当前位置:网站首页>Codeforces Global Round 19
Codeforces Global Round 19
2022-07-05 22:43:00 【eyuhaobanga】
Sign in problem , Judge whether the input sequence has been arranged
AC Code :
/* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ #pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n + 5); for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } if(is_sorted(a.begin(), a.begin() + n)){ cout << "NO" << endl; } else{ cout << "YES" << endl; } return; } int main() { IOS1; //IOS2; int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */Problem - B - Codeforces
It is known that the length used is 1 Instead of a line segment with a length of k(k>1) Its contribution will not change . Consider two situations ,1. There is 0,2. There is no 0, Because if there is no 0,mex Always equal to 0, At this time, each length is 1 The contribution of the line segment is 1,k The first contribution is k, If there is 0, that 1+mex<=1+k, But the length is 1 The line segment of contributes at least 1+k, So you can use all the length 1 Instead of the line segment of and will not reduce the contribution , Therefore, to calculate the total value, we need to calculate the length and 0 The contribution of , From mathematical knowledge, we know that the sum of all field lengths is n*(n+1)*(n+2)/6, The first i In position 0 Contribution: i*(n-i+1) (DP Good idea , Time complexity O(n))
AC Code :
/* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ #pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n + 5); for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } int ans = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { ans += i * (n - i + 1) * (1 + (a[i] == 0)); } cout << ans << endl; return; } int main() { IOS1; //IOS2; int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */The meaning of the title is generally from 2 To n-1 Traverse every heap , Take two at a time , Then assign to any two , The minimum number of 2 To n-1 All the stones are allocated to 1 and n In the pile , When 2 To n-1 It's all about 1 I can't take any of them at the time of , Output -1, When n=3 And a2 When it is an odd number, no matter how you make it, the last thing left 1 You can't get all of them , Others should have a non 1 Under the circumstances , It can be proved that even numbers can be constructed continuously without appearing 1 The situation of .
AC Code :
/* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ #pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n + 5); int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; } if (n == 3 && a[2] & 1) { cout << "-1" << endl; return; } bool ok = false; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) { if (a[i] != 1) { ok = true; } } if (!ok) { cout << "-1" << endl; return; } long long ans = 0; for (int i = 2; i < n; i++) { ans += (a[i] + 1) / 2; } cout << ans << endl; return; } int main() { IOS1; //IOS2; int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */
Official simplification , So the topic becomes let suma The square of +sumb The sum of the squares of is the smallest , According to the mean inequality , Must be suma and sumb The smaller the absolute value of the difference , The smaller their sum ,01 knapsack ,i Said go ai,j Before presentation i individual ai And ,dp[i][j] Before presentation i One of the suma and sumb Difference
AC Code :
/* Tips: 1.int? long long? 2.don't submit wrong answer 3.figure out logic first, then start writing please 4.know about the range 5.check if you have to input t or not 6.modulo of negative numbers is not a%b, it is a%b + abs(b) */ #pragma GCC optimize(2) #pragma GCC optimize(3) #pragma GCC optimize("Ofast") #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define lowbit(x) ((x) & -(x)) #define endl '\n' #define IOS1 ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr); #define IOS2 ios::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0); typedef vector<int> vi; typedef vector<long long> vll; typedef vector<char> vc; typedef long long ll; template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) { return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) { return a / gcd(a, b) * b; } template<class T> T power(T a, int b) { T res = 1; for (; b; b >>= 1, a = a * a) { if (b & 1) { res = res * a; } } return res; } template <typename T> inline void read(T& x) { x = 0; int f = 1; char ch = getchar(); while (!isdigit(ch)) { if (ch == '-') f = -1; ch = getchar(); } while (isdigit(ch)) { x = x * 10 + ch - '0', ch = getchar(); } x *= f; } const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const int mod = 1000000007; const double PI = acos(-1.0); const double eps = 1e-6; inline int sgn(double x) { return x < -eps ? -1 : x > eps; } void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector<int> a(n + 5); vector<int> b(n + 5); long long sum = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i]; sum += a[i]; } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> b[i]; sum += b[i]; } vector<vector<int>> dp(110, vector<int> (10010, INF)); dp[0][0] = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 10010; j++) { if (j >= a[i + 1] && abs(dp[i + 1][j]) > abs(dp[i][j - a[i + 1]] + a[i + 1] - b[i + 1])) { dp[i + 1][j] = dp[i][j - a[i + 1]] + a[i + 1] - b[i + 1]; } if (j >= b[i + 1] && abs(dp[i + 1][j]) > abs(dp[i][j - b[i + 1]] + b[i + 1] - a[i + 1])) { dp[i + 1][j] = dp[i][j - b[i + 1]] + b[i + 1] - a[i + 1]; } } } int ans = INF, pos = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 10010; j++) { if (abs(dp[n][j]) < ans) { ans = abs(dp[n][j]); pos = j; } } long long res = 0; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { res += (a[i] * a[i] + b[i] * b[i]) * (n - 2); } res += pos * pos + (sum - pos) * (sum - pos); cout << res << endl; return; } int main() { IOS1; //IOS2; int __t = 1; cin >> __t; for (int _t = 1; _t <= __t; _t++) { solve(); } return 0; } /* */
边栏推荐
- 请求二进制数据和base64格式数据的预览显示
- QT creator 7 beta release
- Win11 runs CMD to prompt the solution of "the requested operation needs to be promoted"
- Damn, window in ie open()
- Solve the problem of "no input file specified" when ThinkPHP starts
- Technology cloud report won the special contribution award for the 10th anniversary of 2013-2022 of the "cloud Ding Award" of the global cloud computing conference
- Hcip day 16
- Global and Chinese markets for reciprocating seal compressors 2022-2028: Research Report on technology, participants, trends, market size and share
- [untitled]
- Event trigger requirements of the function called by the event trigger
猜你喜欢
Promql demo service
MySQL服务莫名宕机的解决方案
Spectrum analysis of ADC sampling sequence based on stm32
The difference between MVVM and MVC
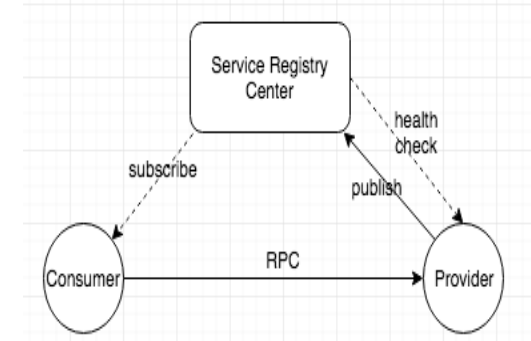
Nacos installation and service registration

Metaverse Ape猿界应邀出席2022·粤港澳大湾区元宇宙和web3.0主题峰会,分享猿界在Web3时代从技术到应用的文明进化历程
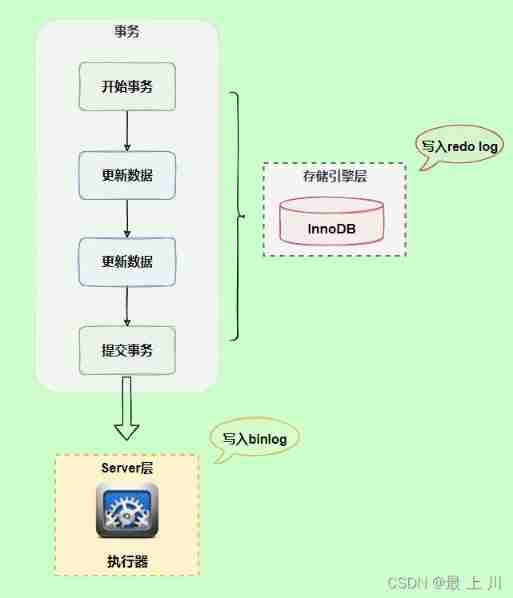
MySQL actual combat 45 lecture learning (I)

Calculation method of boundary IOU
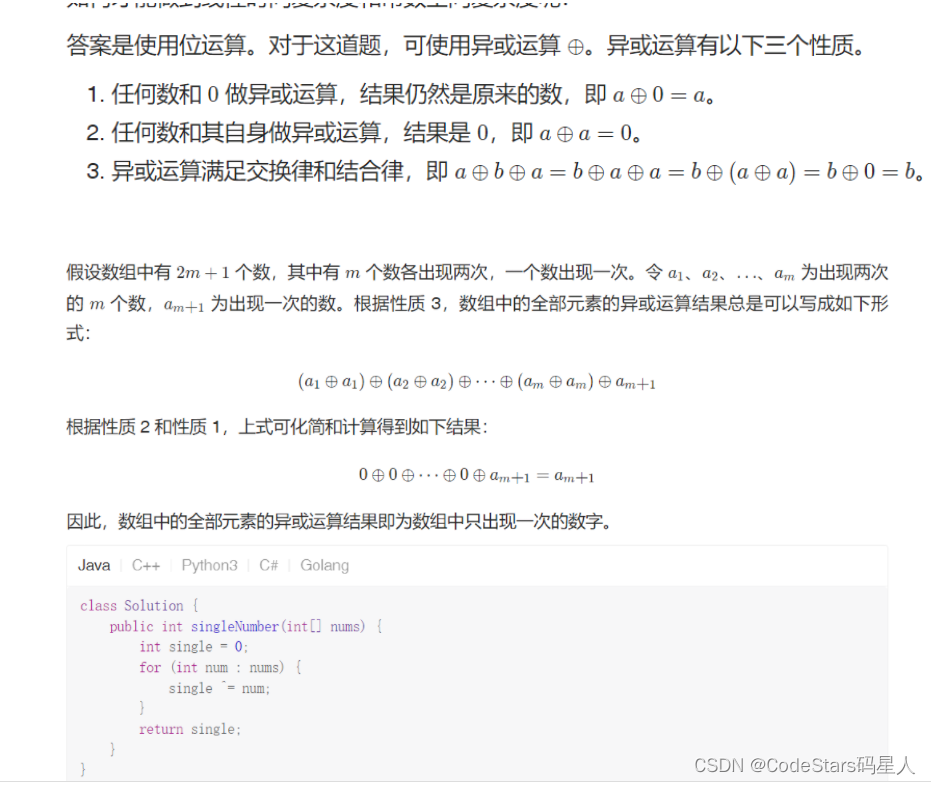
【无标题】
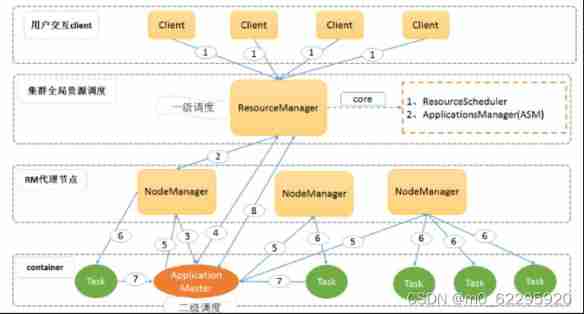
Distributed resource management and task scheduling framework yarn
随机推荐
EasyCVR集群部署如何解决项目中的海量视频接入与大并发需求?
抖音__ac_signature
[Chongqing Guangdong education] National Open University autumn 2018 0088-21t Insurance Introduction reference questions
VOT Toolkit环境配置与使用
Matlab draws a cute fat doll
实战:fabric 用户证书吊销操作流程
Draw a red lantern with MATLAB
Editor extensions in unity
Depth first DFS and breadth first BFS -- traversing adjacency tables
How to reverse a string fromCharCode? - How to reverse String. fromCharCode?
Navigation day answer applet: preliminary competition of navigation knowledge competition
Starting from 1.5, build a micro Service Framework -- log tracking traceid
Technology cloud report won the special contribution award for the 10th anniversary of 2013-2022 of the "cloud Ding Award" of the global cloud computing conference
我把开源项目alinesno-cloud-service关闭了
谷歌地图案例
[groovy] mop meta object protocol and meta programming (Introduction to groovyobject interface | introduction to metaclass | implementation of class methods using groovyobject invokemethod)
Paddle Serving v0.9.0 重磅发布多机多卡分布式推理框架
链表之双指针(快慢指针,先后指针,首尾指针)
请求二进制数据和base64格式数据的预览显示
VOT toolkit environment configuration and use
