当前位置:网站首页>Learn more TypeScript 】 【 TypeScript modular
Learn more TypeScript 】 【 TypeScript modular
2022-08-03 00:32:00 【Grill the ai on the ocean floor】
TypeScript学习:TypeScript从入门到精通
蓝桥杯真题解析:蓝桥杯Web国赛真题解析
个人简介:incoming third-year students,热爱前端,热爱生活
Your one-key three-link is the biggest motivation for my update️!
前言
最近博主一直在创作
TypeScript的内容,所有的TypeScript文章都在我的TypeScript从入门到精通专栏里,每一篇文章都是精心打磨的优质好文,并且非常的全面和细致,期待你的订阅️
This article will go into depthTypeScript中的模块化,This may be the most comprehensive and detailed you've ever seenTypeScript教程,Like, follow and collect, don't get lost!
1、模块定义
在TypeScript中,就像在EC5中一样,任何包含顶级import 或export The files are considered one模块
相反的,A file without any top-level import or export declarations is considered one脚本,其内容可在全局范围内使用(因此也可用于模块)
模块在自己的范围内执行,而不是在全局范围内.这意味着在模块中声明的变量、函数、类等在模块外是不可见的,除非它们被明确地用某种导出形式导出.相反,要使用从不同模块导出的变量、函数、类、接口等,必须使用导入的形式将其导入.
JavaScript规范声明,任何没有export或顶层await的JavaScriptfiles should all be considered one脚本而不是一个模块
如果你有一个目前没有任何导入或导出的文件,But you want it to be handled as a module,可以添加这一行:
export {
};
这将改变该文件,使其成为一个什么都不输出的模块.无论你的模块目标是什么,这个语法都有效
TypeScript中能够使用JavaScript的模块化语法,and provides some additional syntax on top of that
2、ES模块语法
一个文件可以通过export default 声明一个主要出口:
// @filename: hello.ts
export default function helloWorld() {
console.log("Hello, world!");
}
一个文件中
export default只能有一个
通过import导入:
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
import hello from "./hello";
hello();
import引入export defaultYou can customize the import name when exporting the content,The function name exported as above is namedhelloWorld,But we customized it when we introduced ithello的名称
除了默认的导出,It can also be omitteddefault 的export ,导出多个变量和函数的:
// @filename: hello.ts
export var a = 3.14;
export let b = 1.41;
export const c = 1.61;
export class D {
}
export function fn(num: number) {
console.log(num);
}
可以只使用一个export导出:
var a = 3.14;
let b = 1.41;
const c = 1.61;
class D {
}
function fn(num: number) {
console.log(num);
}
export {
a, b, c, D, fn };
通过import和{}实现按需导入:
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
import {
a, b, c, D, fn } from "./hello";
console.log(a, b, c, new D());
fn(1);
可以使用 import {old as new} 这样的格式来重命名一个导入:
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
// 仅引入a,c,fn 并重命名a和fn
import {
a as A, c, fn as FN } from "./hello";
console.log(A, c);
FN(1);
Can put all exported objects,用* as name ,Put them in the same namespacename:
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
// exportEverything that is exported is put into the namespace F 中
import * as F from "./hello";
console.log(F.a, F.c);
F.fn(1);
export default与export一起使用:
// @filename: hello.ts
export var a = 3.14;
export let b = 1.41;
export const c = 1.61;
export class D {
}
export function fn(num: number) {
console.log(num);
}
export default function helloWorld() {
console.log("Hello, world!");
}
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
import hello, {
a, b, c, D, fn } from "./hello";
console.log(a, b, c, new D());
fn(1);
hello();
Import a file directly
通过import "file Path" 导入一个文件,而不把任何变量纳入你的当前模块:
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
import "./hello";
在这种情况下, import 没有任何作用,但 hello.ts All code in will be parsed,这可能引发影响其他对象的副作用
TS特定的语法
类型可以使用与JavaScript值相同的语法进行导出和导入:
// @filename: hello.ts
export type Cat = {
};
export interface Dog {
}
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
import {
Cat, Dog } from "./hello";
let a: Cat, b: Dog;
TypeScript用两个概念扩展了 import 语法,用于声明一个类型的导入:
import type
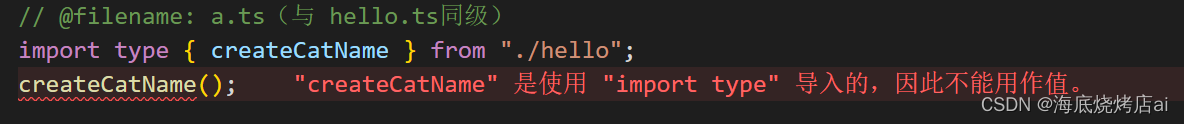
这是一个导入语句,Imported variables can only be used as types:
// @filename: hello.ts
export const createCatName = () => "fluffy";
内联类型导入
TypeScript 4.5还允许以type为前缀的单个导入,以表明导入的引用是一个类型:
// @filename: hello.ts
export type Cat = {
};
export interface Dog {
}
export const createCatName = () => "fluffy";
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
// 表明Cat和Dog为类型
import {
createCatName, type Cat, type Dog } from "./hello";
type Animals = Cat | Dog;
const name = createCatName();
3、CommonJS语法
若使用CommonJS语法报错,You need to run it in the project root directory first:
npm i --save-dev @types/node安装声明文件
By calling in a global module 上设置 exports 属性来导出:
// @filename: hello.ts
function absolute(num: number) {
return num;
}
const a = 3;
let b = 4;
var c = 5;
module.exports = {
a,
b,
newC: c, // 将c以newCname export
d: 12, // 直接导出一个值
fn: absolute, // 将absolute以fnname export
};
通过require 语句导入:
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
const m = require("./hello");
console.log(m.a, m.b, m.newC, m.fn(1));
使用JavaScriptThe destructuring function in :
// @filename: a.ts(与 hello.ts同级)
const {
d, fn } = require("./hello");
console.log(d, fn(1));
4、TypeScript模块选项
模块解析选项
模块解析是指从import 或require 语句中获取一个字符串,并确定该字符串所指的文件的过程
TypeScript包括两种解析策略:
- 经典
Node
当编译器选项(tsconfig.json配置文件)中 module 不是commonjs 时,经典策略是默认的,是为了向后兼容.
Node策略复制了Node.js在CommonJS模式下的工作方式,对.ts 和.d.ts 有额外的检查
在TypeScript中,有许多TSConfig标志影响模块策略:
关于这些策略如何工作的全部细节,你可以参考《模块解析》
模块输出选项
tsconfig.jsonThere are two options in the configuration file that affectJavaScript的输出:
target,它决定了TS代码编译成JS的版本module,它决定了哪些代码用于模块之间的相互作用
所有模块之间的通信都是通过模块加载器进行的,编译器选项 module decides which one to use
在运行时,模块加载器负责在执行一个模块之前定位和执行该模块的所有依赖项
可以在TSConfig 模块参考 to see all available options and what they compile out ofJavaScript代码是什么样子
5、TypeScript命名空间
TypeScript有自己的模块格式,称为 命名空间(namespaces) ,这比ES模块标准要早
这种语法对于创建复杂的定义文件有很多有用的功能,并且在DefinitelyTyped中仍然被积极使用.虽然没有被废弃,但命名空间中的大部分功能都存在于ES Modules中,It is officially recommended to use it with JavaScript的方向保持一致
More information about namespaces can be found here: namespaces参考页
结语
至此,TypeScriptThe modular content is all over,Pay attention to the blogger's next article for more exciting!
博主的TypeScript从入门到精通专栏正在慢慢的补充之中,赶快关注订阅,与博主一起进步吧!期待你的三连支持.
参考资料:TypeScript官网
如果本篇文章对你有所帮助,还请客官一件四连!️
边栏推荐
- What is the core business model of the "advertising e-commerce" that has recently become popular in the circle of friends, and is the advertising revenue really reliable?
- 【DEBUG】ImportError: Unable to import required dependencies: numpy: DLL load failed: 找不到指定的模块。
- golang刷leetcode:拼接数组的最大分数
- hi!Don't look at how to SAO gas dye-in-the-wood in MySQL?
- 成功解决TypeError: can‘t multiply sequence by non-int of type ‘float‘
- 搭建Spark开发环境(第二弹)
- [C题目]力扣141. 环形链表
- YOLOv5+BiSeNet——同时进行目标检测和语义分割
- 30天啃透这份Framework 源码手册直接面进大厂
- JumpServer开源堡垒机完成龙芯架构兼容性认证
猜你喜欢
随机推荐
用户之声 | GBASE南大通用实训有感
七夕到了——属于程序员的浪漫
最近火爆朋友圈的“广告电商”,核心商业模式是什么,广告收入真实靠谱吗?
微软SQL服务器被黑客入侵以窃取代理服务的带宽
golang刷leetcode: 在每个树行中找最大值
【DEBUG】ImportError: Unable to import required dependencies: numpy: DLL load failed: 找不到指定的模块。
Vscode快速入门、 插件安装、插件位置、修改vscode默认引用插件的路径、在命令行总配置code、快捷键
JS函数防抖&函数节流及其使用场景
【流媒体】推流与拉流简介
2022-08-02 第六小组 瞒春 学习笔记
Byte's internal technical map is amazing and practical
[C题目]力扣142. 环形链表 II
模糊查询like用法实例(Bee)
JMeter的基本使用
Win10怎么开启自带的游戏录屏功能?
golang刷leetcode: 小于等于 K 的最长二进制子序列
golang 刷leetcode:从栈中取出 K 个硬币的最大面值和
解道8-编程技术5
【C语言进阶】--指针典题剖析
解道7-编程技术4