course.create({
name: 'JavaScript12',
author: '星辰大海',
isPublished: false
}).then(result => console.log(result)).catch(err => console.log(err));
3.mongoDB数据库导入数据
找到mongodb数据库的安装目录,将安装目录下的bin目录放置在环境变量中。
在项目根目录下输入以下命令导入
mongoimport -d 数据库名称 -c 集合名称 --file 要导入的数据文件
4.查询文档
find()方法
返回一组文档
// 根据条件查找文档(条件为空则查找所有文档)
Course.find().then(result => console.log(result))
// 返回文档集合(数组形式)
[{
_id: 5c0917ed37ec9b03c07cf95f,
name: 'node.js基础',
author: 'xc-dh‘
},{
_id: 5c09dea28acfb814980ff827,
name: 'Javascript',
author: 'xc-dh‘
}]
findOne()方法
返回一条文档
// 根据条件查找文档
Course.findOne({name: 'node.js基础'}).then(result => console.log(result))
// 返回文档 只返回一条,默认返回第一条
{
_id: 5c0917ed37ec9b03c07cf95f,
name: 'node.js基础',
author: 'xc-dh‘
}
// 匹配大于,小于
// User.find({
// age: {
// $gt: 20, //大于
// $lt: 40 // 小于
// }
// }).then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// 匹配包含 返回爱好包含敲代码的文档
// User.find({
// hobbies: {
// $in: ['敲代码']
// }
// }).then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// 选择要查询的字段 字段前加上-表示不查询此字段
// User.find().select('name age -_id').then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// 根据年龄字段进行升序排列
// User.find().sort('age').then(result => {
// console.log(result)
// })
// 降序排列,添加负号就可以
// User.find().sort('-age').then(result => {
// console.log(result)
// })
// skip 跳过多少条数据 limit 限制查询数量
User.find().skip(2).limit(3).then(result => {
console.log(result)
})
5.删除文档
// 删除单个文档 如果条件包含多个文档,默认删除符合条件的第一个文档 返回删除的文档
User.findOneAndDelete({
_id: '5c09f1e5aeb04b22f8460965'
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
});
// 删除多个 如果条件为空,默认删除所有文档 返回一个对象,n代表删除的文档数,OK表示是否删除成功
User.deleteMany({}).then(result => console.log(result)) //{ n: 4, ok: 1, deletedCount: 4 }
6.更新文档
// 更新单个
User.updateOne({查询条件}, {要修改的值}).then(result => console.log(result))
// 更新多个
User.updateMany({查询条件}, {要更改的值}).then(result => console.log(result))
// 更新单条文档 如果条件满足多个文档,也是默认只更新第一个
User.updateOne({
name: '李四'
}, {
name: '李狗蛋'
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
});
// 更新多条文档 {}为空即默认选择所有文档
User.updateMany({}, {
age: 45
}).then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
7. mongoose验证
在创建集合规则时,可以设置当前字段的验证规则,验证失败则插入失败。
-
required: true必传字段
-
minlength: 3字符串最小长度
-
maxlength: 20字符串最大长度
-
min: 2数值最小为2
-
max: 100数值最大为100
-
enum: ['html', 'css', "javascript, 'nodejs]
-
trim: true去除字符串两边的空格
-
validate: 自定义验证器
-
default: 默认值
-
获取错误信息:error.errors['字段名称'].message
// 验证规则可以跟两个参数,第二个参数表示自定义错误提示信息
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String,
// 必传字段,不传就会报错
required: [true, '请传入文章标题'],
minlength: 2,
maxlength: [6, '标题长度不能大于6个字符'],
trim: true //去除字符串两边空格
},
age: {
type: Number,
min: 24, //最小数值
max: 80 //最大数值
},
publishDate: {
type: Date,
// 默认值,没有插入信息时默认显示的值
default: Date.now
},
category: {
type: String,
// 枚举,列出当前字段可拥有的值
enum: ['HTML', 'css', 'javascript', 'node.js']
},
author: {
type: String,
// 自定义验证器
validate: {
validator: v => {
// 返回布尔值
// true验证成功
// false验证失败
// v 要验证的值
return v && v.length > 4;
},
// 自定义错误信息
message: '您输入的值不符合验证规则'
}
}
});
// 使用规则创建集合
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema);
// create方法插入数据
Post.create({
title: 'aaa',
age: 68,
category: 'javascript',
author: 'db'
}).then(result => console.log(result))
// 获取错误提示信息
.catch((error) => {
// 获取错误信息对象
const err = error.errors;
// 循环错误信息对象
for (var k in err) {
// console.log(err[k].message);
// 打印错误信息
console.log(err[k]['message']);
}
})
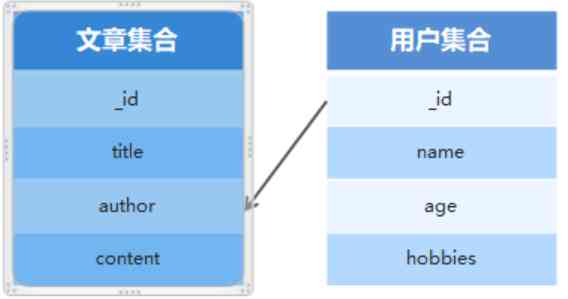
8.集合关联
通常不同集合的数据之间是有关系的,例如文章信息和用户信息存储在不同集合中,但文章是某个用户发表的 要查询文章的所有信息包括发表用户,就需要用到集合关联。
-
使用id对集合进行关联
-
使用populate方法进行关联集合查询
// 关联集合
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 连接数据库
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost/playground', {
useUnifiedTopology: true,
useNewUrlParser: true
}).then(() => {
console.log('数据库连接成功');
}).catch((error) => {
console.log(error, '数据库连接失败');
});
// 创建集合规则
const userSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String
}
});
const postSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String
},
// 1、使用ID将文章集合和作者集合进行关联
author: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'User'
}
});
// 创建集合
const User = mongoose.model('User', userSchema);
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', postSchema);
// 插入文档数据
// User.create({
// name: 'xc'
// }).then(result => {
// console.log(result);
// });
// Post.create({
// title: 'html',
// author: '5f9668bb20347221d49d0254'
// }).then((result => {
// console.log(result);
// }));
// 2、联合查询
Post.find().populate('author').then(result => {
console.log(result);
})
// 返回结果如下 [ { _id: 5f966a51c70ba932880c36d3, title: 'html', author: { _id: 5f9668bb20347221d49d0254, name: 'xc', v: 0 },v: 0 } ]
9. 案例:用户信息增删改查
-
搭建网站服务器,实现客户端与服务器端的通信
-
连接数据库,创建用户集合,向集合中插入文档
-
当用户访问/list时, 将所有用户信息查询出来
-
将用户信息和表格HTML进行拼接并将拼接结果响应回客户端
-
当用户访问/add时, 呈现表单页面,并实现添加用户信息功能
-
当用户访问/modify时,呈现修改页面,并实现修改用户信息功能
-
当用户访问/delete时, 实现用户删除功能